Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Emt 2 Marks
Загружено:
Anbu ArasanОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Emt 2 Marks
Загружено:
Anbu ArasanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY: TWO MARKS:
UNIT I 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. State the conditions for a vector A to be (a) solenoidal (b) irrational Mention the sources of electromagnetic fields? State the physical significance of curl of a vector field? State the physical significance of divergence of a vector field? State the strokes theorem? State the divergence theorem? Define divergence. Define curl. and are said to be oriented 9. Two vectorial questions in two unique directions. Determine the angular separation between them UNIT II 1. What is meant by equipotential surface? 2. Electric field is conservative field. Justify?
3. A parallel plate capacitor has a charge of 10-3C on each of the plate, while the potential difference between the plates is 1000V. Calculate the value of capacitance.
4. Define electric potential and potential difference? 5. State the properties of electric flux lines? 6. A dielectric slab of flat surface with relative permittivity 4 is disposed with its surface normal to a uniform filed with flux density 1.5 C/m2. The slab is uniformly polarized. Determine the polarization in the slab. 7. At the boundary between copper and aluminum the electric field makes an angle of 450 with the normal to the interface. Find the angle of emergence. The conductivity of copper and aluminum are 5.8 X 105 S/m and 3.5X 105 S/m, respectively. 8. State Coulombs law? 9. State Gauss law? UNIT III
1. Define Biot Savarat Law. 2. State Amperes Circuital Law?
3. Find the value of magnetic field intensity at the center of a circular loop of radius 1m carrying a current of 10A.
4. Find the inductance per unit length of a long solenoid of N turns having a length of L meters. Assume that it carries a current of T amperes. 5. Distinguish between scalar and Vector magnetic potential? 6. Write the expression for magnetic field H at the center of a circular coil carrying a current of I amperes. The radius of the coil is a meter. 7. Write the expression for magnetic force between an electromagnet and armature to be attracted. 8. What is the point form of Amperes Circuital Law? UNIT IV 1. What type of voltage is induced in a loop which is rotating about y-axis in a magnetic field of flux density Tesla? 2. What is the significance of displacement current? 3. A conductor of length 1m length is moving with a velocity of 100m/sec perpendicular to a field of 1 Tesla. What is the value of emf induced? 4. State the continuity equations? 5. What is displacement current? 6. Give Lorentz force equation? 7. Compare circuit and field theory? 8. State faradays law? 9. State ohms law for magnetic circuits?
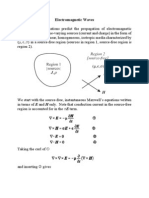
UNIT V 1. What are standing waves? 2. Give the applications of wave guides? 3. Calculate the depth of penetration in copper at 2MHz, given the conductivity of copper =5.8X107 S/m and its permittivity =1.26H/m. 4. A plane wave is travelling in free space has an average power of 2W/m2. Find the average power density. 5. Calculate the characteristic impedance of free space? 6. What is standing wave ratio? 7. What is standing wave ratio? 8. What is voltage reflection coefficient at the load end of a transmission line?
