Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Abruptio Placenta NCP
Загружено:
Nichole Audrey SaavedraОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Abruptio Placenta NCP
Загружено:
Nichole Audrey SaavedraАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
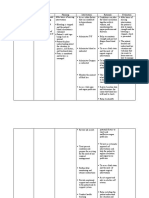
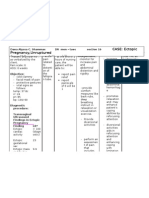
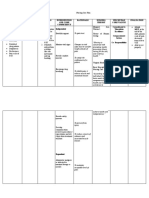
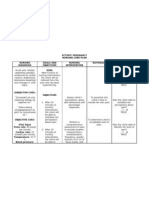
Needs/ Problems/ Cues I. Physiologic A.Deficit Objective: -abdominal guarding -muscle tension -irritability Vital signs: T: 37.
3 P: 95 R: 22 BP: 100/70 Subjective: Nakapamati ko ug sakit sa akong pus-on, bisan ika-20 nga simana
Nursing Diagnosis Acute pain related to accumulation of blood between uterine wall and placenta
Scientific Basis Abruptio placenta refers to the premature serparation of the normally implanted placenta from the uterine wall. Blood vessels at the placental bed rupture spontaneously. It occurs when there is heavy maternal bleeding and may necessitate termination of the pregnancy.
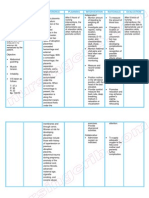
Objectives Nursing of Care Intervention After 8 hour of nursing care, the mother will demonstra te use of relaxation skills, and other methods to promote comfort. Interventions to promote comfort:
Rationale
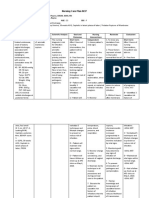
1. Monitor amount 1. To measure the of blood by amount of blood weighing all pads. loss. 2. Investigate reports, noting location, duration, intensity (010scale) and characteristics (dull, sharp, constant). 3. Monitor maternal vital signs and fetal heart rate through continuous monitoring. 2. Changes in location or intensity are not uncommon buy may reflect developing complications. 3. Early recognition of possible adverse effect allows for prompt interventions.
pa sa akong pagbuntis as verbalized by the mother.
Source: Straight As in MaternalNeonatal Nursing 2nd Edition, Lippincott. P114-115
4. Measure and record fundal height.
4. Fundal height may increase with concealed bleeding.
5. Position the 5. To enhance mother in a sideplacental lying position, with perfusion. the head of the bed elevated. 6. Provide comfort measure, like back rubs, deep breathing. Instruct in relaxation or visualization Source: Delmars Maternal-Infant Nursing Care Plans 2nd Edition 6. Promotes relaxation and may enhance patients coping ability by refocusing.
Вам также может понравиться
- Abruptio NCPДокумент4 страницыAbruptio NCPShien Samalea Vasquez100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plans (NCP) of Abruptio PlacentaДокумент13 страницNursing Care Plans (NCP) of Abruptio PlacentaKath76% (21)
- Abruptio Placenta NCPДокумент5 страницAbruptio Placenta NCPTinОценок пока нет
- After 8 Hours of Nursing Interventions Patient Will Be Able To: Demonstrate Adequate Perfusion. Demonstrate Stable Vital SignsДокумент3 страницыAfter 8 Hours of Nursing Interventions Patient Will Be Able To: Demonstrate Adequate Perfusion. Demonstrate Stable Vital Signsroma_elonaОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan Abrubtio PlacentaДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan Abrubtio PlacentaLei Ortega0% (1)
- NCP For EclampsiaДокумент6 страницNCP For EclampsiaXtine Soliman Zamora100% (3)
- Abruptio Placenta NCP 2 FinalДокумент19 страницAbruptio Placenta NCP 2 FinalTin100% (1)
- NCP Abruptio PlacentaДокумент2 страницыNCP Abruptio PlacentaCarson Birth100% (1)
- NCP For Delivery RoomДокумент4 страницыNCP For Delivery RoomGiselle EstoquiaОценок пока нет
- NCP PPHДокумент2 страницыNCP PPHmikee-berredo-9975Оценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan Abruptio PlacentaeДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan Abruptio Placentaederic93% (29)
- NCP Placenta PreviaДокумент2 страницыNCP Placenta PreviaCathy CnlsОценок пока нет
- Abruptio Placenta Nursing Care PlanДокумент2 страницыAbruptio Placenta Nursing Care PlanJharene Basbaño100% (5)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pregnancy Induced HypertensionДокумент9 страницNursing Care Plan For Pregnancy Induced HypertensionMurugham DineshОценок пока нет
- NCP Gestational HypertensionДокумент2 страницыNCP Gestational Hypertensionshila_glangОценок пока нет
- Hemorrhage NCPДокумент4 страницыHemorrhage NCPElishaОценок пока нет
- Nursing Diagnosis: May Be Related To: Fluid Volume Deficit (Isotonic)Документ26 страницNursing Diagnosis: May Be Related To: Fluid Volume Deficit (Isotonic)Ric Nacional75% (4)
