Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
NCP - Impaired Gas Exchange
Загружено:
Rene John FranciscoИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
NCP - Impaired Gas Exchange
Загружено:
Rene John FranciscoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
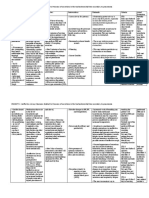
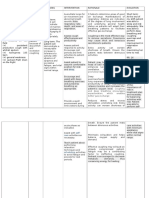
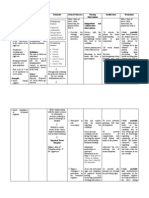
Patient: D.
Age: 82 years old
Gender: Male Attending Physician: Dr. Garlitos Expected Outcome After 8 hours of nursepatient intervention, the patient will be able to: 1. Demonstrate improved ventilation and adequate O2, and absence of symptoms of respiratory distress. Nursing Intervention Independent nursing interventions: Justification Independent nursing interventions: Evaluation After 8 hours of nurse-patient intervention, the patient was be able to:
Medical Diagnosis: COPD in AE, Varicelle infection Assessment Data Actual/Abnormal Cues: Patient verbalized, kis.a budlayan ko mag-ginhawa na daw indi gid maayo ang akon baga. Productive cough Respiratory rate of 26 cpm tachypnic; with irregular rhythm of the rise and fall of chest. Nursing Diagnosis Impaired gas exchange r/t ventilation perfusion imbalance as evidenced by dyspnea, productive cough, abnormal respiratory rate and rhythm, and abnormal arterial blood gas values. Rationale Predisposing factors: - Old age (82 years old) - Gender: Male Precipitating factors: - History of cigarette smoking - Environmental exposure to outdoor air pollution - Upper respiratory tract infection entrance of pathologic agents in conjunction with harmful pollutants Irritation of the airways causing inflammation Bodys compensatory mechanism release histamine, histamine and prostaglanidin Increase capillary permeability
1.1 Assess respirations: quality, rate, pattern, depth and breathing effort.
Definition: Excess or deficit in Arterial Blood Gas oxygenation and/or results: decrease pH= CO2 elimination at 7.235 (abnormal) and the alveoli-capillary increase PCO2= 47.2 membrane meq/dL (abnormal) Risk Factors: Poor ventilation and hot weather condition in the ward. Strengths: Strong spiritual Source: Nursing Care Plan 6th Ed by Doenges, et al pp 800-801
1.1 Rapid, shallow breathing and hypoventilation affect gas exchange by affecting CO2 levels. Flaring of the nostrils, dyspnea, use of accessory muscles, tachypnea and /or apnea are all signs of severe distress that require immediate intervention.
1.2 Monitor vital signs.
1.2 Initially with hypoxia and hypercapnia blood pressure (BP), heart rate and respiratory rate all increase. As the condition becomes more severe BP may drop, heart rate continues to be rapid with arrhythmias and respiratory failure may
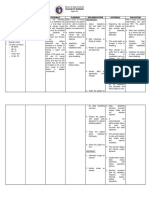
belief Good family support Disciplined Good compliance to treatment regimen Willingness to change Cooperation
Fluid and cellular exudation Decrease O2 and CO2 passage Impaired gas exchange r/t ventilation perfusion imbalance Source: Crib, N. (2008, 26 November). Pathophysiology of COPD. Retrieved August 30, 2012, from http://nursingcrib.com/ pathophysiology/ pathophysiology-ofchronic-bronchitis-copd/
ensue. 1.3 Auscultated breath sounds noting crakles, wheezes 1.3 Reveals presence of pulmonary congestion/ collection of secretion, indicating need for further intervention. 1.4 For mobilization of secretions.
