Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
SHIATS - Metch Geotech PDF
Загружено:
thadikkaranОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
SHIATS - Metch Geotech PDF
Загружено:
thadikkaranАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
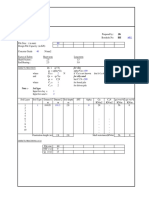
Department of Civil Engineering
M. Tech Geotechnical Engineering
Basic Supporting Courses
Course Code Course Name L T P Credits
COMP-805 MAS-781 CE-705
Computer Programming Advance Engineering Mathematics Finite Element & Finite Difference Methods Total
2 2 2
0 1 1
1 0 1
3 3 4 10
Core Courses
Course Code Course Name L T P Credits
CE-701 CE-707 CE-708 CE-780 CE-718 CE-880 CE899
Theory of Elasticity & Visco Elasticity
Advanced Geotechnical Engg-1 Geotechnical Processes Seminar-I Advanced Geotechnical Engg-2 Seminar-II Thesis Total
3 3 3 0 3 0 0
0 1 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 1 0 1 15
3 4 3 1 4 1 15 31
Specialized Courses
CE-820 CE-819 CE-818 CE-821 CE-822 CE-823 Soil Exploration, Testing And Evaluation Structural design of foundation Reinforced Soil Structure Earthquake Geotechnical Engg Fuzzy Logic and its Application in Civil Engineering Rock Engineering 0 3 3 3 3 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 2 3 3 3 3 3
CE-824 CE-825 CE-826 CE-827 CE-828 CE-829 CE-830 CE-831 CE-832
Analysis and Design of Pavements Computer Methods in geotechnical Engineering Clay Mineralogy and Expansive Soil Ground Modification and Land Reclamation. Advanced Environmental Engineering Geoinformatics Pile Foundation Stability of Slopes Advanced Fluid Mechanics and Ground Water Engineering
3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
M.Tech. (All Branches) Computer Programming Comp-805 Credits: 3(2+0+2)
1. Algorithms & Flow Charts 2. C Programming (i) Preliminaries (ii) Constants & Variables (iii) Arithmetic Expressions (iv) Input-Output Statements (v) Control Statements (vi) Looping Statements (vii) Subscripted Variables (viii) Elementary Format Specifications (ix) Logical Statements & Decision Tables (x) Functions & Subroutines 3. Computer Oriented Numerical Methods (a) Solution of Non Linear Equation (i) Bisection Method (ii) Newton Method (b) Numerical Integration (i) Trapezoidal Method (ii) Simpsons 1/3 & 3/8 rule (c) Curve Fitting (i) Construction of forward, backward difference table (ii) Interpolation 4. Application of statistical packages
Reference Books:
Let Us C by Yashwant Kanetkar BPB publications Computer Oriented Numerical Methods by R. S. Salaria, Khanna Book Publishing Co. Practical List: 1. To find the largest among three numbers 2. To check whether a given string is a palindrome or not. 3. To find factorial of a given number by iteration. 4. To find whether the given integer is a prime number. 5. To find sum of n terms of series: a. n n*2/2! + n*3/3! - n*4/4! + .............. 6. To find sum and average of n integers using a linear array. 7. To read n numbers from the keyboard and display these numbers in the reverse order their entry. 8. To search a given number within a linear array. 9. To generate the fibbonacci series. 10. To find factorial of a given number using a function. 11. To deduce error involved in polynomial equation. 12. To Find out the root of the Algebraic and Transcendental equations using Bisection, Regula-falsi, Newton Raphson and Iterative Methods. Also give the rate of convergence of roots in tabular form for each of these methods. 13. To implement Newtons Forward and Backward Interpolation formula.
