Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Module-78A: Sewage and Sewerage Treatment, Quantity and Characteristics of Wastewater
Загружено:
jhacademyhydОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Module-78A: Sewage and Sewerage Treatment, Quantity and Characteristics of Wastewater
Загружено:
jhacademyhydАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Sub: Environmental Engineering
Topic : Waste water Engineering
MODULE- 78A
Sewage and sewerage treatment, quantity and characteristics of wastewater.
___________________________________________________________________________ Sullage: This refers to the waste water generated from bathrooms, kitchens, washing place and wash basins etc. composition of this waste does not involve higher concentration of organic matter and it is less polluted water as compared to sewerage. Sewage: It indicates the liquid waste originating from the domestic uses of water. It includes Sullage, discharge from toilets, urinals, waste water generated from commercial establishments, institutions, industrial establishments and also the ground water, storm water that may enter into the sewers. Its decomposition produces large quantities of malodorous gases and it contains numerous pathogenic bacteria, along with concentration of organic matter and suspended solids. Domestic sewage: Consists of liquid wastes originations from urinals, bathrooms, kitchen sinks, wash basins etc. Industrial sewage: Liquid wastes originating from industrial processes of various industries like dying, paper making etc. Aerobic decomposition: If air or oxygen is available freely to waste water is dissolved form than the biodegradable organic matter will undergo aerobic decomposition, caused by aerobic bacteria as well as by facultative bacteria. This bacterium utilizes the free oxygen as electron acceptor, there by oxidizing the organic matter to stable and unobjectionable end products. Nitrogenous organic matter Carbonaceous organic matter Sulphurous organic matter Anaerobic decomposition: If free dissolved oxygen is not available to the sewage, then anaerobic decomposition, called putrefaction will occur. Anaerobic bacteria as well as facultative bacteria operating anaerobically will then flourish and convert the complex organic matter into simpler organic compounds of nitrogen, carbon and sulphur. Nitrogenous organic matter Carbonaceous organic matter Sulphurous organic matter
JH ACADEMY
Page 1
Sub: Environmental Engineering Aerobic bacteria: Flourish in presence of oxygen Anaerobic bacteria: Flourish in absence of oxygen
Topic : Waste water Engineering
Facultative bacteria: can operate either as aerobically or as anaerobically. Characteristics of sewage: 1. Physical characteristics: a) Turbidity: Measured by turbidity rod or turbidity meter. b) Color: Black in color indicates state of decomposition. c) Odour: Measured as Thresold odour number. TON, which represents the extent of dilution required to just make the sample free of odour. d) Temperature: It has an effect on the biological activity of bacteria present in sewage and it also affects the solubility of gases in sewage. 2. Chemical characteristics: a) Total solids, suspended solids, Settleable solids, dissolved solids. Total solids: Determined by evaporation Suspended solids: Determined by using 1 pore filters. Dissolved solids: Total - suspended. Suspended solids= volatile solids + fixed solids. Loss of weight due to burning of suspended solids is called volatile solids and residue is called fixed solids. b) Settleable solids: Can be determined by Imhoff cone. The capacity of the cone is 1 litre and it is graduated up to about 50ml. sewage is allowed to stand in this cone for a period of 2 hours and the quantity of solids can be measured. c) PH value: The efficiency of certain treatment methods depends upon the availability of a suitable PH value. d) Chloride content: Normal chloride content of sewage is 120 indicate mixing of industrial wastes. . Higher values
e) Nitrogen content: Nitrogen is in four forms: 1. free ammonia 2. Organic nitrogen 3. Nitrites 4. Nitrates. Free ammonia indicates quantity of nitrogen present in sewage before the decomposition of organic matter is started. The nitrites indicate the presence of partly decomposed organic matter. Nitrates indicate the presence of fully oxidized organic matter. In drinking water nitrates should be less than 45mg/ . Excess of nitrates causes blue baby or methamoblobinamia disease in children. f) Presence of fats, oils and greases: It interferes with treatment process like filtration so needs to be removed.
g) Sulphides, sulphates & lines.
gas: Cause smell and corrosion of concrete sewer
JH ACADEMY
Page 2
Sub: Environmental Engineering
Topic : Waste water Engineering
h) Dissolved oxygen: (DO): Determined by Winklers method. While discharging into streams, do in sewage must be more than 4ppm to protect fish. i) Chemical oxygen demand: Oxygen required to completely matter to , and other oxidized species. oxidize the organic
j) Total organic carbon: Known concentrations of chemical components in waste water will enable us to calculate carbon content present in sewage.
