Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
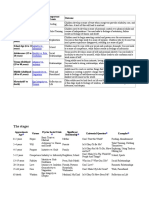
Food Sources and Stages
Загружено:
Lheidaniel MMM.Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Food Sources and Stages
Загружено:
Lheidaniel MMM.Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Stage Infancy (birth to 18 months) Early Childhood (2 to 3 years)
Basic Conflict
Important Events
Outcome
Children develop a sense of trust when caregivers provide reliability, care, and affection. A lack of this will lead to mistrust. Children need to develop a sense of personal control over physical skills and a sense of independence. Success leads to feelings of autonomy, failure results in feelings of shame and doubt. Children need to begin asserting control and power over the environment. Success in this stage leads to a sense of purpose. Children who try to exert too much power experience disapproval, resulting in a sense of guilt. Children need to cope with new social and academic demands. Success leads to a sense of competence, while failure results in feelings of inferiority. Teens need to develop a sense of self and personal identity. Success leads to an ability to stay true to yourself, while failure leads to role confusion and a weak sense of self. Young adults need to form intimate, loving relationships with other people. Success leads to strong relationships, while failure results in loneliness and isolation. Adults need to create or nurture things that will outlast them, often by having children or creating a positive change that benefits other people. Success leads to feelings of usefulness and accomplishment, while failure results in shallow involvement in the world. Older adults need to look back on life and feel a sense of fulfillment. Success at this stage leads to feelings of wisdom, while failure results in regret, bitterness, and despair.
Trust vs. Mistrust Feeding
Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt
Toilet Training
Preschool (3 to 5 years)
Initiative vs. Guilt Exploration
School Age (6 to 11 years) Adolescence (12 to 18 years)
Industry vs. Inferiority Identity vs. Role Confusion
School
Social Relationships
Yound Adulthood (19 to 40 years) Middle Adulthood (40 to 65 years)
Intimacy vs. Isolation
Relationships
Generativity vs. Stagnation
Work and Parenthood
Maturity(65 to death)
Ego Integrity vs. Despair
Reflection on Life
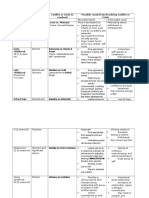
Stage Oral
Age Range Birth1 year
Erogenous zone
Consequences of Psychologic fixation
Anal
13 years
Phallic
36 years
Orally aggressive: chewing gum and the ends of pencils, etc. Orally Passive: smoking, eating, kissing, oral sexual practices. Oral stage fixation might result in a passive, gullible, immature, manipulative personality. Bowel and blad Anal retentive: Obsessively der elimination organized, or excessively neat Anal expulsive: reckless, careless, defiant, disorganized, coprophiliac Genitalia Oedipus complex (in boys) Electra complex (in girls)
Mouth
Latency
6puberty
Dormant sexual feelings Sexual interests mature
Sexual unfulfillment if fixation occurs in this stage. Frigidity, impotence, unsatisfactory relationships
Genital
Pubertydeath
