Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Nursing Care Plan Rheumatoid Arthritis
Загружено:
Lighto RyusakiОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Nursing Care Plan Rheumatoid Arthritis
Загружено:
Lighto RyusakiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Student Nurses Community
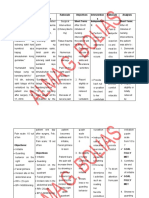
NURSING CARE PLAN Rheumatoid Arthritis ASSESSMENT SUBJECTIVE: Napakasakit ng mga kasukasuhan ko (I'm having severe joint pain) as verbalized by the patient. DIAGNOSIS Acute pain r/t distension of tissues by accumulation of fluid. INFERENCE destruction and proliferation of the synovial membrane joint destruction, ankylosis, and deformity PLANNING After 8 hours of nursing intervention the patient will: INTERVENTION Independent RATIONALE EVALUATION Goal met, patient has Verbalize relief of pain.
OBJECTIVE: Guarding/protectiv e behavior Restlessness facial grimacing pain scale of 7 out of 10 V/S taken as follows T: 37.5C P: 100 R: 20 BP: 120/ 80 distension of tissues by accumulation of fluid/inflammatory process acute pain
Investigate reports of pain, noting location and intensity(scale of >Report pain is 010). Note relieved/controlled. precipitating factors and nonverbal pain >Appear relaxed, cues. able to sleep/rest and participate in Recommend/provide activities firm mattress or appropriately bedboard, small pillow. Elevate linens with bed >Follow cradle as needed. prescribed pharmacological regimen. >Incorporate relaxation skills and diversional activities into pain control program
Helpful in determining pain management needs and effectiveness of >Demonstrated program relaxed body posture and be able to sleep/rest appropriately. Soft/sagging mattress, large pillows prevent maintenance of proper body alignment, placing stress on affected joints. Elevation of bed linens reduces pressure on inflamed/painful joints. In severe disease/acute exacerbation, total bedrest may be necessary (until objective and subjective improvements are noted) to limit pain/injury to joint.
Suggest patient assume position of comfort while in bed or sitting in chair. Promote bedrest as indicated.
Collaborative Apply ice or cold packs when indicated Cold may relieve pain and swelling during acute episodes.
Student Nurses Community
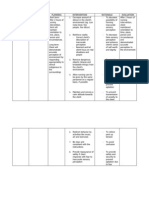
Provides sustained heat to reduce pain and improve ROM of affected joints
. Assist with physical therapies, e.g., paraffin glove, whirlpool baths.
Administer medications as indicated Salicylates, e.g., aspirin (ASA) (Acuprin, Ecotrin, ZORprin);
ASA exerts an anti-inflammatory and mild analgesic effect, decreasing stiffness and increasing mobility. ASA must be taken regularly to sustain a therapeutic blood level. Research indicates that ASA has the lowest toxicity index of commonly prescribed NSAIDs. Characteristics of anti-inflammatory and immune modifier effects coupled with ability to block metalloproteinases
Tetracyclines, e.g., minocycline (Minocin);
Student Nurses Community
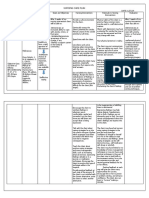
Nursing Interventions and Rational - Nursing Care Plan for Rheumatoid Arthritis 1. Record complaints of pain, record the location and intensity (scale 0-10). Write down the factors that accelerate and signs of pain - non-verbal. Rational: To assist in determining the need for pain management and program effectiveness. 2. Give a hard mattress, a small pillow. Elevate the bed linen as needed. Rational: a soft mattress, pillow that would prevent maintenance of proper body alignment, placing stress on the joints that hurt. Elevation of the bed linen lowering the pressure in the inflamed joints / pain. 3. Place / monitor the use of pillows, sandbags, splint, brace. Rational: Resting sore joints and maintain a neutral position. The use of the brace can reduce pain and can reduce damage to the joints. 4. Advise to change position frequently. Help to move in bed, prop joint pain above and below, avoid jerky movements. Rationale: Prevent the occurrence of general fatigue and joint stiffness. Stabilize joints, reduce the movement / pain in the joints. 5. Instruct the patient to a warm bath or shower at the time awake and / or at bedtime. Provide a warm washcloth compress for sore joints several times a day. Monitor the temperature of the water compresses, baths, and so on. Rational: The heat increases muscle relaxation, and mobility, reduce pain and stiffness in the morning release. Sensitivity to heat can be removed and dermal wound can be healed. 6. Give a gentle massage Rationale: Increase relaxation / reducing pain. 7. Encourage the use of stress management techniques, such as progressive relaxation, therapeutic touch, biofeed back, visualization, guidelines imagination, self hypnosis, and breath control. Rationale: Increase relaxation, provide a sense of control and may enhance coping abilities. 8. Engage in activities appropriate entertainment for individual situations. Rationale: Focusing attention back, providing stimulation, and increased self-confidence and feeling healthy. 9. Give drug before the activity / planned exercise as directed. Rationale: Increasing realaksasi, reduce muscle tension / spasm, making it easier to participate in therapy.