Вам также может понравиться
- EC2253 - ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS Question BankДокумент8 страницEC2253 - ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS Question Bankkalyan thallapaneniОценок пока нет
- QB EmtДокумент5 страницQB EmtSankar KaruppaiahОценок пока нет
- Physics Important QuestionsДокумент3 страницыPhysics Important QuestionsLaxman KumawatОценок пока нет
- What Are The Boundary Condition For Electrostatic Potential at An Interface Between Two Different Electric Media?Документ6 страницWhat Are The Boundary Condition For Electrostatic Potential at An Interface Between Two Different Electric Media?patasutoshОценок пока нет
- II PUC PHYSICS Enrichment PackageДокумент4 страницыII PUC PHYSICS Enrichment PackageSohum VenkatadriОценок пока нет
- ECT & RFT - Tube TestingДокумент228 страницECT & RFT - Tube Testingquyettd0706Оценок пока нет
- 12th Physics Worksheet (ch3 To ch7)Документ3 страницы12th Physics Worksheet (ch3 To ch7)lovecatsaninalsОценок пока нет
- REVISION SHEETS GR 12Документ13 страницREVISION SHEETS GR 12itachirao5Оценок пока нет
- Physics Shorthand Guide by Ri DaДокумент5 страницPhysics Shorthand Guide by Ri DaGAME DEVОценок пока нет
- Sr. PhysicsДокумент6 страницSr. PhysicsMavuluri UmamaheshОценок пока нет
- Ts SR Physics Imp Questions 2023-24Документ5 страницTs SR Physics Imp Questions 2023-24s.pranay11.reddy100% (1)
- PhysicsДокумент12 страницPhysicsAriyanayaka SundaramОценок пока нет
- Rajiv Gandhi College of Engineering and Technologies Department of Eee Ee T35 Electromagnetic Theory Unit I: Electrostatic Field 2 MarksДокумент5 страницRajiv Gandhi College of Engineering and Technologies Department of Eee Ee T35 Electromagnetic Theory Unit I: Electrostatic Field 2 MarksgondesianandОценок пока нет
- Chapter Wise Important QuestionsДокумент4 страницыChapter Wise Important QuestionsTechnical Hacks100% (1)
- Tutorial QuestionsДокумент20 страницTutorial Questionsharshiika kathiravanОценок пока нет
- Reduced Syllabus Questions (Physics)Документ15 страницReduced Syllabus Questions (Physics)Saher SaghirОценок пока нет
- Important Physics Questions for TS Senior InterДокумент5 страницImportant Physics Questions for TS Senior InterKota ๖ۣۜRαkͥesͣhͫ0% (1)
- TS - SR - Physics - Imp - Questions 2023-24-1Документ5 страницTS - SR - Physics - Imp - Questions 2023-24-1jsjhhahsjnkkjsjОценок пока нет
- Resistivity and Conductivity of MaterialsДокумент3 страницыResistivity and Conductivity of MaterialsAsher MuhammedОценок пока нет
- Important QuestionsДокумент26 страницImportant QuestionsAyush TomarОценок пока нет
- Suggestion PhysicsДокумент4 страницыSuggestion PhysicsAltaf AliОценок пока нет
- W 2Документ2 страницыW 2ypurushothamreddy006Оценок пока нет
- Senior Physics Ipe Imp Question Bank 2019-20Документ10 страницSenior Physics Ipe Imp Question Bank 2019-20Soumendu KonaeОценок пока нет
- Ee2102 Emt - Cat2 - QBДокумент1 страницаEe2102 Emt - Cat2 - QBsjuma7125Оценок пока нет
- Sr. Inter Physics Question BankДокумент12 страницSr. Inter Physics Question Bankyasaswi sonyОценок пока нет
- 9A04406 Electromagnetic Theory and Transmission LinesДокумент4 страницы9A04406 Electromagnetic Theory and Transmission LinessivabharathamurthyОценок пока нет
- PTU Emi 2007 Question PaperДокумент2 страницыPTU Emi 2007 Question Papersaurabh rathorОценок пока нет
- SR Physics - Narayana Imp QuestionsДокумент5 страницSR Physics - Narayana Imp Questionsyogendrareddy018100% (4)