NUTRIENTS SOURCES Complex wholemeal bread, wholegrain cereals, baked beans, carbohydrate pasta, potatoes, peas, other starchy vegetables & fiber Protein lean meat, chicken, fish, cheese, milk, eggs, bread, nuts, legumes Fat oils, butter, margarine, cream, meat, cheese, pastry, biscuits, nuts Preformed butter, margarine, cream, cheese, eggs, meat Vitamin A Beta-carotene carrots, spinach, pumpkin, broccoli, tomatoes, (converts to apricots, rockmelon vitamin A) Vitamin D Fatty/canned fish, butter, margarine, cream, cheese, eggs Vitamin E Polyunsaturated oils, polyunsaturated margarine, nuts, olive oil, fatty fish and small amounts in wholegrain cereals and green vegetables Vitamin K green vegetables, cheese, butter, pork, eggs Thiamin Wholegrain cereals, pork, bread, nuts, peas Riboflavin milk, meat, eggs, cheese, wholegrain, cereals, nuts, mushrooms Niacin fish, meat, peanuts, wholegrain cereals, nuts, mushrooms Pantothenic eggs, wholegrain cereals, peanuts, fish, meat, acid vegetables Vitamin B6 Wholegrain cereals, meat, fish, peanuts, bananas Folic acid green vegetables, wholegrain cereals, wholemeal bread, nuts
Vitamin B12 Biotin Vitamin C Calcium Phosphorus Iron Sodium Potassium Iodine
Zinc
meat, fish, eggs, cheese, milk, oysters eggs, cheese, milk, fish, wholegrain cereals Oranges, tomatoes, potatoes, broccoli, cabbage, Brussels sprouts, Strawberries cheese, milk, yoghurt, canned fish, nuts, sesame seeds (tahini), dried fruit meat, fish, poultry, eggs, milk, cheese, nuts, cereals, bread meat, poultry, wholegrain cereals, wholemeal bread, eggs table salt, meat, milk, cheese, seafood, spinach, celery Potatoes, bananas, oranges, apricots, other fruit and vegetables, meat, fish, nuts Sea foods, milk and cereals and vegetables from areas with high iodine content in the soil, iodised table salt oysters, meat, fish, poultry, eggs, wholegrain cereals, peanuts
Вам также может понравиться
- Erikson Stages of Psychosocial DevelopmentДокумент20 страницErikson Stages of Psychosocial DevelopmentJonalyn Carandang100% (3)
- Psychosocial Development Erik EriksonДокумент2 страницыPsychosocial Development Erik EriksonA.LiyanaVОценок пока нет
- Erikson's Psychosocial Stages Summary Chart: Stage Basic Conflict Important Events Key Questions To Be Answered OutcomeДокумент2 страницыErikson's Psychosocial Stages Summary Chart: Stage Basic Conflict Important Events Key Questions To Be Answered OutcomeLaurie RNtobeОценок пока нет
- Understanding Dysfunction in The FamilyДокумент44 страницыUnderstanding Dysfunction in The Familyquixoticdreamer100% (2)
- NCM 102 Power Point (Pedia)Документ174 страницыNCM 102 Power Point (Pedia)Mika Samson100% (1)
- Perdev Chapter 4Документ38 страницPerdev Chapter 4Donita BinayОценок пока нет
- Developmental Stages in Middle and Late AdolescenceДокумент33 страницыDevelopmental Stages in Middle and Late AdolescenceAldine RaytanОценок пока нет
- Perdev Chapter 4Документ38 страницPerdev Chapter 4Donita BinayОценок пока нет
- How to Raise a Son as a Single Mother: Mastering Motherhood and Raising a Strong Son on Your OwnОт EverandHow to Raise a Son as a Single Mother: Mastering Motherhood and Raising a Strong Son on Your OwnРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- Growth and Development TheoriesДокумент20 страницGrowth and Development TheoriesDennis RagudoОценок пока нет
- Nursing ManagementДокумент4 страницыNursing ManagementLheidaniel MMM.Оценок пока нет
- Institutional Group Agencies For EducationДокумент22 страницыInstitutional Group Agencies For EducationGlory Aroma100% (1)
- PETAL Sentence StartersДокумент1 страницаPETAL Sentence StartersSnip x Hunt manОценок пока нет
- Erik Erikson: Psychosocial DevelopmentДокумент22 страницыErik Erikson: Psychosocial DevelopmentThia SolveОценок пока нет
- Alchemy of The HeartДокумент7 страницAlchemy of The HeartAbdul RahimОценок пока нет
- Prepared By:: Walter Phillip Sp. Palad, R.NДокумент79 страницPrepared By:: Walter Phillip Sp. Palad, R.NctuagentОценок пока нет
- Erikson's Psychosocial Stages Summary ChartДокумент1 страницаErikson's Psychosocial Stages Summary ChartMark Robbiem BarcoОценок пока нет
