Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ramipril
Загружено:
Michael KuzbytАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Ramipril
Загружено:
Michael KuzbytАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
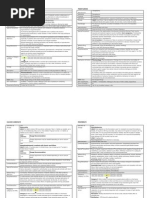
Clinical Medications Worksheets Generic Name
Ramipril
Trade Name
Altace
Classification
antihypertensives
Dose
25mg
Route
po
Time/frequency
1000
Peak
3-6h
Onset
1-2h
Duration
24h
For IV meds, compatibility with IV drips and /or solutions Nursing Implications (what to focus on) Contraindications/warnings/interactions Hypersensitivity; History of angioedema with previous use of ACE inhibitors; OB: Potential for injury or death of fetus. If pregnancy occurs, discontinue immediately.; Lactation: Discontinue drug or use formula.Use Cautiously in:Black patients (monotherapy for hypertension less effective, may require additional therapy; higher risk of angioedema); Surgery/anesthesia (hypotension may be exaggerated); Women of childbearing potential; Renal impairment (especially renal artery stenosis), hypovolemia, hyponatremia, concurrent diuretic therapyinitial dose recommended; Pedi: Safety not established; Geri: Initial dose recommended.Exercise Extreme Caution in:Family history of angioedema.Adverse Reactions/Side Effectsdizziness, fatigue, headache, vertigo, weakness.cough.hypotension, chest pain.diarrhea, nausea, vomiting.impaired renal function.rashes.hyperkalemia.ANGIOEDEMA Common side effects cough hypotension dizziness fatigue hyperkalemia nausea/vomiting BUN, Cr elevated photosensitivity
Mechanism of action and indications (Why med ordered)
HTN
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors block the conversion of angiotensin I to the vasoconstrictor angiotensin II. ACE inhibitors also prevent the degradation of bradykinin and other vasodilatory prostaglandins. ACE inhibitors also plasma renin levels and aldosterone levels. Net result is systemic vasodilation.
Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or herbal medicines (ask patient specifically)
Excessive hypotension may occur with concurrent use of
hyperuricemia Lab value alterations caused by medicine
diuretics .Additive hypotension with other antihypertensive agents . risk of hyperkalemia with concurrent use of potassium supplements , potassium-sparing diuretics, potassium-containing salt substitutes , or angiotensin II receptor antagonists. NSAIDs and selective COX-2 inhibitors may blunt the antihypertensive effect and the risk of renal dysfunction levels and may the risk of lithium toxicity. risk of renal dysfunction when used with telmisartan ; concurrent use not recommended.
Be sure to teach the patient the following about this medication
Stop taking ramipril and call your doctor at once if you have a serious side effect such as: feeling like you might pass out; high potassium level (slow heart rate, weak pulse, muscle weakness, tingly feeling; dry mouth, thirst, confusion, swelling, and urinating less than usual or not at all; pale skin, dark colored urine, easy bruising or bleeding; jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes); or fever, chills, body aches, flu symptoms, sores in your mouth and throat.
Ramipril can be taken with or without food. Swallow the ramipril tablet whole. You may open the ramipril capsule and sprinkle the medicine into a half-cup (4 ounces) of water, apple juice, or applesauce to make swallowing easier. Swallow without chewing. You may store the mixture for up to 24 hours at room temperature, or up to 48 hours in a refrigerator. Conditions that may cause very low blood pressure include: vomiting, diarrhea, heavy sweating, dehydration, a low salt diet, or taking diuretics (water pills). Tell your doctor if you have a prolonged illness that causes diarrhea or vomiting. To be sure this medication is helping your condition, your blood pressure will need to be checked often. Your kidney or liver function may also need to be tested. Visit your doctor regularly.
Nursing Process- Assessment (Pre-administration assessment) BUN/Cr at baseline, then periodically, or more frequently if CHF, renal artery stenosis; electrolytes; BP; WBC if collagen vascular disease, especially if renal impairment
Assessment Why would you hold or not give this med?
