Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Kidney Failure (Reference Summary) : Anatomy
Загружено:
USMP FN ARCHIVOSИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Kidney Failure (Reference Summary) : Anatomy
Загружено:
USMP FN ARCHIVOSАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Kidney Failure (Reference Summary)
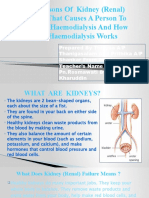
Introduction Kidneys are very important organs. They clean the blood and regulate the fluids in the body. Kidneys are vulnerable to many diseases. Some kidney diseases are life threatening, and others can lead to complete kidney failure and require dialysis. This reference summary explains how the kidneys work, as well as a serious disease of the kidneys called end-stage renal disease, or ESRD. Anatomy Kidneys are bean-shaped organs located in the middle to lower back, on both sides of the spine. The urine that is formed in the kidneys flows through tubes, called ureters, to be stored in the bladder. When the bladder is full, a person feels the urge to urinate. Urine is emptied through the urethra. The main purpose of the kidneys is to make urine by filtering harmful chemicals, called toxins, out of the blood. The kidneys also help to keep necessary chemical substances in the blood, such as sodium, proteins, and sugars. The kidneys control the amount of fluid we keep in our bodies. For example, when we drink more fluids then we need, the kidneys secrete extra urine. On the other hand, when we do not drink as much fluid as we need, the kidneys make less urine. The kidneys help to regulate hormones that strengthen our bones and produce red blood cells. Since the kidneys constantly filter the blood, they are very sensitive to anything we eat or drink, or to any medications we take. The kidneys also help to keep our blood pressure regular; this is why many kidney diseases result in high blood pressure. Damage to only 1 kidney is not usually a major problem, since the other kidney can take over for it. However, if both kidneys get damaged, a person will die within a few days if they do not get dialysis. ESRD ESRD, short for end-stage renal disease, develops when both kidneys are not able to function. Sometimes it happens gradually and sometimes all at once. The following are diseases that can lead to ESRD: diabetes hypertension lupus repeated kidney infections kidney stones kidney cysts infection in the blood called sepsis
The constant use of painkillers, alcohol, or other medications can also lead to ESRD. A kidney specialist, called a nephrologist, can sometimes help to slow the development of ESRD. This is usually done using medications and changes in the patients diet. It is very important to have kidney function checked regularly if you: have a disease that could lead to ESRD or take any medication regularly To check on how the kidneys are functioning, blood tests and urine tests are needed. Signs & Symptoms When the kidneys are not working right, the body retains water, which leads to swelling in the face, ankles, legs, and throughout the body. The extra fluid can cause shortness of breath. Since toxins build up in the body when the kidneys are not filtering them out, patients with ESRD feel very tired and weak. They have no stamina or energy. This is partly due to the body not producing enough red blood cells, a condition called anemia. Kidney failure patients sometimes feel pain below the rib cage. As kidney failure gets worse, blood pressure tends to rise and the body makes less urine. With time, kidney failure causes the skin to become pale. If nothing is done to treat kidney failure, death can result from toxins building up in the body, as well as high levels of potassium in the blood. Treatment The main treatment for ESRD is dialysis. Dialysis is a process that replaces the function of the kidneys. More than 300,000 patients in the USA depend on dialysis in order to stay alive. In some cases, dialysis is temporary, and can be stopped as soon as the kidneys are able to function again. However, dialysis is usually a lifetime treatment. There are 2 types of dialysis: hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Each works differently to filter toxins out of the blood, as the kidneys normally do. Hemodialysis reroutes the blood to a dialysis machine. The machine cleans toxins from the blood and regulates the levels of essential chemicals, such as potassium. Hemodialysis is done 3-4 times per week and each session takes around 4-5 hours. Special IVs are needed for good blood flow to and from the dialysis machine. Peritoneal dialysis uses the peritoneum, which is the lining of the abdominal cavity, to clean the blood. A tube, also known as a catheter, is surgically placed in the peritoneal cavity. A solution called dialysate is allowed to flow into the peritoneal cavity through it the catheter. The dialysate solution interacts with the blood through the peritoneum, filtering out toxins and cleaning it over a period of several hours.