- Electricity & Magnetism Study PlanДокумент3 страницыElectricity & Magnetism Study PlanCss Aspirant0% (1)
- Logic Academy computer Science Marks 83 Subjective ExamДокумент2 страницыLogic Academy computer Science Marks 83 Subjective ExamYasir Faraz Chishti FarooqiОценок пока нет
- Physics Xii Chapter 4,5,6Документ7 страницPhysics Xii Chapter 4,5,6SatvikОценок пока нет
- Second Year Physics QuestionsДокумент6 страницSecond Year Physics QuestionsRaj KumarОценок пока нет
- Electro Statics - Balaji PaperДокумент2 страницыElectro Statics - Balaji PaperKrishna Vijay Kumar GangisettyОценок пока нет
- 12thQuestionBank (KSU)Документ9 страниц12thQuestionBank (KSU)sohailmushtaq1001Оценок пока нет
- Kings: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringДокумент6 страницKings: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringHarish Pandian RОценок пока нет
- Anna University - Electromagnetic Theory (EMT) - Question Bank - All UnitsДокумент7 страницAnna University - Electromagnetic Theory (EMT) - Question Bank - All UnitsMunish KalimuthuОценок пока нет
- Indus Universal School Physics Theory QuestionsДокумент2 страницыIndus Universal School Physics Theory QuestionsTulika BholaОценок пока нет
- Physics 3Документ6 страницPhysics 3Aadit “ThePROkiller”Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 8 - Electromagnetic Waves - WatermarkДокумент16 страницChapter 8 - Electromagnetic Waves - WatermarkRajath S KashyapОценок пока нет
- PHYSICSДокумент7 страницPHYSICSSurya A S100% (1)
- Dsunzh Fo - Ky Vfecdkiqj LJXQTK N-X: ElectrostaticsДокумент6 страницDsunzh Fo - Ky Vfecdkiqj LJXQTK N-X: Electrostaticshimanshu sihmarОценок пока нет
- ATC Booster PS 1Документ48 страницATC Booster PS 1Souradip DasОценок пока нет
- Valliammai Engineering CollegeДокумент11 страницValliammai Engineering CollegeRagunathan NarayananОценок пока нет
- Important Questions EmtДокумент9 страницImportant Questions EmtDinesh PeterОценок пока нет
- Electrostatics and Current Electricity GuideДокумент11 страницElectrostatics and Current Electricity GuideMirza SabeelОценок пока нет
- Electrostatics and Current Electricity ConceptsДокумент10 страницElectrostatics and Current Electricity ConceptsAbhishek AgrawalОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 Magnetism and ElectromagnetismДокумент53 страницыUnit 1 Magnetism and ElectromagnetismOdellien SajaОценок пока нет
- Worksheet For Volume - 1Документ3 страницыWorksheet For Volume - 1pranavtsababayagaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8 (Assignment)Документ6 страницChapter 8 (Assignment)asmaaysha121Оценок пока нет
- Phy - TopicsДокумент2 страницыPhy - Topicslgtv3679Оценок пока нет
- Electro Magnetic FieldsДокумент6 страницElectro Magnetic FieldshelenarajОценок пока нет
- Hiranandani Foundation School Physics Worksheet on Electromagnetic WavesДокумент2 страницыHiranandani Foundation School Physics Worksheet on Electromagnetic WavesManjula MishraОценок пока нет
- Khalidkhawaja74@gmail - Com 12th-Physics-Important-questions-for-BoardДокумент3 страницыKhalidkhawaja74@gmail - Com 12th-Physics-Important-questions-for-Boardabdulkhalid0745Оценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic Fields ExplainedДокумент9 страницElectromagnetic Fields ExplainedranddeceОценок пока нет
- School WorksheetДокумент4 страницыSchool WorksheetNoel BinuОценок пока нет
- Frequently Asked Questions 2023 XiiДокумент4 страницыFrequently Asked Questions 2023 XiiBala MugeshОценок пока нет
