Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Laboratory Safety Protocol
Загружено:
djanisz2Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Laboratory Safety Protocol
Загружено:
djanisz2Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
1 Laboratory Techniques in Exercise Physiology Lab 1 House Rules and Laboratory Safety House Rules 1.
Clean-up the lab when you are finished. If you don't have time to clean up after the lab you don't have time to work. Leave the laboratory clean, return all equipment and chemicals back to its proper location, and wash glassware. Remember you are not the only one working in the lab. 2. Report all damaged or broken equipment immediately to the lab instructor. Failure to do so will impede the progress of other experiments in the lab and can become hazardous to other users. 3. We have a limited amount of supplies. Please conserve disposable supplies when possible, prevent contamination of stock reagents and never open new containers without the consent of the lab instructor. 4. Be courteous of others, keep music and conversation at low levels and clean-up when you are finished. 5. Unauthorized experiments are not allowed. 6. You may use lab equipment only after you have been checked out on the proper use of the equipment by the lab instructor. 7. Be alert to unsafe conditions and actions and call attention to them so that corrections can be made as soon as possible. Someone elses accident can put you in danger. 8. Avoid distracting or startling any other worker. Practical jokes or horseplay have no place in the lab. 9. Think, act, and encourage safety until it becomes a habit.
2 Laboratory Safety Guidelines Rules of laboratory safety and chemical handling are not designed to impede productivity, nor should they instill a fear of chemicals or laboratory procedures. Rather, their purpose is to create a healthy awareness of potential laboratory hazards, to improve the efficiency of each student worker, and to protect the general public and the environment from waste contamination. Laboratory Safety Rules: 1. Lab coats should be worn at all times. 2. Some form of eye protection should be worn at all times. Eye injuries can be very serious and injury is usually nonreversible. Safety glasses with wide side shields are recommended, but normal eyeglasses with safety lenses may be permitted. Contact lenses can be problematic while working in the laboratory. The major problem with contact lenses is that they reduce the rate of self-cleansing of the eye. If a chemical splatters into the eye of a contact lens wearer, he or she will possibly have greater injury because of less effective irrigation of the eye. Furthermore, the wearer may be reluctant to use an eyewash for fear of losing the contact lens. 3. Never work alone in the laboratory. 4. Be familiar with the physical properties of all chemicals used in the laboratory. This includes their flammability, reactivity, toxicity, and proper disposal. 5. Eating, drinking, and smoking in the laboratory are strictly prohibited. 6. Use the fume hood when working with any toxic or volatile chemical. 7. Know the location and proper use of the fire extinguishers, eye wash station, and deluge/shower. 8. Wash hands thoroughly before leaving the lab. 9. Use of disposable gloves is mandatory when working with any human blood or tissues. 10. Mouth pipetting is never allowed. 11. Report any spill, accident, or injury, no matter how minor to the lab instructor immediately.
3 Lab Assignments 1. Complete the online training course on lab safety (link is provided below). Print the last page of the course as verification that you completed the course. When asked , select researcher and cell biology. It will take you 45-60 minutes to complete the course. http://www.hhmi.org/about/harvest/labsafe/safescience.html 2. Complete the lab safety questionnaire. Due Date: Sept 7th
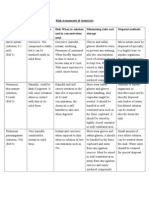
4 Laboratory Techniques in Exercise Physiology Lab Safety Questionnaire Exercise Biology Laboratories 1. Number and location of fire extinguishers. List the last inspection date and the type of fire extinguisher. List the proper procedures for using a fire extinguisher.
2. Location of telephone and emergency procedures
3. Number and location of spill clean-up kits (blood and chemical). Familiarize your self with the procedures for their use.
4. Number and location of first aide kits. List the contents of the first aide kits. Do the first aide kits appear to be complete?
5 5. Locations of safety showers and eyewash stations. When should they be used? Have they be flushed and cleaned regularly to minimize microbial contamination?
6. Location and type (safety glasses with full side shields, safety chemical goggles, plastic face shields) of personal eye protection. When should these be used?
7. Location of appropriate rubber gloves and other safety equipment for handling hazardous chemicals.
8. Location of appropriate rubber gloves for handling biohazardous materials.
9. Location of hot plates
10. Identify electrical outlets without ground, with ground, and with ground fault interrupter.
6 11. Location of compressed gas cylinders. Are they properly secured?