After peritoneal dialysis, the fluid in the peritoneum is drained to the outside of the body into a special bag. The same cycle is repeated many times a week; it is sometimes started before the patient goes to bed and the fluid emptied in the morning. For dialysis to be successful, patients have to follow strict dietary restrictions on the amount of salts, proteins, and fluids they eat and drink. A kidney transplant can cure some cases of ESRD. Unfortunately, there are not enough kidneys available for all ESRD patients. In addition, a kidney transplant is not the best option for every ESRD patient. There are currently 35,000 people on kidney transplant waiting lists! Prevention People who are at risk of getting ESRD should be closely monitored by a family doctor or nephrologist for early signs of it. People who have any of the following conditions are at risk of ESRD: known kidney diseases: diabetes hypertension lupus Some dietary restrictions may be needed to slow down and possibly stop the process that leads to ESRD. Some of these restrictions include eating less: salt (or sodium) potassium proteins Other general healthy lifestyles changes may also help, including: regular exercise not smoking maintaining an ideal weight Summary Kidneys are extremely important organs that filter harmful substances out of the body. The kidneys are susceptible to many diseases, some may be life threatening. Others can lead to complete kidney or renal failure, requiring dialysis. End-stage renal disease, or ESRD, is a very serious condition. Thanks to recent medical advances, patients with ESRD can live normal lives within the restrictions of their dialysis schedule. Kidney transplant, if available and appropriate, can cure kidney disease. The role of the patient in making lifestyle changes and keeping up with the dialysis schedule is very important for successfully treating ESRD.
Вам также может понравиться
- DR. SEBI KIDNEY FAILURE SOLUTION: Dialysis-Free Living. A Natural Approach to Treating and Preventing Chronic Kidney Disease (2022 Guide for Beginners)От EverandDR. SEBI KIDNEY FAILURE SOLUTION: Dialysis-Free Living. A Natural Approach to Treating and Preventing Chronic Kidney Disease (2022 Guide for Beginners)Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- Grimoire of Baphomet A-Z EditionДокумент18 страницGrimoire of Baphomet A-Z EditionTheK1nGp1N100% (1)
- Easy Renal Diet Cookbook: Ultimate Guide To Manage Kidney DiseaseОт EverandEasy Renal Diet Cookbook: Ultimate Guide To Manage Kidney DiseaseОценок пока нет
- Chronic Kidney Disease OverviewДокумент12 страницChronic Kidney Disease OverviewHalles Beverlyn Crisostomo GeraldeОценок пока нет
- Conditionals SentencesДокумент49 страницConditionals SentencesUSMP FN ARCHIVOS100% (5)
- A Comparative Look at Jamaican Creole and Guyanese CreoleДокумент18 страницA Comparative Look at Jamaican Creole and Guyanese CreoleShivana Allen100% (3)
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseДокумент12 страницChronic Kidney DiseaseRoseben SomidoОценок пока нет
- Emilia Perroni-Play - Psychoanalytic Perspectives, Survival and Human Development-Routledge (2013) PDFДокумент262 страницыEmilia Perroni-Play - Psychoanalytic Perspectives, Survival and Human Development-Routledge (2013) PDFMihaela Ioana MoldovanОценок пока нет
- Cancer of LarynxДокумент29 страницCancer of LarynxQasim HaleimiОценок пока нет
- Ascites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandAscites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- CKD Overview: Causes, Symptoms and Stages of Chronic Kidney DiseaseДокумент15 страницCKD Overview: Causes, Symptoms and Stages of Chronic Kidney Diseasejames100% (1)
- Chronic Kidney Disease OverviewДокумент28 страницChronic Kidney Disease Overviewomie22100% (9)
- DialysisДокумент34 страницыDialysisAntonio Junior CastroОценок пока нет
- The Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionОт EverandThe Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionОценок пока нет
