Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
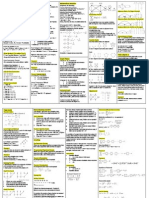
CS1231 Cheat Sheet 2
Загружено:
jieboАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CS1231 Cheat Sheet 2
Загружено:
jieboАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Algorithm Base Expansion:
Example
( )
incidence
COMPLETE BIPARTITE GRAPH denoted ,
;
LIST Prims Algorithm (1) Choose any edge with min weight (2) Among adjacent vertices, choose one of minimum weight (3) Stop when we have edges Kruskals Algorithm
(1) Sort all edges in order of increasing weight (2) Select the edges s.t. it joins two distinct components (3) Stop when after edges
Find (1) (2) (3)
(1)
MATRIX
adj
(2) All congruence modulo 100
Same as Prims Algorithm
(1) (2) Select from the list and reject any that closes a circuit or overlaps
No. of paths from to
( ) ( ) ( )
(3)
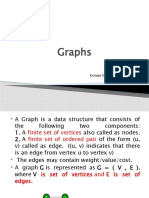
Chapter 7: Graphs
Euclidean Algorithm
int gcd(int a, int b) { Int temp ;
Type
Simple Graph Multigraph Pseudograph
By extension,
Edges
Undirected Undirected Undirected
Multiple Edges?
No Yes Yes
Loops?
No No Yes
A path is a CIRCUIT if A path or circuit is SIMPLE if the edges it passes are pairwise distinct An EULER CIRCUIT is a simple circuit that contains every vertex edge A connected graph has Euler circuit iff every vertex is of even deg An EULER PATH is a simple path which is not a circuit and contains all the edges and vertices all vertices, but two, have even degrees.
} }
Reverse Euclidean
Chapter 8: Trees A TREE is a connected graph with NO cycles
Edges with as terminal vertex
Depth First Search: Spanning Trees
(1) Randomly choose one vertex (2) Add its neighbors that has not been searched until the end (3) Backtrack to search unmarked for neighbors
An
-ary is FULL if every internal vertex has
Breadth First Search
(1) Randomly choose one vertex (2) Add in all its adjacent vertices (3) Repeat for all vertices until all vertices are marked
exactly m children. An ORDERED ROOTED TREE is a rooted tree in which children of each vertex are ordered. E.g. for T2, the left subtree of is the subtree rooted at while the right subtree if a single vertex
Edges with
as initial vertex
Tree with vertices has at least two vertices of degree 1 Tree with vertices has edges sum of deg A full -ary tree internal vertex has vertices Suppose full -ary tree with vertices, internal vertices and leaves, then
A rooted -ary tree of height is BALANCED if all leaves are at level or In an -ary tree there are at most vertices at level . If the height is , there are at most leaves.
Вам также может понравиться
- Sequence of Attacking:: Proof by Mathematical InductionДокумент3 страницыSequence of Attacking:: Proof by Mathematical InductioncbsbrainОценок пока нет
- ST1131 Cheat Sheet Page 1Документ1 страницаST1131 Cheat Sheet Page 1jiebo0% (1)
- ACC1002X Cheat Sheet 2Документ1 страницаACC1002X Cheat Sheet 2jieboОценок пока нет
- Xam Idea Mathematics - Class 12 Term 1 and 2 Question BankДокумент563 страницыXam Idea Mathematics - Class 12 Term 1 and 2 Question BankAkshya PatelОценок пока нет
- GraphsДокумент39 страницGraphsLavanya JОценок пока нет
- G10 - Matrix and VectorsДокумент11 страницG10 - Matrix and VectorsEduar RodriguezОценок пока нет
- DSA DAY 6 - GraphsДокумент45 страницDSA DAY 6 - GraphsVritika Naik67% (3)
- Differentiation Cheat SheetДокумент15 страницDifferentiation Cheat SheetjieboОценок пока нет
