Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Gprs and Edge
Загружено:
Tushar SaxenaАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Gprs and Edge
Загружено:
Tushar SaxenaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
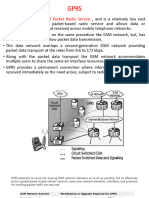
GPRS BACK GROUND With Mobile penetration reaching its full potential, GPRS gives Mobile operators competitive
e edge and optimum use of the infrastructure. SMS is a good example of just how hungry users are for data services. The main Objective of GPRS is to offer the access to standard data networks, using protocols e.g. TCP/IP and X.25 Transactions such as Credit Card checks and a variety of telemetric applications benefit from the fast session set-ups. GPRS enables efficient use of radio resources by allowing many data users to share the same interface on a statistical basis. The main benefits of GPRS are that it reserves radio resources only when there is data to be sent Mobile users doesnt have to connect to the network each time he wants to transfer the data, he can stay connected all day.
MAIN ADVANTAGES FOR OPERATORS More Revenue : By providing more than a mobile connection. Also operator can charge on the basis of type and amount of content accessed. Huge Potential Market for Data Sevices :
Mobile Phone and Internet, both are fastest growing technologies and GPRS is the merger of two. Fast Roll-out and Continuous Network Expansion : GPRS is an integral part of GSM. GPRS uses excess voice capacity for data : GPRS Packets are transmitted in short, free periods between busy hour calls. GPRS Vs GSM GPRS 1. SUPPORTS BOTH CKT. SWITCHED as well as packet switched service. 2. MS Utilizes Automatic retransmission (ARQ) at data link layer to re-transmit error frames. 3. Multiple time slots can be allotted to a single user 4. One time slot can be allotted to several users. 5. Charging/ billing more complex (Volume based, Q.O.S. based) TYPICAL GPRS SERVICES * CommunicationsE-mail, fax, intranet/ internet access. * Value added services Information services, games, e-commerce. Simple time-based billing. Single time slot per user. Single time slot per user. No re-transmission is provided. Vs GSM Only circuit switched.
* Location-based applications - Navigation, traffic conditions, airline/rail schedule, location finder. * Vertical applications Freight delivery, fleet management, sales-force automation * Location sensitive Advertising A user nearing a cinema hall or a restaurant receives flashes of advertisement
GSM NETWORK ELEMENTS The Main elements of GSM are: NSS : BSS : NMS Fault Management Configuration Management Performance Management BSC BTS Transcoder MSC VLR HLR (Includes Authentication Center and Equipment Identity Register)
GPRS Network Elements Network Element Software Hardware
SGSN GGSN Firewall Ethernet Switch DNS CG Border Gateway DHCP
SG1 G1 Checkpoint N/A HP-UX 11.00
DX Platform IP650 IP650 Cisco Catalyst HP 9000 A class
HP-UX 10.20 HP K class BGP4 HP-UX 11.00 IP650 HP 9000 A class
GPRS Interface
MSC/ VLR HLR EIR SMSGMSC
Signalling and data
Gs
SGSN BSC
Gr
Gf
Gd
Signalling
GGSN
Gb
Gn
Gi
External packet network
Air (Um)
Gn
GGSN
Gp
Inter-PLMN GPRS Backbone
SGSN Role Authentication, Authorization GTP tunneling to GGSN Ciphering & compression Mobility Management Session Management
Interaction with HLR, MSC/VLR Charging & statistics NMS interfaces
GGSN Role Interface to external data networks Encapsulate in GTP and forwards end user data to right SGSN Routes mobile originated packets to right destination Filters end user traffic Collects charging and statistic information for data network usage
Different GPRS Capacity Types
MS Class CLASS A: Supports simultaneous attach, simultaneous activation, simultaneous monitor, simultaneous invocation, and simultaneous traffic. CLASS B: Simultaneous traffic shall is not supported. The mobile user can make and/or receive calls on either of the two services sequentially but not simultaneously. The selection of the appropriate service is performed automatically
CLASS C: Supports only non-simultaneous attach. Alternate use only.
The status of the service which has not been selected is detached, that is, not reachable GPRS Channel Coding Schemes
Mobility Management State
Routing Area
RAI = MCC+MNC+LAC+RAC
GPRS Mobility Management Routing Area : The RA is a new concept for tracing the MS location. Cell =< RA =< LA served by one SGSN RAI = MCC + MNC + LAC + RAC Every time the MS sees the new RAI is has to initiate the RA update procedure. Mobility Management States : The IDLE State is when the MS is not connected. The Standby State is when the MS is connected to the GPRS Network
The Ready State is when the MS is ready to connect to the external IP Network.
