Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Orif
Загружено:
Gene Edward D. ReyesИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Orif
Загружено:
Gene Edward D. ReyesАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
ORIF O.R.I.F. is an abbreviation for Open Reduction Internal Fixation.
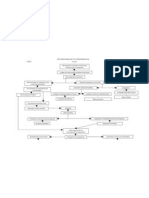
Open reduction internal fixation is a method of surgically repairing a fractured bone. Generally, this involves either the use of plates and screws or an intramedullary (IM) rod to stabilize the bone. If you are having a broken bone treated by ORIF, you will be taken to the operating room, given anesthesia so that you will not feel the surgery, and have your bones repaired by an orthopedic surgeon. Methods of ORIF 1. Intramedullary (IM) rods are used to align and stabilize fractures. IM rods are inserted into the bone marrow canal in the center of the long bones of the extremities (e.g. femur or tibia). One of the significant advantages of IM rods over other methods of fixation is IM rods share the load with the bone, rather that entirely support the bone. Because of this, patients are able to use the extremity more quickly. IM rods cannot be used for all fractures, and there are often associated complaints of pain and other symptoms at the site the IM rods are inserted. For this reason, a second operation may be needed to remove the IM device if you have painful symptoms. Otherwise, the IM nail can usually stay inside your bone forever. 2. Using of plates and screws which will serves as a support to the bones due to the healing process and can be removed if the client wants to. 3. External fixation is a method of immobilizing bones to allow a fracture to heal. External fixation is accomplished by placing pins or screws into the bone on both sides of the fracture. The pins are then secured together outside the skin with clamps and rods. The clamps and rods are known as the "external frame." Some of the advantages of external fixation are that it is quickly and easily applied. The risk of infection at the site of the fracture is minimal, but there is a risk of infection where the pins are inserted from the skin into the bone. Indications of ORIF Absolute 1. Unable to obtain an adequate reduction 2. Displaced intra-articular fractures 3. Certain types of displaced epiphyseal fractures 4. Major avulsion fractures where there is loss of function of a joint or muscle group 5. Non-unions 6. Re- implantations of limbs or extremities Relative 1. Delayed unions 2. Multiple fractures to assist in care and general management 3. Unable to maintain a reduction
4. Pathological fractures 5. To assist in nursing care 6. To reduce morbidity due to prolonged immobilisation 7. For fractures in which closed methods are known to be ineffective Procedure of ORIF The surgical procedure is performed by a doctor who specializes in orthopedics, which is a branch of medicine concerning the musculoskeletal structure of the body. Under general anesthesia, an incision is made at the site of the break or injury, and the fracture is carefully re-aligned or the joint replaced. The hardware is installed, and the incision is closed with staples or stitches. The steel rods, screws, or plates can be permanent, or temporary and removed when healing takes place. Once the open reduction internal fixation is performed, a cast is usually applied. In the case of an ankle fracture, for instance, the first cast is a non-weight bearing cast, and crutches can be used to help keep weight off the healing bones. Later, when the healing has progressed, this cast will be replaced with one that can bear weight. Eventually, after a period of some weeks, the cast will be removed entirely. Recovery rate and Process of ORIF Recovery from a bone fracture after an open reduction internal fixation can be quite painful, and pain management becomes a concern. Commonly, acetaminophen with codeine is prescribed, as research has shown ibuprofen or other non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may slow down or inhibit the rate of healing. It is important to take the drugs as prescribed to help manage the pain cycle. Physical therapy is also an important part of the recovery process after an open reduction internal fixation. Since the part of the body that has been injured is usually held still or immobilized for a long period of time, the muscles, tendons, and ligaments can become weak. Physical therapy helps to restore the strength, range of motion, and endurance of the affected area. It can also help with pain management. Physical therapy can consist of exercises, hot or cold packs, ultrasound, and nerve stimulation, or a combination of treatments. Complications Complications of ORIF can include infection, swelling, and movement of the installed hardware. The recovery process can take months, because bones grow slowly. Other factors that can affect recovery are the location and severity of the break, the age of the person, and the type of bone broken.
