Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Lactic Acid Was Isolated and Refined For The First Time by The Swedish Chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele in 1780 From Sour Milk
Загружено:
Namaku WahyuИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lactic Acid Was Isolated and Refined For The First Time by The Swedish Chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele in 1780 From Sour Milk
Загружено:
Namaku WahyuАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lactic Acid
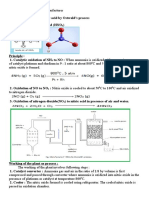
Lactic acid was isolated and refined for the first time by the Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele in 1780 from sour milk. In 1856, Louis Pasteur discovered Lactobacillus and its role in the making of lactic acid. Lactic acid started to be produced commercially by the German pharmacy Boehringer Ingelheim in 1895. Lactic acid is found primarily in sour milk products, such as koumiss, laban, yogurt, kefir, and some cottage cheeses. The casein in fermented milk is coagulated (curdled) by lactic acid. Methane Converting methane to H2 In the chemical industry, methane is converted to synthesis gas, a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, by steam reforming. This endergonic process (requiring energy) utilizes nickel catalysts and requires high temperatures, around 7001100 C: CH4 + H2O CO + 3 H2 Related chemistries are exploited in the Haber-Bosch Synthesis of ammonia from air, which is reduced with natural gas to a mixture of carbon dioxide, water, and ammonia. Industrial Hydrogen production Commercial bulk hydrogen is usually produced by the steam reforming of natural gas.[75] At high temperatures (10001400 K, 7001100 C or 13002000 F), steam (water vapor) reacts with methane to yield carbon monoxide and H2. CH4 + H2O CO + 3 H2
Posphorous Hening Brand experimented with urine, which contains considerable quantities of dissolved phosphates from normal metabolism. His process originally involved letting urine stand for days until it gave off a terrible smell. Then he boiled it down to a paste, heated this paste to a high temperature, and led the vapours through water, where he hoped they would condense to gold. Instead, he obtained a white, waxy substance that glowed in the dark. Brand had discovered phosphorus, the first element discovered since antiquity. We now know that Brand produced ammonium sodium hydrogen phosphate, (NH4)NaHPO4. While the quantities were essentially correct (it took about 1,100 L of urine to make about 60 g of phosphorus), it was unnecessary to allow the urine to rot. Later scientists would discover that fresh urine yielded the same amount of phosphorus and improved Brand's process by using sand in the reaction (still using urine as base material), 4 NaPO3 + 2 SiO2 + 10 C 2 Na2SiO3 + 10 CO + P4 methane Laboratory synthesis Methane can also be produced by the destructive distillation of acetic acid in the presence of soda lime or similar. Acetic acid is decarboxylated in this process. Methane can also be prepared by reaction of aluminium carbide with water or strong acids. cryogenics In physics, cryogenics is the study of the production of very low temperature (below 150 C, 238 F or 123 K) and the behavior of materials at those temperatures. Etymology The word cryogenics stems from Greek and means "the production of freezing cold"; however, the term is used today as a synonym for the low-temperature state. It is not welldefined at what point on the temperature scale refrigeration ends and cryogenics begins, but most scientists[2] assume it starts at or below -150 C or 123 K (about -240 F). The National Institute of Standards and Technology at Boulder, Colorado has chosen to consider the field of cryogenics as that involving temperatures below 180 C (-292 F or 93.15 K). This is a logical dividing line, since the normal boiling points of the so-called permanent gases (such as helium, hydrogen, neon, nitrogen, oxygen, and normal air) lie below 180 C while the Freon refrigerants, hydrogen sulfide, and other common refrigerants have boiling points above 180 C.