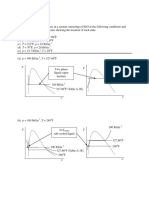
Bio chemical oxygen demand BOD: The amount of oxygen required to decompose the organic matter present in sewage is called BOD. : BOD during 5 days at = D.O consumed by diluted sample Consumed dilution factor Amount of organic matter Present at time t L= Ultimate BOD. BO
Integrating At t=0, =L C=
= 2.3
JH ACADEMY
Page 3
Sub: Environmental Engineering
Topic : Waste water Engineering
= = ]
( )
where
BOD at time t= L =L[
( )
De-oxygenation constant ]
.[
Population equivalent: Relative stability S=
It is the ratio of oxygen available in effluent to the total oxygen required to satisfy first stage BOD.
JH ACADEMY
Page 4
Вам также может понравиться
- Engineering Standard Specification For Steam TracingДокумент53 страницыEngineering Standard Specification For Steam Tracingkaruna346100% (1)
- Sewage Disposal and TreatmentДокумент268 страницSewage Disposal and TreatmentAMANUEL WORKU100% (3)
- Ion Exchange Resins and Adsorbents in Chemical Processing: Second EditionОт EverandIon Exchange Resins and Adsorbents in Chemical Processing: Second EditionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- 51CДокумент6 страниц51Cjhacademyhyd100% (5)
- 45CДокумент8 страниц45Cjhacademyhyd100% (4)
- Sand Slurry TestДокумент5 страницSand Slurry TestAnkit Singh100% (1)
- Stone Blower 1Документ22 страницыStone Blower 1kbaker001Оценок пока нет
- Unit-5. Examination of WastewaterДокумент26 страницUnit-5. Examination of WastewaterIshwar singh DhamiОценок пока нет
- Dr. Ramakrishna Bag Dept of Civil Engineering NIT RourkelaДокумент18 страницDr. Ramakrishna Bag Dept of Civil Engineering NIT RourkelaJon JimmyОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ81 страницаChapter 3ashu100% (1)
- Waste Water TreatmentДокумент4 страницыWaste Water TreatmentAuguestina Maria JosephineОценок пока нет
- Notes Sem IV Microbiology PII U2Документ19 страницNotes Sem IV Microbiology PII U2nebex12Оценок пока нет
- Lecture 9 - Water PollutionДокумент42 страницыLecture 9 - Water PollutionCiara Crew100% (1)
- Bharati Vidyapeeth Deemed University, Pune Department of Chemical EngineeringДокумент18 страницBharati Vidyapeeth Deemed University, Pune Department of Chemical EngineeringSnehal Dawkhar patilОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Industrial Wastewater TreatmentДокумент91 страницаChapter 1 Industrial Wastewater TreatmentSophie LvОценок пока нет
- BlaДокумент264 страницыBlaReymandha Aprilia Hutami100% (1)
- Project Report On Waste Water TreatmentДокумент35 страницProject Report On Waste Water TreatmentSami Zama100% (1)
- Unit 1. Itroduction To Wastewater TreatmentДокумент28 страницUnit 1. Itroduction To Wastewater Treatmentsssshekhar100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Quality of WastewaterДокумент39 страницChapter 3 Quality of Wastewatershiksha gauliОценок пока нет
- Environmental Chemistry: Presented By: Javaid HassanДокумент4 страницыEnvironmental Chemistry: Presented By: Javaid Hassansehrish duuraniОценок пока нет
- EWC 333 Introduction To Wastewater EngineeringДокумент24 страницыEWC 333 Introduction To Wastewater EngineeringAzgar AliОценок пока нет
- Wastewater - Types, Characteristics & RegulationДокумент50 страницWastewater - Types, Characteristics & Regulationsam samОценок пока нет
- Wastewater Characteristics1Документ23 страницыWastewater Characteristics1Gajendra KumarОценок пока нет
- Chapter - 5 Characteristics and Treatment of SewageДокумент72 страницыChapter - 5 Characteristics and Treatment of SewageUnHKОценок пока нет
- Physical, Chemical and Biological Characteristics of WastewaterДокумент27 страницPhysical, Chemical and Biological Characteristics of WastewaterRushed AlamaОценок пока нет