Вам также может понравиться
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceДокумент6 страницA Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceJohny Villanueva78% (72)
- Client Profile: Case StudyДокумент1 страницаClient Profile: Case Studysivakamasundari pichaipillaiОценок пока нет
- Tooth WhiteningДокумент165 страницTooth Whiteningionut1ilie-1100% (2)
- 2017 Coca Cola Foundation GrantsДокумент51 страница2017 Coca Cola Foundation GrantsPrincess PatagocОценок пока нет
- Intestinal Obstruction: Methas Arunnart MDДокумент42 страницыIntestinal Obstruction: Methas Arunnart MDJhe-sie AngelinaОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыDrug StudyKorina FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Osteogenesis ImperfectaДокумент52 страницыOsteogenesis ImperfectaTrias AdnyanaОценок пока нет
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Evaluation Nsg. Action RationaleДокумент2 страницыAssessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Evaluation Nsg. Action RationaleRhea Mae Valles - ReyesОценок пока нет
- NCP, PL, DPДокумент6 страницNCP, PL, DPJazel Algara JompillaОценок пока нет
- Open Reduction and Internal Fixation Surgery (Orif) Definition (Mau)Документ14 страницOpen Reduction and Internal Fixation Surgery (Orif) Definition (Mau)krizzia raymundoОценок пока нет
- Post Op ThyroidectomyДокумент1 страницаPost Op Thyroidectomyzulkiflim88Оценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan With A FractureДокумент11 страницNursing Care Plan With A FractureHasanah EkaОценок пока нет
- CC Er Reflection PaperДокумент2 страницыCC Er Reflection Paperapi-545031607Оценок пока нет
- Case Report - Juliet - Closed Fracture Middle of The Left FemurДокумент28 страницCase Report - Juliet - Closed Fracture Middle of The Left FemurGupiesОценок пока нет
- HernioplastyДокумент6 страницHernioplastyCherry Delos ReyesОценок пока нет
- HNP Case Scenario For Case StudyДокумент2 страницыHNP Case Scenario For Case StudyDeinielle Magdangal RomeroОценок пока нет
- Clinical Portrait Pertinent DataДокумент9 страницClinical Portrait Pertinent DataGermin CesaОценок пока нет
- NCP For Acute PainДокумент4 страницыNCP For Acute PainimnasОценок пока нет
- Or RRLДокумент4 страницыOr RRLAlponce Edal AdagОценок пока нет
- Burn - Daily Physical AssessmentДокумент8 страницBurn - Daily Physical AssessmentkrishcelОценок пока нет
- Propranolol 1 PresentationДокумент17 страницPropranolol 1 Presentationapi-284092317100% (1)
- Post Cesarean Section DeliveryДокумент5 страницPost Cesarean Section Deliveryᒙᕧᖇᕦᙏᖻ ᗴᔛᓦᗩᖆᗩОценок пока нет
- Psych - Chapter 23 Into To Milieu ManagementДокумент4 страницыPsych - Chapter 23 Into To Milieu ManagementKaren かれんОценок пока нет
- Case Study Medical WardДокумент4 страницыCase Study Medical WardFrancis Antonio Llenaresas QuijanoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study EditedДокумент5 страницDrug Study EditedfabtaciousVeelaОценок пока нет
- MannitolДокумент3 страницыMannitolAlexandra AntondyОценок пока нет
- NCP AnxietyДокумент1 страницаNCP AnxietyUnang MagnayeОценок пока нет
- Open FractureДокумент9 страницOpen FractureAnnyl LaurelОценок пока нет
- Cellulitis Discharge PlanДокумент1 страницаCellulitis Discharge PlanJuvy Rose Tinga YeeОценок пока нет
- NCP For Rapid Shallow BreathingДокумент1 страницаNCP For Rapid Shallow Breathingbamboo2dОценок пока нет