- Ts Senior Inter Sub: Physics Important Questions I Very Short Questions: Question No:1Документ5 страницTs Senior Inter Sub: Physics Important Questions I Very Short Questions: Question No:1Yuga Tejeshwar ReddyОценок пока нет
- VBQ Physics XiiДокумент6 страницVBQ Physics Xiipace_saОценок пока нет
- Electricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsОт EverandElectricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- An Advanced Optimal Approach For High Voltage AC Bushing DesignДокумент6 страницAn Advanced Optimal Approach For High Voltage AC Bushing DesignAnbu ArasanОценок пока нет
- EncephalopathyДокумент9 страницEncephalopathyAnbu ArasanОценок пока нет
- PDFДокумент10 страницPDFAnbu ArasanОценок пока нет
- Numerical Analysis of Electric-Field Distribution Around Composite Insulator and Head of Transmission TowerДокумент7 страницNumerical Analysis of Electric-Field Distribution Around Composite Insulator and Head of Transmission TowerAnbu ArasanОценок пока нет
- Effects of Corona Ring Design On Electric FieldДокумент5 страницEffects of Corona Ring Design On Electric FieldSugiharnoОценок пока нет
- Comparative Analysis of Methods For Computing and Electric FieldsДокумент8 страницComparative Analysis of Methods For Computing and Electric FieldsAnbu ArasanОценок пока нет
- PDFДокумент12 страницPDFAnbu ArasanОценок пока нет
- Ieee PaperДокумент2 страницыIeee PaperAnbu ArasanОценок пока нет
- TransformerДокумент50 страницTransformerDaniel WoodwardОценок пока нет
- EDM Neural Network GeneticДокумент97 страницEDM Neural Network GeneticAnbu ArasanОценок пока нет
- Potential Distribution Computation and Structure Optimization For Composite Cross-Arms in 750 KV AC Transmission LineДокумент10 страницPotential Distribution Computation and Structure Optimization For Composite Cross-Arms in 750 KV AC Transmission LineAnbu ArasanОценок пока нет
- Manual Maxwell 2DДокумент334 страницыManual Maxwell 2Dacidangelux100% (2)
- Air-X Maxwell Simulation Student ProceduresДокумент37 страницAir-X Maxwell Simulation Student ProceduresHamid RezaОценок пока нет
- Comparative Analysis of Methods For Computing and Electric FieldsДокумент8 страницComparative Analysis of Methods For Computing and Electric FieldsAnbu ArasanОценок пока нет
- CH 9Документ11 страницCH 9Anbu ArasanОценок пока нет
- 01 Magmagnetci Netic CircuitsДокумент24 страницы01 Magmagnetci Netic CircuitsAnbu ArasanОценок пока нет
- Circuit TheoryДокумент4 страницыCircuit TheoryAnbu ArasanОценок пока нет
- Operation of The Tesla CoilДокумент6 страницOperation of The Tesla CoiltowfiqeeeОценок пока нет
- Fuel Cell7Документ6 страницFuel Cell7Anbu ArasanОценок пока нет
- Fuel Cell1Документ7 страницFuel Cell1Anbu ArasanОценок пока нет
- 351 E977Документ4 страницы351 E977Anbu ArasanОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic Theory-Model 2Документ1 страницаElectromagnetic Theory-Model 2Anbu ArasanОценок пока нет
- Emt QuestiuonsДокумент3 страницыEmt QuestiuonsAnbu ArasanОценок пока нет
- 01 Magmagnetci Netic CircuitsДокумент24 страницы01 Magmagnetci Netic CircuitsAnbu ArasanОценок пока нет
- Ece 3324 Notes 10Документ45 страницEce 3324 Notes 10Andre Francois ThunotОценок пока нет
- Circuit TheoryДокумент4 страницыCircuit TheoryAnbu ArasanОценок пока нет
- Control Systems 2marksДокумент20 страницControl Systems 2marksAnbu ArasanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 - Cementing - Part 1 PDFДокумент32 страницыChapter 6 - Cementing - Part 1 PDFfadz607Оценок пока нет