12. Location of waste receptacles for glass. 13. Location of waste receptacles for hazardous chemicals.
14. Location, and type of special cabinets to store hazardous or flammable chemicals. 15. List the chemicals found in the special cabinets. Are the chemicals found in the chemical cabinets appropriate for the cabinet?
16.Describe the OSHA labeling system for chemicals. When should the labels be checked?
7 17. Identify the location of the fume hood. What type of chemicals should be pipetted under the fume hood? Describe its proper use.
18. Identify the location of the biological safety cabinet. When should it be used? When was it last certified?
19. Are exits properly marked? 20. Location of the MSDS notebook. Describe the contents of this notebook. What is the purpose of the notebook and when should it be consulted?
21. Location of the master cut-off switch for electricity
22. Location of biohazardous bags (empty and active) and boxes. When and where should the used biohazard bags be stored? Describe the procedures for handling biohazardous waste.
8 25. Location of sharps containers. What should be included in these containers? When and where should the used sharps containers be stored?
26. What type of materials should go into a biohazardous bag and into a sharps container?
27.Identify the powdered chemical cabinet. How can you determine if the chemicals in this cabinet are hazardous and whether special precautions should be taken when handling these chemicals?
28. Location of the fire alarm.
29. Suggestions for improving the safety of the Laboratory. What safety equipment would you purchase for the lab? Why?
Вам также может понравиться
- Safety in the Chemical Laboratory and Industry: A Practical GuideОт EverandSafety in the Chemical Laboratory and Industry: A Practical GuideОценок пока нет
- Lab Self Inspection Checklist PDFДокумент11 страницLab Self Inspection Checklist PDFarif_fatur324872Оценок пока нет
- SOP For MonitoringДокумент29 страницSOP For MonitoringShreya Test HouseОценок пока нет
- Veena SeminarДокумент41 страницаVeena SeminarVeena PatilОценок пока нет
- High Efficiency Poly Electrolytes For Solid-Liquid SeparationДокумент1 страницаHigh Efficiency Poly Electrolytes For Solid-Liquid SeparationSIVAPATHASEKARANОценок пока нет
- OSHAquickfacts Lab Safety Chemical Fume Hoods PDFДокумент2 страницыOSHAquickfacts Lab Safety Chemical Fume Hoods PDFacanis1016Оценок пока нет
- Manual HandlingДокумент20 страницManual HandlingZain Ali KidwaiОценок пока нет
- Risk AssesmentsДокумент11 страницRisk AssesmentsSalvacion JaroОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Inspection Checklist Form Hsse World: SN Observations Recommendation (S) By: StatusДокумент4 страницыLaboratory Inspection Checklist Form Hsse World: SN Observations Recommendation (S) By: StatusMyolwinooОценок пока нет
- Toluene:: Standard Operating ProcedureДокумент7 страницToluene:: Standard Operating ProcedureRicardo VilchezОценок пока нет
- Risk Assessment of ChemicalsДокумент3 страницыRisk Assessment of ChemicalsKingsley WongОценок пока нет
- Emergency Eyewash Shower Sop FinalДокумент8 страницEmergency Eyewash Shower Sop FinalDominic EmerencianaОценок пока нет
- Compressed Gas Cylinder Safety SOPДокумент5 страницCompressed Gas Cylinder Safety SOPIdris AdeniranОценок пока нет
- Checklist Biosafety Level - 2Документ5 страницChecklist Biosafety Level - 2Vincent Reyes100% (1)
- EVT (Sop)Документ21 страницаEVT (Sop)Farvin FleetОценок пока нет
- Risk Assessment Guidelines - 9cb0Документ11 страницRisk Assessment Guidelines - 9cb0andaminiОценок пока нет
- ICH Guideline For Elemental ImpuritiesДокумент77 страницICH Guideline For Elemental ImpuritiesMohd AfzanizamОценок пока нет
- D3437 - 15 Standard Practice For Sampling and Handling Liquid Cyclic Products PDFДокумент5 страницD3437 - 15 Standard Practice For Sampling and Handling Liquid Cyclic Products PDFJacques BlueqОценок пока нет
- Safty Symbols: Assignment of Chemical Reaction Engineering LabДокумент4 страницыSafty Symbols: Assignment of Chemical Reaction Engineering LabAyesha SarwarОценок пока нет
- SOP Housekeeping&CleaningДокумент3 страницыSOP Housekeeping&Cleaningmalik234everОценок пока нет
