Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Layout Drawing
Загружено:
Sandesh KumarАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Layout Drawing
Загружено:
Sandesh KumarАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
(For classes held on 26 and 27 th Feb 07) By Dr. G.S.
Suresh, Professor, Civil Engineering Department, NIE, Mysore (Ph:9342188467, email: gss_nie@ yahoo.com) 1.1 Introduction to Structural drawing: Drawing is the language of engineers, which conveys the idea of the engineer about the shape, structural arrangement to builder. Structural drawings guide builders in the construction of apartment blocks, industrial buildings, highways, irrigation structures, bridges and other important structures. The guidelines given in IS 962 (Code of practice for architectural and buildings) and SP 34 (Handbook on Concrete Reinforcement and Detailing) may be adopted while preparing structural drawings for Reinforced Concrete Structures and its elements. Structural drawings are prepared in different sizes and depend on the number of detailed drawings to be presented. In large projects, the structural drawings are of same size. The preferred size of drawing sheets are given in table 1.1 Table 1.1 Drawing Sheet Size Sl. No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 Designation A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 Trimmed Size in mm 841 x 1189 594 x 841 420 x 594 297 x 420 210 x 297 148 x 210 Un Trimmed Size (Min) in mm 880 x 1230 625 x 880 450 x 625 330 x 450 240 x 330 165 x 240
1. LAYOUT DRAWING
Margins and the divisions of drawings sheets into zones are given in Fig 1.1 a to f. The title block is an important feature in a drawing and should be placed at the bottom right-hand corner of the sheet, where it is readily seen when the prints are folded in the prescribed manner. The size of the title block recommended by SP 34 is 185 x 65 mm. Layout of drawings is not standardized in detailing of reinforced concrete structures. However in practice, the key plan is placed in the upper left hand corner of the sheet, with the elevations and details below and on to the right side of the plan. Schedules and bending details are place in the upper right corner of the drawing. Fig. 1.2 gives a broad outline of layout recommended. In large projects, the bending schedule can be given separately and omitted in the structural drawing. Scale for drawings is selected based on the convenience to include all the details within workable size. Some commonly used scales are :
Plan:- 1:100, 1:50 Elevation:- 1:5, 1:30 Sections:- 1:50, 1:30, 1:25, 1:20,1:15,1:10
Fig.1.1a A0 Size Sheet
Fig.1.1b A1 Size Sheet
Fig.1.1c A2 Size Sheet
Fig.1.1d A3 Size Sheet
Fig.1.1e A4 Size Sheet
Fig.1.1f A5 Size Sheet and Division of sheets
Fig.1.2 Typical Layout of a Drawing Notes containing specifications of the concrete and steel to be used, size of chamfers and fillets, concrete cover, live load, SBC of soil, lap lengths for different diameter of bars etc,. Symbols and abbreviations to be adopted in the drawings are given below: Symbols Relating to Cross-Sectional Shape and Size of Reinforcement a) plain round bar or diameter of plain round bar; b) plain, square bar or side of plain square bar; and c) # deformed bar (including square twisted bar) or nominal size (equivalent diameter or side) of the deformed bar . Symbols Relating to Shape of the Bar along its Lengths Alt Alternate bar Bt Bent bar B Bottom bar min Minimum max Maximum St Straight bar Stp Stirrup Sp Spiral Ct Column tie T Top bar Symbols Relating to Position and Direction EW Each way @ Spacing centre-to-centre Limit of area covered by bars Direction in which bars extend Symbols Relating to Various Structural Members Bm or B Beams Col Column(s) Fg Footing(s) GR Girders JT Joints(s) LL Lintel(s) LB Lintel beam(s) Sb or S Slab(s) WL Longitudinal wall Wx Cross wall C Centre line Graphical symbols given in Fig. 1.3 are recommended by SP34. Additional drawing conventions for use on drawings for reinforcement as suggested in ISO 3766-1977 is reproduced in Fig 1.4
Fig. 1.3 Graphical symbols
Fig. 1.4 Drawing conventions
Fig. 1.4 Drawing conventions (Contd.)
