Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Answers To Quiz 10
Загружено:
George RahwanИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Answers To Quiz 10
Загружено:
George RahwanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Answers to the questions in Quiz 10: 1.
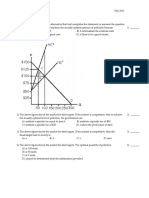
Definition of Efficient Scale: the quantity of output that minimizes average total cost (ATC).
That is Q* in the above figure. 2. When economists speak of a firms cost of production, they include all the opportunity costs of making its output of goods and services. This is consistent with Principle #2 that the cost of something is what you give up to get it. Total opportunity cost includes both implicit and explicit costs. That is, Total opportunity cost = implicit cost + explicit cost Definition of explicit costs: input costs that require a payment of money by the firm. Definition of implicit costs: input costs that do not require a payment of money by the firm. 3. Marginal cost (MC) is the cost of an extra unit of output produced. Definition of MC: the additional cost (or the increase in total cost) that arises from producing an extra unit of production. The marginal cost is the slope of total cost curve. That is,
Change in total cost Change in output total cost output
Marginal cost = =
Note that the total cost curve slopes up at an increasing rate. The increasing rate refers to the fact that MC is an increasing function of output (Q).
4. Definition of Economic Profit: total revenue minus total cost, including both explicit and implicit costs. That is, Economic profit = total revenue (explicit costs + implicit costs) Accountants, however, do not consider implicit costs as part of the total cost. Thus, Accounting profit = total revenue explicit costs Accordingly, we can write Accounting Profit = economic profit + implicit costs and that when economic profit is zero, accounting profit will be equal to implicit cost as follows: Accounting Profit = 0 + implicit costs 5&6. Definition of AFC: fixed costs (FC) divided by the quantity of output (Q). Definition of AVC: variable costs (VC) divided by the quantity of output (Q). Definition of ATC: total costs (TC) divided by the quantity of output (Q). FC AFC = ; Q and that VC AVC = ; Q TC ATC = . Q
ATC = AFC + AVC
As shown in the above figure, AFC is continuously decreasing as output is increasing. At the low levels of output, AFC decreases at a very rapid rate and pulls down ATC. As a result, ATC keeps declining. At higher levels of output AFC is still decreasing but at a very slow rate and loses its ability to pull down ATC. As a result ATC starts increasing as output increases.
7&8.
The relationship between marginal cost (MC) and average total cost (ATC) is as follows: (i) (ii) (iii) when marginal cost is less than average total cost, average total cost is falling. That is, when MC < ATC, then ATC . when marginal cost is more than average total cost, average total cost is rising. That is, when MC > ATC, then ATC . Marginal cost crosses average total cost at the minimum of the average total cost (the efficient scale.) That is, when MC = ATC, then ATC is minimum.
9&10.
The graph of the production function slopes up at a decreasing rate. The slope is the marginal product of labor, and it is decreasing because of diminishing marginal product of labor. As a result, the total cost curve slopes up at an increasing rate. The slope of the total cost curve is marginal cost. The increase in the slope of the total cost curve or marginal cost is due to diminishing marginal product.
Вам также может понравиться
- CH 7 Costs of Production Spring 2023Документ52 страницыCH 7 Costs of Production Spring 2023sayidОценок пока нет
- Ch-3-2-Theory of CostДокумент33 страницыCh-3-2-Theory of Costyonatan gizawОценок пока нет
- Lec06 Cost Concepts & Interrelations - Optimum Level of Input Use and Optimum ProductionДокумент8 страницLec06 Cost Concepts & Interrelations - Optimum Level of Input Use and Optimum ProductionAZIZRAHMANABUBAKARОценок пока нет
- Module-6 Cost and Revenue AnalysisДокумент46 страницModule-6 Cost and Revenue Analysiskarthik21488Оценок пока нет
- COST ConceptsДокумент22 страницыCOST ConceptsPriya KalaОценок пока нет
- Analysis of CostsДокумент26 страницAnalysis of CostsTanvi ThakurОценок пока нет
- Unit 6Документ42 страницыUnit 6unstopable 7 rodiesОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 - The Theory of CostДокумент11 страницChapter 6 - The Theory of Costjcguru2013Оценок пока нет