- SOP For Preparation of TrendsДокумент2 страницыSOP For Preparation of TrendsАнна ОрлеоглоОценок пока нет
- SOP For Handling of Waste Paper in Pharmaceutical IndustryДокумент3 страницыSOP For Handling of Waste Paper in Pharmaceutical IndustryMubarak PatelОценок пока нет
- 5S Production Area Audit: Location: Date: Scored By: Score: Previous ScoreДокумент2 страницы5S Production Area Audit: Location: Date: Scored By: Score: Previous ScoreGeeTheWhizz100% (1)
- Sop ASP HPLCДокумент12 страницSop ASP HPLCAngel PalominoОценок пока нет
- GPCB SOP For De-Contamination FacilityДокумент9 страницGPCB SOP For De-Contamination FacilityEHS HalolОценок пока нет
- IPQA A Beginner's GuideДокумент170 страницIPQA A Beginner's GuideGoran MickoОценок пока нет
- Reserve SamplesДокумент2 страницыReserve SamplesSrikanth NagabiruОценок пока нет
- List of SOP's: Dhaka, BangladeshДокумент1 страницаList of SOP's: Dhaka, BangladeshPharmacistОценок пока нет
- Safe Storage HC PDFДокумент65 страницSafe Storage HC PDFSahanara shaikhОценок пока нет
- 2019 - GMP - CLASS A - GROUP 11 - TASK 4 - Validasi Pembersihan AlatДокумент34 страницы2019 - GMP - CLASS A - GROUP 11 - TASK 4 - Validasi Pembersihan Alatega aaОценок пока нет
- Personal Protective Equipment ProceduresДокумент7 страницPersonal Protective Equipment ProceduresIbrahim Azam IbrahimОценок пока нет
- c1079 USP36 PDFДокумент8 страницc1079 USP36 PDFHassan HoudoudОценок пока нет
- Sop Fume HoodДокумент2 страницыSop Fume HoodKoko AshourОценок пока нет
- Current Good Manufacturing Practices: For Ninth Semester Pharmacy StudentsДокумент36 страницCurrent Good Manufacturing Practices: For Ninth Semester Pharmacy StudentsAdelio MercadejasОценок пока нет
- Good Laboratory PracticesДокумент24 страницыGood Laboratory PracticesGerald Limo Arap ChebiiОценок пока нет
- Source Water STP 31-05-2019Документ11 страницSource Water STP 31-05-2019saptaksamadder4Оценок пока нет
- Temperature Mapping & Validation, Monitoring and Alert Solutions For Sensitive Cold StoragesДокумент12 страницTemperature Mapping & Validation, Monitoring and Alert Solutions For Sensitive Cold StoragesVacker Group UAE100% (1)
- Volumetric SolutionsДокумент6 страницVolumetric SolutionsssnoormОценок пока нет
- 2848i Hood PDFДокумент24 страницы2848i Hood PDFgustavo_altamirano22Оценок пока нет
- LirДокумент5 страницLirHimatushОценок пока нет
- Hazardouas Chemicals Safe Work InstructionДокумент3 страницыHazardouas Chemicals Safe Work Instructiontelteguh01Оценок пока нет
- 03 Flash Point PDFДокумент10 страниц03 Flash Point PDFالعراقي الفضلي100% (1)
- Food Safety Auditing - Practice and PrinciplesДокумент96 страницFood Safety Auditing - Practice and PrinciplesmkrchgОценок пока нет
- SOP of INSTRUMENTS REVДокумент9 страницSOP of INSTRUMENTS REVShreya RoyОценок пока нет
- Content: Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Use and Maintenance of A PH MeterДокумент6 страницContent: Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Use and Maintenance of A PH MeterChristian JosephОценок пока нет
- Is 5572 - Hazardous ClassificationДокумент2 страницыIs 5572 - Hazardous ClassificationMathavaraj DharmarajОценок пока нет
- Handling of Out of Specification Results: International Journal of Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance April 2015Документ8 страницHandling of Out of Specification Results: International Journal of Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance April 2015Pavana KharwalОценок пока нет
- VtMA A 20083103 VO Merkblatt Riboflavin Test Englisch DДокумент10 страницVtMA A 20083103 VO Merkblatt Riboflavin Test Englisch Dmcasey32943Оценок пока нет
- Guide For Lab Compliance With NFPA 45Документ5 страницGuide For Lab Compliance With NFPA 45Kamran JawaidОценок пока нет
- Organic SolventsSOPДокумент6 страницOrganic SolventsSOPNikhilesh KumarОценок пока нет
- 5 S - A PresentationДокумент38 страниц5 S - A Presentationpbalawin43900% (1)
- Iso 14001 English PDFДокумент5 страницIso 14001 English PDFkemalОценок пока нет
- Using A Fume Hood: RiskwareДокумент7 страницUsing A Fume Hood: RiskwaretafouzeltОценок пока нет
- 06 Breakout D-Quality Risk Management-Key MessagesДокумент26 страниц06 Breakout D-Quality Risk Management-Key Messageshenrykayode4100% (1)