ADVANCE ENGINEERING MATHMATICS
MAS-781
3(2-1-0)
Runge- Kutta methods derivation, error bounds and error estimates. Weak stability theory form Runge-kutta methods. Order and convergence of the general explicit one step methods. Linear multi step methods- derivation, order consistency, zero stability and convergence. Predictorcorrector methods, stiff system. Polynomial ring over fields, extension of fields, Computation in GF(q), root fields of polynomials, Vector field over finite field, binary group codes, hamming codes, polynomials codes, the structure of cyclic codes, quadratic residue codes, reed Mueller Codes, Simplex codes. Review of basic linear algebra, canonical factorization, Q-forms. Courant- Fischer minmax and related theorem. Matrix stability, Inequalities, g-inverse (A-, Am, A+). Direct, iterative, projection and rotation mretho0ds for solving linear system and eigen value problems, application.
FINITE ELEMENT & FINITE DIFFERENCE METHOD
CE-705
4(2-1-2)
Finite Element Technique. Derivation of the elemental characteristics, condensation technique, conformable and non-conformable fields. Application of the method to plane stress and plane strain problems. Asymmetric and three dimensional bodies. Plate bending problems. Dams, frames, shear walls, grid floors and rafts. Derivation of difference relations. Richardsons extrapolation. Application of the Finite Difference Method to beam, buckling, vibration, plate and seepage. Flow Net and Flow Distribution problems. References: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Finite Element Method for Engineers and scientists O.C.Zienkiewicz Numerical Methods in Finite Element Analysis K.J.Bathe & E.L.Wilson Matrix Computations for Engineers & scientists Alan Jennings Introduction to Finite Element Method C.S.Desai & J.F.Abel Finite Element Method in Engineering S.S. Rao
THEORY OF ELASTICITY AND VISCO ELASTICITY
CE-701
3(3-0-0)
Analysis of stress, components of stress invariants, principal stresses, equations of equilibrium, stress transformation formulae, boundary conditions.
Analysis of strain, components of strain displacement relationship, strain invariants, principal strain, strain transformation formulae, compatibility equation. Strain Stress relations of elasticity, basic assumptions, isotropy, homogeneity, continuity, generalized Hook's law, formulation of elasticity problems, existence and uniqueness of solution, Saint Venant's principle, strain energy Plane stress/strain problems, airy stress function, governing differential equation, problems in rectangular coordinates, bending of beams, and comparison with solution from bending theory. Plane stress/plane strain problems in polar coordinate, equilibrium strain displacement, compatibility equations, stress concentration around holes in plates, stresses in rotating disks. Torsion of noncircular section, St.Venant's theory, Warping function, membrane analogy, Solution for rectangular, elliptical/triangular sections, torsion of thin walled closed and open sections. Yielding and various yield criterion, yield surface, Haigh- Westergard stress space, loading and unloading, plastic stress-strain relation/equations, Tresca criterion, General derivation of stress strain relation. Plasticity: Yielding and various yield criteria, yield surface, Haigh- Wesetergard stress space subsequent yield surface, loading and unloading, plastic stress-strain relations. Visco elasticity: Introduction to linear theory of viscoelasticity. Visco-elastic method, constitutive relations, correspondence principle. References 1. Theory of Elasticity - Timoshenko & Goodier 2. Elasticity and Plasticity Flugges. S. 3. Applied Elasticity -Wang.C.T.
ADVANCED GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING 1
CE-707
4(3-1-0)
Soil aggregate and classification; Clay mineralogy; Permeability, Steady state flow, Seepage, Flow nets, Design of filters. Shear strength of cohesive and cohesion less soils: Stress-Strain
behaviour, Drained and undrained shear strength of soils; Stress-pore pressure relationships; Critical void ratio. Stress paths; Relationships between effective stress-water content; Hvorslev's strength parameters. Transient Flow: 1D and generalised consolidation theories, Primary and secondary consolidation settlements; Corrections to 1-d consolidation settlements; Stress path method for settlement computations
GEOTECHNICAL PROCESSES
CE-708
3(3-0-0)
Dewatering,/Methods sumps and ditches, well point systems, deep well sumps, sheeting and open plumbing, electro osmosis, theory and analysis of groundwater lowering, choice, and design of dewatering system. Grouting, Purpose, Impermeability, consolidation, grouting classification, grouting materials, grouting pattern, selection of grouts, method of grouting and grouting pressure. Field test to check the effectiveness. Compaction, factors affecting compaction of soils, field compaction, field control tests. Stabilization, Necessity, mechanism, effects of engineering properties, design and construction techniques of soil cement, soil line, soil asphalt, soil chemical, mechanical, thermal and electroosmotic stabilization. Special techniques, vibrofloatation, compaction by impact, sand drain, stone columns, sand lime cement columns, compaction pile. Reinforced earth, Materials, application and design.