Changing between states can be initiated from the MS, from the network and from the timers set. PDP Context Activation Accessing the HLR
SECURITY IN GPRS GPRS SYSTEM HAS INHERITED THE GSM PH-2 SECURITY FUNCTIONS Authentication of the subscriber IMEI Checking User Identity Confidentiality (TMSI in GSM, P-TMSI in GPRS) Ciphering of the data traffic between MS and SGSN
ADDITIONAL GPRS SECURITY FEATURES ARE Private IP Addressing in the GPRS backbone. Ciphered links and authentication between nodes in the GPRS Backbone. Screening of packets coming from the external networks (Firewall).
(P-TMSI is used to derive the Temp Logical Link Identity (TLLI))
EDGE Provide 3G services today Provide 3G services with existing licenses New modulation optimized for wireless data services Link adaptation: Take highest possible rate Covered by existing GSM licenses Same channel structure, network infrastructure, frequency
planning and protocol as todays GSM
What EDGE would mean to subscribers Streaming Applications Very high speed downloads Corporate Intranet connections Quicker MMS Video Phone Vertical corporate applications Video
Conference, Remote presentations
Вам также может понравиться
- General Packet Radio Service: Atanu Ansuman Regd. No.-0301227337Документ18 страницGeneral Packet Radio Service: Atanu Ansuman Regd. No.-0301227337Va SuОценок пока нет
- GSM To 3G: A Journey of Wireless CommunicationДокумент45 страницGSM To 3G: A Journey of Wireless Communicationsrshelke100% (1)
- GPRSДокумент11 страницGPRSZahra ZeeОценок пока нет
- GPRS LecДокумент37 страницGPRS LecRussell F PhiriОценок пока нет
- GprsДокумент5 страницGprsRavi Ranjan KumarОценок пока нет
- GPRS BasicsДокумент47 страницGPRS BasicsMohit RautelaОценок пока нет
- Mobile Comm Short NoteДокумент8 страницMobile Comm Short NoteSarthak BhattacharjeeОценок пока нет
- What is GPRS? Everything You Need to KnowДокумент5 страницWhat is GPRS? Everything You Need to KnowMayank BansalОценок пока нет
- Unit 4Документ57 страницUnit 4Utsav SoniОценок пока нет
- Gujarat Technological University: UNIT: 4 Third Generation CommunicationДокумент65 страницGujarat Technological University: UNIT: 4 Third Generation CommunicationUtsav SoniОценок пока нет
- GPRS Lecture - Packet Data Network and ArchitectureДокумент29 страницGPRS Lecture - Packet Data Network and ArchitectureLatera FekedeОценок пока нет
- Assalm-O-Alikum: Group MembersДокумент21 страницаAssalm-O-Alikum: Group MembersHassan AminОценок пока нет
- Module 5 GPRS and EdgeДокумент37 страницModule 5 GPRS and EdgeSwapnil NageОценок пока нет
- GprsДокумент21 страницаGprsPhanishankarОценок пока нет
- MCN Unit 4.2Документ18 страницMCN Unit 4.2venkatОценок пока нет
- GPRSДокумент20 страницGPRSshashiОценок пока нет
- By: Richa SachdevДокумент18 страницBy: Richa SachdevRicha SachdevОценок пока нет
- Understanding GPRS and its EvolutionДокумент25 страницUnderstanding GPRS and its EvolutionmixtureboyОценок пока нет
- An Overview of Wireless Data CommunicationsДокумент63 страницыAn Overview of Wireless Data CommunicationsebinVettuchirayilОценок пока нет
- Mobile Devices Guide: Smartphones, PDAs and GPRS TechnologyДокумент125 страницMobile Devices Guide: Smartphones, PDAs and GPRS TechnologyChaitanyaОценок пока нет
- Everything You Need to Know About GPRSДокумент46 страницEverything You Need to Know About GPRSDamo DharanОценок пока нет
- Evolution to 3G Networks: Understanding the Transition from 2G to 3GДокумент33 страницыEvolution to 3G Networks: Understanding the Transition from 2G to 3GNavaneeth KrishnanОценок пока нет
- GPRS Architecture: Ayan Ganguly Bishakha Roy Akash DuttaДокумент24 страницыGPRS Architecture: Ayan Ganguly Bishakha Roy Akash DuttaAyan GangulyОценок пока нет
- GPRS BenefitsДокумент27 страницGPRS BenefitsMohamedSalahОценок пока нет
- GPRS Seminar Presentation on Wireless Packet Data TechnologyДокумент57 страницGPRS Seminar Presentation on Wireless Packet Data TechnologyAziz Ur RehmanОценок пока нет