Hypotensive Bradycardia
Evaluation
Lowering of BP in hypertensive patients. Decreased risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, or death from cardiovascular causes in high-risk patients. Increased survival and decreased heart failure progression after myocardial infarction.
Вам также может понравиться
- RamiprilДокумент2 страницыRamiprilNinoska Garcia-OrtizОценок пока нет
- College of Nursing: Pharmacology Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыCollege of Nursing: Pharmacology Drug StudyChristine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- DuphalacДокумент2 страницыDuphalacianecunarОценок пока нет
- Propranolol - Drug InformationДокумент18 страницPropranolol - Drug InformationhexxxxОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыDrug StudyKristine Joy A. AniОценок пока нет
- Cetuximab Drug Study for Metastatic Colorectal CancerДокумент2 страницыCetuximab Drug Study for Metastatic Colorectal CancerTarquin TomadaОценок пока нет
- Drug Study Ko ToДокумент4 страницыDrug Study Ko ToGian Carlo FernandezОценок пока нет
- Drug StudiesДокумент16 страницDrug Studiesvitcloud23100% (2)
- Week 10 Drug Card - Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ)Документ2 страницыWeek 10 Drug Card - Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ)RCurry09Оценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент5 страницDrug Studyjanelle123 toribioОценок пока нет
- HYDROXYZINE DIHCL (Iterax)Документ1 страницаHYDROXYZINE DIHCL (Iterax)Rye Anch100% (1)
- LantusДокумент1 страницаLantusCassie100% (4)
- Ofloxacin Drug StudyДокумент4 страницыOfloxacin Drug StudyMikko Anthony Pingol Alarcon100% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент2 страницыAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAbigail BascoОценок пока нет
- Prescribed Fluanxol Depot dosage and administrationДокумент4 страницыPrescribed Fluanxol Depot dosage and administrationHavier EsparagueraОценок пока нет
- Proton Pump Inhibitor Suppresses Gastric AcidДокумент1 страницаProton Pump Inhibitor Suppresses Gastric AcidEngelbert CruzОценок пока нет
- Front of Me. She Is A Good Cook." For The Past Few Months, Mrs. Jenaro HasДокумент5 страницFront of Me. She Is A Good Cook." For The Past Few Months, Mrs. Jenaro Hasnct thomasОценок пока нет
- Xanax Drug CardДокумент3 страницыXanax Drug Cardnasir khanОценок пока нет
- Filgrastim Boosts Neutrophil Recovery After ChemotherapyДокумент3 страницыFilgrastim Boosts Neutrophil Recovery After ChemotherapyKyla Barrera TabungarОценок пока нет
- Pioglitazone (Actos, Lilly) : May Be Confused With Actidose, ActonelДокумент3 страницыPioglitazone (Actos, Lilly) : May Be Confused With Actidose, Actonelshidyakg100% (1)
- CloxacillinДокумент3 страницыCloxacillinRoberto Manuel IIОценок пока нет
- SpironolactoneДокумент2 страницыSpironolactoneNinoska Garcia-Ortiz100% (1)
- Ferrous GluconateДокумент2 страницыFerrous GluconateMichael Kuzbyt0% (1)
- NPH Insulin NPHДокумент1 страницаNPH Insulin NPHE100% (1)
- Lansoprazole (Prevacid)Документ3 страницыLansoprazole (Prevacid)tripj33Оценок пока нет
- Ramipril Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыRamipril Drug StudyCheezy Bread0% (1)