- AIRs LM Business-Finance Q1 Module-5Документ25 страницAIRs LM Business-Finance Q1 Module-5Oliver N AnchetaОценок пока нет
- Dialysis CompactДокумент16 страницDialysis CompactTue100% (1)
- AIX For System Administrators - AdaptersДокумент2 страницыAIX For System Administrators - Adaptersdanielvp21Оценок пока нет
- The Eye WorksheetДокумент3 страницыThe Eye WorksheetUSMP FN ARCHIVOS100% (2)
- Cirrhosis Liver Causes Symptoms TreatmentДокумент4 страницыCirrhosis Liver Causes Symptoms TreatmentDaphineОценок пока нет
- Conditionals WorksheetДокумент2 страницыConditionals WorksheetUSMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- Dialysis EducationДокумент7 страницDialysis Educationkeren100% (1)
- Training Plan JDVP 2020 - BPP (40days)Документ36 страницTraining Plan JDVP 2020 - BPP (40days)Shallimar Alcarion100% (1)
- What Are The Kidneys?: Kidney FailureДокумент9 страницWhat Are The Kidneys?: Kidney FailureNurfarhanim Akmal Mohd KhalidОценок пока нет
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseДокумент7 страницChronic Kidney Diseasekzbreakerr100% (1)
- Reported Speech Exercises 2013 PDFДокумент13 страницReported Speech Exercises 2013 PDFjesusjaviermartin86% (7)
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseДокумент33 страницыChronic Kidney DiseasesexiiimammaОценок пока нет
- L.10 Kidney HealthДокумент37 страницL.10 Kidney HealthMunira SulimanОценок пока нет
- Kidney FailureДокумент8 страницKidney FailureКатя ДементьеваОценок пока нет
- Kidney Problems and DialysisДокумент3 страницыKidney Problems and DialysismarymakinОценок пока нет
- CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE: CAUSES, STAGES, SYMPTOMS, AND TREATMENTДокумент14 страницCHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE: CAUSES, STAGES, SYMPTOMS, AND TREATMENTPatricia LeonorОценок пока нет
- SN Allen F. RojasДокумент22 страницыSN Allen F. Rojaskane1978Оценок пока нет
- KidneyДокумент3 страницыKidneyAngelicaОценок пока нет
- The Reasons For Kidney Failure Requiring Haemodialysis And How It WorksДокумент16 страницThe Reasons For Kidney Failure Requiring Haemodialysis And How It WorksPrithika ShankarОценок пока нет
- Spectrum September KidneyДокумент29 страницSpectrum September KidneyParth LandeОценок пока нет
- Managing KidneyДокумент4 страницыManaging KidneyPalaОценок пока нет
- Bio Project1Документ3 страницыBio Project1Nishanth TunikiОценок пока нет
- Name:: Class: Biology Investigatory FileДокумент18 страницName:: Class: Biology Investigatory FileNityam Kumar TIWARIОценок пока нет
- Case Study: Managing End-Stage Renal DiseaseДокумент7 страницCase Study: Managing End-Stage Renal Diseasemarvin de castroОценок пока нет
- Your Amazing KidneysДокумент13 страницYour Amazing KidneysjerinthomasrajanОценок пока нет
- What Is Kidney DiseaseДокумент6 страницWhat Is Kidney DiseaseEllie ELLОценок пока нет
- Kidney Works: Can Kidney Disease Cured?Документ4 страницыKidney Works: Can Kidney Disease Cured?Jacinto Adolph Agustin CagorolОценок пока нет
- Acute Kidney Failure OverviewДокумент4 страницыAcute Kidney Failure OverviewchichauskyОценок пока нет
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseДокумент7 страницChronic Kidney DiseaseHennah ReblandoОценок пока нет
- Activity No. 5 Principles of DialysisДокумент5 страницActivity No. 5 Principles of DialysisKatrina Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- Kidney FailureДокумент2 страницыKidney Failuredanee しОценок пока нет
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseДокумент17 страницChronic Kidney DiseaseAdelle SmithОценок пока нет
- Circulatory SystemДокумент33 страницыCirculatory SystemJennifer SamaniegoОценок пока нет
- Kidney Failure FactsДокумент19 страницKidney Failure Factss.khan9211rediffmail.comОценок пока нет
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseДокумент8 страницChronic Kidney DiseaseAyiessa_AJОценок пока нет
- Dialysis FunctionДокумент12 страницDialysis Functionmanisha maniОценок пока нет
- BubreДокумент10 страницBubreharryОценок пока нет