- GPRS Architecture and GTP Protocol OverviewДокумент57 страницGPRS Architecture and GTP Protocol OverviewShriraj07Оценок пока нет
- GPRSДокумент18 страницGPRSpapayee lakshmananОценок пока нет
- Copy (2) of GPRS2Документ14 страницCopy (2) of GPRS2saha_debajyoti0Оценок пока нет
- 3g Core1Документ19 страниц3g Core1Pramod RaiОценок пока нет
- Mobile GenerationДокумент24 страницыMobile GenerationPhantom FireОценок пока нет
- GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) : ArchitectureДокумент7 страницGPRS (General Packet Radio Service) : ArchitectureSrinivas KaratlapelliОценок пока нет
- General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Документ32 страницыGeneral Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Zatin GuptaОценок пока нет
- General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Документ42 страницыGeneral Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Santoshkumar ShelkeОценок пока нет
- EDGEДокумент43 страницыEDGEPramod RaiОценок пока нет
- Electronics - Communication Engineering Topic: (Type The Company Address)Документ34 страницыElectronics - Communication Engineering Topic: (Type The Company Address)Varun SainiОценок пока нет
- General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Документ32 страницыGeneral Packet Radio Service (GPRS)divyeshchauhan014Оценок пока нет
- GPRS Lecture 22Документ21 страницаGPRS Lecture 22Puneet ManglaОценок пока нет
- VASДокумент50 страницVASPrashant BediОценок пока нет
- An Overview of Wireless Data Communications TechnologiesДокумент63 страницыAn Overview of Wireless Data Communications TechnologiesnahuОценок пока нет
- Gprs Architecture: General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Документ6 страницGprs Architecture: General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Vam ArmodiaОценок пока нет
- DE1.1 6th Sem.08 WirelessДокумент202 страницыDE1.1 6th Sem.08 WirelessgpsonlineОценок пока нет
- Chap 26 General Packet Radio Service (Compatibility Mode)Документ19 страницChap 26 General Packet Radio Service (Compatibility Mode)Mahesh SinghОценок пока нет
- WCIICh 02Документ100 страницWCIICh 02Siddhant AgrawalОценок пока нет
- GPRS Network ArchitectureДокумент133 страницыGPRS Network ArchitectureNagashruthi BalasubramanyaОценок пока нет
- E5-E6 - Text - Chapter 11. CM TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEW 4G 5GДокумент13 страницE5-E6 - Text - Chapter 11. CM TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEW 4G 5Gsumit15sksОценок пока нет
- 3.1 Basic Terms of Data Communications: Real TimeДокумент10 страниц3.1 Basic Terms of Data Communications: Real Timeeng.tahasulimanОценок пока нет
- GPRS: How It Works: An O2 White PaperДокумент23 страницыGPRS: How It Works: An O2 White PaperKonstantinos ChrisОценок пока нет
- GPRS Presentation: An Introduction to General Packet Radio ServiceДокумент26 страницGPRS Presentation: An Introduction to General Packet Radio ServiceAnonymous xsK0G4IОценок пока нет
- E4-E5 - Text - Chapter 2. Migration To Mobile Technologies Upto 5gДокумент19 страницE4-E5 - Text - Chapter 2. Migration To Mobile Technologies Upto 5gAGM CMS&MОценок пока нет
- Gprs Demystified: CommunicationsДокумент2 страницыGprs Demystified: Communicationsbhuvi2312Оценок пока нет
- Radio: ServiceДокумент18 страницRadio: ServiceMayur GudiОценок пока нет
- GPRSДокумент14 страницGPRSSaumil MaheshwariОценок пока нет
- 3g Core1Документ19 страниц3g Core1AbhilashОценок пока нет
- Seminar On GPRS: Sonam SoniДокумент27 страницSeminar On GPRS: Sonam Soniurveshp21Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Mobile Telecommunication and GSMДокумент21 страницаChapter 1 - Introduction To Mobile Telecommunication and GSMNur NabiОценок пока нет
- Huawei GPRS Core Network SolutionДокумент70 страницHuawei GPRS Core Network SolutionSandjay Singh50% (2)
- Mobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationОт EverandMobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (3)