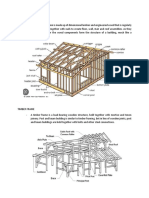
1.2 General Layout of Building: After the preparation of architectural plan of the buildings, the structural planning of the building frame is done. This involves determination of i) Positioning and orientation of columns, ii) Positioning of beams, iii) Spanning of slabs, iv) Layout of stairs, v) Selecting proper type of footing. Different structural members of a structure shall be marked using symbols, abbreviations and notations. A key framing plan shall be prepared to a convenient scale and the two axes marked one side with alphabets A, B, C etc, and the other with numbers. If the structural arrangement in all the floors is same then only one key plan is prepared titling it as typical plan. If the arrangement varies for different floors a separate key framing plan with grid arrangement and areas may be used for each of the floor. The floors shall be specified in accordance with the requirements of IS 2332-1973 (Specifications for nomenclature of floors and storeys) . According to this code BT symbol is used for Basement, MZ for Mezzanine, Floor 1, Floor 2 etc for first, second etc floors respectively. Columns and foundations shall be specified by grid arrangements giving reference to the floor. For example FG Col C2 with reference to Fig 1.5 indicates Footing for column C2, Col 2C2 indicates column C2 at floor 2.
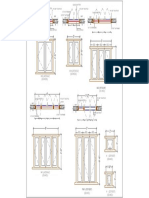
Fig. 1.5 Typical Arrangement for the Key Framing Plan and marking Different Structural Members Beams, slabs and lintels and tie beams shall be consecutively numbered from lefthand top corner as shown in Fig. 1.5. Lay out building are generally drawn i) Drawing showing position of columns along with excavation plan for footing and ii) Key plan showing arrangements of beams and plans and called as form work drawing. Fig 1.6 and 1.7 shows a typical lay out drawing developed for a building.
10
Fig. 1.6 Typical Drawing for a Multi-Storied Building showing column position and excavation plan.
Fig. 1.7 Typical Drawing for a Multi-Storied Building showing Slab and Beam alignment
11
Problem1: Prepare a general layout showing the positions and sizes of columns and footing to a suitable scale for an industrial building: A clear dimension of factory floor is 11.75 m x 19.75 m Spacing of columns 4m c/c Size of columns 250 mm x 450 mm Span of steel truss is 12.25 m c/c At the ends to support the gable wall additional two RCC columns of size 250 mm x 450 mm are to be provided at 4m c/c measured from end columns All the walls all-round are 250 mm thick Height of columns = 3m Size of footing 1.4m x 1.8m Thickness of footing 300 mm uniform Depth of foundation 1.2m below ground level Also show the line of steel truss on the drawing Solution: External dimensions of the building: Along X-direction = 11.75 + 2 x 0.25 = 12.25 m Along Z-direction = 19.75 + 2 x 0.25 = 20.25 m Centre line dimensions of the building: Along X-direction = 12.25 0.45 = 11.80 m Along Z-direction = 20.25 -0.25 = 20.00 m Procedure for drawing the lay out plan Note: Use Millimeter units for linear dimensions 1. Draw the centerline of the building having 11,800mm along X-direction and 20,000 mm along Z-directions 2. Mark these centre lines as grid lines A and D for lines parallel to Z-directions & grid lines 1 and 6 for lines parallel to X-axis 3. Measure 4000mm from grid lines A and D to get grid line B and C 4. Measure 4000mm c/c along Z-axis starting from grid line 1 to get grid lines 2, 3, 4 and 5 5. Draw rectangular filled box of size 250mm x 450mm at the intersection of gird lines along A and D to indicate the position of column along these grid lines as shown in Fig. 1.8 6. Draw rectangular filled box of size 250mm x 450mm at the intersection of grid lines 1,6 with B and C respectively as shown in Fig. 1.8 7. Draw rectangles each of size 1400 mm x 1800mm symmetrically with respect to centre of column to indicate excavation marking for all columns. Here the 12
