Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
The Kinetics of The Reaction Between Bromate
Загружено:
zainabpetalИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
The Kinetics of The Reaction Between Bromate
Загружено:
zainabpetalАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
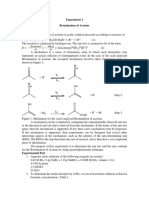
The kinetics of the reaction between bromate(V), bromide and hydrogen ions Bromate(V), bromide and hydrogen ions
react according to the following equation: 5Br + BrO3 + 6H+ 3Br2 + 3H2O
As bromate and bromide react, they produce Br2, which then reacts with methyl orange to dissipate the colour of the solution and show completion of the reaction. This dissipation of colour can be timed and used for calculation. However, this reaction happens very quickly, and under normal circumstances would not be able to be timed. By adding phenol to the solution, the reaction of Br2 with methyl orange can be slowed down with the following side reaction: BrC6H4OH + H+ + Br-
C6H5OH + Br2 >
This reaction of Br2 with phenol slows down the reaction with methyl orange enough that it is able to be timed. Otherwise, the reaction would happen very quickly and it would not be possible to time it. I intend to vary the amounts of potassium bromide, bromate(V) and hydrogen ions and work out the reaction rate and prove that the rate equation is: rate = k [Br] [BrO] [H] This will allow me to determine the rate constant and the order of reaction. I will also investigate the effect of the presence of a catalyst on the rate and work out the change in activation enthalpy.
Requirements: phenol solution, 0.00010 mol dm3 potassium bromide solution, 0.010 mol dm3 potassium bromate(V) solution, 0.0050 mol dm3 methyl orange solution (1.0 g dm3) sulfuric acid, 1.0 mol dm3
1. Take 5 burettes, which should be washed out with water. They are then washed out with the solution going into them and filled with one of the solutions listed above. All the burettes are labelled to avoid any confusion with the solutions. When filling a burette it should always be held below head height to allow it to be controlled better and to avoid spillage. 2. 10cm of potassium bromate(V) solution, 15cm of sulphuric acid solution and 10cm of phenol solution are added to a beaker. Always read the burette at eye level. 5 drops of methyl orange indicator is also added to the beaker. The same bottle should be used in each trial. 3. 10cm of potassium bromide solution of the required concentration is added to another beaker. For most trials the potassium bromide will need mixing with distilled water to lower the concentration. 4. The potassium bromide solution is poured into the first beaker and the stopwatch is started. The complete mixture is stirred and the time taken for it to go completely colourless is recorded. 5. The beakers are then washed out and the experiment is repeated with varying concentrations of potassium bromide. But the volume of potassium bromide solution is always made up to 10cm with distilled water to make it a fair test. Each concentration is repeated 3 times. All other factors such as temperature should be kept constant and the same apparatus should be used each time. Any anomalous results should be investigated
Вам также может понравиться
- Manual OccultismДокумент390 страницManual OccultismJikker Gigi Phatbeatzz Barrow100% (11)
- The Art of Logical ThinkingДокумент210 страницThe Art of Logical ThinkingAndyAyam100% (1)
- Lion's Path - Charles MuseeДокумент57 страницLion's Path - Charles MuseeBob Sagat75% (4)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisОт EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Planetary Characteristics: © Sarajit Poddar, SJC AsiaДокумент11 страницPlanetary Characteristics: © Sarajit Poddar, SJC AsiaVaraha Mihira100% (11)
- Pnbcontr0223en (Web)Документ308 страницPnbcontr0223en (Web)James GeorgeОценок пока нет
- Welrod Silenced PistolДокумент2 страницыWelrod Silenced Pistolblowmeasshole1911Оценок пока нет
- 08 Hydrolysis of StarchДокумент4 страницы08 Hydrolysis of StarchRoshen BajajОценок пока нет
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Movement of substancesОт EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Movement of substancesОценок пока нет
- The Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresОт EverandThe Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Unit 2 Lab ManualДокумент19 страницUnit 2 Lab Manualkari1995Оценок пока нет
- Titration Lab ReportДокумент20 страницTitration Lab Reportapi-427983093Оценок пока нет
- Agricultural Extension and CommunicationДокумент173 страницыAgricultural Extension and CommunicationAlfredo Conde100% (1)