- Physical, Chemical and Biological Characteristics of WastewaterДокумент28 страницPhysical, Chemical and Biological Characteristics of WastewaterRushed AlamaОценок пока нет
- Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) (Closed Reflux Method)Документ8 страницChemical Oxygen Demand (COD) (Closed Reflux Method)hayder alaliОценок пока нет
- Siddharth Final Mini ProjectДокумент15 страницSiddharth Final Mini ProjectAnurag yadavОценок пока нет
- Practical-Characteristics of Waste WaterДокумент19 страницPractical-Characteristics of Waste WatersarfaОценок пока нет
- Lec 8 (Wastewater Characteristics)Документ29 страницLec 8 (Wastewater Characteristics)MiansyedNawabОценок пока нет
- Wastewater CharacteristicsДокумент64 страницыWastewater CharacteristicsRicamaeОценок пока нет
- Oxygen Demand Biological and ChemicalДокумент45 страницOxygen Demand Biological and ChemicalBailey Torres100% (1)
- Chapter # 7 Characteristics and Analysis of SewageДокумент32 страницыChapter # 7 Characteristics and Analysis of Sewagebashir ahmadОценок пока нет
- Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD)Документ35 страницBiochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD)wahyu hidayatОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7. Water QualityДокумент34 страницыChapter 7. Water QualityCheng Chiv Ïï100% (1)
- Wastewater Treatment PlantДокумент8 страницWastewater Treatment PlantAira Mae MisolaОценок пока нет
- Bod Cod Toc - Gaman HiteshДокумент29 страницBod Cod Toc - Gaman HiteshDevendra SharmaОценок пока нет
- IntroductionДокумент15 страницIntroductionDeepak SahОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4Документ25 страницChapter 4Siraj mojОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Introduction To Wastewater EngineeringДокумент27 страницChapter 2 Introduction To Wastewater Engineeringkheng weiОценок пока нет
- Biotechnology MaterialДокумент83 страницыBiotechnology MaterialIkha Setya AminatiОценок пока нет
- Chep3 pdf2Документ35 страницChep3 pdf2BEZU A.GERESUОценок пока нет
- Operators - Water and Wastewater Treatment Plant and System Operators Manage A System ofДокумент9 страницOperators - Water and Wastewater Treatment Plant and System Operators Manage A System ofElmer RemediosОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 PDFДокумент4 страницыChapter 5 PDFNiraj KhanalОценок пока нет
- Chapter One WWTДокумент30 страницChapter One WWTsintayehu sirahbizuОценок пока нет
- Water and WastewaterДокумент41 страницаWater and WastewaterRushanth ChandraboseОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Sewage Treatment PlantДокумент3 страницыChapter 5 Sewage Treatment PlantJasleneDimarananОценок пока нет
- Sustainable Production: Effluent Treatment PlantДокумент12 страницSustainable Production: Effluent Treatment PlantKush SharmaОценок пока нет
- Presentationn Chapter 9 Water QualityxДокумент34 страницыPresentationn Chapter 9 Water Qualityxlerato guguОценок пока нет
- CEB707 - 8 - Wastewater Quality and QuantityДокумент16 страницCEB707 - 8 - Wastewater Quality and QuantityalexОценок пока нет
- LECTURE - 18 - CDB 3044 - Environmental Studies - Waste Water TreatmentДокумент51 страницаLECTURE - 18 - CDB 3044 - Environmental Studies - Waste Water TreatmentOng Jia YeeОценок пока нет
- Cod and BodДокумент57 страницCod and Boddinesh kumarОценок пока нет
- Q. Enumerate The Undesirable Characteristics of Industrial Wastewater??????Документ14 страницQ. Enumerate The Undesirable Characteristics of Industrial Wastewater??????Sudipta kumar muduliОценок пока нет
- Biochemical Oxygen Demand: by DR Utpal Sharma Assist. Professor Department of Community Medicine, SMIMSДокумент24 страницыBiochemical Oxygen Demand: by DR Utpal Sharma Assist. Professor Department of Community Medicine, SMIMSZaman RaiОценок пока нет
