Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Dopamine increases heart pumping strength for heart failure
Загружено:
Princess Gutierrez RositaИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Dopamine increases heart pumping strength for heart failure
Загружено:
Princess Gutierrez RositaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
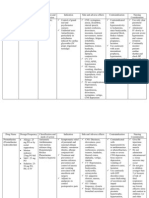
GENERIC NAME Dopamine
BRAND NAME Intropin
CLASSIFICATI ON Catecholamines , inotropic agents, vasopre ssors
DOSAGE/ ROUTE Important- This is a potent drug: It must be diluted before administration to the patient. Adult: IV- The recommended initial dose is 1-5 mcg/kg/min, up to 5-10 mcg/kg/min according to patient's response. IV infusion Initial dose of 0.5 to 1 mcg/kg/min; titrate every few min to desired response. Usual dosage is 2 to 20 mcg/kg/min, with rates up to 40 mcg/kg/min rarely used
INDICATION This medication is an adrenergic and dopaminergic cardiac stimulant, prescribed for heart failure. It increases the pumping strength of the heart.
CONTRAINDICATION Contraindicated in patients with pheochromocytoma, uncorrected tachyarrhythmias or ventricular fibrillation and hypersensitivity.
ADVERSE REACTION nausea, vomiting, tachycardia, ectopic beats, palpitation, anginal pain, hypotension, vasoconstriction, bradycardia, hypertension, dyspnea, headache, widened QRS complexes, azotemia.
NURSING CONSIDERATION Monitor vital signs , and ECG during infusion, watch for dsyarrythmias and ischemia also monitor, PCWP,CVP, CO2, and urinary output Monitor for possible adverse reaction Assess for heart failure: dyspnea, neck vain distention, Assess for oxygenation and perfusion deficit Before starting therapy, give a plasma volume to correct hypovolemia and cardiac glycoside Continuously monitor ECG, blood pressure, pulmonary artery wedge pressure, cardiac output and urine output
Dobutamiine
Dobutrex
Vasopressors
Treatment of cardiac decompensation caused by organic heart disease or cardiac surgical procedures
Nitroglycerin
Nitrostat
Nitrates
IV Initial dose, 5 mcg/min delivered through an infusion pump. Increase by 5mcg/min-increments every 35 min as needed. If no response at 20 mcg/min, increase increments to 1020 mcg/min. Once a partial BP response is obtained, reduce dose and lengthen dosage intervals; continually monitor response and titrate carefully
IV Treatment of perioperative hypertension; control of CHF in the setting of acute MI; treatment of angina pectoris in patients not responding to sublingual nitroglycerin and beta-blockers; induction of intraoperative hypotension.
Idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis; hypersensitivity to any component of the product; Dobutamine with dextrose should not be administered simultaneously with blood through the same infusion set because of the possibility of pseudoagglutination of red cells. Contraindicated with allergy to nitrates, severe anemia, early MI, head trauma, cerebral hemorrhage, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, pregnancy, lactation
CNS: headache CV: hypertension, increased heart rate
Adverse effects CNS: Headache, apprehension, restlessness, weakness, vertigo, dizziness, faintness CV: Tachycardia, retrosternal discomfort, palpitations, hypotension, syncope, collapse, orthostatic hypotension, angina Dermatologic: Rash, exfoliative dermatitis, cutaneous vasodilation with flushing, pallor, perspiration, cold sweat, contact dermatitis transdermal preparations,
Assessment History: Allergy to nitrates, severe anemia, early MI, head trauma, cerebral hemorrhage, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, hepatic or renal disease, hypotension or hypovolemia, increased intracranial pressure, constrictive pericarditis, pericardial tamponade, low ventricular filling pressure or low PCWP, pregnancy, lactation. Physical: Skin color, temperature, lesions; orientation, reflexes, affect; P, BP, orthostatic BP, baseline ECG, peripheral perfusion; R, adventitious sounds; liver
topical allergic reactionstopical nitroglycerin ointment GI: Nausea, vomiting, incontinence of urine and feces, abdominal pain Local: Local burning sensation at the point of dissolution (sublingual) Other: Ethanol intoxication with highdose IV use (alcohol in diluent) Furosemide Lasix Loop diuretic 20 mg, 40 mg, 80 mg tablets; 10 mg/mL, 40 mg/5 mL oral solution; 10 mg/mL injection
evaluation, normal output; liver and renal function tests (IV); CBC, Hgb
Oral, IV: Edema associated with CHF, cirrhosis, renal disease
Severe sodium and water depletion, hypersensitivity to sulphonamides and furosemide, hypokalaemia, hyponatraemia, precomatose states associated with liver cirrhosis, anuria or renal failure. Addisons disease.