- NCP OsteosarcomaДокумент6 страницNCP OsteosarcomaNiksОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology AbrasionДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology AbrasionVito VitoОценок пока нет
- NCP MentalДокумент6 страницNCP MentalMarius Clifford BilledoОценок пока нет
- NCP (Or) ThyroidectomyДокумент3 страницыNCP (Or) ThyroidectomyChiz CorreОценок пока нет
- NCP - Impaired Gas Exchange (COPD)Документ3 страницыNCP - Impaired Gas Exchange (COPD)Karen Joy ItoОценок пока нет
- Ferrous SulfateДокумент2 страницыFerrous SulfateMiEr Cañas AzenicОценок пока нет
- Appendicitis NCPДокумент5 страницAppendicitis NCPEarl Joseph DezaОценок пока нет
- ASSESSMENTДокумент2 страницыASSESSMENTColeen PequitОценок пока нет
- History of Past and Present IllnessДокумент10 страницHistory of Past and Present IllnessRenea Joy ArruejoОценок пока нет
- Oa Case ReportДокумент26 страницOa Case Reportaliffikri52100% (1)
- HA-RLE-WS # 8 Assessing CultureДокумент5 страницHA-RLE-WS # 8 Assessing CultureJULIE ANNE CORTEZОценок пока нет
- Posterior Mold: PurposeДокумент3 страницыPosterior Mold: PurposeSheryl Ann Barit PedinesОценок пока нет
- Discharge PlanДокумент4 страницыDischarge PlanKabang MoaОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan & Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan & Drug StudyKyrie Silatory VillarosaОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of OsteomyelitisДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of Osteomyelitissorryandreosayanisalreadytaken100% (1)
- Acute AppendicitisДокумент23 страницыAcute AppendicitisSandie Daniel GabalunosОценок пока нет
- Cu 3 Week 3Документ3 страницыCu 3 Week 3Maica LectanaОценок пока нет
- Gordon's Functional Health PatternДокумент5 страницGordon's Functional Health PatternnerlynОценок пока нет
- PyomyositisДокумент31 страницаPyomyositisAezl Mercado0% (1)
- ER Journal Summary - Effects of An Ethical Empowerment Program On Critical Care Nurses' Ethical Decision-MakingДокумент1 страницаER Journal Summary - Effects of An Ethical Empowerment Program On Critical Care Nurses' Ethical Decision-MakingWyen CabatbatОценок пока нет
- Herniated Nucleus PulposusДокумент14 страницHerniated Nucleus PulposusJm Fernandez Gan RNОценок пока нет
- Cholecystectomy (: Laparoscopic GallstonesДокумент4 страницыCholecystectomy (: Laparoscopic GallstonesAlexia BatungbacalОценок пока нет
- NCP Close Complete Fracture AnxietyДокумент2 страницыNCP Close Complete Fracture AnxietyArt Christian RamosОценок пока нет
- Case File GERDДокумент9 страницCase File GERDMutiara Shifa100% (1)
- EBNДокумент22 страницыEBNLouis Ann BautistaОценок пока нет
- CP On OsteomyelitisДокумент147 страницCP On Osteomyelitiskathy50% (2)
- Pa Tho Physiology of OsteoporosisДокумент2 страницыPa Tho Physiology of Osteoporosisjcam_o9Оценок пока нет
- Propylthiouracil Is Used ForДокумент6 страницPropylthiouracil Is Used Forghazy galibieОценок пока нет
- Discharge PlanДокумент4 страницыDischarge PlanPaul Loujin LeeОценок пока нет
- Open Surgery Bones Fractures: DescriptionДокумент5 страницOpen Surgery Bones Fractures: DescriptionaleeverdiОценок пока нет
- The Ilizarov Method of TreatmentДокумент20 страницThe Ilizarov Method of Treatmentashley_magsinoОценок пока нет