- Why We Have Kidneys: Vital Organs Filter BloodДокумент33 страницыWhy We Have Kidneys: Vital Organs Filter Bloodcrs4321Оценок пока нет
- Kidney Transplant in Delhi, Kidney Stone Treatment in DelhiДокумент3 страницыKidney Transplant in Delhi, Kidney Stone Treatment in DelhiDr. Anant KumarОценок пока нет
- Renal Failure NoteДокумент27 страницRenal Failure Notechiemerieagana3Оценок пока нет
- Introduction To Urinary System:-: Antilithiatic Activity of Ethanolic Extract of Dried Leaves of Fragaria Vesca Linn."Документ41 страницаIntroduction To Urinary System:-: Antilithiatic Activity of Ethanolic Extract of Dried Leaves of Fragaria Vesca Linn."Rohit PatilОценок пока нет
- UREMIAДокумент10 страницUREMIAAkanksha TiwariОценок пока нет
- Kidney FailureДокумент7 страницKidney Failureapi-320844972Оценок пока нет
- Vishnu Dental CollegeДокумент6 страницVishnu Dental CollegeudayОценок пока нет
- To Study About The Kidney Transplantation and DialysisДокумент9 страницTo Study About The Kidney Transplantation and DialysisAnonymous 5quBUnmvm1Оценок пока нет
- CKD-CHF ScriptДокумент5 страницCKD-CHF ScriptAirglow GОценок пока нет
- Kidney Failure: Causes, Signs, and TreatmentДокумент6 страницKidney Failure: Causes, Signs, and TreatmentDiane Agcaoili EdraОценок пока нет
- Dialysis ReportДокумент3 страницыDialysis ReportAnabel UnidaОценок пока нет
- Causes: o o o oДокумент5 страницCauses: o o o oyarem01Оценок пока нет
- Nephrotic Syndrome + ArfДокумент64 страницыNephrotic Syndrome + ArfkrishnasreeОценок пока нет
- Kidney DialysisДокумент2 страницыKidney DialysisVenus BunaganОценок пока нет
- Chronic Renal FailureДокумент7 страницChronic Renal FailureMary Jane Tiangson100% (1)
- Renal Departemen: Sih Winedar, Sri Rahayu, Susi Wulandari Vincesia Sulastri, Yuli Hartini, Yunita SetyaДокумент17 страницRenal Departemen: Sih Winedar, Sri Rahayu, Susi Wulandari Vincesia Sulastri, Yuli Hartini, Yunita Setyavincensia sulasОценок пока нет
- End-Stage Renal Disease Kidney Transplantation TopДокумент8 страницEnd-Stage Renal Disease Kidney Transplantation Topmondae175934Оценок пока нет
- Cirrhosis of The Liver: CausesДокумент6 страницCirrhosis of The Liver: CausespakdejackОценок пока нет
- Modals PracticeДокумент2 страницыModals PracticeUSMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- A Tour of The Cardiovascular SystemДокумент2 страницыA Tour of The Cardiovascular SystemUSMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- Medicina III - Insuficiencia AdrenalДокумент41 страницаMedicina III - Insuficiencia AdrenalUSMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- (Lab) Patología II - Esófago y EstómagoДокумент82 страницы(Lab) Patología II - Esófago y EstómagoUSMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- Genomic Medicine - A PrimerДокумент8 страницGenomic Medicine - A PrimerUSMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- Passive Voice WorksheetДокумент2 страницыPassive Voice WorksheetUSMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- How Is Osteoporosis DiagnosedДокумент3 страницыHow Is Osteoporosis DiagnosedUSMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- English Practice Passive VoiceДокумент2 страницыEnglish Practice Passive VoiceUSMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- The New Stem Cell Biology (Something For Everyone)Документ14 страницThe New Stem Cell Biology (Something For Everyone)USMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- Daily AspirinДокумент2 страницыDaily AspirinUSMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- PassiveДокумент20 страницPassiveUSMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- By The Early 2020sДокумент1 страницаBy The Early 2020sUSMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- Future Simple WorksheetДокумент2 страницыFuture Simple WorksheetUSMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- Oncogenes and CancerДокумент7 страницOncogenes and CancerUSMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- How Can You Relieve MigraineДокумент3 страницыHow Can You Relieve MigraineUSMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- Breast Cancer (En)Документ7 страницBreast Cancer (En)USMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- Diabetes WorksheetДокумент1 страницаDiabetes WorksheetUSMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- Bases Moleculares Del CáncerДокумент15 страницBases Moleculares Del CáncerMairim Adn-a JóasОценок пока нет