shorter side of this rectangle box is parallel to the shorter side of column as shown in Fig. 1.8 8. Sectional elevation and plan of the footing of column is drawn just to the right of the key plan drawn as shown in Fig. 1.8
Fig. 1.8a Layout Drawing
13
Fig. 1.8b Footing Details
14
Problem2: Prepare a general layout showing the positions and sizes of Beams and Slabs to a suitable scale for a Community Hall: Clear dimension of hall is 12.05 m x 19.8 m Three rows of columns are to be provided along the width with spacing of 6 m c/c Six rows of columns are to be provided along the length with spacing of 4 m c/c All the walls all-round are 200 mm thick Size of columns 200 mm x 450 mm Main beams are of size 200 mm x 600 mm Secondary beams are of size 200 mm x 300 mm Thickness of slab = 150 mm Solution: External dimensions of the building: Along X-direction = 12.05 + 2 x 0.2 = 12.45 m Along Z-direction = 19.8 + 2 x 0.2 = 20.2 m Centre line dimensions of the building: Along X-direction = 12.45 -0.45 = 12 m Along Z-direction = 20.2 -0.2 = 20.00 m Procedure for drawing the lay out plan Note: Use Millimeter units for linear dimensions 1. Draw the centerline of the building having 12,000 mm along X-direction and 20,000 mm along Z-directions 2. Mark these centre lines as grid lines A and C for lines parallel to Z-directions & grid lines 1 and 6 for lines parallel to X-axis 3. Measure 6000mm from grid lines A to get grid line B 4. Measure 4000mm c/c along Z-axis starting from grid line 1 to get grid lines 2, 3, 4 and 5 5. Draw rectangular filled box of size 200mm x 450mm at the intersection of gird lines along A and C to indicate the position of column along these grid lines as shown in Fig. 1.9 6. Draw parallel lines spaced at 200mm symmetrically about the grid lines 1 to 6 to indicate main beams having effective span of 6m as shown in Fig. 1.9 7. Draw parallel lines spaced 200 mm abutting to end columns to indicate secondary beams as shown in Fig. 1.9. Also draw 200 mm wide secondary beam along grid line B as shown in Fig.1.9 8. Mark all the main beams as B1 and Secondary beams as B2 9. Indicate the slab as one way slab as shown in Fig. 1.9 and mark the slabs as S1.
15
16
Fig. 1.9 Layout Drawing
17
Exercise Problems: 1. Prepare a general layout drawing including the details of columns and foundation for a shopping complex with four shops in the ground floor with the following details: Column size : 230 x 450 mm Spacing : 3.5 m c/c Span of the beam supported by columns = 6m c/c Depth of foundation : 1.2 m below GL Depth of Footing : 450 mm Also draw to a suitable scale the details of typical column and foundation 2. Prepare a general lay out drawing for the ground floor of a community centre in a land measuring 35m x 50 m for the following particulars: Plinth area to be limited to 450 m2 (15m x 30m) Height of each column : 3.5m Size of columns : 300 mm x 450 mm Effective span of each continuous beam 5m of size 300 mm x 500 mm Secondary beams to be provided for a span of 4m and of size 300 mm x 400 mm Plinth beam 300 mm x 400 mm all-round 0.6m above ground level Footing of size 1.2 m x 2.8 m for each column has its uniform thickness= 600mm 3. Prepare