1.4 Maintain adequate intake and output but avoid fluid overload
2. Verbalize understanding of causative factors and appropriate intervention.
1.5 Elevated head of bed/ position client appropriately, provide airway adjuncts and suction as indicated. 2.1 Discuss implications of smoking related to illness/ condition
1.5 To maintain airway
2.1 Smoking is the leading cause of COPD which accounts for high mortality rate.
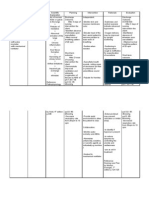
2.2 Discuss reasons for allergy testing when indicated. Review individual drug regimen and ways of dealing with side effects. 2.3 Reinforce need for
2.2 To rule out allergy to the prescribed drug and prevent complications. Enforce knowledge for patients benefit.
adequate rest while encouraging activities and exercise.
2.3 To decrease dyspnea and improve quality of life.
3. Participate in the treatment regimen within the level of ability/situation.
2.4 Emphasize importance of nutrition most especially high protein foods such as fish, milk, green leafy vegetables and fruits.
2.4 To repair damage tissues and improve stamina.
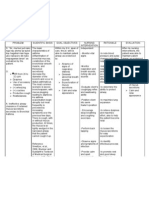
3.1 Encouraged frequent deep breathing/ coughing exercises.
3.1 Promotes optimal chest expansion and drainage of secretions.
3.2 Pace activities and provide rest periods to prevent fatigue.
3.2 Even simple activities, such as bathing, can increase oxygen consumption and cause fatigue.
Collaborative interventions: 1.1 Administer prescribed meds by the physician such as Budesonide and Combivent via
Collaborative interventions: 1.1 To loosen secretions of the airways thus improving gas exchange.
inhalation.
Вам также может понравиться
- NCP - Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент1 страницаNCP - Impaired Gas ExchangeRryje Salleva100% (1)
- Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент2 страницыImpaired Gas ExchangeHanya Bint PotawanОценок пока нет
- Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент5 страницImpaired Gas ExchangeKM67% (3)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance For PneumoniaДокумент5 страницNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance For PneumoniaKullin Rain100% (1)
- NCP For Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент2 страницыNCP For Impaired Gas ExchangeSweetie Star94% (16)
- Copd NCPДокумент16 страницCopd NCPSuperMaye100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент1 страницаNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceImation DataОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент1 страницаNursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceLei OrtegaОценок пока нет
- Impaired Gas Exchange R/T Ventilation-Perfusion Imbalance Care PlanДокумент2 страницыImpaired Gas Exchange R/T Ventilation-Perfusion Imbalance Care PlanCristina Centurion100% (10)
- NCP Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент2 страницыNCP Impaired Gas ExchangeGabriel Tolentino70% (10)
- NCP Impaired Gas Exchange STROKEДокумент2 страницыNCP Impaired Gas Exchange STROKEMa. Elaine Carla TatingОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент1 страницаNursing Care Plan Impaired Gas Exchangecuicuita100% (3)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmДокумент2 страницыIneffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmReylan Garcia100% (4)
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern - NCPДокумент2 страницыIneffective Breathing Pattern - NCPHsintan HsuОценок пока нет
- Impaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPДокумент1 страницаImpaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPKaycee BinanОценок пока нет
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент4 страницыNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceMary Joyce Limoico100% (1)
- NCP-Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент13 страницNCP-Ineffective Airway ClearancePaulo Manlangit86% (22)