- Concrete ON MALDIVESДокумент55 страницConcrete ON MALDIVESKãrthìçk JkrОценок пока нет
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesОт EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- The Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterОт EverandThe Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterОценок пока нет
- Titration Lab ReportДокумент20 страницTitration Lab Reportapi-410426030Оценок пока нет
- Chem TitrationДокумент14 страницChem Titrationapi-441551987Оценок пока нет
- Titration of Vinegar Lab ExperimentДокумент11 страницTitration of Vinegar Lab ExperimentAchinthya PereraОценок пока нет
- Barilla SpaДокумент11 страницBarilla Spavariapratik100% (1)
- Atlas-Complejidad Económica PDFДокумент362 страницыAtlas-Complejidad Económica PDFRafael QuiñonesОценок пока нет
- 300.91C - Fire Alarm System Pre-Test and Acceptance Test Checklist 3-27-14Документ2 страницы300.91C - Fire Alarm System Pre-Test and Acceptance Test Checklist 3-27-14mthuyaОценок пока нет
- Microscopio Olympus CX31 Serv PDFДокумент36 страницMicroscopio Olympus CX31 Serv PDFalejandra0% (1)
- Quantitative Determination of Soda Ash Composition by Double Indicator Titration PDFДокумент6 страницQuantitative Determination of Soda Ash Composition by Double Indicator Titration PDFHanzLouelLazaroFlorendoОценок пока нет
- Brenda Patton Guided Reflection QuestionsДокумент3 страницыBrenda Patton Guided Reflection QuestionsCameron JanzenОценок пока нет
- Hydrogen Peroxide Analysis Lab: Redox Titration With Potassium PermanganateДокумент3 страницыHydrogen Peroxide Analysis Lab: Redox Titration With Potassium Permanganateapi-297044435100% (1)
- Titration Lab ReportДокумент13 страницTitration Lab Reportapi-341133750Оценок пока нет
- AntacidДокумент40 страницAntacidmadmelzarОценок пока нет
- Exp 7 Phenol PDFДокумент8 страницExp 7 Phenol PDFArtОценок пока нет
- Biological Chemistry LabreportДокумент7 страницBiological Chemistry LabreportJerry CaldwellОценок пока нет
- J. Biol. Chem.-1907-Levene-481-4Документ5 страницJ. Biol. Chem.-1907-Levene-481-4Kim PajinagОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Activity No 3Документ6 страницLaboratory Activity No 3Bok MatthewОценок пока нет
- Experiment 3: Preparing SolutionДокумент4 страницыExperiment 3: Preparing SolutionÇiğdem DÜLGERBAKİОценок пока нет
- Praktikum Kimia Organik 1 Uin Jakarta PkimДокумент31 страницаPraktikum Kimia Organik 1 Uin Jakarta PkimNur BillahОценок пока нет
- Lab Report ChemДокумент8 страницLab Report Chemapi-489918414Оценок пока нет
- Spectrophotometric Determination of The PK of An Acid-Base IndicatorДокумент4 страницыSpectrophotometric Determination of The PK of An Acid-Base Indicatorseqhatsi shataОценок пока нет
- 124 10 Titration of A Cola Product 2011Документ10 страниц124 10 Titration of A Cola Product 2011MaMtОценок пока нет
- TitrationДокумент12 страницTitrationMiranda Amiroh SulaimanОценок пока нет
- Somogyi NelsonДокумент6 страницSomogyi NelsonPhichamon NoisuwanОценок пока нет
- Lab Report ChemДокумент15 страницLab Report Chemapi-328401829Оценок пока нет
- Lab ManualДокумент32 страницыLab Manualnikhil110705Оценок пока нет
- 11 Fruit JuicesДокумент8 страниц11 Fruit Juicesjules blancoОценок пока нет
- Titrimetric AnalysisДокумент7 страницTitrimetric AnalysisLisa DentonОценок пока нет
- Cbse Test Paper-01 Class - 12 Chemistry (Solutions) : Vapour Pressure of The SolutionДокумент5 страницCbse Test Paper-01 Class - 12 Chemistry (Solutions) : Vapour Pressure of The SolutionTr Mazhar PunjabiОценок пока нет
- Lab ReportДокумент10 страницLab Reportapi-327825157Оценок пока нет
- Experiment 2 - Preparation of A Standard Solution & TitrationДокумент5 страницExperiment 2 - Preparation of A Standard Solution & TitrationAtn YoungОценок пока нет
- ChemistryДокумент11 страницChemistryapi-327825016Оценок пока нет
- Titrimetric DeterminationДокумент3 страницыTitrimetric DeterminationJohn Anthony BaluyutОценок пока нет
- Standard Methods Bromide3Документ6 страницStandard Methods Bromide3maría joséОценок пока нет
- Mud TestДокумент8 страницMud TestNakkolopОценок пока нет
- Lesson Redoxreactiontitration Student LabДокумент5 страницLesson Redoxreactiontitration Student LabThành Huỳnh QuanОценок пока нет
- 05 - To Determine The Concentration of Hydrogen Peroxide in A Solution Using A Back TitrationДокумент2 страницы05 - To Determine The Concentration of Hydrogen Peroxide in A Solution Using A Back TitrationBeyonce NoelОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Practical Report: Date of Submission Received by Score 5th March 2018Документ10 страницChemistry Practical Report: Date of Submission Received by Score 5th March 2018prettyОценок пока нет