a key plan at foundation level of a community hall building. Building has an auditorium of clear dimensions 12m x 19.7 m. Corridor of 4 m wide on either side (Parallel to longer side) of auditorium have to be provided. The roofing for auditorium is AC sheets supported on steel trusses. The end gable walls are supported on wall foundations. Roofing for corridor is RCC slab at 3m above floor level. Other details are: Clear span of roof truss = 12m Size of all RCC columns = 300 mm x 600 mm BBM columns of size 300 mm x 300 mm at 4 m c/c is to be provided in corridors to support slab Assume suitable foundation for RCC columns and BBM columns
18
Вам также может понравиться
- Manual of Engineering Drawing: British and International StandardsОт EverandManual of Engineering Drawing: British and International StandardsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (4)
- Structural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsОт EverandStructural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsОценок пока нет
- Design&Drng Compiled G.S.sureshДокумент82 страницыDesign&Drng Compiled G.S.sureshBilal Ahmed Barbhuiya100% (1)
- Structural Detailing IntroДокумент11 страницStructural Detailing IntroLimuel Samontina PagadorОценок пока нет
- Section 3 Structural Drawing For Detailing Table 3Документ9 страницSection 3 Structural Drawing For Detailing Table 3swatiОценок пока нет
- Design Example of A Six Storey Building: Dr. H. J. ShahДокумент51 страницаDesign Example of A Six Storey Building: Dr. H. J. ShahArman MoralesОценок пока нет
- Flat Slab BhavikattiДокумент23 страницыFlat Slab BhavikattiSharath GuptaОценок пока нет
- Design of 6 Storey Building in EtabsДокумент51 страницаDesign of 6 Storey Building in EtabsMisqal A Iqbal100% (2)
- Design Example of Six Storey BuildingДокумент51 страницаDesign Example of Six Storey BuildingRajendra PrasadОценок пока нет
- Design Example of Six Storey BuildingДокумент51 страницаDesign Example of Six Storey BuildingsidhujosephОценок пока нет
- Compliance On Column DriawngsДокумент2 страницыCompliance On Column DriawngspandyatusharОценок пока нет
- Dimension Assignments by Groups: Ce 405: Reinforced Concrete Design - Ii GROUP ASSIGNMENT (Due On Thursday 12 April 2012)Документ5 страницDimension Assignments by Groups: Ce 405: Reinforced Concrete Design - Ii GROUP ASSIGNMENT (Due On Thursday 12 April 2012)Taqi ZaidiОценок пока нет
- TremorProblemStatement 2Документ7 страницTremorProblemStatement 2Jayanta DasОценок пока нет
- EQ26Документ15 страницEQ26Dattatreya DattuОценок пока нет
- ENGINEERING DROWING Chapter 2Документ22 страницыENGINEERING DROWING Chapter 2DT artОценок пока нет
- Structural Lay-Out Drawings: Dr. Niranga AmarasinghaДокумент16 страницStructural Lay-Out Drawings: Dr. Niranga AmarasinghaFearless HeroОценок пока нет
- IC Workshop Materials 09 - Construction Drawing PracticesДокумент43 страницыIC Workshop Materials 09 - Construction Drawing PracticesooiОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 Construction Drawing - Principles and Practice: StructureДокумент21 страницаUnit 1 Construction Drawing - Principles and Practice: StructureRahul H Rahul HОценок пока нет
- BS8888 DraftingДокумент35 страницBS8888 DraftingJonathan Lynch100% (3)
- Sheet Metal Pattern DevelopmentДокумент6 страницSheet Metal Pattern Developmentpamopar86% (7)
- Tools and Techniques for Architectural DraftingДокумент41 страницаTools and Techniques for Architectural Draftinggsreads470% (1)
- Sab 4333 Set AДокумент8 страницSab 4333 Set AUsama EL AlaouiОценок пока нет