Fluid and electrolyte imbalance. Rashes, photosensitivity, nausea, diarrhoea, blurred vision, dizziness, headache, hypotension. Bone marrow depression (rare), hepatic dysfunction. Hyperglycaemia, glycosuria, ototoxicity. Potentially Fatal: Rarely, sudden death and cardiac arrest. Hypokalaemia and magnesium depletion can cause cardiac arrhythmias.
Assessment & Drug Effects Observe patients receiving parenteral drug carefully; closely monitor BP and vital signs. Sudden death from cardiac arrest has been reported. Monitor BP during periods of diuresis and through period of dosage adjustment. Observe older adults closely during period of brisk diuresis. Sudden alteration in fluid and electrolyte balance may precipitate significant adverse reactions. Report symptoms to physician. Lab tests: Obtain frequent blood count, serum and urine electrolytes, CO2, BUN, blood sugar, and uric acid values during first few months of therapy and periodically thereafter. Monitor for S&S of hypokalemia . Monitor I&O ratio and pattern. Report decrease or unusual increase in output. Excessive diuresis
can result in dehydration and hypovolemia, circulatory collapse, and hypotension. Weigh patient daily under standard conditions. Monitor urine and blood glucose & HbA1C closely in diabetics and patients with decompensated hepatic cirrhosis. Drug may cause hyperglycemia. Note: Excessive dehydration is most likely to occur in older adults, those with chronic cardiac disease on prolonged salt restriction, or those receiving sympatholytic agents.
Вам также может понравиться
- XU-AC Emergency Drugs GuideДокумент14 страницXU-AC Emergency Drugs GuideSheila_Mae_Fai_5510Оценок пока нет
- Emergency DrugsДокумент40 страницEmergency Drugsmattheus101Оценок пока нет
- Pharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardДокумент7 страницPharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardyannahmaeОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент8 страницDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoОценок пока нет
- Imdur for Angina Relief in 60 SecondsДокумент23 страницыImdur for Angina Relief in 60 SecondsJoyce Anne SupnetОценок пока нет
- DRUG STUDY SUMMARYДокумент7 страницDRUG STUDY SUMMARYEloisa Abarintos RacalОценок пока нет
- Centrally Acting Alpha Agonist Lowers BP & HRДокумент4 страницыCentrally Acting Alpha Agonist Lowers BP & HRAriadne MangondatoОценок пока нет
- Propranolol Hydro ChlorideДокумент4 страницыPropranolol Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941Оценок пока нет
- Piperacillin-Tazobactam AntibioticДокумент9 страницPiperacillin-Tazobactam Antibiotic배기숭Оценок пока нет
- Emergency Cardiac Medications for ArrhythmiasДокумент14 страницEmergency Cardiac Medications for ArrhythmiasRomzy BasañesОценок пока нет
- عرض تقديمي2Документ18 страницعرض تقديمي2Sabrina ShalhoutОценок пока нет
- DrugДокумент1 страницаDrugFloidas FernandoОценок пока нет
- Antiplatelet and Proton Pump Inhibitor Drug Study SummaryДокумент9 страницAntiplatelet and Proton Pump Inhibitor Drug Study SummaryrocketwapОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент10 страницDrug StudyHelen ReonalОценок пока нет
- Jerald Silva Olalo, RN Renal Unit: Generic NameДокумент4 страницыJerald Silva Olalo, RN Renal Unit: Generic NameSherlyn KirisakiОценок пока нет
- Drug Study Feu NRMF IcuДокумент9 страницDrug Study Feu NRMF IcuAnne Genesis V. PinedaОценок пока нет
- Generic Name Captopril Brand NamesДокумент18 страницGeneric Name Captopril Brand NamesAiko Villacortes100% (1)
- Bisoprolol FumarateДокумент3 страницыBisoprolol Fumarateapi-37979410% (1)