- Wisdom Classes Classification and AnalogyДокумент26 страницWisdom Classes Classification and AnalogyTushar SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Signals and CommunicationДокумент3 страницыSignals and CommunicationTushar SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Andhra Bank - Recruitment of Probationary Officers (PGDBF 2016 - 17)Документ1 страницаAndhra Bank - Recruitment of Probationary Officers (PGDBF 2016 - 17)Tushar SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Di Capsule BA Part 1Документ5 страницDi Capsule BA Part 1Tushar SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Basic Electrical NotesДокумент58 страницBasic Electrical NotesKamal Joshi100% (2)
- Signal Processing:: ACF PDF CDF Communication:: Block Diagram Analog and Digital Modulation Schemes NoiseДокумент1 страницаSignal Processing:: ACF PDF CDF Communication:: Block Diagram Analog and Digital Modulation Schemes NoiseTushar SaxenaОценок пока нет
- L-26 (TB) Three Phase TransformerДокумент16 страницL-26 (TB) Three Phase Transformervelisbar100% (1)
- Syll ELitmusДокумент2 страницыSyll ELitmusTushar SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Syll ELitmusДокумент2 страницыSyll ELitmusTushar SaxenaОценок пока нет
- CWE-SPL-IV-Recruitment of Specialist Officers PDFДокумент2 страницыCWE-SPL-IV-Recruitment of Specialist Officers PDFTushar SaxenaОценок пока нет
- UPTU Syllabus for Computer Science & Engineering 2nd YearДокумент16 страницUPTU Syllabus for Computer Science & Engineering 2nd YearPrakash KumarОценок пока нет
- Some Basic ConceptsДокумент10 страницSome Basic ConceptsTushar SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Cse 2ndyear SyllabusДокумент11 страницCse 2ndyear Syllabusashish jainОценок пока нет
- Elitmus Probability Questions For Elitmus - Elitmus Questions For PH Test Page 1 PDFДокумент3 страницыElitmus Probability Questions For Elitmus - Elitmus Questions For PH Test Page 1 PDFTushar Saxena0% (1)
- BtechДокумент27 страницBtechakash nairОценок пока нет
- BCAДокумент23 страницыBCATushar SaxenaОценок пока нет
- 8085 Microprocessor Lab ManualДокумент43 страницы8085 Microprocessor Lab ManualMukulSinghОценок пока нет
- CL 11Документ8 страницCL 11Tushar SaxenaОценок пока нет
- BJTДокумент14 страницBJTTushar SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Banking Pathway 2015: English (Mix Quiz) : Bankers Adda Old Logo SeminarДокумент7 страницBanking Pathway 2015: English (Mix Quiz) : Bankers Adda Old Logo SeminarTushar SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Features of IndiaДокумент2 страницыFeatures of IndiaTushar SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Michelle Obama wife of Barack ObamaДокумент7 страницMichelle Obama wife of Barack ObamaTushar SaxenaОценок пока нет
- EMI BasicsДокумент11 страницEMI BasicsTushar SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Days of National and International Importance JanurayДокумент7 страницDays of National and International Importance JanurayTushar SaxenaОценок пока нет
- AdvertisementДокумент2 страницыAdvertisementTushar SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Class 11 Syllabus - 2015-2016 CBSEsyllabusДокумент4 страницыChemistry Class 11 Syllabus - 2015-2016 CBSEsyllabusTushar SaxenaОценок пока нет
- P-N Junction DiodeДокумент7 страницP-N Junction DiodeTushar SaxenaОценок пока нет
- InjusticeДокумент1 страницаInjusticeTushar SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Progrmming LanguageДокумент2 страницыProgrmming LanguageTushar SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Why BPSKДокумент1 страницаWhy BPSKTushar SaxenaОценок пока нет
- CN Full Manual r2021Документ44 страницыCN Full Manual r2021chandrakanth.bОценок пока нет
- T Rec G.988 201010 S!!PDF eДокумент552 страницыT Rec G.988 201010 S!!PDF eRahul JainОценок пока нет