- Breast Cancer WorksheetДокумент2 страницыBreast Cancer WorksheetUSMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- How Bacteria Could Cause CancerДокумент7 страницHow Bacteria Could Cause CancerUSMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- The Expanding Spectrum of G Protein DiseasesДокумент6 страницThe Expanding Spectrum of G Protein DiseasesUSMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- LASIK (En)Документ4 страницыLASIK (En)USMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- Inherited Diseases Involving G ProteinsДокумент6 страницInherited Diseases Involving G ProteinsUSMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- Diabetes (En)Документ4 страницыDiabetes (En)USMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- Lasik TestДокумент2 страницыLasik TestUSMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- Reference Summary: X-Plain LasikДокумент0 страницReference Summary: X-Plain LasikUSMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- Eng10 LPQ3_4 Coherence and CohesionДокумент2 страницыEng10 LPQ3_4 Coherence and CohesionNiña RasonableОценок пока нет
- A Model For Blockchain-Based Distributed Electronic Health Records - 2016Документ14 страницA Model For Blockchain-Based Distributed Electronic Health Records - 2016Asif KhalidОценок пока нет
- Arraignment PleaДокумент4 страницыArraignment PleaJoh SuhОценок пока нет
- 1 Minute Witness PDFДокумент8 страниц1 Minute Witness PDFMark Aldwin LopezОценок пока нет
- FIN 1050 - Final ExamДокумент6 страницFIN 1050 - Final ExamKathi100% (1)
- Krittika Takiar PDFДокумент2 страницыKrittika Takiar PDFSudhakar TomarОценок пока нет
- The 4Ps of Labor: Passenger, Passageway, Powers, and PlacentaДокумент4 страницыThe 4Ps of Labor: Passenger, Passageway, Powers, and PlacentaMENDIETA, JACQUELINE V.Оценок пока нет
- Introduction To ResearchДокумент5 страницIntroduction To Researchapi-385504653Оценок пока нет
- Public Policy For Nigerian EnviromentДокумент11 страницPublic Policy For Nigerian EnviromentAbishai Auta GaiyaОценок пока нет
- Electrical Power System Protection BookДокумент2 страницыElectrical Power System Protection BookHimanshu Kumar SagarОценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes - Design of RC Structure - Day 5Документ6 страницLecture Notes - Design of RC Structure - Day 5Tapabrata2013Оценок пока нет
- English Literature RevisionДокумент61 страницаEnglish Literature RevisionAlex Cobain Glinwood100% (1)
- 1 Chapter I Translation TheoryДокумент19 страниц1 Chapter I Translation TheoryAditya FirmansyahОценок пока нет
- Mixed-Use Proposal Dormitory and Hotel High-RiseДокумент14 страницMixed-Use Proposal Dormitory and Hotel High-RiseShanaia BualОценок пока нет
- AefiДокумент38 страницAefizedregga2Оценок пока нет
- 2020 Non Student Candidates For PCL BoardДокумент13 страниц2020 Non Student Candidates For PCL BoardPeoples College of LawОценок пока нет
- Brochure For Graduate DIploma in Railway Signalling 2019 v1.0 PDFДокумент4 страницыBrochure For Graduate DIploma in Railway Signalling 2019 v1.0 PDFArun BabuОценок пока нет
- Visual AnalysisДокумент4 страницыVisual Analysisapi-35602981850% (2)
- Traditional Knowledge - The Changing Scenario in India PDFДокумент9 страницTraditional Knowledge - The Changing Scenario in India PDFashutosh srivastavaОценок пока нет
- Safety Data Sheet Highlights Key Hazards and ProtectionsДокумент7 страницSafety Data Sheet Highlights Key Hazards and ProtectionsOm Prakash RajОценок пока нет
- Aerospace & Aviation Job RolesДокумент74 страницыAerospace & Aviation Job RolesBharat JainОценок пока нет
- Euro Tuner 1 2008 PDFДокумент2 страницыEuro Tuner 1 2008 PDFDarwinОценок пока нет