- Civil Surveying and Drawing - A1Документ8 страницCivil Surveying and Drawing - A1Parangat SharmaОценок пока нет
- Reinforced Concrete DesignДокумент73 страницыReinforced Concrete DesignUtkarsh KumarОценок пока нет
- Reinforced Concrete DetailingДокумент7 страницReinforced Concrete DetailingGerald MagingaОценок пока нет
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignОт EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Composite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsОт EverandComposite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsОценок пока нет
- A Manual of Elementary Geometrical Drawing Involving Three Dimensions: In Five Divisions, Div. I. Elementary Projections Div. II. Details of Constructions in Masonry Wood, and Metal Div. III. Rudimentary Exercises in Shades and Shadows Div. IV. Isometrical Drawing Div. V. Elementary Structural DrawingОт EverandA Manual of Elementary Geometrical Drawing Involving Three Dimensions: In Five Divisions, Div. I. Elementary Projections Div. II. Details of Constructions in Masonry Wood, and Metal Div. III. Rudimentary Exercises in Shades and Shadows Div. IV. Isometrical Drawing Div. V. Elementary Structural DrawingРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Practical Stair Building and Handrailing: By the square section and falling line systemОт EverandPractical Stair Building and Handrailing: By the square section and falling line systemОценок пока нет
- The Practical Builder: The Classic 18th-Century HandbookОт EverandThe Practical Builder: The Classic 18th-Century HandbookРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Structural Drafting - A Practical Presentation of Drafting and Detailed Methods used in Drawing up Specifications for Structural Steel WorkОт EverandStructural Drafting - A Practical Presentation of Drafting and Detailed Methods used in Drawing up Specifications for Structural Steel WorkРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- Autodesk 3ds Max 2015 Essentials: Autodesk Official PressОт EverandAutodesk 3ds Max 2015 Essentials: Autodesk Official PressРейтинг: 1 из 5 звезд1/5 (1)
- Designs for Street Fronts, Suburban Houses and CottagesОт EverandDesigns for Street Fronts, Suburban Houses and CottagesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2)
- A Guide to Making a Leather Wallet - A Collection of Historical Articles on Designs and Methods for Making Wallets and BillfoldsОт EverandA Guide to Making a Leather Wallet - A Collection of Historical Articles on Designs and Methods for Making Wallets and BillfoldsОценок пока нет
- How to Build a Global Model Earthship Operation II: Concrete WorkОт EverandHow to Build a Global Model Earthship Operation II: Concrete WorkОценок пока нет
- Stress in ASME Pressure Vessels, Boilers, and Nuclear ComponentsОт EverandStress in ASME Pressure Vessels, Boilers, and Nuclear ComponentsОценок пока нет
- Autodesk 3ds Max 2014 Essentials: Autodesk Official PressОт EverandAutodesk 3ds Max 2014 Essentials: Autodesk Official PressОценок пока нет
- Engineering Vibroacoustic Analysis: Methods and ApplicationsОт EverandEngineering Vibroacoustic Analysis: Methods and ApplicationsStephen A. HambricОценок пока нет
- Sustainable Steel Buildings: A Practical Guide for Structures and EnvelopesОт EverandSustainable Steel Buildings: A Practical Guide for Structures and EnvelopesBernhard HaukeОценок пока нет
- Dimensions, Weights and Properties of Special and Standard Structural Steel Shapes Manufactured by Bethlehem Steel CompanyОт EverandDimensions, Weights and Properties of Special and Standard Structural Steel Shapes Manufactured by Bethlehem Steel CompanyОценок пока нет