- Trust vs. Mistrust Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt Initiative vs. GuiltДокумент1 страницаTrust vs. Mistrust Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt Initiative vs. GuiltPatricia Camille FermoОценок пока нет
- Psycho Social DevelopmentДокумент1 страницаPsycho Social DevelopmentJason GuttmanОценок пока нет
- MuriumFatima - 2335 - 12364 - 3-Erikson Theory of DevelopmentДокумент2 страницыMuriumFatima - 2335 - 12364 - 3-Erikson Theory of DevelopmentKhan KhanОценок пока нет
- Erik Erikson Psychosocial Stages of DevelopmentДокумент11 страницErik Erikson Psychosocial Stages of DevelopmentSanemie FototanaОценок пока нет
- At The End of This Module, You Should Be Able To: Explain The Eight Stages of Psychosocial DevelopmentДокумент5 страницAt The End of This Module, You Should Be Able To: Explain The Eight Stages of Psychosocial DevelopmentChris KabilingОценок пока нет
- Growth and DevelopmentДокумент2 страницыGrowth and DevelopmentAnne JusonОценок пока нет
- Stage 1: Trust vs. MistrustДокумент3 страницыStage 1: Trust vs. MistrustCep Loreine GendranoОценок пока нет
- Erik EriksonДокумент29 страницErik EriksonAumi MarquezОценок пока нет
- UNIT II Developmental PsychologyДокумент62 страницыUNIT II Developmental PsychologyMuhammad AsifОценок пока нет
- Family With An AdolescentДокумент94 страницыFamily With An AdolescentJayson King Legaspi CruzОценок пока нет
- CombinepdfДокумент81 страницаCombinepdfTikTok TrendzОценок пока нет
- Psychosocial Development Theory: By: Erik EriksonДокумент14 страницPsychosocial Development Theory: By: Erik EriksonJudith Mae CaparosoОценок пока нет
- PreschoolerДокумент42 страницыPreschoolerJils SureshОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Pediatric Nursing 2012 Student VersionДокумент71 страницаIntroduction To Pediatric Nursing 2012 Student Versionm1k0eОценок пока нет
- Module AdolescenceДокумент6 страницModule AdolescenceMichael GrajeraОценок пока нет
- Lesson 2 Developmental Challenges in Knowing OneselfДокумент25 страницLesson 2 Developmental Challenges in Knowing Oneselfjoshladac94Оценок пока нет
- Human Development ReportДокумент19 страницHuman Development ReportJuliet C. ClementeОценок пока нет
- Stage Influential Conflict or Crisis To Resolved Possible Result From Resolving Conflict or Crisis Infancy Trust vs. MistrustДокумент7 страницStage Influential Conflict or Crisis To Resolved Possible Result From Resolving Conflict or Crisis Infancy Trust vs. MistrustEduard Espeso Chiong-Gandul Jr.Оценок пока нет
- Blue Boxes Indicate Concepts That Were Not Formally Associated With Any One Psychologist, But Rather Concepts That Were Discussed in GeneralДокумент11 страницBlue Boxes Indicate Concepts That Were Not Formally Associated With Any One Psychologist, But Rather Concepts That Were Discussed in GeneralEdward RudnevОценок пока нет
- Q2 HEALTH 8 LP StudentДокумент5 страницQ2 HEALTH 8 LP StudentheheignoremeplsОценок пока нет
- Resilience Bouncing Back FromДокумент3 страницыResilience Bouncing Back FromJulie JОценок пока нет
- School Age ChildДокумент5 страницSchool Age ChildAndrea SandaloОценок пока нет
- 11 - Erikson's Theory of Psychosocial DevelopmentДокумент20 страниц11 - Erikson's Theory of Psychosocial DevelopmentSumit MalaanОценок пока нет
- Unit 3 An Introduction To Child and Adolescent Development (Erik Erikson) Slides 13-27Документ15 страницUnit 3 An Introduction To Child and Adolescent Development (Erik Erikson) Slides 13-27Sabali TsofelaОценок пока нет
- WK 02.lecture 2 Family 2019 PDFДокумент47 страницWK 02.lecture 2 Family 2019 PDFjamesngОценок пока нет
- Stages of Growth and Development Ppt. NEWДокумент11 страницStages of Growth and Development Ppt. NEWArt AlbayОценок пока нет