- Mapagod at Manghina" As: Nursing Care Plan (NCP) For A Patient With AsthmaДокумент2 страницыMapagod at Manghina" As: Nursing Care Plan (NCP) For A Patient With AsthmaKian Herrera100% (1)
- NCP Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент4 страницыNCP Impaired Gas ExchangeKen Simon100% (1)
- NCP TBДокумент6 страницNCP TBGrhace Aquino100% (3)
- NURSING CARE PLAN Alvarez - Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент2 страницыNURSING CARE PLAN Alvarez - Impaired Gas ExchangeNader AbdurasadОценок пока нет
- Asthma Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент2 страницыAsthma Impaired Gas ExchangeNedeve Ozned100% (5)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Excessive Mucus Production COPDДокумент7 страницNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Excessive Mucus Production COPDMa. Elaine Carla Tating67% (3)
- NCP - CopdДокумент3 страницыNCP - CopdhystericoОценок пока нет
- NCP Difficulty of Breathing R/T SecretionДокумент3 страницыNCP Difficulty of Breathing R/T Secretionherscentasiascribd50% (8)
- Impaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaДокумент2 страницыImpaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaAngel Cabatingan100% (4)
- Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент2 страницыImpaired Gas Exchangeiloveanne87% (30)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance (Retained Secretions)Документ1 страницаIneffective Airway Clearance (Retained Secretions)Danna Tan50% (2)
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To Bronchospasm, Decreased Lung ExpansionДокумент2 страницыIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To Bronchospasm, Decreased Lung ExpansionReylan Garcia43% (7)
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance (Bronchi)Документ2 страницыNursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance (Bronchi)deric94% (17)
- NCP Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент1 страницаNCP Impaired Gas ExchangeLaidy Aizahlyn Indoc Angod0% (3)
- NCP - Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент2 страницыNCP - Impaired Gas Exchangejanelee2824Оценок пока нет
- NCP Ineffective Breathing Pattern TalaДокумент1 страницаNCP Ineffective Breathing Pattern TalaJhen Bitco Fidel70% (10)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternДокумент8 страницIneffective Breathing PatternJansen Arquilita Rivera100% (2)
- NCP Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент2 страницыNCP Impaired Gas ExchangeCharissa Magistrado De LeonОценок пока нет
- Pneumonia-Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент2 страницыPneumonia-Ineffective Airway ClearanceNursesLabs.com86% (7)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternДокумент3 страницыIneffective Breathing PatternTrixie Anne Gamotin100% (3)
- NCP BaiaeДокумент7 страницNCP BaiaeJonathan Delos ReyesОценок пока нет
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент1 страницаIneffective Airway ClearancejomerdalonaОценок пока нет
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Lung Impairment PNEUMOTHORAXДокумент5 страницNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Lung Impairment PNEUMOTHORAXMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (2)
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansДокумент7 страниц6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansShaina Fe RabaneraОценок пока нет
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBДокумент3 страницыNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (1)
- Activity Intolerance NCPДокумент3 страницыActivity Intolerance NCPGen RodriguezОценок пока нет
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент2 страницыNCP Ineffective Airway Clearanceniomi0884% (31)
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент22 страницыNursing Care Planaln00550% (2)
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент2 страницыNursing Care PlanAl RizkyОценок пока нет
