Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Exam1 2013 Spring Me 200 Purdue
Загружено:
sugar_87Исходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Exam1 2013 Spring Me 200 Purdue
Загружено:
sugar_87Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Last Name: ___________________ First Name:
Middle Initial:
Problem 1: (30/100 points) Each part of this problem is worth 6 points. There is no partial credit and your answer must be placed in the box. The standard problem solving procedure is not required for Problem 1, but you must support your answers by providing appropriate equations, tables, or charts. Without appropriate equations, tables, or charts, you will receive zero score although the answer may be correct. (a) The pressure in a rigid tank of 0.1 m3 containing liquid water at 20oC is decreased from 10 atm to 1 atm. Estimate the work done by the system, in kJ.
(b) An object of 10 lbm is lifted by 10 feet. Which case will need more energy, on the earth or on the moon?
(c) In a piston-cylinder device containing air, can the state be changed from 1 to 2 at constant internal energy while producing work? Neglect kinetic energy and potential energy change.
(d) A mixture of water liquid and vapor in a container is compressed at constant volume. Will it be possible to compress the mixture to liquid?
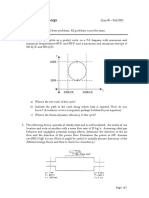
(e) Determine if the following cycle is a power cycle or a refrigeration cycle.
Last Name: ___________________ First Name:
Middle Initial:
Problem 2: (35/100 points) Given: A well-insulated vertical piston-cylinder device contains air. The diameter of the piston is 8 inches. Atmospheric pressure of 14.7 lbf/in2 acts outside the cylinder and the piston mass is 165 lbm. An electric resistor within the cylinder receives a current of 1 A from an external battery of 10 V for a duration of 60 minute causing the piston to move upwards by 9.85 inches. Consider that changes in kinetic and potential energy of air are negligible and that the acceleration due to gravity g = 32.2 ft/s2. Find: (a) Draw the system sketch in the following space provided; (b) Draw qualitatively the process for air on the P-v diagram provided and label the initial state as 1 and the final state as 2; (c) Calculate the pressure of air inside the cylinder before the piston moves, in lbf/in2; (d) Calculate the work due to expansion of air in the cylinder, in Btu; (e) Indicate whether the work is done by the system or on the system used for part (d); (f) Determine the electrical work from the resistor, in Btu; (g) Calculate the change in internal energy of air, in Btu. System sketch: (a)
(b)
P
Assumptions:
Basic equations:
Last Name: ___________________ First Name: Solution: (c)
Middle Initial:
Last Name: ___________________ First Name: Problem 3: (35/100 points)
Middle Initial:
Given: A piston-cylinder assembly contains 0.5 kg water-vapor mixture with 80.8% of quality and 2 bar (state 1). The piston is initially resting on a set of stops. Then, the cylinder is heated from an external heat source until the piston head just starts to move at a pressure of 0.3 MPa (state 2). Now the volume increases with an additional heat addition from the heat source until the specific internal energy (u3) of the final state reaches 3030.6 kJ/kg (state 3). (Neglect the changes in kinetic and potential energy. Do not interpolate and use the closest table value) Find: (a) Mark the system boundary to be used for process 2-3 in the system sketch provided and show heat and work through the system boundary; (b) Draw approximately the processes for the water-vapor mixture on the P-v diagram provided and label the states on the diagram; (c) Determine the specific internal energy at state 1 and state 2, respectively, in kJ/kg; (d) Calculate the final volume (V3) of the piston-cylinder assembly, in m3; (e) Find the total work produced by the system, in kJ; (f) Calculate the total heat addition to the system, in kJ. System sketch: (a) (b)
Piston Piston stops Water vapor Liquid water
v
Assumptions:
Basic equations:
Last Name: ___________________ First Name: Solution: (c)
Middle Initial:
Вам также может понравиться
- T1 Ug 90Документ6 страницT1 Ug 90germangsilvaОценок пока нет
- Basic ThermodynamicsДокумент8 страницBasic ThermodynamicsVivek VermaОценок пока нет
- Assignment 2 Second Law 2016Документ7 страницAssignment 2 Second Law 2016Mohit SInhaОценок пока нет
- II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Dec - 2015 ThermodynamicsДокумент8 страницII B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Dec - 2015 ThermodynamicsAshok DaraОценок пока нет