- 16.0 Re-Validation / RequalificationДокумент3 страницы16.0 Re-Validation / RequalificationBhavik YadavОценок пока нет
- Internal Audit Training Schedule and Outline (Sample)Документ2 страницыInternal Audit Training Schedule and Outline (Sample)Zul KarimanОценок пока нет
- PRESERVATIVESДокумент25 страницPRESERVATIVESimran aliОценок пока нет
- Lab 3 Cleanroom Gowning Requirements: Procedure Before Entry Into Gowning AreaДокумент5 страницLab 3 Cleanroom Gowning Requirements: Procedure Before Entry Into Gowning AreaGymdheeОценок пока нет
- Audit Sheet For 5S Evaluation - Shop Floor: 1S2S3S Score (1S + 2S + 3S) / 50Документ1 страницаAudit Sheet For 5S Evaluation - Shop Floor: 1S2S3S Score (1S + 2S + 3S) / 50BALACHANDAR SОценок пока нет
- VTU 7 Sem B.E (CSE/ISE) : Java/ J2EeДокумент57 страницVTU 7 Sem B.E (CSE/ISE) : Java/ J2EeNikhilGuptaОценок пока нет
- Grammatical Development in A Mayan Sign Language-Austin German-CILLA - IXДокумент26 страницGrammatical Development in A Mayan Sign Language-Austin German-CILLA - IXAustin Allen GermanОценок пока нет
- #4 Nov.7-11, 2016 DLLДокумент3 страницы#4 Nov.7-11, 2016 DLLRoselyn MyerОценок пока нет
- Bridge Embankment FailuresДокумент13 страницBridge Embankment Failuresirmreza68Оценок пока нет
- Bcpp6e TB Ch01Документ32 страницыBcpp6e TB Ch01tnguyen194Оценок пока нет
- Data ModelingДокумент98 страницData ModelingparthascОценок пока нет
- Acceleration Unit Plan 1Документ3 страницыAcceleration Unit Plan 1api-3954318210% (1)
- DIctogloss Group 5 Teaching WritingДокумент2 страницыDIctogloss Group 5 Teaching WritingteeshuminОценок пока нет
- DHAVAL Resume 1Документ3 страницыDHAVAL Resume 1garvi_gujaratОценок пока нет
- Xfoil - Users - Manual 6.9 PDFДокумент38 страницXfoil - Users - Manual 6.9 PDFSepideОценок пока нет
- Mickey WateractivityДокумент3 страницыMickey Wateractivityapi-293006069Оценок пока нет
- 2016/2017 Master Timetable (Tentative) : Published: May 2016Документ19 страниц2016/2017 Master Timetable (Tentative) : Published: May 2016Ken StaynerОценок пока нет
- University of Khartoum Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Fourth YearДокумент61 страницаUniversity of Khartoum Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Fourth YearMohamed AlserОценок пока нет
- Cold-Water Corals PDFДокумент351 страницаCold-Water Corals PDFAlbert Wahyu50% (2)
- Safety Training For The Oil and Gas Worker: WhitepaperДокумент6 страницSafety Training For The Oil and Gas Worker: WhitepaperfahdОценок пока нет
- Intel (R) ME Firmware Integrated Clock Control (ICC) Tools User GuideДокумент24 страницыIntel (R) ME Firmware Integrated Clock Control (ICC) Tools User Guidebox.office1003261Оценок пока нет
- Convolutional Neural Networks Based Intra-PredictionДокумент21 страницаConvolutional Neural Networks Based Intra-PredictionMohsin Khan JadoonОценок пока нет
- On The Potential and Limits of (Global) Justice Through Law. A Frame of Research. Gianluigi PalombellaДокумент12 страницOn The Potential and Limits of (Global) Justice Through Law. A Frame of Research. Gianluigi Palombellaben zilethОценок пока нет
- Hydraulics and Geotechnical TermsДокумент4 страницыHydraulics and Geotechnical TermsAndrea RamirezОценок пока нет
- Reflection Week 3 - The Sensible ThingДокумент3 страницыReflection Week 3 - The Sensible Thingtho truongОценок пока нет
- Stage 1 Handwriting Program Term 2Документ4 страницыStage 1 Handwriting Program Term 2api-206221838Оценок пока нет
- Keshav Mohaneesh Aumeer 16549793 Assignment 2 Case Study Managing Change 3002Документ12 страницKeshav Mohaneesh Aumeer 16549793 Assignment 2 Case Study Managing Change 3002pri demonОценок пока нет
- Project Management Methodologies and ConceptsДокумент24 страницыProject Management Methodologies and ConceptsrnvvprasadОценок пока нет
- English 9 DLPДокумент6 страницEnglish 9 DLPbeb100% (1)
- Chapter 5, Soil Engineering For Highway DesignДокумент57 страницChapter 5, Soil Engineering For Highway DesignIsmail Hrichi100% (1)
- FCOE Directory 2015-16Документ196 страницFCOE Directory 2015-16Cheryl WestОценок пока нет
- TetrabiblosДокумент583 страницыTetrabiblosOrion627Оценок пока нет