- Generic NameДокумент2 страницыGeneric NamePerdie Branden ReizОценок пока нет
- Biperiden Generic and Brand Names, Uses, Side EffectsДокумент1 страницаBiperiden Generic and Brand Names, Uses, Side EffectsMFQ.RN100% (2)
- Drug Study - CefradoxilДокумент13 страницDrug Study - CefradoxilJohara G'naid0% (1)
- Drug StudyДокумент4 страницыDrug StudyXio PauОценок пока нет
- Darbepoetin AlfaДокумент3 страницыDarbepoetin Alfaapi-3797941Оценок пока нет
- DesyrelДокумент1 страницаDesyrelKatie McPeekОценок пока нет
- Allopurinol Drug Study for Gout TreatmentДокумент1 страницаAllopurinol Drug Study for Gout TreatmentAbigail CastroОценок пока нет
- MG Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыMG Drug StudySandra MedinaОценок пока нет
- Ditropan Drug CardДокумент2 страницыDitropan Drug CardBenОценок пока нет
- Atrovent (Ipratropium)Документ1 страницаAtrovent (Ipratropium)E100% (2)
- Drug StudyДокумент14 страницDrug StudyNikki RodrigoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study of ChloramphenicolДокумент3 страницыDrug Study of Chloramphenicolcasimir1128Оценок пока нет
- CyclosporineДокумент2 страницыCyclosporineMuhammad ArsalanОценок пока нет
- Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine) : 1mg/mLДокумент5 страницNoradrenaline (Norepinephrine) : 1mg/mLBrian RelsonОценок пока нет
- AldactoneДокумент2 страницыAldactoneianecunarОценок пока нет
- FluconazoleДокумент3 страницыFluconazoleMary Kate ClarosОценок пока нет
- AcetaminophenДокумент3 страницыAcetaminophenShaira Tan100% (1)
- ItoprideДокумент2 страницыItoprideLesValenzuelaОценок пока нет
- New DS3Документ3 страницыNew DS3dakieОценок пока нет
- Drug Study - AmlodipineДокумент1 страницаDrug Study - AmlodipineDanielle Marie SamblacenoОценок пока нет
- Verapamil HCLДокумент3 страницыVerapamil HCLMae Ann Bueno CastillonОценок пока нет
- DocetaxelДокумент4 страницыDocetaxelfnurdiansah002Оценок пока нет
- Olmesartan Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыOlmesartan Drug StudydyndzОценок пока нет
- Drug Tabulation orДокумент23 страницыDrug Tabulation orChin Villanueva UlamОценок пока нет
- DRUG STUDY (Diphenhydramine)Документ2 страницыDRUG STUDY (Diphenhydramine)Avianna CalliopeОценок пока нет
- Dutasteride 0.5mg + Tamsulosin HCL 0.4mg (Duodart)Документ19 страницDutasteride 0.5mg + Tamsulosin HCL 0.4mg (Duodart)ddandan_2Оценок пока нет
- Levetiracetam PDFДокумент3 страницыLevetiracetam PDFShaira TanОценок пока нет
- Novolog (Insulin Aspart)Документ3 страницыNovolog (Insulin Aspart)EОценок пока нет
- DS (Calcium + Vit. D)Документ6 страницDS (Calcium + Vit. D)Mary April MendezОценок пока нет
- Methylprednisolone AlphapharmДокумент5 страницMethylprednisolone AlphapharmMarthin TheservantОценок пока нет
- Drugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcДокумент12 страницDrugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcMargaret Cortinas75% (4)
- Drug StudyДокумент10 страницDrug StudyHelen ReonalОценок пока нет
- CarvedilolДокумент3 страницыCarvedilolapi-3797941100% (3)
- Drugs StudyДокумент35 страницDrugs StudyMark CapillanesОценок пока нет
- Interpretation of Up & Go Test For Older AdultsДокумент1 страницаInterpretation of Up & Go Test For Older AdultsMichael KuzbytОценок пока нет