Student Nurses Community 10. Collaboration: Give medications as directed. Rational: As an anti-inflammatory and mild analgesic effect in reducing stiffness and increasing mobility. 11. Give ice-cold compress if needed Rational: The cold can relieve pain and swelling during the acute period
ered.] Provide emotional support and reassurance to help the patient cope with limited mobility. Encourage the patient to perform as much self-care as his immobility and pain allow. To help promote sleep, adjust pain medications to allow for maximum rest. Help the patient identify techniques and activities that promote rest and relaxation. For joints in hand, provide hot soaks and paraffin dips to relieve pain as ordered. Check crutches, cane, braces, or walker for proper fit. Assess the patients pain patterns. Watch for skin irritation caused by prolonged use of assistive devices. Instruct the patient to plan for adequate rest during the day. Instruct the patient to take medications exactly as prescribe
Вам также может понравиться
- Ethics in Pharmacy PracticeДокумент21 страницаEthics in Pharmacy PracticeLighto Ryusaki100% (1)
- HAF F16 ManualДокумент513 страницHAF F16 Manualgreekm4dn3ss86% (7)
- Diagnostic Laboratory TestsДокумент6 страницDiagnostic Laboratory TestsKiana Mae Wong Diwag100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Functional Urinary Incontinence NCPДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plan For Functional Urinary Incontinence NCPderic58% (12)
- ACL Tear & Knee Arthroplasty Nursing CareДокумент2 страницыACL Tear & Knee Arthroplasty Nursing CareEd Pascasio100% (2)
- Drug CalculationsДокумент6 страницDrug CalculationsLighto RyusakiОценок пока нет
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Nursing Care PlanДокумент3 страницыRheumatoid Arthritis Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis95% (21)
- Acute PainДокумент5 страницAcute PainBrix ValdrizОценок пока нет
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Nursing Care Plan PDFДокумент3 страницыRheumatoid Arthritis Nursing Care Plan PDFIzhra MargateОценок пока нет
- NCP Rheumatoid ArthritisДокумент3 страницыNCP Rheumatoid ArthritisJanieross Lamboso100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Sexual DysfunctionДокумент10 страницNursing Care Plan for Sexual DysfunctionDeca Tan50% (6)
- Multiple MyelomaДокумент2 страницыMultiple MyelomaKolin JandocОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan - Posterior Hip Dislocation LeftДокумент1 страницаNursing Care Plan - Posterior Hip Dislocation LeftJasmin Jacob100% (7)
- NCP - GlaucomaДокумент1 страницаNCP - GlaucomaKath CuevasОценок пока нет
- NCP CataractДокумент2 страницыNCP CataractMaureen Gay Acierto Tegui67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisLighto RyusakiОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisLighto RyusakiОценок пока нет
- Student Nurses' Rheumatoid Arthritis Care PlanДокумент3 страницыStudent Nurses' Rheumatoid Arthritis Care PlanKath Mendoza Ü63% (8)
- Schneider Electric Strategy PresentationДокумент10 страницSchneider Electric Strategy PresentationDeepie KaurОценок пока нет
- NCP Spiritual DistressДокумент3 страницыNCP Spiritual DistressAngelo ArabejoОценок пока нет
- Ortho NCPДокумент26 страницOrtho NCPNessan TagaroОценок пока нет
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент10 страницAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJay Villasoto100% (1)