- Chapter One: Introduction To Environment ManagementДокумент32 страницыChapter One: Introduction To Environment ManagementMahmudul Hasan DulalОценок пока нет
- Case Study For Soap Waste WaterДокумент6 страницCase Study For Soap Waste WaterKari ConwayОценок пока нет
- Potable Water From Industrial Wastewater: M. S. AliДокумент4 страницыPotable Water From Industrial Wastewater: M. S. AliEr Omkar Ravindra MhatreОценок пока нет
- Document TitleДокумент8 страницDocument Titlehusam mahdiОценок пока нет
- Chapter IДокумент9 страницChapter ISulOgikpcОценок пока нет
- Objective of The Environment LabДокумент14 страницObjective of The Environment LabAsma FayyazОценок пока нет
- The Odor Treatment Methods of Wastewater Treatment Plant Based On Biological Oxidation ProcessДокумент6 страницThe Odor Treatment Methods of Wastewater Treatment Plant Based On Biological Oxidation ProcessFabio RibeiroОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Treatment Processes: Wastewater (Sewage)Документ66 страницChapter 1: Introduction To Treatment Processes: Wastewater (Sewage)ashe zinabОценок пока нет
- Sewage Treatment Is A Multi-Stage ProcessДокумент14 страницSewage Treatment Is A Multi-Stage ProcessHiten AhujaОценок пока нет
- RankersДокумент2 страницыRankersjhacademyhydОценок пока нет
- JH Academy: Gate-2014 4Th Year StudentsДокумент2 страницыJH Academy: Gate-2014 4Th Year StudentsjhacademyhydОценок пока нет
- JH Academy: Gate-2014 4Th Year StudentsДокумент2 страницыJH Academy: Gate-2014 4Th Year StudentsjhacademyhydОценок пока нет
- JH Academy: Gate-2014 4Th Year StudentsДокумент2 страницыJH Academy: Gate-2014 4Th Year StudentsjhacademyhydОценок пока нет
- JH Academy: Gate-2014 4Th Year StudentsДокумент2 страницыJH Academy: Gate-2014 4Th Year StudentsjhacademyhydОценок пока нет
- RankersДокумент2 страницыRankersjhacademyhydОценок пока нет
- RankersДокумент2 страницыRankersjhacademyhydОценок пока нет
- Is 4968 (Iii) 1976Документ16 страницIs 4968 (Iii) 1976jhacademyhydОценок пока нет
- 50CДокумент6 страниц50Cjhacademyhyd89% (9)
- F First Revision: Method For Subsurface So-Und-Ing For SoilsДокумент11 страницF First Revision: Method For Subsurface So-Und-Ing For SoilsAbhijeet SwainОценок пока нет
- 4968 1Документ12 страниц4968 1Amardeep Singh MultaniОценок пока нет
- 43CДокумент17 страниц43Cjhacademyhyd100% (4)
- Test 1Документ2 страницыTest 1jhacademyhydОценок пока нет
- 44CДокумент9 страниц44Cjhacademyhyd100% (3)
- Test 5Документ2 страницыTest 5jhacademyhydОценок пока нет
- Test 3Документ2 страницыTest 3jhacademyhyd100% (1)
- Module-55A: Sub: Water Resources Engineering Topic: Fluid Mechanics & HydraulicsДокумент2 страницыModule-55A: Sub: Water Resources Engineering Topic: Fluid Mechanics & HydraulicsjhacademyhydОценок пока нет
- TEST-6: Sub: Fluid Mechanics Module: 63-66Документ2 страницыTEST-6: Sub: Fluid Mechanics Module: 63-66jhacademyhydОценок пока нет
- Test 2Документ2 страницыTest 2jhacademyhydОценок пока нет
- 3BДокумент2 страницы3Bjhacademyhyd100% (1)
- Test 2Документ2 страницыTest 2jhacademyhydОценок пока нет
- 1BДокумент5 страниц1BjhacademyhydОценок пока нет
- Module-72A: Design Of: Lined and Unlined Canals, Waterways, Head Works, Gravity Dams and SpillwaysДокумент4 страницыModule-72A: Design Of: Lined and Unlined Canals, Waterways, Head Works, Gravity Dams and SpillwaysjhacademyhydОценок пока нет
- Module-87A: Sub: Transportation Engineering Topic: Highway PlanningДокумент9 страницModule-87A: Sub: Transportation Engineering Topic: Highway PlanningjhacademyhydОценок пока нет