- Hypervolemia and Hypovolemia Nursing CareДокумент2 страницыHypervolemia and Hypovolemia Nursing CareMichael KuzbytОценок пока нет
- Opioid Equianalgesic ChartДокумент1 страницаOpioid Equianalgesic Chartdamondouglas100% (7)
- TelmisartanДокумент2 страницыTelmisartanMichael Kuzbyt100% (1)
- Windshield Survey ToolДокумент8 страницWindshield Survey Toolkenneth_rhea100% (1)
- Oxycodone Hydro ChlorideДокумент3 страницыOxycodone Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941Оценок пока нет
- Pharm Article#1Документ14 страницPharm Article#1Michael KuzbytОценок пока нет
- Windshield Survey TemplateДокумент6 страницWindshield Survey TemplateMichael Kuzbyt100% (1)
- Windshield Survey ToolДокумент8 страницWindshield Survey Toolkenneth_rhea100% (1)
- Interpretation of Up & Go Test For Older AdultsДокумент1 страницаInterpretation of Up & Go Test For Older AdultsMichael KuzbytОценок пока нет
- Zocor SimvastatinДокумент1 страницаZocor SimvastatinMichael KuzbytОценок пока нет
- TB Standards 2007Документ450 страницTB Standards 2007Michael Kuzbyt100% (1)
- VerapamilДокумент2 страницыVerapamilMichael KuzbytОценок пока нет
- Aminoxin: Clinical Medications WorksheetsДокумент1 страницаAminoxin: Clinical Medications WorksheetsMichael KuzbytОценок пока нет
- VerapamilДокумент2 страницыVerapamilMichael KuzbytОценок пока нет
- BetamethasoneДокумент3 страницыBetamethasoneMichael KuzbytОценок пока нет
- Zopiclone clinical worksheetДокумент2 страницыZopiclone clinical worksheetMichael KuzbytОценок пока нет
- Atenolol drug guide for hypertension and anginaДокумент2 страницыAtenolol drug guide for hypertension and anginaMichael Kuzbyt100% (1)
- Venlafaxine XRДокумент2 страницыVenlafaxine XRMichael KuzbytОценок пока нет
- Fall Prevention FactSheetДокумент2 страницыFall Prevention FactSheetMichael KuzbytОценок пока нет
- XareltoДокумент2 страницыXareltoMichael Kuzbyt100% (1)
- IsoniazidДокумент2 страницыIsoniazidMichael Kuzbyt100% (1)
- Aminoxin: Clinical Medications WorksheetsДокумент1 страницаAminoxin: Clinical Medications WorksheetsMichael KuzbytОценок пока нет
- Interpretation of Up & Go Test For Older AdultsДокумент1 страницаInterpretation of Up & Go Test For Older AdultsMichael KuzbytОценок пока нет
- LorazepamДокумент1 страницаLorazepamMichael KuzbytОценок пока нет
- Ferrous GluconateДокумент2 страницыFerrous GluconateMichael Kuzbyt0% (1)
- MMSE Interpretation of ResultsДокумент1 страницаMMSE Interpretation of ResultsMichael KuzbytОценок пока нет
- Clinical Medications WorksheetsДокумент2 страницыClinical Medications WorksheetsMichael Kuzbyt0% (1)
- Dipimide: Clinical Medications WorksheetsДокумент2 страницыDipimide: Clinical Medications WorksheetsMichael KuzbytОценок пока нет
- Guidance on medicinal product registration in Singapore checklistДокумент17 страницGuidance on medicinal product registration in Singapore checklistWilliam ChandraОценок пока нет
- 10.1.5 - Anti-H2 Agents (2007-Jan2016) - 1Документ14 страниц10.1.5 - Anti-H2 Agents (2007-Jan2016) - 1Gabrielle NnomoОценок пока нет
- FDIДокумент16 страницFDIbhartissОценок пока нет