- S-05 (Ground Floor Slab Shuttering Layout) - R-01-Layout1 PDFДокумент1 страницаS-05 (Ground Floor Slab Shuttering Layout) - R-01-Layout1 PDFSandesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Range Gowda QuotationДокумент2 страницыRange Gowda QuotationSandesh KumarОценок пока нет
- OHT Comparision PDFДокумент1 страницаOHT Comparision PDFSandesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Brochure CoffeeGuddaДокумент2 страницыBrochure CoffeeGuddaGanesh KОценок пока нет
- Is 875 Part - 1Документ43 страницыIs 875 Part - 1Abdul HafeezОценок пока нет
- 2020-02-24 Cypress Wood Mechanical PropertiesДокумент3 страницы2020-02-24 Cypress Wood Mechanical PropertiesSandesh KumarОценок пока нет
- TIMBER PILE CONNECTION DESIGNДокумент5 страницTIMBER PILE CONNECTION DESIGNSandesh Kumar100% (1)
- 30x40 East-2 PDFДокумент1 страница30x40 East-2 PDFSandesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Is 3370 1 2009Документ23 страницыIs 3370 1 2009ab5918590Оценок пока нет
- Footing Reinf. DWG PDFДокумент1 страницаFooting Reinf. DWG PDFSandesh KumarОценок пока нет
- African Teak A Technical Data SheetДокумент4 страницыAfrican Teak A Technical Data SheetSandesh Kumar0% (1)
- Is 875 Part - 1Документ43 страницыIs 875 Part - 1Abdul HafeezОценок пока нет
- African Teak B Technical Data SheetДокумент4 страницыAfrican Teak B Technical Data SheetSandesh KumarОценок пока нет
- 2020-03-17 Pine Wood SpecsДокумент4 страницы2020-03-17 Pine Wood SpecsSandesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Column Layout PDFДокумент1 страницаColumn Layout PDFSandesh KumarОценок пока нет
- BOQ MANJESH RESIDENCE Upto Terrace FloorДокумент5 страницBOQ MANJESH RESIDENCE Upto Terrace FloorSandesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Concrete Section Design CalculationsДокумент12 страницConcrete Section Design CalculationsSandesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Is 875 Part - 1Документ43 страницыIs 875 Part - 1Abdul HafeezОценок пока нет
- Ante Room: G.Toilet L.Toilet 3.7MX4.7M 3.1MX4.7MДокумент1 страницаAnte Room: G.Toilet L.Toilet 3.7MX4.7M 3.1MX4.7MSandesh KumarОценок пока нет
- WOOD DETAILS-Model-2 PDFДокумент1 страницаWOOD DETAILS-Model-2 PDFSandesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Is 875 Part - 1Документ43 страницыIs 875 Part - 1Abdul HafeezОценок пока нет
- Ret Walls-MCN PDFДокумент15 страницRet Walls-MCN PDFDivyadristiОценок пока нет
- Detailing of Steel in Stair CasesДокумент9 страницDetailing of Steel in Stair CasesSandesh Kumar100% (1)
- Watertank GS PDFДокумент24 страницыWatertank GS PDFManoj RautОценок пока нет
- The Tentative Schedule of Events Is As Follows: Event D Tentative DateДокумент26 страницThe Tentative Schedule of Events Is As Follows: Event D Tentative Date476Оценок пока нет
- FRPC Reinforced Concrete Beam-Column Joints Under Cyclic ExcitationДокумент15 страницFRPC Reinforced Concrete Beam-Column Joints Under Cyclic ExcitationMagdy BakryОценок пока нет
- FOUNDATIONS FOR INDUSTRIAL MACHINES AND EARTHQUAKE EFFECTS - K.G. Bhatia - ISET Journal of Earthquake Technology, Paper No. 495, Vol. 45, No. 1-2, March-June 2008, Pp. 13-29Документ17 страницFOUNDATIONS FOR INDUSTRIAL MACHINES AND EARTHQUAKE EFFECTS - K.G. Bhatia - ISET Journal of Earthquake Technology, Paper No. 495, Vol. 45, No. 1-2, March-June 2008, Pp. 13-29R Mani MuruganОценок пока нет
- Design of Shear WallДокумент34 страницыDesign of Shear WallSandesh Kumar100% (1)
- Construction Terms Beginning With Letter: ZДокумент52 страницыConstruction Terms Beginning With Letter: ZnotevaleОценок пока нет