- Microeconomics Cha 4Документ8 страницMicroeconomics Cha 4haile GetachewuОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Costs: Book: Economics by Paul Samuelson and William NordhausДокумент19 страницAnalysis of Costs: Book: Economics by Paul Samuelson and William NordhausHiraОценок пока нет
- Cubic Shaped TC CurveДокумент4 страницыCubic Shaped TC CurveSEEMAL JAMILОценок пока нет
- Theory of CostДокумент35 страницTheory of Costarsalan khanОценок пока нет
- Cost of Production Ch.5Документ46 страницCost of Production Ch.5Mahmoud KassemОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 MicreconomicsДокумент21 страницаChapter 4 MicreconomicsAbdo GelgeluОценок пока нет
- Cost of Production or Total Cost (TC) : Fixed Costs (FC)Документ6 страницCost of Production or Total Cost (TC) : Fixed Costs (FC)Ayman FergeionОценок пока нет
- Eco 101 8Документ4 страницыEco 101 8danielhunton91Оценок пока нет
- Cost FunctionДокумент58 страницCost FunctionAishwarya ChauhanОценок пока нет
- A Quick Review On Chapter-5: ProductionДокумент32 страницыA Quick Review On Chapter-5: ProductionKhaled Bin Shahabuddin ShagarОценок пока нет
- CH 4Документ29 страницCH 4Endalk ZewdieОценок пока нет
- Cost Analysis: Dr. Mohsina HayatДокумент36 страницCost Analysis: Dr. Mohsina HayatFaizan QudsiОценок пока нет
- Cost FunctionДокумент6 страницCost FunctionAmrita PorsiyaОценок пока нет
- Pr. of Eco - Prod & CostДокумент38 страницPr. of Eco - Prod & CostmukulОценок пока нет
- Econ IIДокумент28 страницEcon IIworkinehamanuОценок пока нет
- Lecture-10 Cost of Production (1) ..Документ12 страницLecture-10 Cost of Production (1) ..Movie SeriesОценок пока нет
- Long Run Short RunДокумент17 страницLong Run Short RunA PОценок пока нет
- Lecture 7 Production in The SRДокумент36 страницLecture 7 Production in The SRmyturtle gameОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 Cost of ProductionsДокумент9 страницChapter 6 Cost of Productionsra2002ma2002931Оценок пока нет
- Tutorial 5Документ3 страницыTutorial 5biresaw birhanuОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7. Costs: 0. Economic Cost and Accounting CostДокумент14 страницChapter 7. Costs: 0. Economic Cost and Accounting CostLâmViênОценок пока нет
- Lesson 2Документ15 страницLesson 2KeneОценок пока нет
- Theory of Cost NewДокумент4 страницыTheory of Cost NewMahesh ViswanathanОценок пока нет
- Cost Analysis Learning ObjectiveДокумент14 страницCost Analysis Learning ObjectiveRohitPatialОценок пока нет
- Cost Concepts in Economics: Chapter 9: Kay and EdwardsДокумент33 страницыCost Concepts in Economics: Chapter 9: Kay and EdwardsDrBabita SinglaОценок пока нет
- Adigrat University Department of Economics Microeconomics: Chapter Three Theory of Cost of ProductionДокумент14 страницAdigrat University Department of Economics Microeconomics: Chapter Three Theory of Cost of Productionabadi gebruОценок пока нет
- Economics For Managers: Cost FunctionsДокумент42 страницыEconomics For Managers: Cost FunctionsRomit BanerjeeОценок пока нет
- Group 7 HandoutsДокумент10 страницGroup 7 HandoutsCoke Aidenry SaludoОценок пока нет
- Cost Output RelationsДокумент14 страницCost Output Relationskarteek_arОценок пока нет
- Costs & Output DecisionsДокумент18 страницCosts & Output DecisionsIbrahimОценок пока нет
- Chapter11 - Production-And-Cost-Analysis1Документ24 страницыChapter11 - Production-And-Cost-Analysis1Sandara beldoОценок пока нет
- Microeconomics: Lecture 9: The Cost of ProductionДокумент37 страницMicroeconomics: Lecture 9: The Cost of Productionblackhawk31Оценок пока нет
- Cost of ProductionДокумент61 страницаCost of ProductionPankit KediaОценок пока нет
- CostДокумент26 страницCostAnita PanthiОценок пока нет
- CFO CH 8Документ55 страницCFO CH 8ashchua21Оценок пока нет
- Theory of Firm and Production IIДокумент43 страницыTheory of Firm and Production IIivyling29Оценок пока нет
- Unit IV (Cost & Revenue Analysis)Документ26 страницUnit IV (Cost & Revenue Analysis)Helik SoniОценок пока нет
- LIPSEY - CHRYSTAL - FIGTEXT08Visit Us at Management - Umakant.infoДокумент9 страницLIPSEY - CHRYSTAL - FIGTEXT08Visit Us at Management - Umakant.infowelcome2jungleОценок пока нет
- Concept of CostДокумент6 страницConcept of CostRachael KhandelwalОценок пока нет
- COSTДокумент8 страницCOSTHumayun Kabir JimОценок пока нет
- Cost TheoryДокумент8 страницCost TheorytamalbanikcuОценок пока нет
- Theory of CostДокумент49 страницTheory of CostAman Anshu100% (1)
- College of Business Management Institute of Business Management ECO 101 - Principles of Microeconomics Faculty Name: Ms. SABEEN ANWARДокумент3 страницыCollege of Business Management Institute of Business Management ECO 101 - Principles of Microeconomics Faculty Name: Ms. SABEEN ANWARusama farooqОценок пока нет