- Nursing CARE PLAN PsychДокумент7 страницNursing CARE PLAN Psychtiptopyo100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan 1Документ12 страницNursing Care Plan 1Disyme Duron AzuresОценок пока нет
- Disturbed Body ImageДокумент3 страницыDisturbed Body Imagenura100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan FibromyalgiaДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan Fibromyalgiaderic90% (10)
- Pratt & Whitney Engine Training ResourcesДокумент5 страницPratt & Whitney Engine Training ResourcesJulio Abanto50% (2)
- Osteomyelitis NCPДокумент5 страницOsteomyelitis NCPFranzes Janina Sacramento Gabriel100% (8)
- NURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Документ3 страницыNURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Caroline ChaОценок пока нет
- Oxytocin Drug StudyДокумент1 страницаOxytocin Drug Studysweetpixie1887% (15)
- Nursing Diagnosis IdentificationДокумент6 страницNursing Diagnosis Identificationmadhurima kunduОценок пока нет
- History I.M.PeiДокумент26 страницHistory I.M.PeiVedasri RachaОценок пока нет
- NCP - Chronic PainДокумент5 страницNCP - Chronic PainJaye DangoОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan Risk For Urinary RetentionДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plan Risk For Urinary RetentionReginald Julia100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: Phinma University of IloiloДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan: Phinma University of IloiloBeatrice ManingasОценок пока нет
- Orif NCPДокумент1 страницаOrif NCPLighto Ryusaki100% (1)
- NCP Chronic ConfusionДокумент4 страницыNCP Chronic ConfusionLyka DianaОценок пока нет
- Risk For InjuryДокумент4 страницыRisk For InjuryJanina Patricia BuddleОценок пока нет
- Gallbladder Removal Recovery GuideДокумент14 страницGallbladder Removal Recovery GuideMarin HarabagiuОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan (ImpairedphyssicalДокумент5 страницNursing Care Plan (ImpairedphyssicalkuroroexileОценок пока нет
- Importers in BOC List As of June 2, 2015Документ254 страницыImporters in BOC List As of June 2, 2015PortCalls88% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions (3) (Reference) Rationale (Reference) EvaluationДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions (3) (Reference) Rationale (Reference) EvaluationJulvica HeuwОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Planautoeroticasphaxia50% (8)
- Urinary Retention, RevisedДокумент2 страницыUrinary Retention, RevisedKim Beverly100% (5)
- NCPДокумент3 страницыNCPkristina_zamoraОценок пока нет
- Arthritis NCPДокумент2 страницыArthritis NCPTri Sha100% (3)
- NCP StressДокумент2 страницыNCP StressWaqas Javed100% (7)
- NCP Self EsteemДокумент3 страницыNCP Self EsteemAlfadz AsakilОценок пока нет
- NURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired PhysicalДокумент1 страницаNURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Physicalmitchie riveraОценок пока нет
- Hypertonic SolutionsДокумент4 страницыHypertonic SolutionsVanessa PaguiriganОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент1 страницаNursing Care PlanSHeenah Qo100% (1)
- NCP 2Документ2 страницыNCP 2Neil Abraham Mendoza Lalap100% (2)
- Family Nursing Care PlanДокумент2 страницыFamily Nursing Care PlanMatthew Lim Montenegro33% (3)
- Acute Pain Related To Tissue Trauma and InjuryДокумент4 страницыAcute Pain Related To Tissue Trauma and Injuryprickybiik50% (2)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation EvaluationДокумент1 страницаAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation EvaluationJulie Ann100% (2)