- FMDS0122 Maximum Foresseable LossДокумент118 страницFMDS0122 Maximum Foresseable LossAnonymous wtK1AZBiОценок пока нет
- Portal Frame Vs Other FrameДокумент20 страницPortal Frame Vs Other Framepatricklim1982Оценок пока нет
- 1 Fastening Catalogue 2013 Hi ResДокумент30 страниц1 Fastening Catalogue 2013 Hi ResMujjo Sahb100% (1)
- C SD Curtain Wall Aug 061Документ3 страницыC SD Curtain Wall Aug 061Sh KittanehОценок пока нет
- Eichler Design Guidelines: City of SunnyvaleДокумент26 страницEichler Design Guidelines: City of Sunnyvaleasears1984Оценок пока нет
- Independent Cost and Schedule Validation for LACC Expansion ProjectДокумент39 страницIndependent Cost and Schedule Validation for LACC Expansion Projectzaheeruddin_mohdОценок пока нет
- IBC Span Tables for Floors, Roofs and WallsДокумент37 страницIBC Span Tables for Floors, Roofs and WallsSharon KolbekОценок пока нет
- Chapter 19Документ28 страницChapter 19Vidya MohananОценок пока нет
- Revolutionary GigaCrete GigaHouse Utilizes Prefab Insulated Steel Panel SystemДокумент50 страницRevolutionary GigaCrete GigaHouse Utilizes Prefab Insulated Steel Panel SystemAWОценок пока нет
- Ducker Window ReportДокумент38 страницDucker Window Reportschloo0% (1)
- Rough Framing Army FM5-426Документ44 страницыRough Framing Army FM5-426john emerson YabutОценок пока нет
- SFIA 092216 NON-LOAD BEARING COLD-FORMED STEEL FRAMING Final 030522Документ6 страницSFIA 092216 NON-LOAD BEARING COLD-FORMED STEEL FRAMING Final 030522clam2014Оценок пока нет
- Space FrameДокумент46 страницSpace FrameAnonymous Y9dgyXhA100% (2)
- Different Approaches in Modeling of RC Shear Wall: A ReviewДокумент15 страницDifferent Approaches in Modeling of RC Shear Wall: A Reviewrahimmulla100% (2)
- Design CriteriaДокумент21 страницаDesign CriteriaDick Anthony MabaoОценок пока нет
- Miscellaneous Rough CarpentryДокумент11 страницMiscellaneous Rough CarpentryTaher AmmarОценок пока нет
- Framing PDFДокумент5 страницFraming PDFKenneth Ignacio ArcillaОценок пока нет
- Installation Manual for Residential Window and Door ProductsДокумент44 страницыInstallation Manual for Residential Window and Door ProductsAymeeenОценок пока нет
- Ion 2-10 Home Buyers Warranty HBW 307 022009Документ36 страницIon 2-10 Home Buyers Warranty HBW 307 022009gr8_1Оценок пока нет
- Seah 1998Документ299 страницSeah 1998Wallison MedeirosОценок пока нет
- 31 Guideline - For - Cyclone - Resistant - Construction - of - Building PDFДокумент29 страниц31 Guideline - For - Cyclone - Resistant - Construction - of - Building PDFDepanshu GolaОценок пока нет
- Shear Wall - Design of Shear Wall (Using Staad Pro)Документ31 страницаShear Wall - Design of Shear Wall (Using Staad Pro)Djoko Susilo JusupОценок пока нет
- Boq Mofa AG HVAC ElecrДокумент46 страницBoq Mofa AG HVAC Elecrsloba68Оценок пока нет
- Garis Panduan Bim JKR Jadual 5.5: Contoh Family ArkitekДокумент6 страницGaris Panduan Bim JKR Jadual 5.5: Contoh Family ArkitekFadhli ATZОценок пока нет
- VA Seismic Design Requirements Updated for Critical FacilitiesДокумент27 страницVA Seismic Design Requirements Updated for Critical FacilitiesCarl Crow100% (1)
- Composite Steel and Concrete Structural Systems For Seismic Engineering and Axial LoadingДокумент21 страницаComposite Steel and Concrete Structural Systems For Seismic Engineering and Axial Loadingpooria_j92Оценок пока нет
- WBHRMO 3 Timber Frame Solutions 1501 PDFДокумент20 страницWBHRMO 3 Timber Frame Solutions 1501 PDFChris FindlayОценок пока нет
- BNBC Code 2014Документ748 страницBNBC Code 2014Nurus Salam100% (2)