- Erik EriksonДокумент22 страницыErik Eriksonmohana monaОценок пока нет
- Erikson's Stages of Psychosocial Development-1Документ28 страницErikson's Stages of Psychosocial Development-1Huggins MuzvuweОценок пока нет
- 003 Wk03 Entering The Social World Chapter 5Документ45 страниц003 Wk03 Entering The Social World Chapter 5James DboyОценок пока нет
- Humd 100 - Assessment 3Документ8 страницHumd 100 - Assessment 3kiranjitОценок пока нет
- FreudДокумент1 страницаFreudcathesisОценок пока нет
- Child Development Issues and Implications JournalДокумент26 страницChild Development Issues and Implications Journalapi-539933367Оценок пока нет
- Erickson Summary NotesДокумент3 страницыErickson Summary Notesapi-295355929Оценок пока нет
- PSYCHOSOCIAL THEORY - Erik EriksonДокумент39 страницPSYCHOSOCIAL THEORY - Erik Eriksonmeanantig08Оценок пока нет
- Evaluasi Tumbang & Gangguan PertumbuhanДокумент38 страницEvaluasi Tumbang & Gangguan PertumbuhanAdliah ZahiraОценок пока нет
- G&DДокумент33 страницыG&DSaОценок пока нет
- Erikson's Stages of Life: First!)Документ3 страницыErikson's Stages of Life: First!)zar aperoОценок пока нет
- Psych PresentationДокумент33 страницыPsych Presentationapi-356203884Оценок пока нет
- Health G7 Q1Документ93 страницыHealth G7 Q1Meloueen Tolentino Osillos-AcdalОценок пока нет
- Week 2 Fem2101 Family Life CycleДокумент30 страницWeek 2 Fem2101 Family Life CycleSerena SakaОценок пока нет
- Why Am I Like ThisДокумент42 страницыWhy Am I Like ThisKuriok BurnikОценок пока нет
- Advantages and Disadvantages of CompetitionДокумент4 страницыAdvantages and Disadvantages of CompetitionAnonymous WVR7bIFSWОценок пока нет
- Elderly CareДокумент21 страницаElderly CaresvtperjesОценок пока нет
- Care of Children and Families During Health and IllnessДокумент51 страницаCare of Children and Families During Health and IllnessMikeAndersonОценок пока нет
- Module 5 Health PromotionДокумент59 страницModule 5 Health PromotionZaren James D. RacaОценок пока нет
- Erickson Psychosocial StagesДокумент35 страницErickson Psychosocial Stagesisiderioshane2004Оценок пока нет
- Abegail BautistaДокумент1 страницаAbegail BautistaLheidaniel MMM.Оценок пока нет
- Angels We Have Heard On HighДокумент3 страницыAngels We Have Heard On HighLheidaniel MMM.Оценок пока нет
- Silent NightДокумент1 страницаSilent NightLheidaniel MMM.Оценок пока нет
- ALLELUIAДокумент1 страницаALLELUIALheidaniel MMM.Оценок пока нет
- ChordschurchalleliaДокумент1 страницаChordschurchalleliaLheidaniel MMM.Оценок пока нет
- AlleluiaДокумент1 страницаAlleluiaLheidaniel MMM.Оценок пока нет
- Chords Church All EliaДокумент1 страницаChords Church All EliaLheidaniel MMM.Оценок пока нет
- Eb Gm7 Ab BBДокумент2 страницыEb Gm7 Ab BBLheidaniel MMM.Оценок пока нет
- Generic Name Brand Name Purpose Dea SCH C-IiДокумент1 страницаGeneric Name Brand Name Purpose Dea SCH C-IiLheidaniel MMM.Оценок пока нет
- ALLELUIAДокумент1 страницаALLELUIALheidaniel MMM.Оценок пока нет
- CM DB BBM Eb AbДокумент2 страницыCM DB BBM Eb AbLheidaniel MMM.Оценок пока нет
- Repeat Chorus 2xДокумент2 страницыRepeat Chorus 2xLheidaniel MMM.Оценок пока нет
- Professional Adjustment and Nursing JurisprudenceДокумент8 страницProfessional Adjustment and Nursing JurisprudenceLheidaniel MMM.Оценок пока нет
- ALWAYS BE MY BABY CHORDS (Ver 2) by David Cook at Ultimate-GuitarДокумент2 страницыALWAYS BE MY BABY CHORDS (Ver 2) by David Cook at Ultimate-GuitarLheidaniel MMM.Оценок пока нет
- ChorusДокумент3 страницыChorusLheidaniel MMM.Оценок пока нет
- As High As The HeavensДокумент2 страницыAs High As The HeavensLheidaniel MMM.Оценок пока нет
- 4th Tranche ArmmcДокумент2 страницы4th Tranche ArmmcLheidaniel MMM.Оценок пока нет
- Jake 2 TooolsДокумент8 страницJake 2 TooolsLheidaniel MMM.Оценок пока нет