- Uterine Atony - NCPДокумент17 страницUterine Atony - NCPMonica BorjaОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan Postpartum HemorrhageДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan Postpartum HemorrhageLei Ortega95% (21)
- Predisposing Factors:: Placenta Previa Lower Uterine SegmentДокумент11 страницPredisposing Factors:: Placenta Previa Lower Uterine Segmentjhachers100% (1)
- Placenta Previa NCP 1Документ6 страницPlacenta Previa NCP 1Faye Nervanna Alecha Alferez83% (18)
- NCP - PreeclampsiaДокумент3 страницыNCP - PreeclampsiaRap De la Cruz50% (2)
- NCP (Acute Pain, Episiotomy)Документ6 страницNCP (Acute Pain, Episiotomy)Jenny AjocОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For Postpartum HemorrhageДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan For Postpartum HemorrhageDianne Mae100% (1)
- All NCPsДокумент83 страницыAll NCPsDennis Nyambane Momanyi100% (6)
- NCP EctopicДокумент1 страницаNCP Ectopicmusicath_07Оценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan Abruptio PlacentaeДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan Abruptio PlacentaeWann WannОценок пока нет
- NCP Post PartumДокумент2 страницыNCP Post PartumsteffiОценок пока нет
- Nursing Crib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionДокумент2 страницыNursing Crib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionJustin PasaronОценок пока нет
- BOX 17.4 NCP Postpartum HemorrhageДокумент4 страницыBOX 17.4 NCP Postpartum HemorrhageJam AliОценок пока нет
- Care Plan PostpartumДокумент2 страницыCare Plan PostpartumSiwei Yang100% (1)
- Placenta Previa NCP 1Документ6 страницPlacenta Previa NCP 1Nicole ArandingОценок пока нет
- NCP Case Study 1Документ3 страницыNCP Case Study 1Kristinelou Reyna100% (5)
- NCP HmoleДокумент5 страницNCP HmolemeriiОценок пока нет
- Final NCP For PostpartumДокумент8 страницFinal NCP For PostpartumJam Ali100% (1)
- N E E D S C O G N I T I V E P E R P E T U A L RationaleДокумент14 страницN E E D S C O G N I T I V E P E R P E T U A L RationaleArianna Jasmine MabungaОценок пока нет
- Placenta Previa (NCP)Документ2 страницыPlacenta Previa (NCP)jonna casumpangОценок пока нет
- Dilatation and CurettageДокумент2 страницыDilatation and CurettageBheru Lal50% (2)
- Placenta Previa NCP 1Документ6 страницPlacenta Previa NCP 1Madhu Bala100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Interference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент2 страницыAssessment Diagnosis Interference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMelDred Cajes BolandoОценок пока нет
- Pre EclampsiaДокумент3 страницыPre EclampsiaJon Sayson100% (1)
- NCPДокумент10 страницNCPR-Chian Jose Germanp100% (2)
- Care Plan PostpartumДокумент2 страницыCare Plan Postpartumteokie082483% (6)
- Impaired Skin IntegrityДокумент9 страницImpaired Skin IntegrityJamila Angeli Valle100% (2)
- Precipitous Labor/Delivery or Unplanned/Out-of-Hospital DeliveryДокумент7 страницPrecipitous Labor/Delivery or Unplanned/Out-of-Hospital DeliveryLei Ortega100% (1)
- NCP Preeclampsia and EclampsiaДокумент14 страницNCP Preeclampsia and EclampsiaBiway RegalaОценок пока нет
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент2 страницыCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationCarmina DinerosОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care With EclampsiaДокумент40 страницNursing Care With EclampsiaNadia DesyerianОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент3 страницыNursing Care PlanArvan James Cabugayan TalboОценок пока нет
- Ectopic PregnancyДокумент2 страницыEctopic PregnancyKim GalamgamОценок пока нет
- Ectopic PregnancyДокумент2 страницыEctopic PregnancyRex Dave Guinoden100% (1)
- Abruptio Placenta NCPДокумент2 страницыAbruptio Placenta NCPjohncarlo ramos100% (1)
- JINGCO - BSN 2-D - Module-6-Storified-Case-ScenarioДокумент13 страницJINGCO - BSN 2-D - Module-6-Storified-Case-ScenarioJashtine JingcoОценок пока нет
- Postpartum Assessment and CareДокумент14 страницPostpartum Assessment and CareGail Chantel Spring PerlasОценок пока нет
- Principles of Postpartum CareДокумент2 страницыPrinciples of Postpartum CareZaire DylanОценок пока нет
- East Avenue Medical CenterДокумент8 страницEast Avenue Medical CenterMelizaMamarilPadagdagОценок пока нет
- Assigment VДокумент4 страницыAssigment VJoey ParkОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan of The MotherДокумент21 страницаNursing Care Plan of The MotherCristina L. JaysonОценок пока нет
- Assessment of Maternal MeasuresДокумент13 страницAssessment of Maternal Measuresvikas tak100% (1)