- Integration Cheat SheetДокумент7 страницIntegration Cheat Sheetjiebo100% (1)
- Max Flow Lecture NotesДокумент12 страницMax Flow Lecture NotesamessbeeОценок пока нет
- CRE8 TeamsДокумент8 страницCRE8 TeamsjieboОценок пока нет
- DAA Unit3 Notes and QBankДокумент37 страницDAA Unit3 Notes and QBankyamuna100% (1)
- Chapter 10 - Eigenvalues and EigenvectorsДокумент16 страницChapter 10 - Eigenvalues and EigenvectorsEnos Lolang100% (6)
- D.M. Final 2Документ17 страницD.M. Final 2Series MkОценок пока нет
- Graphs: Presented By, M.Sangeetha, Ap/Cse, Kongu Engineering CollegeДокумент61 страницаGraphs: Presented By, M.Sangeetha, Ap/Cse, Kongu Engineering CollegesangeethaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 11Документ43 страницыLecture 11varunsingh214761Оценок пока нет
- Greedy AlgorithmДокумент28 страницGreedy AlgorithmSyed Aoun AbbasОценок пока нет
- 06 Basic Graph AlgorithmsДокумент31 страница06 Basic Graph AlgorithmsPratik JainОценок пока нет
- CS1231 Cheat Sheet Part 1Документ1 страницаCS1231 Cheat Sheet Part 1jieboОценок пока нет
- T R E E: University of SALAHADDIN - Erbil College of Engineering Software & Informatics DepДокумент20 страницT R E E: University of SALAHADDIN - Erbil College of Engineering Software & Informatics DepBawer AliОценок пока нет
- DMGT-module6 and 7Документ50 страницDMGT-module6 and 7manish 2003Оценок пока нет
- Graph Data Structure: Breadth First Search (BFS)Документ11 страницGraph Data Structure: Breadth First Search (BFS)vishnu neupaneОценок пока нет
- Spanning Tree and Minimum Spanning TreeДокумент4 страницыSpanning Tree and Minimum Spanning Treeapi-3844034Оценок пока нет
- DSAДокумент48 страницDSAfNxОценок пока нет
- Ada NotesДокумент16 страницAda NotesRenukaОценок пока нет
- Graphs - DAAДокумент68 страницGraphs - DAAD07Vaishnavi ShindeCEОценок пока нет
- 6.1 Spanning Trees - AlfredBarbosa - MarkEmanDigdigan - ManaloДокумент14 страниц6.1 Spanning Trees - AlfredBarbosa - MarkEmanDigdigan - ManaloJaxon RiegoОценок пока нет
- DMGT Module 6 TreesДокумент53 страницыDMGT Module 6 TreesteeshtakparmarОценок пока нет
- Module 7Документ43 страницыModule 7Kshitiz GoyalОценок пока нет
- Solution-: Prim's Algorithm Kruskal's AlgorithmДокумент5 страницSolution-: Prim's Algorithm Kruskal's AlgorithmRejithaVijayachandranОценок пока нет
- Ass 3Документ3 страницыAss 3Rao AfrasiabОценок пока нет
- Zero DeterminantsДокумент4 страницыZero DeterminantsMiliyon TilahunОценок пока нет
- Graph: By: Deepak Kumar SinghДокумент55 страницGraph: By: Deepak Kumar Singhसुरज पौडेलОценок пока нет
- Daa Mod - 3-1Документ14 страницDaa Mod - 3-1Disha GudigarОценок пока нет
- Hamiltonian Graphs & Spanning TreesДокумент5 страницHamiltonian Graphs & Spanning TreesfatfakernigОценок пока нет
- The Maximum Network Flow ProblemДокумент10 страницThe Maximum Network Flow ProblemRomar PanopioОценок пока нет
- A New Approach To Find Minimum Spanning Tree For Undirected GraphsДокумент3 страницыA New Approach To Find Minimum Spanning Tree For Undirected GraphsInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 PT 6 Det of Matrix Part 1Документ15 страницUnit 1 PT 6 Det of Matrix Part 1sprinklesdb16Оценок пока нет
- GraphДокумент15 страницGraphmugiii321Оценок пока нет
- MIT math for computer science lecture covers graphs, trees, sums, and probabilityДокумент2 страницыMIT math for computer science lecture covers graphs, trees, sums, and probabilityalkalacidОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 2Документ14 страницTutorial 2rickyarya2000Оценок пока нет