- 02 Object Modeling TechniqueДокумент50 страниц02 Object Modeling TechniqueMuhammad Romadhon Batukarang EsdОценок пока нет
- Department of Education: Template No. 1 Teacher'S Report On The Results of The Regional Mid-Year AssessmentДокумент3 страницыDepartment of Education: Template No. 1 Teacher'S Report On The Results of The Regional Mid-Year Assessmentkathrine cadalsoОценок пока нет
- W.C. Hicks Appliances: Client Name SKU Item Name Delivery Price Total DueДокумент2 страницыW.C. Hicks Appliances: Client Name SKU Item Name Delivery Price Total DueParth PatelОценок пока нет
- Grade 3 - Unit 1 Increase and Decrease PatternДокумент7 страницGrade 3 - Unit 1 Increase and Decrease PatternKyo ToeyОценок пока нет
- Central University of Karnataka: Entrance Examinations Results 2016Документ4 страницыCentral University of Karnataka: Entrance Examinations Results 2016Saurabh ShubhamОценок пока нет
- Traditional Perceptions and Treatment of Mental Illness in EthiopiaДокумент7 страницTraditional Perceptions and Treatment of Mental Illness in EthiopiaifriqiyahОценок пока нет
- Debate ReportДокумент15 страницDebate Reportapi-435309716Оценок пока нет
- The Ovation E-Amp: A 180 W High-Fidelity Audio Power AmplifierДокумент61 страницаThe Ovation E-Amp: A 180 W High-Fidelity Audio Power AmplifierNini Farribas100% (1)
- 4th Sept - Marathon Series Lecture 8 - General AwarenessДокумент208 страниц4th Sept - Marathon Series Lecture 8 - General AwarenessManbir ArinОценок пока нет
- Bcom (HNRS) Project Final Year University of Calcutta (2018)Документ50 страницBcom (HNRS) Project Final Year University of Calcutta (2018)Balaji100% (1)
- EMD Question Bank II 2Документ4 страницыEMD Question Bank II 2Soham MisalОценок пока нет
- Smart Door Lock System Using Face RecognitionДокумент5 страницSmart Door Lock System Using Face RecognitionIJRASETPublicationsОценок пока нет
- Worst of Autocall Certificate With Memory EffectДокумент1 страницаWorst of Autocall Certificate With Memory Effectapi-25889552Оценок пока нет
- Lacey Robertson Resume 3-6-20Документ1 страницаLacey Robertson Resume 3-6-20api-410771996Оценок пока нет
- Lodge at The Ancient City Information Kit / Great ZimbabweДокумент37 страницLodge at The Ancient City Information Kit / Great ZimbabwecitysolutionsОценок пока нет
- Genuine Fakes: How Phony Things Teach Us About Real StuffДокумент2 страницыGenuine Fakes: How Phony Things Teach Us About Real StuffGail LeondarWrightОценок пока нет
- Answers For Some QuestionsДокумент29 страницAnswers For Some Questionsyogeshdhuri22Оценок пока нет
- KPI AssignmentДокумент7 страницKPI AssignmentErfan Ahmed100% (1)
- A P P E N D I X Powers of Ten and Scientific NotationДокумент5 страницA P P E N D I X Powers of Ten and Scientific NotationAnthony BensonОценок пока нет
- IR2153 Parte6Документ1 страницаIR2153 Parte6FRANK NIELE DE OLIVEIRAОценок пока нет
- Ateneo de Manila University: Submitted byДокумент5 страницAteneo de Manila University: Submitted byCuster CoОценок пока нет
- Literature Review Template DownloadДокумент4 страницыLiterature Review Template Downloadaflsigfek100% (1)
- PDFДокумент40 страницPDFAndi NursinarОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Myocardial Infarction and Acute Management StrategiesДокумент11 страницPathophysiology of Myocardial Infarction and Acute Management StrategiesnwabukingzОценок пока нет
- Mueller Hinton Agar (M-H Agar) : CompositionДокумент2 страницыMueller Hinton Agar (M-H Agar) : CompositionRizkaaulyaaОценок пока нет
- Introduction CompilerДокумент47 страницIntroduction CompilerHarshit SinghОценок пока нет
- Mission and VisionДокумент5 страницMission and VisionsanjedОценок пока нет