- RamiprilДокумент3 страницыRamiprilapi-3797941Оценок пока нет
- Psych Drug StudyДокумент5 страницPsych Drug StudyLorina Lynne Apelacio100% (4)
- DrugsДокумент20 страницDrugsLee Won100% (1)
- Drug Study Mother TДокумент14 страницDrug Study Mother TEuzelle Jeena ArandaОценок пока нет
- Emergency Drugs Crash CartДокумент14 страницEmergency Drugs Crash CartEricson SomeraОценок пока нет
- Carved I LolДокумент2 страницыCarved I LolmariaclaramutyaОценок пока нет
- Drug Dosage, Classification, Indications, and Nursing ResponsibilitiesДокумент12 страницDrug Dosage, Classification, Indications, and Nursing ResponsibilitiesCamilley De Vera100% (1)
- DisulfiramДокумент3 страницыDisulfiramapi-3797941100% (1)
- Labetalol Hydro ChlorideДокумент3 страницыLabetalol Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Non-Steroidal Anti - Inflammatory DrugДокумент27 страницNon-Steroidal Anti - Inflammatory DrugMelissa SalayogОценок пока нет
- CaptoprilДокумент3 страницыCaptoprilapi-3797941100% (1)
- Medications on Med Test: Metoprolol, Lisinopril, Furosemide, Warfarin, Insulin, Metformin, Lispro, Docusate Sodium, HydrochlorothiazideДокумент8 страницMedications on Med Test: Metoprolol, Lisinopril, Furosemide, Warfarin, Insulin, Metformin, Lispro, Docusate Sodium, Hydrochlorothiazidetina100% (1)
- HypertensiveДокумент2 страницыHypertensiveReinhard Lumbag PacitengОценок пока нет
- 1medication List: Hit The Tab Key in The Bottom Row, Right Hand Column To Add More Rows As NeededДокумент4 страницы1medication List: Hit The Tab Key in The Bottom Row, Right Hand Column To Add More Rows As NeededSamantha FarrarОценок пока нет
- Drug Study ICUДокумент15 страницDrug Study ICUJulie Nambatac100% (1)
- Drugs - Icu (Group)Документ7 страницDrugs - Icu (Group)Patricia LuceroОценок пока нет
- Drugs Used in Cardio Vascular SystemДокумент138 страницDrugs Used in Cardio Vascular SystemSagun lohalaОценок пока нет
- AtenololДокумент3 страницыAtenololapi-3797941Оценок пока нет
- Cardio DrugsДокумент68 страницCardio DrugsIconMaicoОценок пока нет
- ANTIPSYCHOTICS Olanzapine (Zyprexa), Aripiprazole (Abilify), Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)Документ5 страницANTIPSYCHOTICS Olanzapine (Zyprexa), Aripiprazole (Abilify), Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)Rhanne BolanteОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент5 страницDrug StudyClarissa ValenciaОценок пока нет
- Dopamine HCLДокумент2 страницыDopamine HCLianecunarОценок пока нет
- LisinoprilДокумент3 страницыLisinoprilapi-37979410% (1)
- Drug Study GuideДокумент9 страницDrug Study GuideSh3meeОценок пока нет
- Co DiovanДокумент2 страницыCo DiovanianecunarОценок пока нет
- Drug Study CARDIOДокумент17 страницDrug Study CARDIODiannetotz Morales100% (1)
- Drug Study JrodДокумент8 страницDrug Study JrodGaez ﭢ UlpindoОценок пока нет
- E CartДокумент16 страницE Cartwowowee15Оценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент28 страницDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoОценок пока нет
- Epinephrine Classifications: Therapeutic: Antiasthmatics, Bronchodilators, Vasopressors Pharmacologic: Adrenergics IndicationsДокумент14 страницEpinephrine Classifications: Therapeutic: Antiasthmatics, Bronchodilators, Vasopressors Pharmacologic: Adrenergics IndicationsLindy Shane BoncalesОценок пока нет
- Enalapril MaleateДокумент4 страницыEnalapril Maleateapi-3797941Оценок пока нет
- Review of Advancements in Heart Failure 81220Документ65 страницReview of Advancements in Heart Failure 81220Dr MustafaОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент17 страницDrug StudyJoan RabeОценок пока нет