Вам также может понравиться
- Hyster H80XM K005Документ646 страницHyster H80XM K005André Targino75% (4)
- HCLДокумент8 страницHCLRahul MathurОценок пока нет
- CO2 ProductionДокумент111 страницCO2 ProductionGhufran SaeedОценок пока нет
- Applied ChemistryДокумент10 страницApplied ChemistryAngelОценок пока нет
- Production of Ammonia: Sunny ChawlaДокумент6 страницProduction of Ammonia: Sunny ChawlapsshnkrОценок пока нет
- ChemistryДокумент18 страницChemistrysudharsan saiОценок пока нет
- Lect. 2Документ5 страницLect. 2xa53dasОценок пока нет
- Go 5 Ammonia, Sulphuric Acid, Nitric AcidДокумент21 страницаGo 5 Ammonia, Sulphuric Acid, Nitric AcidcikaifaОценок пока нет
- Sulfur and Sulfuric AcidДокумент24 страницыSulfur and Sulfuric AciddhavalОценок пока нет
- 20 Elements and 10 Compounds Relevant To H.R.M: By: Danica MacalalagДокумент51 страница20 Elements and 10 Compounds Relevant To H.R.M: By: Danica MacalalagJorge TinayaОценок пока нет
- Modern Chemical ManufacturerДокумент8 страницModern Chemical ManufacturerUltra Gamer (sishant)Оценок пока нет
- Instant Download Financial Accounting Tools For Business Decision Making 8th Edition Kimmel Test Bank PDF Full ChapterДокумент32 страницыInstant Download Financial Accounting Tools For Business Decision Making 8th Edition Kimmel Test Bank PDF Full Chapterphuhilaryyact2100% (9)
- Carbon Dioxide: CarbohydrateДокумент14 страницCarbon Dioxide: CarbohydratePratik AgajОценок пока нет
- Carbonated Drinks: Western WorldДокумент11 страницCarbonated Drinks: Western WorldJanno GironellaОценок пока нет
- Uses of Sulphuric AcidДокумент14 страницUses of Sulphuric AcidFaizul FaiiziОценок пока нет
- The Mystery of Causticum PDFДокумент8 страницThe Mystery of Causticum PDFMd Jakir HossainОценок пока нет
- Instant Download College English and Business Communication 10th Edition Camp Solutions Manual PDF Full ChapterДокумент33 страницыInstant Download College English and Business Communication 10th Edition Camp Solutions Manual PDF Full ChapterJenniferKellyisfp100% (9)
- Transition Element: The Use of Catalyst in IndustryДокумент9 страницTransition Element: The Use of Catalyst in Industrycuksam27Оценок пока нет
- Hydrochloric Acid ProductionДокумент23 страницыHydrochloric Acid ProductionOnSolomon100% (1)
- HCL 4D4Документ11 страницHCL 4D4Pratik AgajОценок пока нет
- Fischer-Tropsch ProcessДокумент5 страницFischer-Tropsch ProcessBilal Arif100% (1)
- Chem Lab NotesДокумент5 страницChem Lab NotesEyvette GoОценок пока нет
- GEN - Chem. Group 7 Reaction of Organic CompoundsДокумент18 страницGEN - Chem. Group 7 Reaction of Organic CompoundsBeatrice Demonice KimОценок пока нет
- Kamar TimbalДокумент6 страницKamar TimbalAl Akil100% (1)
- Chemistry ProjectДокумент2 страницыChemistry ProjectkhyushiОценок пока нет
- Industrial GasesДокумент56 страницIndustrial GasesnadyahginiceОценок пока нет
- Saminar Report: Hydrogen Is A Chemical Element With Symbol H and Atomic Number 1. With A StandardДокумент25 страницSaminar Report: Hydrogen Is A Chemical Element With Symbol H and Atomic Number 1. With A Standardved prakash raoОценок пока нет
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentДокумент5 страницNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentSangam GuptaОценок пока нет
- Sodium Carbonate: NA COДокумент44 страницыSodium Carbonate: NA COMg HОценок пока нет