- 8 - Lab8-Potentiometric Titration of Acid MixtureДокумент6 страниц8 - Lab8-Potentiometric Titration of Acid MixtureHoang Huong TraОценок пока нет
- Total Acid Number SOPДокумент4 страницыTotal Acid Number SOPArun RamdassОценок пока нет
- Experiment 3 - Bromination of AcetoneДокумент12 страницExperiment 3 - Bromination of AcetoneOsama AnatyОценок пока нет
- Buffer 1Документ13 страницBuffer 1Pauline AlfonsoОценок пока нет
- Activity No.4: InstructionsДокумент7 страницActivity No.4: Instructionsdenshang 10100% (1)
- Taller Trad de 8 Determinaciones de Parametros de Calidad de AguaДокумент11 страницTaller Trad de 8 Determinaciones de Parametros de Calidad de AguaChristian RiveraОценок пока нет
- Titration Lab ReportДокумент8 страницTitration Lab ReportMohamed Gamal Mohamed ShanhoryОценок пока нет
- University of Zululand Faculty of Science and Agriculture: Metabolism (Sbch212) Practical ManualДокумент16 страницUniversity of Zululand Faculty of Science and Agriculture: Metabolism (Sbch212) Practical ManualNomceboОценок пока нет
- Experiment 8 - Br2-Cinnamic AcidДокумент4 страницыExperiment 8 - Br2-Cinnamic AcidLucy grahamОценок пока нет
- Car & BicarДокумент12 страницCar & BicarWard QutaibaОценок пока нет
- 2015 - Expt 2A Acid Base TitrationДокумент8 страниц2015 - Expt 2A Acid Base TitrationPeter HugeОценок пока нет
- Chem Lab-3Документ15 страницChem Lab-3api-389948390Оценок пока нет
- Simon Philip - Criterion B Planning A LabДокумент9 страницSimon Philip - Criterion B Planning A LabSimon PhilipОценок пока нет
- Isolation and Characterization of ProteinsДокумент4 страницыIsolation and Characterization of ProteinsTROY CULDER SZEОценок пока нет
- 09 - Flinn - Stoichiometric Ratio of A ReactionДокумент8 страниц09 - Flinn - Stoichiometric Ratio of A ReactionDerek Hammons100% (1)
- Displacement Reactions of The Halogens: One Drop of Chlorine Water and Gently Shake The Test Tube To Mix The ContentsДокумент1 страницаDisplacement Reactions of The Halogens: One Drop of Chlorine Water and Gently Shake The Test Tube To Mix The Contentslogi_thasanОценок пока нет
- Qualitative Tests For Identification of Carbon Carbon Unsaturation and Alcohol FunctionsДокумент5 страницQualitative Tests For Identification of Carbon Carbon Unsaturation and Alcohol FunctionsMomer50% (2)
- Titration: Lab ReportДокумент18 страницTitration: Lab Reportapi-327697210Оценок пока нет
- A Further Investigation of the Symmetrical Chloride of Paranitroorthosulphobenzoic AcidОт EverandA Further Investigation of the Symmetrical Chloride of Paranitroorthosulphobenzoic AcidОценок пока нет
- Appetizer Summative TestДокумент36 страницAppetizer Summative TestArgelynPadolinaPedernalОценок пока нет
- Carbon Emissions Don't Cause Global Warming: BackgroundДокумент5 страницCarbon Emissions Don't Cause Global Warming: BackgroundLibertyAustraliaОценок пока нет
- Shi Et Al-2019-Intensive Care MedicineДокумент11 страницShi Et Al-2019-Intensive Care MedicineJavier BlancОценок пока нет
- Smart Dust Technology Seminar ReportДокумент32 страницыSmart Dust Technology Seminar ReportSushan Upadhyay67% (3)
- Sample Design Calculations For Block Found. For Vib. Equip.Документ17 страницSample Design Calculations For Block Found. For Vib. Equip.Adam Michael GreenОценок пока нет
- NMMT City Bus SystemДокумент3 страницыNMMT City Bus Systemharish guptaОценок пока нет
- Kia September 2020 Price List: Picanto ProceedДокумент2 страницыKia September 2020 Price List: Picanto ProceedCaminito MallorcaОценок пока нет
- Catalyst Worksheet - SHHSДокумент3 страницыCatalyst Worksheet - SHHSNerd 101Оценок пока нет
- Conduit 5Документ42 страницыConduit 5dediОценок пока нет
- LESSON 2 Facilities Location StrategiesДокумент2 страницыLESSON 2 Facilities Location StrategiesElle LeeОценок пока нет
- Ashok Leyland Project ReportДокумент40 страницAshok Leyland Project ReportGovind kumarОценок пока нет
- Edrolo ch3Документ42 страницыEdrolo ch3YvonneОценок пока нет
- AE451 Aerospace Engineering Design: Team HДокумент140 страницAE451 Aerospace Engineering Design: Team HÖmer Uğur ZayıfoğluОценок пока нет
- Carriages and Mounts SeriesДокумент92 страницыCarriages and Mounts Seriessudhirm16Оценок пока нет
- Https - Threejs - Org - Examples - Webgl - Fire - HTMLДокумент9 страницHttps - Threejs - Org - Examples - Webgl - Fire - HTMLMara NdirОценок пока нет
- Heron's Formula For The Area of A Triangle - Shailesh A ShiraliДокумент9 страницHeron's Formula For The Area of A Triangle - Shailesh A ShiraliAltananyОценок пока нет
- Omyacarb 1t TNДокумент1 страницаOmyacarb 1t TNGİZEM DEMİRОценок пока нет