- Drugs 3aДокумент2 страницыDrugs 3aRowena Rivera CariñoОценок пока нет
- Emergency Drugs KathДокумент29 страницEmergency Drugs Kathmajin655Оценок пока нет
- Spironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationДокумент5 страницSpironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationShermalyn SalahuddinОценок пока нет
- Potassium-Sparing Diuretic Aldacton GuideДокумент8 страницPotassium-Sparing Diuretic Aldacton GuideJoy CalmerinОценок пока нет
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcОт EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcОценок пока нет
- Programme FinalansvhnaДокумент1 страницаProgramme FinalansvhnaPrincess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- Narrative ReportHAGJSGДокумент4 страницыNarrative ReportHAGJSGPrincess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- Pneumonia Vaccine For ChildrenДокумент1 страницаPneumonia Vaccine For ChildrenPrincess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- VRS Brochure 2017Документ1 страницаVRS Brochure 2017Princess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- Lipa City CollegesДокумент30 страницLipa City CollegesPrincess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- pOST oДокумент2 страницыpOST oPrincess Gutierrez Rosita100% (1)
- InvitationДокумент1 страницаInvitationPrincess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- Professional Development ProgramДокумент2 страницыProfessional Development ProgramPrincess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- NCP CholehgxkДокумент9 страницNCP CholehgxkPrincess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- Drugs CholeДокумент20 страницDrugs CholePrincess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- Anti Smoking For PrintДокумент40 страницAnti Smoking For PrintPrincess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- ThesisДокумент122 страницыThesisPrincess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- Intrapartal Checklist (1) HJGHJUGДокумент3 страницыIntrapartal Checklist (1) HJGHJUGPrincess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- NCP TesticularДокумент8 страницNCP TesticularPrincess Gutierrez Rosita50% (2)
- Diagnostic ProcedureДокумент11 страницDiagnostic ProcedurePrincess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- Intra-Op GeloДокумент2 страницыIntra-Op GeloPrincess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- Espite Pharmacologic AdvancesДокумент2 страницыEspite Pharmacologic AdvancesPrincess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- Sample QuestionsjshzjxzДокумент31 страницаSample QuestionsjshzjxzPrincess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- Case Study IN Penile CancerДокумент15 страницCase Study IN Penile CancerPrincess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- 8 4 A Endometrial CancerДокумент37 страниц8 4 A Endometrial CancerPrincess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- Chapter IVzxДокумент4 страницыChapter IVzxPrincess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- Chapter VДокумент5 страницChapter VPrincess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- BibliographyzДокумент1 страницаBibliographyzPrincess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент32 страницыDrug StudyPrincess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- COPARДокумент21 страницаCOPARPrincess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- Com ApДокумент79 страницCom ApPrincess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- Nursing DiagnosisvfsdsДокумент2 страницыNursing DiagnosisvfsdsPrincess Gutierrez Rosita100% (1)