- Closed Fracture Treatment and ManagementДокумент16 страницClosed Fracture Treatment and ManagementMuruga DassОценок пока нет
- External FixationДокумент4 страницыExternal FixationZilbran BerontaxОценок пока нет
- Original PDF Kendigs Disorders of The Respiratory Tract in Children 9th Edition PDFДокумент41 страницаOriginal PDF Kendigs Disorders of The Respiratory Tract in Children 9th Edition PDFmichael.richardson540100% (30)
- 1st Decision - G.R. No. 217872Документ11 страниц1st Decision - G.R. No. 217872MerОценок пока нет
- Rewire Your BrainДокумент0 страницRewire Your BrainJohn Bates100% (1)
- Pest ManagementДокумент5 страницPest Managementkiran100% (1)
- Professional Exchange Program Krakow, Poland By: Luthfiyya Syafiqa TahanyДокумент3 страницыProfessional Exchange Program Krakow, Poland By: Luthfiyya Syafiqa Tahanyluthfiyya syafiqaОценок пока нет
- Review: Curar, Persuadir, Gobernar: La Construcción Histórica de La Profesión Médica en Buenos Aires (1852-1886), by R. González LeandriДокумент2 страницыReview: Curar, Persuadir, Gobernar: La Construcción Histórica de La Profesión Médica en Buenos Aires (1852-1886), by R. González LeandriXoyyo Xoyyodevuelta0% (1)
- SPF 55 BrochureДокумент2 страницыSPF 55 Brochureapi-528907705Оценок пока нет
- Empleyadong Musmos: A Qualitative Study On The Perception of The Youth Towards Child Labor in Taytay, RizalДокумент13 страницEmpleyadong Musmos: A Qualitative Study On The Perception of The Youth Towards Child Labor in Taytay, RizalAngelo DavidОценок пока нет
- Fa Q Internship ProgramДокумент5 страницFa Q Internship ProgramMariam A. KarimОценок пока нет
- Dukungan Sosial Dan Post-Traumatic Stress DisorderДокумент7 страницDukungan Sosial Dan Post-Traumatic Stress DisordercholiidОценок пока нет
- YogaДокумент62 страницыYogaAdityaОценок пока нет
- The Essence of Human Interaction CommunicationДокумент14 страницThe Essence of Human Interaction CommunicationShane WhiteОценок пока нет
- 1 4Документ2 страницы1 4Chenna RoseОценок пока нет
- Echocardiography in Coronary Artery DiseaseДокумент277 страницEchocardiography in Coronary Artery DiseaseMichael HartОценок пока нет
- 365 Land Transport SafetyДокумент24 страницы365 Land Transport Safetyleo limpiasОценок пока нет
- Authentic Happiness PresentationДокумент14 страницAuthentic Happiness Presentationapi-262987602Оценок пока нет
- Electrophysiology StudyДокумент84 страницыElectrophysiology StudySarni100% (1)
- Sta. MariaДокумент15 страницSta. MariaArnel TimonesОценок пока нет
- Hotel BookingДокумент1 страницаHotel BookingJagjeet SinghОценок пока нет
- PhobiasДокумент10 страницPhobiasHafiza Rija ShahidОценок пока нет
- Uterine AtonyДокумент14 страницUterine AtonyLady Jane CaguladaОценок пока нет
- Astm A 10.11Документ13 страницAstm A 10.11edu_caneteОценок пока нет
- Lemon and Baking Soda Miraculous CombinationДокумент14 страницLemon and Baking Soda Miraculous CombinationMoses Apeabu100% (4)
- MetricefДокумент2 страницыMetricefPrakashNallappanОценок пока нет
- Neha Lakka Tamu Resume-2Документ1 страницаNeha Lakka Tamu Resume-2api-696187882Оценок пока нет
- 2013 Nursing BulletsДокумент77 страниц2013 Nursing BulletsHarley Justiniani Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- Aruna Ramchandra Shanbhug V Union of IndiaДокумент4 страницыAruna Ramchandra Shanbhug V Union of IndiaTanya TandonОценок пока нет