- Solutions To Mathematics 17 Exercises On Systems of Equations PDFДокумент6 страницSolutions To Mathematics 17 Exercises On Systems of Equations PDFMichael Christian BaysauliОценок пока нет
- Learning Plan FinalДокумент3 страницыLearning Plan FinalMary AnalynОценок пока нет
- Bca 3rd Sem Data St.Документ40 страницBca 3rd Sem Data St.TECHKNOWLOZY MOHITjiОценок пока нет
- Laws of UX: Using Psychology to Design Better Products & ServicesОт EverandLaws of UX: Using Psychology to Design Better Products & ServicesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (9)
- The ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemОт EverandThe ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemОценок пока нет
- Artificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureОт EverandArtificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- The Age of Agile: How Smart Companies Are Transforming the Way Work Gets DoneОт EverandThe Age of Agile: How Smart Companies Are Transforming the Way Work Gets DoneРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (5)
- Electrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tОт EverandElectrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (27)
- The Design Thinking Playbook: Mindful Digital Transformation of Teams, Products, Services, Businesses and EcosystemsОт EverandThe Design Thinking Playbook: Mindful Digital Transformation of Teams, Products, Services, Businesses and EcosystemsОценок пока нет
- 507 Mechanical Movements: Mechanisms and DevicesОт Everand507 Mechanical Movements: Mechanisms and DevicesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (28)
- Design for How People Think: Using Brain Science to Build Better ProductsОт EverandDesign for How People Think: Using Brain Science to Build Better ProductsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (8)
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersОт EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Redefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesОт EverandRedefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesОценок пока нет
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsОт EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5)
- Analog Design and Simulation Using OrCAD Capture and PSpiceОт EverandAnalog Design and Simulation Using OrCAD Capture and PSpiceОценок пока нет
- Articulating Design Decisions: Communicate with Stakeholders, Keep Your Sanity, and Deliver the Best User ExperienceОт EverandArticulating Design Decisions: Communicate with Stakeholders, Keep Your Sanity, and Deliver the Best User ExperienceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (19)
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisОт EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- UX: Simple and Effective Methods for Designing UX Great Products Using UX Programming TheoriesОт EverandUX: Simple and Effective Methods for Designing UX Great Products Using UX Programming TheoriesОценок пока нет
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsОт EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsОценок пока нет
- Designing for Behavior Change: Applying Psychology and Behavioral Economics 2nd EditionОт EverandDesigning for Behavior Change: Applying Psychology and Behavioral Economics 2nd EditionОценок пока нет
- The Jobs To Be Done Playbook: Align Your Markets, Organization, and Strategy Around Customer NeedsОт EverandThe Jobs To Be Done Playbook: Align Your Markets, Organization, and Strategy Around Customer NeedsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Heat Exchanger Design Guide: A Practical Guide for Planning, Selecting and Designing of Shell and Tube ExchangersОт EverandHeat Exchanger Design Guide: A Practical Guide for Planning, Selecting and Designing of Shell and Tube ExchangersРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (13)
- CATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part I : Getting Started and Sketcher WorkbenchОт EverandCATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part I : Getting Started and Sketcher WorkbenchРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (10)