- Pallava Template For Oral Presentation GeneralДокумент20 страницPallava Template For Oral Presentation GeneralVijay BhaskarОценок пока нет
- Edwards. Shondrell MGT 6685 Phizer Case AnalysisДокумент19 страницEdwards. Shondrell MGT 6685 Phizer Case AnalysisShey Edwards100% (1)
- 1145E Rectal Preparations 2Документ2 страницы1145E Rectal Preparations 2Maja TashtanoskaОценок пока нет
- Glucosami̇ne and Chondroi̇ti̇n SulfateДокумент4 страницыGlucosami̇ne and Chondroi̇ti̇n Sulfatetaner_soysurenОценок пока нет
- Impcops Medicines Price List 01.03.2018 PDFДокумент32 страницыImpcops Medicines Price List 01.03.2018 PDFVinothini0% (1)
- Pharmacy Daily 30th Oct 2023Документ5 страницPharmacy Daily 30th Oct 2023Marinero CzarОценок пока нет
- Pka Algunos FarmacosДокумент9 страницPka Algunos FarmacosTatiana ZeballosОценок пока нет
- Practice Guidelines for Candidiasis TreatmentДокумент17 страницPractice Guidelines for Candidiasis TreatmentCristian HaesbaertОценок пока нет
- LECTURE 2 - Organon 2 The Highest Ideal of A Cure - LECTURES ON HOMOEOPATH1Документ7 страницLECTURE 2 - Organon 2 The Highest Ideal of A Cure - LECTURES ON HOMOEOPATH1madhukarОценок пока нет
- Ph. Eur 5.1.4 - Microbiolgical Quality of Non Sterile Pharm PreparationДокумент1 страницаPh. Eur 5.1.4 - Microbiolgical Quality of Non Sterile Pharm PreparationLuis SanabriaОценок пока нет
- In-Situ Buffered Formulation: An Effective Approach For Acid LabileДокумент10 страницIn-Situ Buffered Formulation: An Effective Approach For Acid LabilevinayОценок пока нет
- Pfizer Inc.: United States Securities and Exchange CommissionДокумент246 страницPfizer Inc.: United States Securities and Exchange CommissionDipanshu NagarОценок пока нет
- Monoclonal AntibodiesДокумент68 страницMonoclonal AntibodiesvedabantiОценок пока нет
- DiphenhydramineДокумент6 страницDiphenhydramineMiriam Defensor Santiago100% (2)
- Assignment - Copy EditorsДокумент4 страницыAssignment - Copy Editors21066 NIDHI NGAIHOIHОценок пока нет
- Loperamide PDFДокумент2 страницыLoperamide PDFaguerro100% (1)
- NFCVersion2012Guidelines PDFДокумент105 страницNFCVersion2012Guidelines PDFsilvanita80Оценок пока нет
- Stok Hari IniДокумент24 страницыStok Hari IniaristhanovyraОценок пока нет
- Homeo TipsДокумент146 страницHomeo TipsBalaji Siddhu100% (2)
- Hyperemesis GravidarumДокумент9 страницHyperemesis GravidarumChyank Qu SaddamОценок пока нет
- PharmacologyДокумент33 страницыPharmacologyYnaffit Alteza Untal100% (1)
- Drug StudyДокумент41 страницаDrug StudyVecky TolentinoОценок пока нет
- Annexure-I Company Requisitions ListДокумент5 страницAnnexure-I Company Requisitions ListShweОценок пока нет
- Daftar Isi Troly EmergencyДокумент3 страницыDaftar Isi Troly EmergencyIntensif UdayanaОценок пока нет
- Almaty-Bishkek Economic Corridor Pharma Testing Pre-Feasibility Study Consultant ReportДокумент32 страницыAlmaty-Bishkek Economic Corridor Pharma Testing Pre-Feasibility Study Consultant ReportMohamed MostafaОценок пока нет
- Bronchial AsthmaДокумент40 страницBronchial Asthmasamson bd mokuntil100% (1)
- Experiential Pharmacy Practice in Institutional Pharmacy: Module 1: Part 2Документ27 страницExperiential Pharmacy Practice in Institutional Pharmacy: Module 1: Part 2levi pinedaОценок пока нет