- Module-74A: Sub: Water Resources Engineering Topic: Irrigation EngineeringДокумент3 страницыModule-74A: Sub: Water Resources Engineering Topic: Irrigation EngineeringjhacademyhydОценок пока нет
- Module-73A: Sub: Water Resources Engineering Topic: Irrigation EngineeringДокумент6 страницModule-73A: Sub: Water Resources Engineering Topic: Irrigation EngineeringjhacademyhydОценок пока нет
- Module-88A: Sub: Transportation Engineering Topic: Highway PlanningДокумент4 страницыModule-88A: Sub: Transportation Engineering Topic: Highway PlanningjhacademyhydОценок пока нет
- Module 66aДокумент7 страницModule 66ajhacademyhydОценок пока нет
- S2K14 SBU1 PIP DOC 1003 Pipe Class SpecificationДокумент7 страницS2K14 SBU1 PIP DOC 1003 Pipe Class SpecificationvivekpecОценок пока нет
- AC Mix DesignДокумент28 страницAC Mix DesignAishAdiyatmaОценок пока нет
- Rigid Electrical Steel ConduitДокумент2 страницыRigid Electrical Steel ConduitBuckОценок пока нет
- Lava Heat Italia - Lava Lite KD Patio Heater - Owners ManualДокумент23 страницыLava Heat Italia - Lava Lite KD Patio Heater - Owners ManuallavaheatitaliaОценок пока нет
- Beam Design To BS 5400 Part 3Документ6 страницBeam Design To BS 5400 Part 3Tamil SelviОценок пока нет
- Containers and Closures of Parenteral ProductДокумент2 страницыContainers and Closures of Parenteral ProductCarlos Alberto Bayona LópezОценок пока нет
- Borgianni, de Filippis - Gasification Process of Wastes Containing PVCДокумент7 страницBorgianni, de Filippis - Gasification Process of Wastes Containing PVCJorge VeraОценок пока нет
- CatalogДокумент482 страницыCatalogAnonymous 6EW2MsFbkОценок пока нет
- Uses of The Elements and Compounds in Our Daily LifeДокумент4 страницыUses of The Elements and Compounds in Our Daily LifeTaibah Nurwahidah Mohamad89% (9)
- enДокумент40 страницenRegistr Registr91% (11)
- SBRG Air Filter Brochure PDFДокумент24 страницыSBRG Air Filter Brochure PDFSBRGОценок пока нет
- RC 15Документ1 страницаRC 15Vicces P. EstradaОценок пока нет
- 6 DZM 20 Electric MotorbikeДокумент3 страницы6 DZM 20 Electric Motorbikebaban aloОценок пока нет
- Lincoln Electric Pro Cut 80Документ39 страницLincoln Electric Pro Cut 80ArturoОценок пока нет
- Dramix 3d 8060bl-8060blДокумент1 страницаDramix 3d 8060bl-8060blcsillag janosОценок пока нет
- Service Bulletin DDДокумент5 страницService Bulletin DDjohn wrightОценок пока нет
- Rock Tunneling Methods: 1. Drill and Blast MethodДокумент14 страницRock Tunneling Methods: 1. Drill and Blast MethodAnish Pathak100% (1)
- Using Waste Plastic Bottles As AdditiveДокумент6 страницUsing Waste Plastic Bottles As AdditiveGyanna LlenaresasОценок пока нет
- NL User Manual Nord Lock WashersДокумент7 страницNL User Manual Nord Lock Washersmohit_mgОценок пока нет
- A Banjo BuildingДокумент20 страницA Banjo BuildingRégis MoewiusОценок пока нет
- Water Distribution System Specifications: St. Charles County Public Water Supply District NO. 2Документ45 страницWater Distribution System Specifications: St. Charles County Public Water Supply District NO. 2muhammad iqbalОценок пока нет
- The World of Chemistry Video Guide SetДокумент10 страницThe World of Chemistry Video Guide SetrkvОценок пока нет
- GlazingДокумент81 страницаGlazingAnjalySinhaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8: Failure: How Do Materials Break?Документ40 страницChapter 8: Failure: How Do Materials Break?Leann FarleyОценок пока нет
- Aluminium Alloy 6061Документ3 страницыAluminium Alloy 6061choobyОценок пока нет
- Course Specs Mar Power CHEDДокумент13 страницCourse Specs Mar Power CHEDClark LlameraОценок пока нет
- ME 231 Montazami Whharris 9-10-18 SOLUTIONДокумент4 страницыME 231 Montazami Whharris 9-10-18 SOLUTIONEduardo Perez UriegasОценок пока нет