- NCPДокумент1 страницаNCPanon-61963867% (3)
- NCP 2Документ3 страницыNCP 2klawdin100% (1)
- NCP For Pain - Rheumatoid ArthritisДокумент5 страницNCP For Pain - Rheumatoid Arthritisveorjan100% (1)
- NCPДокумент3 страницыNCPChrisTine M. MoralesОценок пока нет
- Self-Care DeficitДокумент2 страницыSelf-Care DeficitNDJОценок пока нет
- NCP Cataract SurgeryДокумент5 страницNCP Cataract SurgeryKristaJaneCelmarBagcatОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan Impaired AdjustmentДокумент1 страницаNursing Care Plan Impaired Adjustmentderic100% (2)
- NCP Violence - OtherДокумент2 страницыNCP Violence - OtherRosean Venus SilangОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: DATE: 6/27/19Документ5 страницNursing Care Plan: DATE: 6/27/19Maricris Tac-an Calising-PallarОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationДокумент1 страницаNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationMyrien BanaagОценок пока нет
- Managing Urinary Tract Obstruction Nursing InterventionsДокумент8 страницManaging Urinary Tract Obstruction Nursing Interventionsjyaba0% (1)
- NCPДокумент4 страницыNCPMichelleОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan for Rheumatoid ArthritisДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan for Rheumatoid ArthritisJashAnia MarIe EvArdo FloresОценок пока нет
- Clinical Prep 2Документ9 страницClinical Prep 2Colin FraleyОценок пока нет
- Nursing DiagnosisДокумент4 страницыNursing DiagnosisEnzo DyОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care for Nephrolithiasis and DiabetesДокумент22 страницыNursing Care for Nephrolithiasis and DiabetesNishaThakuriОценок пока нет
- Abdominal PainДокумент3 страницыAbdominal PainReiciel Joy Gombio100% (2)
- Problem:: TherapiesДокумент2 страницыProblem:: TherapiesDhine Dhine ArguellesОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент5 страницNursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationLighto RyusakiОценок пока нет
- IMCI Chart Booklet TrytryДокумент80 страницIMCI Chart Booklet TrytryLighto RyusakiОценок пока нет
- Overview of Measles DiseaseДокумент3 страницыOverview of Measles DiseaseLighto RyusakiОценок пока нет
- Cosmetics: 1) Absorvent CottonДокумент7 страницCosmetics: 1) Absorvent CottonLighto RyusakiОценок пока нет
- Unit 11Документ64 страницыUnit 11Lighto RyusakiОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент5 страницNursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationLighto RyusakiОценок пока нет
- Sample Research Student TitlesДокумент3 страницыSample Research Student Titlesrvmisa15Оценок пока нет
- RubellaДокумент3 страницыRubellaLighto RyusakiОценок пока нет
- QUESTIONNAIRE For Providers - EngДокумент8 страницQUESTIONNAIRE For Providers - EngLighto RyusakiОценок пока нет
- Organ TransplantsДокумент18 страницOrgan Transplantscndy31Оценок пока нет
- Organ Donation Awareness in The Philippines: Duty To Disclose Community and Separate Property in DivorceДокумент1 страницаOrgan Donation Awareness in The Philippines: Duty To Disclose Community and Separate Property in DivorceLighto RyusakiОценок пока нет
- 2013 Yearly Calendar Landscape 01Документ2 страницы2013 Yearly Calendar Landscape 01sbyyyОценок пока нет
- Nec Hiv Nov-Aidsreg2012Документ4 страницыNec Hiv Nov-Aidsreg2012Lighto RyusakiОценок пока нет
- Website:: 24-Hour Public Weather ForecastДокумент1 страницаWebsite:: 24-Hour Public Weather ForecastLighto RyusakiОценок пока нет