- Pneumonia Concept MapДокумент11 страницPneumonia Concept Mapiz11100% (3)
- NCPДокумент3 страницыNCPKrizelle Abadesco Libo-on50% (2)
- CopdДокумент47 страницCopdNingshesil Ny HermantОценок пока нет
- NCP Proper 1Документ6 страницNCP Proper 1Noreen PinedaОценок пока нет
- Case Analysis Bronchial AsthmaДокумент21 страницаCase Analysis Bronchial AsthmaKim LladaОценок пока нет
- Competencymr McdougalcopdДокумент17 страницCompetencymr Mcdougalcopdmac_rymrt7569Оценок пока нет
- Nutrition and Respiratory Diseases PDFДокумент53 страницыNutrition and Respiratory Diseases PDFliggiedy100% (1)
- Plenary Discussion Scenario 3Документ8 страницPlenary Discussion Scenario 3RifaiОценок пока нет
- Research Paper Topics For Respiratory TherapyДокумент6 страницResearch Paper Topics For Respiratory Therapyvehysad1s1w3100% (1)
- ABC NursingДокумент24 страницыABC NursingvengielОценок пока нет
- Josue, Stephanie Canlas Batch 51 Reaction Paper Respiratory FailureДокумент1 страницаJosue, Stephanie Canlas Batch 51 Reaction Paper Respiratory FailureSTEPHANIE JOSUEОценок пока нет
- COPD Concept MapДокумент2 страницыCOPD Concept MapJilian McGugan100% (9)
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Документ21 страницаChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)MudrekaОценок пока нет
- Heart Failure NCPДокумент9 страницHeart Failure NCPMiriam EstradaОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of The Holy Spirit: Derek PrinceДокумент4 страницыThe Gifts of The Holy Spirit: Derek PrinceMauricio Rojas ValdiviaОценок пока нет
- Slides Surgical Instruments Update 1.7Документ43 страницыSlides Surgical Instruments Update 1.7Paul Christian P. Santos, RN100% (32)
- MSPPP 12913337842396 Phpapp01Документ26 страницMSPPP 12913337842396 Phpapp01RI NAОценок пока нет
- Bloom's TaxonomyДокумент26 страницBloom's TaxonomyRene John FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Scientific Death of JesusДокумент7 страницScientific Death of JesusRene John FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Potassium ChlorideДокумент2 страницыPotassium ChlorideRene John Francisco0% (1)
- Basic Delivery Set (Nullipara)Документ1 страницаBasic Delivery Set (Nullipara)Rene John FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study (Seretide)Документ1 страницаDrug Study (Seretide)Rene John Francisco100% (1)
- Facts of The RealityДокумент11 страницFacts of The RealityRene John FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study For Paracetamol, Omeprazole and Vitamin B ComplexДокумент3 страницыDrug Study For Paracetamol, Omeprazole and Vitamin B ComplexMichelle Manibale R.N100% (4)
- Omeprazole and Polynerv (B1,6,12)Документ3 страницыOmeprazole and Polynerv (B1,6,12)Rene John Francisco100% (1)
- NCP-Impaired Physical Mobility - E+ ImbalanceДокумент3 страницыNCP-Impaired Physical Mobility - E+ ImbalanceRene John FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsДокумент14 страницDrug Study On Emergency DrugsRene John FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study - MirceraДокумент2 страницыDrug Study - MirceraRene John FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study (Combivent)Документ2 страницыDrug Study (Combivent)Rene John Francisco100% (3)
- Diazepam, Lanoxin, Hemostan, NaprexДокумент6 страницDiazepam, Lanoxin, Hemostan, NaprexRene John Francisco100% (1)
- Drug Study (Budesonide)Документ1 страницаDrug Study (Budesonide)Rene John Francisco33% (3)
- NCP - Risk For InjuryДокумент3 страницыNCP - Risk For InjuryRene John FranciscoОценок пока нет
- NCP - Acute PainДокумент3 страницыNCP - Acute PainRene John Francisco0% (1)
- All Kinds of DrugsДокумент11 страницAll Kinds of DrugsRene John Francisco100% (1)
- XIV. References: EditionДокумент1 страницаXIV. References: EditionRene John FranciscoОценок пока нет
- XIV. References: For Collaboratice Care, 5 Ed. USA: Elsevier, IncДокумент1 страницаXIV. References: For Collaboratice Care, 5 Ed. USA: Elsevier, IncRene John FranciscoОценок пока нет