- Postpartum Physical AssessmentДокумент60 страницPostpartum Physical AssessmentJhgrace Mary Pacaña Gallo100% (1)
- CPR Final XДокумент38 страницCPR Final XNichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- Bibliography: Achieved? British Journal of Educational Psychology, 1966, 36, 77-86Документ2 страницыBibliography: Achieved? British Journal of Educational Psychology, 1966, 36, 77-86Nichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- Nursing History P H Y S I O L O G I C Body Parts I P P AДокумент3 страницыNursing History P H Y S I O L O G I C Body Parts I P P ANichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- AnxietyДокумент2 страницыAnxietyNichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- Tool For Social Adjustment 20 ItemsДокумент2 страницыTool For Social Adjustment 20 ItemsNichole Audrey Saavedra83% (6)
- UltrasoundДокумент2 страницыUltrasoundNichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- Gastrostomy and Chemotherapy (RLE 4) : Ms. Lucero, ValerieДокумент2 страницыGastrostomy and Chemotherapy (RLE 4) : Ms. Lucero, ValerieNichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- Pa Tho Physiology of Ectopic PregnancyДокумент2 страницыPa Tho Physiology of Ectopic Pregnancynelyang17100% (6)
- Table of Comparison For Performing CPR For Adult, Child, Infant, and Pregnant WomenДокумент3 страницыTable of Comparison For Performing CPR For Adult, Child, Infant, and Pregnant WomenNichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology PRINTДокумент1 страницаPathophysiology PRINTNichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: Problems/Needs /cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives of Care Interventions RationaleДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan: Problems/Needs /cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives of Care Interventions RationaleNichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- Path Opy Hsi OlogyДокумент1 страницаPath Opy Hsi OlogyNichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- Letter For Actual Data GatheringДокумент2 страницыLetter For Actual Data GatheringNichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- Feeding Helpless ClientДокумент26 страницFeeding Helpless ClientNichole Audrey Saavedra100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Problems/Needs /cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives of Care Interventions RationaleДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan: Problems/Needs /cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives of Care Interventions RationaleNichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- KimДокумент4 страницыKimNichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- Gastrostomy ReportДокумент3 страницыGastrostomy ReportNichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: Problems/Needs /cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives of Care Interventions RationaleДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan: Problems/Needs /cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives of Care Interventions RationaleNichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- Gastrostomy ReportДокумент3 страницыGastrostomy ReportNichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- Also Called As Adjuvant Care, Is A Treatment That Is Given in Addition To The PrimaryДокумент2 страницыAlso Called As Adjuvant Care, Is A Treatment That Is Given in Addition To The PrimaryNichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- Ehu GirlДокумент9 страницEhu GirlNichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- Drug/Dose/Route/ Frequency/Timing Classification/Me-Chanism of Action Indications/Contraindications/ Side Effects Principle of Care Treatment EvaluationДокумент2 страницыDrug/Dose/Route/ Frequency/Timing Classification/Me-Chanism of Action Indications/Contraindications/ Side Effects Principle of Care Treatment EvaluationNichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- Activity IntoleranceДокумент2 страницыActivity IntoleranceNichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- PASKII Indicationsofchemo - Classi.ofchemo - AgentsДокумент6 страницPASKII Indicationsofchemo - Classi.ofchemo - AgentsNichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- Regulations IVДокумент3 страницыRegulations IVNichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- NCP LeukemiaДокумент2 страницыNCP LeukemiaNichole Audrey Saavedra0% (1)