- Cyberbullying Emotional ConsequencesДокумент2 страницыCyberbullying Emotional ConsequencesLighto RyusakiОценок пока нет
- Alkanes and CycloalkanesДокумент17 страницAlkanes and CycloalkanesJzamille Florenz Grantoza AlviorОценок пока нет
- The ICN Code of Ethics For NursesДокумент12 страницThe ICN Code of Ethics For Nursesgmike31100% (3)
- Notes Chapter 01Документ44 страницыNotes Chapter 01Kiki KiranaОценок пока нет
- Atomic StructureaaaДокумент38 страницAtomic StructureaaaLighto RyusakiОценок пока нет
- Nec Hiv Nov-Aidsreg2012Документ4 страницыNec Hiv Nov-Aidsreg2012Lighto RyusakiОценок пока нет
- Economy 1 PDFДокумент163 страницыEconomy 1 PDFAnil Kumar SudarsiОценок пока нет
- One Stop Report - Tata MotorsДокумент119 страницOne Stop Report - Tata MotorsJia HuiОценок пока нет
- Wa0004.Документ85 страницWa0004.sheetalsri1407Оценок пока нет
- Connotative and Denotative, Lexical and StylisticДокумент3 страницыConnotative and Denotative, Lexical and StylisticEman Jay FesalbonОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Phil. HistoryДокумент4 страницыChapter 2 Phil. HistoryJaylene AlbayОценок пока нет
- Commissioning Procedure for JTB-PEPCДокумент17 страницCommissioning Procedure for JTB-PEPCelif maghfirohОценок пока нет
- Miles and Snow's Organizational StrategiesДокумент15 страницMiles and Snow's Organizational StrategiesVirat SahОценок пока нет
- CPB145 CVTДокумент1 страницаCPB145 CVTDantiancОценок пока нет
- What are plot pointsДокумент19 страницWhat are plot pointsOpeeron OpeeОценок пока нет
- Who Is Marine Le PenДокумент6 страницWho Is Marine Le PenYusuf Ali RubelОценок пока нет
- Joey Cena 2Документ1 страницаJoey Cena 2api-635313033Оценок пока нет
- Innovations in Teaching-Learning ProcessДокумент21 страницаInnovations in Teaching-Learning ProcessNova Rhea GarciaОценок пока нет
- Handouts - Entity Relationship DiagramДокумент8 страницHandouts - Entity Relationship Diagramsecret studetОценок пока нет
- Effect of Disinfectants On Highly Pathogenic Avian in Uenza Virus (H5N1) in Lab and Poultry FarmsДокумент7 страницEffect of Disinfectants On Highly Pathogenic Avian in Uenza Virus (H5N1) in Lab and Poultry FarmsBalvant SinghОценок пока нет
- Free ArtistДокумент1 страницаFree Artistnunomgalmeida-1Оценок пока нет
- Yoga For The Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease (Hartley 2014)Документ52 страницыYoga For The Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease (Hartley 2014)Marcelo NorisОценок пока нет
- Cambridge IGCSE: Pakistan Studies 0448/01Документ4 страницыCambridge IGCSE: Pakistan Studies 0448/01Mehmood AlimОценок пока нет
- 3D Model of Steam Engine Using Opengl: Indian Institute of Information Technology, AllahabadДокумент18 страниц3D Model of Steam Engine Using Opengl: Indian Institute of Information Technology, AllahabadRAJ JAISWALОценок пока нет
- MICROHARDNESS TESTER HMV-2 - SeriesДокумент9 страницMICROHARDNESS TESTER HMV-2 - SeriesRicoОценок пока нет
- Revised Organizational Structure of Railway BoardДокумент4 страницыRevised Organizational Structure of Railway BoardThirunavukkarasu ThirunavukkarasuОценок пока нет
- Budget Planner Floral Style-A5Документ17 страницBudget Planner Floral Style-A5Santi WidyaninggarОценок пока нет
- Activity 1: 2. Does His Homework - He S 3 Late ForДокумент10 страницActivity 1: 2. Does His Homework - He S 3 Late ForINTELIGENCIA EDUCATIVAОценок пока нет
- Stakeholder Management Plan Case Study 1Документ2 страницыStakeholder Management Plan Case Study 1Krister VallenteОценок пока нет