- MCA19Документ201 страницаMCA19Bhushan AkolkarОценок пока нет
- Traffic Shaping Using PfSense in Bridged ModeДокумент5 страницTraffic Shaping Using PfSense in Bridged ModeCarlos WehrnОценок пока нет
- Wi-Pms310Gf-Ups+ 8Ge+2Sfp Ports 24V-48V Mixed L2 Managed Ups No-Break Poe Switch With 8-Port Poe Data SheetДокумент10 страницWi-Pms310Gf-Ups+ 8Ge+2Sfp Ports 24V-48V Mixed L2 Managed Ups No-Break Poe Switch With 8-Port Poe Data Sheetjulio vivasОценок пока нет
- Paper - Protección Contra Arco EléctricoДокумент20 страницPaper - Protección Contra Arco EléctricoWalter Castellanos VilcaОценок пока нет
- NETWORKING BCA WBUT 5th SEM NOTESДокумент135 страницNETWORKING BCA WBUT 5th SEM NOTESapi-1958925986% (22)
- R6K+TDM ConfigurationДокумент37 страницR6K+TDM ConfigurationMuhammad Sikander hayat100% (1)
- JN0 661qa132Документ103 страницыJN0 661qa132MateiОценок пока нет
- Sound Level MeterДокумент20 страницSound Level MeterEng13Оценок пока нет
- Full Notes CCIE Enterprise CCNP EncorДокумент462 страницыFull Notes CCIE Enterprise CCNP EncorMohamad Siblini100% (2)
- 22-04-01 PTAB Apple IPR2022-00715 U.S. Patent 8792454Документ69 страниц22-04-01 PTAB Apple IPR2022-00715 U.S. Patent 8792454Florian MuellerОценок пока нет
- S2700, S3700, S5700, S6700, S7700, and S9700 Series Switches Typical Configuration Examples PDFДокумент2 877 страницS2700, S3700, S5700, S6700, S7700, and S9700 Series Switches Typical Configuration Examples PDFEmersonОценок пока нет
- Final Presentation 3 G and GSM SecurityДокумент36 страницFinal Presentation 3 G and GSM SecurityBisimunguОценок пока нет
- Lab 11: Implement Port SecurityДокумент6 страницLab 11: Implement Port SecurityMahnoor MansoorОценок пока нет
- RTN 320 V100R009C00 Product Description 02 PDFДокумент227 страницRTN 320 V100R009C00 Product Description 02 PDFLima Anjos AnjosОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3.2 BDCДокумент36 страницChapter 3.2 BDCNishu Bade ShresthaОценок пока нет
- Siemens BSS-17Документ1 страницаSiemens BSS-17kevinnightОценок пока нет
- James F Durkin Voice-Enabling The Data Network PDFДокумент226 страницJames F Durkin Voice-Enabling The Data Network PDFJose Leonardo Simancas GarciaОценок пока нет
- Introduction of CAN FD Into The Next Generation of Vehicle E/E ArchitecturesДокумент6 страницIntroduction of CAN FD Into The Next Generation of Vehicle E/E ArchitecturesFaisal Mohammad HassaniОценок пока нет
- Siklu EH-1200 Installation User Manual - EH1200-InSTL-04 - Issue1 (October 2014)Документ54 страницыSiklu EH-1200 Installation User Manual - EH1200-InSTL-04 - Issue1 (October 2014)CorvuS013Оценок пока нет
- 9.8 ZoneDirector 9.8 User Guide - Rev A - 20140614Документ430 страниц9.8 ZoneDirector 9.8 User Guide - Rev A - 20140614Carlos Garcia Jacome DarkerОценок пока нет
- Name Permanent Address: St. Francis Vaddo,: ResumeДокумент3 страницыName Permanent Address: St. Francis Vaddo,: ResumedunnomeОценок пока нет
- (AC-S13) Week 13 - Pre Task - Quiz - Reading Comprehension - INGLES I - DeSARROLLADO (27209)Документ4 страницы(AC-S13) Week 13 - Pre Task - Quiz - Reading Comprehension - INGLES I - DeSARROLLADO (27209)Sergio MudarraОценок пока нет
- NEO 2000 /4000 Library: User GuideДокумент150 страницNEO 2000 /4000 Library: User GuideMunteanu MarianОценок пока нет
- 1830 PSS 36-64 Operation and MaintenanceДокумент239 страниц1830 PSS 36-64 Operation and MaintenanceNguyen Xuan NhamОценок пока нет
- Chapitre 5 - NETWORK DESIGN - Conception Physique Reseau PDFДокумент62 страницыChapitre 5 - NETWORK DESIGN - Conception Physique Reseau PDFit sonyОценок пока нет
- NET1846 Final US PDFДокумент60 страницNET1846 Final US PDFMuhammad Majid KhanОценок пока нет
- 2-4 Variable Length Subnet Masks (VLSM) - Free CCNA Study GuideДокумент3 страницы2-4 Variable Length Subnet Masks (VLSM) - Free CCNA Study GuideRobin RohitОценок пока нет
- Huawei S6720-HI Series Switches BrochureДокумент8 страницHuawei S6720-HI Series Switches BrochureVillatoro ChrisОценок пока нет