- Fischer Tropsch - Process 2Документ14 страницFischer Tropsch - Process 2bryan lillibridgeОценок пока нет
- Alkenes: 1. From Dehydration of AlcoholДокумент14 страницAlkenes: 1. From Dehydration of AlcoholPratik TimalsinaОценок пока нет
- Nitric Acid ProductionДокумент15 страницNitric Acid Productiontariq fareedОценок пока нет
- Como CapitalДокумент2 страницыComo CapitalWilder GomezОценок пока нет
- Ind Chem Chapter OneДокумент11 страницInd Chem Chapter OneYareda GeОценок пока нет
- General Chemistry-Non-Metals OxygenДокумент4 страницыGeneral Chemistry-Non-Metals OxygenMarvin IdigaОценок пока нет
- CHM Flio HAHA FAILДокумент26 страницCHM Flio HAHA FAILLoi Reng TeckОценок пока нет
- Soda Ash ProductionДокумент10 страницSoda Ash Productionimjaral75% (4)
- Literature Survey of Oxalic Acid ProductionДокумент8 страницLiterature Survey of Oxalic Acid Productionvarun singhОценок пока нет
- Thionyl Chloride ReactionsДокумент7 страницThionyl Chloride ReactionsMaxim MaximovОценок пока нет
- Production of Sulfuric AcidДокумент29 страницProduction of Sulfuric Aciddeshaka11Оценок пока нет
- Soda Ash ReportДокумент13 страницSoda Ash ReportKaranОценок пока нет
- HCLДокумент13 страницHCLHussein AlkafajiОценок пока нет
- Sulfur and Sulfuric AcidДокумент20 страницSulfur and Sulfuric AcidZakia LuthfianaОценок пока нет
- Manufacturing of Sulfuric Acid by Lead Chamber Process and Contact ProcessДокумент14 страницManufacturing of Sulfuric Acid by Lead Chamber Process and Contact ProcessDian Eka FajriyantoОценок пока нет
- Sulfuric AcidДокумент14 страницSulfuric AcidAkh KreshnaОценок пока нет
- Industrial Acids and Bases NotesДокумент4 страницыIndustrial Acids and Bases NotesEilyza AballaОценок пока нет
- Industrial Acids: I. Properties of AcidsДокумент4 страницыIndustrial Acids: I. Properties of AcidsEilyza AballaОценок пока нет
- Hydrogen: For XI STD ChemistryДокумент139 страницHydrogen: For XI STD ChemistryVed PrakashОценок пока нет
- Chemical Properties of Carbon CompoundsДокумент7 страницChemical Properties of Carbon CompoundsAnonymous HLkNDToОценок пока нет
- Dynamic EquilibriumДокумент9 страницDynamic EquilibriumettyoОценок пока нет
- Water GasДокумент3 страницыWater GaschristopheОценок пока нет
- Chemical Process Industries: Industrial GasesДокумент5 страницChemical Process Industries: Industrial GasesjantskieОценок пока нет
- Chapter-17 Modern Chemical ManufacturersДокумент10 страницChapter-17 Modern Chemical Manufacturersraeesandip10Оценок пока нет
- Unit 14 HydrocarbonsДокумент63 страницыUnit 14 Hydrocarbonsnischalghising16Оценок пока нет
- Hydrogen Chloride 2023Документ9 страницHydrogen Chloride 2023Parthap D DattaОценок пока нет
- Process For The Manufacturing of Copper SulphateДокумент3 страницыProcess For The Manufacturing of Copper Sulphaterajesh80% (5)
- Fischer TropschДокумент9 страницFischer Tropschpranavaggarwal05sepОценок пока нет
- Nitrogen Products: Ariziel Ruth D. MarquezДокумент9 страницNitrogen Products: Ariziel Ruth D. MarquezPaolo GochingcoОценок пока нет
- Group 6-SODA ASH ProductionДокумент20 страницGroup 6-SODA ASH ProductionOghale OmuaborОценок пока нет
- HCLДокумент8 страницHCLlalit shakhaОценок пока нет
- A Further Investigation of the Symmetrical Chloride of Paranitroorthosulphobenzoic AcidОт EverandA Further Investigation of the Symmetrical Chloride of Paranitroorthosulphobenzoic AcidОценок пока нет