- Activity IntoleranceДокумент2 страницыActivity IntoleranceNichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- Let's Get LoudДокумент1 страницаLet's Get LoudNichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- Lesson 2Документ2 страницыLesson 2Nichole Audrey SaavedraОценок пока нет
- Tool For Social Adjustment 20 ItemsДокумент2 страницыTool For Social Adjustment 20 ItemsNichole Audrey Saavedra83% (6)
- Nursing Informatics: Sanil VargheseДокумент55 страницNursing Informatics: Sanil VarghesePalwasha KhanОценок пока нет
- The Flowers of May by Francisco ArcellanaДокумент5 страницThe Flowers of May by Francisco ArcellanaMarkNicoleAnicas75% (4)
- Ra 9048 Implementing RulesДокумент9 страницRa 9048 Implementing RulesToffeeОценок пока нет
- Gallirei Weekend 2018Документ7 страницGallirei Weekend 2018Reiner Albert BraunОценок пока нет
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesДокумент3 страницыDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesReno TadashiОценок пока нет
- YaalДокумент25 страницYaalruseenyОценок пока нет
- Mag Issue137 PDFДокумент141 страницаMag Issue137 PDFShafiq Nezat100% (1)
- COMPOSITION Analysis of A Jazz StandardДокумент9 страницCOMPOSITION Analysis of A Jazz StandardAndresОценок пока нет
- Management of Liver Trauma in Adults: Nasim Ahmed, Jerome J VernickДокумент7 страницManagement of Liver Trauma in Adults: Nasim Ahmed, Jerome J VernickwiraОценок пока нет
- Bootstrap Aggregating Multivariate Adaptive Regression Spline For Observational Studies in Diabetes CasesДокумент8 страницBootstrap Aggregating Multivariate Adaptive Regression Spline For Observational Studies in Diabetes CasesTika MijayantiОценок пока нет
- SakalДокумент33 страницыSakalKaran AsnaniОценок пока нет
- Quality of Life After Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in Patients With Chronic RhinosinusitisДокумент15 страницQuality of Life After Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in Patients With Chronic RhinosinusitisNarendraОценок пока нет
- Process Plant Layout - Becoming A Lost ArtДокумент7 страницProcess Plant Layout - Becoming A Lost ArtRajendraОценок пока нет
- Marriage and Divorce Conflicts in The International PerspectiveДокумент33 страницыMarriage and Divorce Conflicts in The International PerspectiveAnjani kumarОценок пока нет
- Urban Design ToolsДокумент24 страницыUrban Design Toolstanie75% (8)
- Worksheet For Mathematics For ManagementДокумент3 страницыWorksheet For Mathematics For Managementabel shimeles100% (1)
- 18 Ex Parte Applic Shorten Time Consolidate 11/01/21Документ13 страниц18 Ex Parte Applic Shorten Time Consolidate 11/01/21José DuarteОценок пока нет
- Castigliano's 2nd TheoremДокумент29 страницCastigliano's 2nd TheoremMiddle East100% (4)
- Fernando Pessoa LectureДокумент20 страницFernando Pessoa LecturerodrigoaxavierОценок пока нет
- Cyclosporin ARCДокумент9 страницCyclosporin ARCSean GreenОценок пока нет
- Stripper Bolt, Coil Spring, Dowel PinДокумент3 страницыStripper Bolt, Coil Spring, Dowel Pinmuhamad laaliОценок пока нет
- Course Content: SAP Fiori Implementation (SAPX03)Документ3 страницыCourse Content: SAP Fiori Implementation (SAPX03)Jathin Varma KanumuriОценок пока нет
- USA V Rowland - Opposition To Motion To End Probation EarlyДокумент12 страницUSA V Rowland - Opposition To Motion To End Probation EarlyFOX 61 WebstaffОценок пока нет
- Literacy Block Lesson PlanДокумент5 страницLiteracy Block Lesson Planapi-286592038Оценок пока нет
- Law On Common Carriers: Laws Regulating Transportation CompaniesДокумент3 страницыLaw On Common Carriers: Laws Regulating Transportation CompaniesLenoel Nayrb Urquia Cosmiano100% (1)
- Utsourcing) Is A Business: Atty. Paciano F. Fallar Jr. SSCR-College of Law Some Notes OnДокумент9 страницUtsourcing) Is A Business: Atty. Paciano F. Fallar Jr. SSCR-College of Law Some Notes OnOmar sarmiento100% (1)
- Eaap Critical Approaches SamplesДокумент2 страницыEaap Critical Approaches SamplesAcsana LucmanОценок пока нет
- Handling Qualites of CanardДокумент49 страницHandling Qualites of CanardUsman GhummanОценок пока нет
- Organisational Behaviour - II India Yamaha Motors Interim PPT (Download To View Full Presentation)Документ28 страницOrganisational Behaviour - II India Yamaha Motors Interim PPT (Download To View Full Presentation)mahtaabkОценок пока нет
- Text Mapping: Reading For General InterestДокумент17 страницText Mapping: Reading For General InterestIndah Rizki RamadhaniОценок пока нет