- Physics I ProblemsДокумент1 страницаPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenОценок пока нет
- MEGR3210 Homework4Документ2 страницыMEGR3210 Homework4ruukiОценок пока нет
- Thermo OldStylePastPaper 2007-19Документ54 страницыThermo OldStylePastPaper 2007-19manjeet gajbhiyeОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ11 страницChapter 2anil thakurОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamic Question BankДокумент10 страницThermodynamic Question BankRaj PratyushОценок пока нет
- A6DEC19BMEAДокумент4 страницыA6DEC19BMEA2K19/EC/101 LOKESHОценок пока нет
- 05-1-Collection of Problems PDFДокумент15 страниц05-1-Collection of Problems PDFFistia MaulinaОценок пока нет
- System. What Will Be The First Law Equation For The Below System?Документ3 страницыSystem. What Will Be The First Law Equation For The Below System?dpurnimaОценок пока нет
- Prob SetДокумент4 страницыProb SetJuliet NakilaОценок пока нет
- Mech-Engg., Thermal EngineeringДокумент8 страницMech-Engg., Thermal Engineeringnims1964Оценок пока нет
- MEC1405 - Thermodynamics I 2009Документ4 страницыMEC1405 - Thermodynamics I 2009Maria CutajarОценок пока нет
- Air Conditioning and Refrigeration Exam PaperДокумент9 страницAir Conditioning and Refrigeration Exam PaperYean Ghing Tong100% (1)
- Soal Uas NmeДокумент1 страницаSoal Uas Nmefaizal irsyadОценок пока нет
- Thermo 1 - Mid TermДокумент4 страницыThermo 1 - Mid TermMohammad Faiz AkbarОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics Cengel ProblemsДокумент3 страницыThermodynamics Cengel ProblemsHaardikGargОценок пока нет
- Microsoft Word Chapter 15Документ20 страницMicrosoft Word Chapter 15Shashank ShekharОценок пока нет
- TD QP UPTO Nov 2012 18092012Документ31 страницаTD QP UPTO Nov 2012 18092012Narayanan Srinivasan100% (1)
- HW4VM235SU2016Документ2 страницыHW4VM235SU2016tony960129Оценок пока нет
- Thermo QualsДокумент26 страницThermo QualsLuc LeОценок пока нет
- Ps 1Документ9 страницPs 1Maulana ArifОценок пока нет
- HW9VM235SU2016Документ2 страницыHW9VM235SU2016tony960129Оценок пока нет
- Tutorial QuestionsДокумент6 страницTutorial QuestionsLadnilrebОценок пока нет
- ThermodynamicsДокумент6 страницThermodynamicsPrincess LlaneraОценок пока нет
- Indian Institute of Technology Tirupati: Roll No: NameДокумент27 страницIndian Institute of Technology Tirupati: Roll No: NameKriti SharmaОценок пока нет
- Principles of Thermodynamics NotesДокумент12 страницPrinciples of Thermodynamics NotesSaniya SohailОценок пока нет
- IES CONV Mechanical Engineering 1985Документ8 страницIES CONV Mechanical Engineering 1985coolpawan10Оценок пока нет
- RAC April-May 2013 PDFДокумент3 страницыRAC April-May 2013 PDFShashi Bhushan PatelОценок пока нет
- Problem Sheet 3 Heat, Work and The First Law of Thermodynamics PDFДокумент4 страницыProblem Sheet 3 Heat, Work and The First Law of Thermodynamics PDFS DОценок пока нет
- Taller Final de EjerciciosДокумент7 страницTaller Final de EjerciciosEduar QuirozОценок пока нет
- AE May 2013 04 BS 10Документ4 страницыAE May 2013 04 BS 10Amber HarrisОценок пока нет
- Me2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - Nov Dec 2010Документ4 страницыMe2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - Nov Dec 2010BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANОценок пока нет
- 1418395957089Документ3 страницы1418395957089MahendraMeenaОценок пока нет
- r7210305 ThermodynamicsДокумент4 страницыr7210305 ThermodynamicssivabharathamurthyОценок пока нет
- Group - A (Multiple Choice Type Questions)Документ7 страницGroup - A (Multiple Choice Type Questions)Prem sharmaОценок пока нет
- Assignment 3Документ2 страницыAssignment 3Khayyam JahangirОценок пока нет
- 16.050 Thermal Energy: Page 1 of 2Документ2 страницы16.050 Thermal Energy: Page 1 of 2ZeroRecoОценок пока нет
- Sheet No 2 NewДокумент2 страницыSheet No 2 NewabdulqadirОценок пока нет
- ThermoДокумент3 страницыThermopranavОценок пока нет
- 2016 Mid Term ExamДокумент3 страницы2016 Mid Term ExamMahmoud AsemОценок пока нет
- Tutorial Topic 2 2020 RevisedДокумент3 страницыTutorial Topic 2 2020 RevisedTara PillayОценок пока нет
- B7: Applied Thermodynamics: Hilary Term 2018 Richard StoneДокумент4 страницыB7: Applied Thermodynamics: Hilary Term 2018 Richard StoneMoemen MetwallyОценок пока нет
- TF II Revision TutorialДокумент2 страницыTF II Revision TutorialsubipuruОценок пока нет
- Chapter 15 - GiancoliДокумент5 страницChapter 15 - GiancoliHectorCabz100% (1)