- NCP - Impaired Tissue IntegrityДокумент3 страницыNCP - Impaired Tissue IntegrityRene John FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Kurukshetra University Civil Engineering Syllabus For 8th SemesterДокумент7 страницKurukshetra University Civil Engineering Syllabus For 8th SemesterabhinavsinghliveОценок пока нет
- 5262 Foster Wheeler Oxy-Combustion Materials Robertson) MarДокумент19 страниц5262 Foster Wheeler Oxy-Combustion Materials Robertson) MarMahmoud Abou KhattabОценок пока нет
- ACEA Engine Oil in ShortДокумент2 страницыACEA Engine Oil in ShortRajiv SrivastavaОценок пока нет
- Position Paper Mexico EcosocДокумент2 страницыPosition Paper Mexico Ecosocjprateek140Оценок пока нет
- Clean Development Mechanism Explained: EfficientcarbonДокумент22 страницыClean Development Mechanism Explained: EfficientcarbonanilminhansОценок пока нет
- Best Management Practices For Treating Waste Polyester-Resin and GelcoatДокумент4 страницыBest Management Practices For Treating Waste Polyester-Resin and GelcoatTaraknath MukherjeeОценок пока нет
- JJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJ: FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF FFFJJJFFJJFJFFJJFJДокумент11 страницJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJ: FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF FFFJJJFFJJFJFFJJFJAyansa ErgibaОценок пока нет
- Oil Record Book InstructionsДокумент6 страницOil Record Book InstructionsNamal Fernando100% (1)
- Apex Manual 5.10.2013Документ101 страницаApex Manual 5.10.2013Suresh KumarОценок пока нет
- Annex 2 - EPR Negorci - Gevgelija - ENG - FINAL PDFДокумент146 страницAnnex 2 - EPR Negorci - Gevgelija - ENG - FINAL PDFvlatkoodgranitОценок пока нет
- Sumesh Sir CFBC Log SheetДокумент2 страницыSumesh Sir CFBC Log SheetSIPL CPPОценок пока нет
- Planning For Environment Sustainability: RPK 238 Sustainable Development PlanningДокумент27 страницPlanning For Environment Sustainability: RPK 238 Sustainable Development PlanningJohn ChaiОценок пока нет
- Env. Sci AssignmentДокумент8 страницEnv. Sci AssignmentSyed NaqeeОценок пока нет
- Essay On EnvironmentДокумент5 страницEssay On Environmentshanesawada67% (3)
- Reduce Research PaperДокумент17 страницReduce Research PaperTata Duero LachicaОценок пока нет
- Acetic AnhydrideДокумент5 страницAcetic AnhydrideChern YuanОценок пока нет
- Impact of Induction Motor On EnvironmentДокумент11 страницImpact of Induction Motor On EnvironmentUsama HabibОценок пока нет
- Internal Combustion EngineДокумент13 страницInternal Combustion EngineNAITAJIОценок пока нет
- Cce 408Документ4 страницыCce 408Neetor TendekayiОценок пока нет
- Ultra Low Nox Conventional and Regenerative Burner Retrofits: September 2015Документ11 страницUltra Low Nox Conventional and Regenerative Burner Retrofits: September 2015Gabriel AlbornozОценок пока нет
- 11 Advanced WB T3 2021-2022 Unit 8Документ13 страниц11 Advanced WB T3 2021-2022 Unit 8Fatimah HussainОценок пока нет
- Inorganic BindersДокумент4 страницыInorganic Bindersadeniyi-sam100% (1)
- A1188 - R0962 - PER - Volume 1Документ193 страницыA1188 - R0962 - PER - Volume 1Geoff HunterОценок пока нет
- Tintaya FinalДокумент44 страницыTintaya Finalapi-276979938Оценок пока нет
- Kruger Kaldness - Ras For Salmon - NorwayДокумент4 страницыKruger Kaldness - Ras For Salmon - Norwayfshirani7619Оценок пока нет
- Problem Statement DraftДокумент4 страницыProblem Statement Draftapi-491319450Оценок пока нет
- 50% Construction Documents: Jacobs Medical Center East Campus Bed TowerДокумент35 страниц50% Construction Documents: Jacobs Medical Center East Campus Bed TowerSoumitra GuptaОценок пока нет
- NSTP ResearchДокумент2 страницыNSTP ResearchKaye PurificacionОценок пока нет
- Grundfos Submersible Wastewater Pump - With Grinder - SEGДокумент16 страницGrundfos Submersible Wastewater Pump - With Grinder - SEGGeorge CobraОценок пока нет
- CV ThomasBooth EngДокумент3 страницыCV ThomasBooth EngThomas BoothОценок пока нет