- ATT III - 2. Use Internal Communication SystemsДокумент9 страницATT III - 2. Use Internal Communication Systemsedwin90276Оценок пока нет
- Schering Bridge For Capacitance MeasurementДокумент11 страницSchering Bridge For Capacitance MeasurementERI0% (2)
- Is 10028 3 1981 PDFДокумент27 страницIs 10028 3 1981 PDFManoj MishraОценок пока нет
- Physical Chemistry-Problems and Solutions-1 - MiesslerДокумент836 страницPhysical Chemistry-Problems and Solutions-1 - MiesslerAKHILA MОценок пока нет
- Molarity and Polarity Report ChemistryДокумент23 страницыMolarity and Polarity Report ChemistryLydia Mae S. Ela100% (1)
- Virial Equation of StateДокумент9 страницVirial Equation of StateSaba ArifОценок пока нет
- Crompton GrevesДокумент4 страницыCrompton Grevesabhinav4440Оценок пока нет
- Final Report IOCL GuwahatiДокумент17 страницFinal Report IOCL GuwahatiSonu KumarОценок пока нет
- MEROXДокумент8 страницMEROXZubyr AhmedОценок пока нет
- Welding ParametersДокумент34 страницыWelding ParametersmilindОценок пока нет
- Laporan Praktik Mesin ListrikДокумент4 страницыLaporan Praktik Mesin ListrikFatimah azzahraОценок пока нет
- Auma Sa 07.2-Sa 16.2....Документ56 страницAuma Sa 07.2-Sa 16.2....Q Llanos HenryОценок пока нет
- PC-1 Form of SharifДокумент3 страницыPC-1 Form of SharifujjancricketОценок пока нет
- Exploring Science Edition © Pearson Education Limited 2008Документ2 страницыExploring Science Edition © Pearson Education Limited 2008Victor Barber SanchisОценок пока нет
- Internship Report WaterДокумент54 страницыInternship Report WaterEphrem Gizachew100% (1)
- Revision For Final Exam - Unit 5Документ8 страницRevision For Final Exam - Unit 5Nam TửОценок пока нет
- PRD 104 Archivo Ingeteam Inc Wind Catalogue May 2013 Low ResДокумент32 страницыPRD 104 Archivo Ingeteam Inc Wind Catalogue May 2013 Low ResAII2013Оценок пока нет
- 3.3 Diesel Engine Manual Gi1ek1Документ136 страниц3.3 Diesel Engine Manual Gi1ek1Ljupco RistovskiОценок пока нет
- Chapter25 PDFДокумент8 страницChapter25 PDFElizabeth DouglasОценок пока нет
- General Knowledge For General PaperДокумент14 страницGeneral Knowledge For General PaperLilian LimОценок пока нет
- Troubleshooting and Service Manual 120V-240VДокумент48 страницTroubleshooting and Service Manual 120V-240Vkloberg123Оценок пока нет
- Test116 3 PlusansДокумент5 страницTest116 3 PlusansAvnish GargОценок пока нет
- John Yesua S. Hermo From BSME 2-1: Easy Eda Mini ProjectДокумент2 страницыJohn Yesua S. Hermo From BSME 2-1: Easy Eda Mini ProjectRaymond Carreon DomingoОценок пока нет
- Presentation: Modes of TransportationДокумент16 страницPresentation: Modes of Transportationranjeet1ranaОценок пока нет
- ORTON - Company Profile 31-12-09Документ14 страницORTON - Company Profile 31-12-09Fabrizio DelledonneОценок пока нет
- MCQ For Midsem - Ind - Inst.Документ5 страницMCQ For Midsem - Ind - Inst.Nirav ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Inert GasДокумент3 страницыInert Gasankitshr09Оценок пока нет
- G5 Low Profile Unit Cooler Ver 2.0Документ10 страницG5 Low Profile Unit Cooler Ver 2.0Wawan NuryanaОценок пока нет
- Hydraulics 2 Part I: Orifices, Weirs & Tubes: Polytechnic University of The PhilippinesДокумент99 страницHydraulics 2 Part I: Orifices, Weirs & Tubes: Polytechnic University of The Philippinesacurvz2005Оценок пока нет