- Greedy Technique and Minimum Spanning Tree AlgorithmsДокумент14 страницGreedy Technique and Minimum Spanning Tree AlgorithmsPrateekMandiОценок пока нет
- MST of GraphДокумент14 страницMST of GraphAniruddha BhadraОценок пока нет
- OCR D1 Revision SheetДокумент5 страницOCR D1 Revision Sheetnsph2326Оценок пока нет
- Unit IV Trees Concepts and TraversalsДокумент107 страницUnit IV Trees Concepts and TraversalsIan Dave D. EjercitoОценок пока нет
- DataStructures_Unit_3Документ49 страницDataStructures_Unit_3DIVAKAR .K.GОценок пока нет
- On The Alexander Polynomial of Alternating Algebraic Knots - Kunio MurasugiДокумент18 страницOn The Alexander Polynomial of Alternating Algebraic Knots - Kunio MurasugihGanieetОценок пока нет
- Tree Graph Properties and Searching MethodsДокумент15 страницTree Graph Properties and Searching MethodsSarah FergusonОценок пока нет
- Ch-8-Daa-Mb StudentsДокумент27 страницCh-8-Daa-Mb Students0101191713Оценок пока нет
- Kruskal's algorithm minimum spanning treeДокумент16 страницKruskal's algorithm minimum spanning treeshubhamgupta007Оценок пока нет
- Network Topology: PPT By:-D V S RamanjaneyuluДокумент25 страницNetwork Topology: PPT By:-D V S RamanjaneyuluRamanjaneyulu Anji YadavОценок пока нет
- Spanning TreeДокумент15 страницSpanning TreeNishtha DhariwalОценок пока нет
- DFS vs BFS: Key Differences Explained in 40 CharactersДокумент6 страницDFS vs BFS: Key Differences Explained in 40 CharactersKartheeswari SaravananОценок пока нет
- Unit 4Документ71 страницаUnit 4Shikhar AshishОценок пока нет
- DS IV Unit NotesДокумент29 страницDS IV Unit NotesAlagandula KalyaniОценок пока нет
- GraphsДокумент41 страницаGraphsNik HakimiОценок пока нет
- Grade 10. 3.9-3.13Документ36 страницGrade 10. 3.9-3.13Улдана ГарифоллакызыОценок пока нет
- DS 3Документ45 страницDS 3Sreehari EОценок пока нет
- A spanning tree is a subset of Graph GДокумент8 страницA spanning tree is a subset of Graph GsaumyaОценок пока нет
- Fibonacci NumbersДокумент19 страницFibonacci Numbersalok_bОценок пока нет
- Graph TheoryДокумент76 страницGraph Theoryjfhapac0718valОценок пока нет
- Ds Unit 5 (Graphs)Документ35 страницDs Unit 5 (Graphs)ashishmohan625Оценок пока нет
- Trees: Lecturer. Ahmed Hadi Al-ShamaryДокумент21 страницаTrees: Lecturer. Ahmed Hadi Al-ShamaryAhmed HussainОценок пока нет
- Approximate TSP AlgorithmsДокумент13 страницApproximate TSP AlgorithmsjollydmelloОценок пока нет
- Data StructureДокумент11 страницData StructureSachin SharmaОценок пока нет
- Ada MTE PresentationДокумент20 страницAda MTE Presentationanuraagkumar 24Оценок пока нет
- CH 05Документ52 страницыCH 05Tấn PhátОценок пока нет
- IS4203 - RevisionДокумент37 страницIS4203 - RevisionjieboОценок пока нет
- IS4241 - RevisionДокумент13 страницIS4241 - RevisionjieboОценок пока нет
- SSA2211 - Evolution of A Global City-StateДокумент19 страницSSA2211 - Evolution of A Global City-StatejieboОценок пока нет
- GEM2900 Cheat Sheet 2Документ2 страницыGEM2900 Cheat Sheet 2jieboОценок пока нет
- GEM2900 ProbabilityДокумент2 страницыGEM2900 ProbabilitywakakkaОценок пока нет
- IS2103 - SummaryДокумент22 страницыIS2103 - SummaryjieboОценок пока нет
- GEK2013 Real Estate FinanceДокумент20 страницGEK2013 Real Estate FinanceUnknown uploaderОценок пока нет