- The MouthДокумент39 страницThe MouthPrincess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- Thesis AbstractДокумент3 страницыThesis AbstractPrincess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- What's New in Oral Cavity and Oropharyngeal Cancer Research and Treatment?Документ4 страницыWhat's New in Oral Cavity and Oropharyngeal Cancer Research and Treatment?Princess Gutierrez RositaОценок пока нет
- الورقة الثالثة- القبالة-2Документ4 страницыالورقة الثالثة- القبالة-2Habebt MusabОценок пока нет
- Journal Homepage: - : IntroductionДокумент3 страницыJournal Homepage: - : IntroductionIJAR JOURNALОценок пока нет
- Ethics in Practice - at End of Life - Part 1Документ20 страницEthics in Practice - at End of Life - Part 1anushavergheseОценок пока нет
- Email chat about sex actsДокумент10 страницEmail chat about sex actsrishav kumar agarwalОценок пока нет
- UV-VIS Method for Estimating Fat-Soluble Vitamins in MultivitaminsДокумент6 страницUV-VIS Method for Estimating Fat-Soluble Vitamins in MultivitaminsTisenda TimiselaОценок пока нет
- Kidde Fire Systems Nitrogen Engineered Systems: Design, Installation, Operation and Maintenance ManualДокумент110 страницKidde Fire Systems Nitrogen Engineered Systems: Design, Installation, Operation and Maintenance ManualYoyon HaryonoОценок пока нет
- Oferta Hexis - Multisign: Preturile Sunt in EURO Si Nu Includ TVAДокумент9 страницOferta Hexis - Multisign: Preturile Sunt in EURO Si Nu Includ TVAPoschina CiprianОценок пока нет
- Eo No. 013 - 2018 Reorganization of BhertДокумент2 страницыEo No. 013 - 2018 Reorganization of BhertAnne Kimberly Peñalba BabaanОценок пока нет
- Dowtherm TДокумент3 страницыDowtherm Tthehoang12310Оценок пока нет
- Stetler Model EBP PosterДокумент1 страницаStetler Model EBP PosterEmily MОценок пока нет
- Jha For Painting of EquipmentДокумент1 страницаJha For Painting of EquipmentShahid RazaОценок пока нет
- Endocrine DisruptorsДокумент50 страницEndocrine DisruptorsSnowangeleyes AngelОценок пока нет
- Manu SkripДокумент20 страницManu SkripzanimarОценок пока нет
- Q1. Read The Passage Given Below and Answer The Questions That FollowДокумент2 страницыQ1. Read The Passage Given Below and Answer The Questions That FollowUdikshaОценок пока нет
- Enemies of BeerДокумент24 страницыEnemies of Beerpana0048100% (1)
- API SM Part 1Документ7 страницAPI SM Part 1Ronaldo JanglinОценок пока нет
- Octopi RoxДокумент29 страницOctopi Roxlam2289Оценок пока нет
- Pain AssessmentДокумент10 страницPain Assessmentaashika15Оценок пока нет
- Postpartum Health TeachingДокумент8 страницPostpartum Health TeachingMsOrange96% (24)
- 1866 PSC Iasc Ref Guidance t2 DigitalДокумент11 страниц1866 PSC Iasc Ref Guidance t2 DigitalDama BothОценок пока нет
- 31congenital GlaucomasДокумент12 страниц31congenital GlaucomasShari' Si WahyuОценок пока нет
- AgraLi The Low Chloride Liquid Fertilizer For Sensitive Crops enДокумент2 страницыAgraLi The Low Chloride Liquid Fertilizer For Sensitive Crops enASHОценок пока нет
- Hvis Msds PDFДокумент6 страницHvis Msds PDFsesbasar sitohangОценок пока нет
- 1.2.1 Log 1Документ3 страницы1.2.1 Log 1linuspauling101100% (6)
- Newborn Care Volume 1 2020-1Документ192 страницыNewborn Care Volume 1 2020-1Shyvonne PeirisОценок пока нет
- TULUA Lipoabdominoplasty Transversal Aponeurotic.12Документ14 страницTULUA Lipoabdominoplasty Transversal Aponeurotic.12Carolina Ormaza Giraldo100% (1)
- Yoga Your Home Practice CompanionДокумент257 страницYoga Your Home Practice Companionjohncoltrane97% (33)
- Zhou 2008Документ10 страницZhou 2008zael18Оценок пока нет
- Symbols On PackegingДокумент3 страницыSymbols On PackegingsakibarsОценок пока нет