- Mex306 - Thermodynamics and Fluid Mechanics Referred/Deferred ExaminationДокумент4 страницыMex306 - Thermodynamics and Fluid Mechanics Referred/Deferred ExaminationNiroshan VaratharajahОценок пока нет
- IES CONV Mechanical Engineering 1991Документ7 страницIES CONV Mechanical Engineering 1991GURURAJ CОценок пока нет
- MECE 2334 Final ExamДокумент9 страницMECE 2334 Final Examdroblesb91Оценок пока нет
- Qbank 18me32 BTDДокумент6 страницQbank 18me32 BTDAmaresh Movies ASОценок пока нет
- Homework #7Документ3 страницыHomework #7Sebastián SantarrosaОценок пока нет
- Vm235: Thermodynamics Homework 2: Assigned Tues May 24, 2016 Due Tues May 31 at The Start of ClassДокумент3 страницыVm235: Thermodynamics Homework 2: Assigned Tues May 24, 2016 Due Tues May 31 at The Start of Classtony960129Оценок пока нет
- Thermo Assignment #10Документ15 страницThermo Assignment #10mohamedОценок пока нет
- Tutorial Sheet 02 2014Документ11 страницTutorial Sheet 02 2014checkmeout803Оценок пока нет
- Homework 10 SolutionsДокумент8 страницHomework 10 Solutionscalebgriffin31Оценок пока нет
- 3 Mass Balance Agro1Документ28 страниц3 Mass Balance Agro1Jaya Wijaya100% (1)
- Principles Thermodynamic Functions - The Ideal GasДокумент17 страницPrinciples Thermodynamic Functions - The Ideal GasLê Xuân NamОценок пока нет
- ETD Unit 1 OriginalДокумент16 страницETD Unit 1 Originaltamilselvan nОценок пока нет
- ExergyДокумент70 страницExergyفضائح لا تصدقОценок пока нет
- PHYS1121 Course NotesДокумент45 страницPHYS1121 Course NotesLight95Оценок пока нет
- Energy Analysis of Closed Systems: Mehmet KanogluДокумент18 страницEnergy Analysis of Closed Systems: Mehmet KanogluNeydenОценок пока нет
- Steamtab BrochureДокумент2 страницыSteamtab Brochurenayi vishal natverbhaiОценок пока нет
- 19a. Thermo Dynamics (365-400)Документ36 страниц19a. Thermo Dynamics (365-400)Pathan KausarОценок пока нет
- Bab 2 TermoДокумент44 страницыBab 2 TermoChella YuanharОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics For Beginners - Chapter 5 WORKING WITH IDEAL GASДокумент35 страницThermodynamics For Beginners - Chapter 5 WORKING WITH IDEAL GASDudu MamanОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamic ProcessesДокумент32 страницыThermodynamic ProcessesAleem AhmedОценок пока нет
- Steam Engineering Principles and Heat TransferДокумент99 страницSteam Engineering Principles and Heat Transferalex mobileОценок пока нет
- MSC Chem SyllabusДокумент29 страницMSC Chem SyllabusKundan DeoreОценок пока нет
- 21 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (A2) : E E E EДокумент3 страницы21 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (A2) : E E E EvinuyeОценок пока нет
- Aqa 2455 W TRB U04asqspbДокумент74 страницыAqa 2455 W TRB U04asqspbtomtaylor200Оценок пока нет
- 10ME33 Basic ThermodynamicsДокумент4 страницы10ME33 Basic ThermodynamicsHemanth KumarОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics ReviewerДокумент2 страницыThermodynamics ReviewerRogelioB.AlobIIОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ28 страницChapter 2Siti Hajar Mohd PodziОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Energy Conversion Engineering: August 2019Документ40 страницFundamentals of Energy Conversion Engineering: August 2019M Sohaib100% (1)
- TONGO - Final ProjectДокумент71 страницаTONGO - Final ProjectJhon Nicko TongoОценок пока нет
- Worksheet Week 6Документ3 страницыWorksheet Week 6Jaybie TejadaОценок пока нет
- New Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationДокумент18 страницNew Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationLokesh BaviskarОценок пока нет
- Understanding Heat Exchangers - Types, Designs, Applications and Selection GuideДокумент13 страницUnderstanding Heat Exchangers - Types, Designs, Applications and Selection GuideVipin Kumar SinghОценок пока нет
- III Year I Sem High Speed AerodynamicsДокумент113 страницIII Year I Sem High Speed AerodynamicsIron Mike VimalОценок пока нет
- 22 B.SC., ChemistryДокумент46 страниц22 B.SC., ChemistryK KANNANОценок пока нет
- IB Physics - Thermal - Grade GorillaДокумент4 страницыIB Physics - Thermal - Grade Gorillamona safwatОценок пока нет
- Workbook Chapter 3 - Thermal PropertiesДокумент25 страницWorkbook Chapter 3 - Thermal PropertiesFarhan AdyansyahОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamic Property RelationsДокумент26 страницThermodynamic Property RelationsSec CОценок пока нет
- Chem332 Spring 13Документ313 страницChem332 Spring 13Mashai LesenyehoОценок пока нет
- The First Law and Other Basic Concepts: Joule's ExperimentsДокумент4 страницыThe First Law and Other Basic Concepts: Joule's ExperimentsnnbОценок пока нет