- ST1131 Cheat Sheet Page 2Документ1 страницаST1131 Cheat Sheet Page 2jieboОценок пока нет
- CS1231 Cheat Sheet Part 1Документ1 страницаCS1231 Cheat Sheet Part 1jieboОценок пока нет
- ACC1002X Cheat Sheet 1Документ2 страницыACC1002X Cheat Sheet 1jieboОценок пока нет
- Complex DerivativeДокумент2 страницыComplex DerivativeDhamu DharanОценок пока нет
- Cbcs Syllabus 2016-17 Admn Batch 30.07.16Документ23 страницыCbcs Syllabus 2016-17 Admn Batch 30.07.16Sushree sonali NayakОценок пока нет
- 17 Differentiation and Continuity PDFДокумент19 страниц17 Differentiation and Continuity PDFRaphael Angelo GonzalesОценок пока нет
- Indefinite IntegrationДокумент29 страницIndefinite IntegrationBharti Pant GahtoriОценок пока нет
- Functions and Calculus ConceptsДокумент18 страницFunctions and Calculus ConceptsMichael AliagaОценок пока нет
- Solved Problems Continuous Random VariablesДокумент4 страницыSolved Problems Continuous Random VariablesbossishereОценок пока нет
- Section 7.4 MAДокумент39 страницSection 7.4 MAvinothОценок пока нет
- A13 IFT2125 Intra1 enДокумент7 страницA13 IFT2125 Intra1 enSherjil OzairОценок пока нет
- Functional Equations: Problems with SolutionsДокумент14 страницFunctional Equations: Problems with SolutionsSharat SachinОценок пока нет
- Mtap G10S2 Polynomial FunctionsДокумент2 страницыMtap G10S2 Polynomial FunctionsLedesma, Elijah O.Оценок пока нет
- Assignment 1Документ2 страницыAssignment 1Vibhanshu PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- 1.4 TB - EstimatingLimitValuesfromTablesQuiz - 628c95a8255554.628c95aaa0add4.78852521Документ4 страницы1.4 TB - EstimatingLimitValuesfromTablesQuiz - 628c95a8255554.628c95aaa0add4.78852521Hassan Ehsaiyan SaqerОценок пока нет
- ch9 FollandДокумент1 страницаch9 FollandHONGBO WANGОценок пока нет
- Sets & RelationsДокумент5 страницSets & RelationsNew OneОценок пока нет
- Optimality Conditions For General Constrained Optimization: CME307/MS&E311: Optimization Lecture Note #07Документ28 страницOptimality Conditions For General Constrained Optimization: CME307/MS&E311: Optimization Lecture Note #07Ikbal GencarslanОценок пока нет
- AAD Flow Networks and Divide and ConquerДокумент17 страницAAD Flow Networks and Divide and ConquerSIET CSE DEPARTMENTОценок пока нет
- Pajek ManualДокумент104 страницыPajek Manualmnkrose100% (1)
- Numerical Analysis: X F Initial DX X G X FДокумент4 страницыNumerical Analysis: X F Initial DX X G X FShahrul NizamОценок пока нет
- Greedy Algorithms for Optimization ProblemsДокумент39 страницGreedy Algorithms for Optimization ProblemsHarsh SoniОценок пока нет
- Power Rule For IntegrationДокумент4 страницыPower Rule For IntegrationKeana AgregadoОценок пока нет
- D3 Matrices Jan14Документ68 страницD3 Matrices Jan14Iamhere IamhereОценок пока нет
- BSc Honours Applied Mathematics ProgrammeДокумент30 страницBSc Honours Applied Mathematics ProgrammeHassan FarukОценок пока нет
- Proofs That Det (A) Det A.: 1 Proof 1Документ2 страницыProofs That Det (A) Det A.: 1 Proof 1Jorge FajardoОценок пока нет
- Transforms and Moment Generating Functions ExplainedДокумент12 страницTransforms and Moment Generating Functions Explainedladida1234567Оценок пока нет
- Group 61labДокумент26 страницGroup 61labRizza Mae SorianoОценок пока нет
- Calculating Areas Under Curves Using IntegrationДокумент41 страницаCalculating Areas Under Curves Using IntegrationNghia Tuan NghiaОценок пока нет