- BIE201 Handout03Документ22 страницыBIE201 Handout03andersonmapfirakupaОценок пока нет
- Total Fixed CostДокумент4 страницыTotal Fixed Costanaas133Оценок пока нет
- CostconceptsДокумент20 страницCostconceptsesranganadhОценок пока нет
- CA CPT Micro Economics PPT Theory of CostДокумент119 страницCA CPT Micro Economics PPT Theory of CostShobi DionelaОценок пока нет
- CostconceptsДокумент20 страницCostconceptsShobi DionelaОценок пока нет
- Costconcepts 090715160417 Phpapp01Документ20 страницCostconcepts 090715160417 Phpapp01Subhankar PatraОценок пока нет
- Theory of Production CostДокумент17 страницTheory of Production CostDherya AgarwalОценок пока нет
- 10e 08 Chap Student Workbook PDFДокумент20 страниц10e 08 Chap Student Workbook PDFPRAGYAN PANDAОценок пока нет
- Solution Manual Health Care Economics 7th Edition by Paul J. Feldstein SLC1106Документ4 страницыSolution Manual Health Care Economics 7th Edition by Paul J. Feldstein SLC1106Thar AdeleiОценок пока нет
- Answers To Multiple Choice QuestionsДокумент5 страницAnswers To Multiple Choice QuestionsDanish Us SalamОценок пока нет
- Module 7 AssignmentДокумент3 страницыModule 7 AssignmentRosario CabarrubiasОценок пока нет
- Solutions ProblemsДокумент14 страницSolutions ProblemsbagussmОценок пока нет
- Notes of Managerial EconomicsДокумент24 страницыNotes of Managerial EconomicsJaved HussainОценок пока нет
- Economics HelpsДокумент3 страницыEconomics HelpssahilsureshОценок пока нет
- Review Problems 2Документ18 страницReview Problems 2xbdrsk6fbgОценок пока нет
- Chapter 14 Firms in Competitive Markets 08042021 075713pmДокумент18 страницChapter 14 Firms in Competitive Markets 08042021 075713pmHasnain GoharОценок пока нет
- Eco515 - Managerial EconomicsДокумент14 страницEco515 - Managerial EconomicsBryan ShieldsОценок пока нет
- Unit - Ii: Production FunctionДокумент32 страницыUnit - Ii: Production FunctionSai Srinivas BodapatiОценок пока нет
- Economics QuestДокумент10 страницEconomics QuestMd Ikrama AkhtarОценок пока нет
- 20: Theory of CostДокумент44 страницы20: Theory of CostKeahlyn Boticario CapinaОценок пока нет
- European Car IndustryДокумент43 страницыEuropean Car IndustryMario Zambrano CéspedesОценок пока нет
- 8a. Profit Maximization by A Competitive Firm: A. Cost and Revenue: Total, Average and MarginalДокумент5 страниц8a. Profit Maximization by A Competitive Firm: A. Cost and Revenue: Total, Average and MarginalHamza ZainОценок пока нет
- Water Scarcity-The Next Global CrisisДокумент10 страницWater Scarcity-The Next Global CrisisViswa PillayОценок пока нет
- 8.1 Costs in The Short RunДокумент54 страницы8.1 Costs in The Short RunBAYU KHARISMAОценок пока нет
- Question and Answer - 30Документ31 страницаQuestion and Answer - 30acc-expertОценок пока нет
- Unit 4 Module 6 Absorption Costing and Marginal Costing: Topics To Be EnlightenedДокумент28 страницUnit 4 Module 6 Absorption Costing and Marginal Costing: Topics To Be EnlightenedJibran SheikhОценок пока нет
- Chapter Five: Perfect CompetitionДокумент6 страницChapter Five: Perfect CompetitionAbrha636Оценок пока нет
- Ultimate Review Packet: MicroeconomicsДокумент3 страницыUltimate Review Packet: MicroeconomicsabcdeОценок пока нет
- 9706 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2014 SeriesДокумент5 страниц9706 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2014 SeriesMateeh-ur -rehmanОценок пока нет
- Assignment - Managerial EconomicsДокумент12 страницAssignment - Managerial EconomicsAsmaul Husna100% (1)
- EconomicsДокумент348 страницEconomicsSrv Solitario BiswasОценок пока нет
- 460-13-3 Midterm Study QuestionsДокумент12 страниц460-13-3 Midterm Study QuestionsHarry ZhanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 13Документ16 страницChapter 13Precious Katherine Aceveda Andal-Manuebo100% (2)
- Relevant Cost AssignmentДокумент10 страницRelevant Cost AssignmentME ValleserОценок пока нет
- Optimization of A Firm Using The Concept of Derivatives and The Rules of DifferentiationДокумент41 страницаOptimization of A Firm Using The Concept of Derivatives and The Rules of DifferentiationMichelle Batar LibatonОценок пока нет
- Chapter Absorption and Marginal CostingДокумент10 страницChapter Absorption and Marginal CostingINDIAN BEASTОценок пока нет
- Module 8 Managing Competitive, Monopolistic, and Monopolistically Competitive Markets NotesДокумент9 страницModule 8 Managing Competitive, Monopolistic, and Monopolistically Competitive Markets NotesHazel PabloОценок пока нет
- Assignment 2 ITДокумент3 страницыAssignment 2 ITlaiba mujahidОценок пока нет