- Newtonian Fluid - WikipediaДокумент5 страницNewtonian Fluid - Wikipediaamit kumar guptaОценок пока нет
- Math 070838Документ13 страницMath 070838Jeric Boy GarampilОценок пока нет
- Romax 4000 PDFДокумент2 страницыRomax 4000 PDFALEKSANDARОценок пока нет
- Nitric Acid - Nitrous Acid - Nitrogen Oxides - Ullman's EncyclopediaДокумент49 страницNitric Acid - Nitrous Acid - Nitrogen Oxides - Ullman's Encyclopediapoly6icsОценок пока нет
- TankДокумент24 страницыTankUDayОценок пока нет
- Numerical Study of Buckling of Thin PlatesДокумент7 страницNumerical Study of Buckling of Thin PlatesGogyОценок пока нет
- Mendocino Motor Control ApproachesДокумент6 страницMendocino Motor Control ApproachesAngélica María CastrillónОценок пока нет
- Me VR10 PDFДокумент153 страницыMe VR10 PDFeng ameer alburihyОценок пока нет
- Misiulia-Angulo de Helice de EntradaДокумент34 страницыMisiulia-Angulo de Helice de EntradaMiguel AnОценок пока нет
- Photo ResistorДокумент3 страницыPhoto ResistorHarish PrakashОценок пока нет
- Laser Flash Photolysis Purpose A Reactive Free Radical Ketyl IsДокумент16 страницLaser Flash Photolysis Purpose A Reactive Free Radical Ketyl IspathinfoОценок пока нет
- Fire Security NGOAFRДокумент5 страницFire Security NGOAFRseeker05Оценок пока нет
- Air Conditioning: Basic Refrigeration Principles: Unit-1Документ16 страницAir Conditioning: Basic Refrigeration Principles: Unit-1Prabha Karen PalanisamyОценок пока нет
- Electrical Charges and Fields Chapter - 1 PhysicsДокумент61 страницаElectrical Charges and Fields Chapter - 1 PhysicsPrasad PallaОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Surveying - Experiment No. 2Документ6 страницFundamentals of Surveying - Experiment No. 2Jocel SangalangОценок пока нет
- CEIC2000 Thermodynamics - Lecture 2 The First Law Forms of EnergyДокумент49 страницCEIC2000 Thermodynamics - Lecture 2 The First Law Forms of EnergyJoshua JohnОценок пока нет
- Bulk Driven MosfetДокумент3 страницыBulk Driven MosfetAyandev BarmanОценок пока нет
- Linear equations worksheet solutionsДокумент4 страницыLinear equations worksheet solutionsHari Kiran M PОценок пока нет
- Chap 3 DieterДокумент25 страницChap 3 DieterTumelo InnocentОценок пока нет
- Heat Transfer Types and EquationsДокумент10 страницHeat Transfer Types and EquationsRAVEENA RAVIОценок пока нет
- Sample Questions For Practice Fiber LengthДокумент0 страницSample Questions For Practice Fiber LengthShailendra Mishra100% (4)
- $binder 1Документ156 страниц$binder 1fchem11Оценок пока нет
- Toshiba Just Vision 200Документ2 страницыToshiba Just Vision 200kazugawa100% (4)
- Aminpro FK TestДокумент9 страницAminpro FK TestpeilinlanОценок пока нет
- NX Nastran 3 Release GuideДокумент28 страницNX Nastran 3 Release GuideMSC Nastran BeginnerОценок пока нет
- Teaching Quantum Mechanics On An Introductory Level PDFДокумент10 страницTeaching Quantum Mechanics On An Introductory Level PDF24263537Оценок пока нет
- Synthesis and Characterization of Manganese (II), Cobalt (II) and Nickel (II) Complexes of Phenyl Glycine - O-Carboxylic AcidДокумент4 страницыSynthesis and Characterization of Manganese (II), Cobalt (II) and Nickel (II) Complexes of Phenyl Glycine - O-Carboxylic AcidJASH MATHEWОценок пока нет
- Magnetism and Electromagnetism - Electrical Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersДокумент10 страницMagnetism and Electromagnetism - Electrical Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersNagesh GillОценок пока нет
- Cover PrintДокумент4 страницыCover PrintFidel ArroyoОценок пока нет