ADVANCED GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING - II CE-718
4(3-1-0)
Foundation classification; Choice of foundations; Bearing capacity and settlement analysis of shallow foundations like footings and rafts, Deep foundations like piles, piers and Caissons; Foundations on expansive soils, laterites, fills and rock; Construction aspects of foundations; Shoring and underpinning; Groundwater lowering and drainage; Legal aspects of foundation engineering; Field tests in foundation engineering including instrumentation for monitoring of foundation
SOIL EXPLORATION, TESTING AND EVALUATION CE-820
2(0-0-2)
Soil Exploration, Experiments to determine the shear strength properties of soil. Direct shear test, unconfined compression test, vane shear test. Triaxial shear tests, determination of total and effective stress parameters, determination of compaction and consolidation characteristics.
REINFORCED SOIL STRUCTURES
CE-821
3(3-0-0)
Historical background; Principles, concepts and mechanism of reinforced earth; Design consideration for reinforced earth and reinforced soil structures; Geosynthetics-their composition, manufacture, properties, functions, testing and applications in reinforced earth structures; Design of reinforced soil structures like retaining walls, embankments, foundation beds etc.; Designing for Separation, Filtration, Drainage and Roadway Applications; Designing for Landfill Liners and Barrier Applications; Case histories of applications. Textbooks/References 1. Clayton, C. R. I., Milititsky, J. and Woods, R. I., Earth Pressure and Earth Retaining Structures, Blackie Academic & Professional, 1993. 2. Ingold, T, Reinforced Earth, Thomas Telford Ltd., 1982. 3. Jones, C. J. F. P, Earth Reinforcement and Soil Structures, Butterworth, 1985. 4. Koerner, R. M, Designing with Geosynthetics, Prentice Hall, 1993.
EARTHQUAKE GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
CE-818
3(3-0-0)
Pre-requisites: Dynamics of Soils and Foundations (CE 532)/ Structural Dynamics (CE 504) Earthquake seismology Causes of earthquake, Plate tectonics, Earthquake fault sources, Seismic waves, Elastic rebound theory, Quantification of earthquake, Intensity and magnitudes, Earthquake source models. Earthquake ground motion Seismograph, Characteristics of ground motion, Effect of local site conditions on ground motions, Design earthquake, Design spectra, Development of site specification and code-based design. Ground response analysis One-dimensional ground response analysis: Linear approaches, Equivalent linear approximation of non-linear approaches, Computer code SHAKE. Liquefaction and lateral spreading - Liquefaction related phenomena, Liquefaction susceptibility: Historical, Geological, Compositional and State criteria. Evaluation of liquefaction by cyclic stress and cyclic strain approaches, Lateral deformation and spreading, Criteria for mapping liquefaction hazard zones. Seismic design of foundations, Seismic slope stability analysis: Internal stability and weakening instability and Seismic design of retaining walls. Textbooks/References 1. Kramer S. L, Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering, Prentice Hall, 1996. 2. R. W. Day, Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering Handbook, McGraw-Hill, 2002. 3. Seco e Pinto, Seismic behaviour of ground and Geotechnical structure, A. A. Balkema, 1997. 4. Naeim, F, The Seismic Design Handbook, Kluwer Academic Publication, 2nd Edition, 2001. 5. Bolt, B. A, Earthquakes, W. H. Freeman and Company, 4th Edition, 1999. 6. Lourie, W, Fundamentals of geophysics, Cambridge University press, 1997. 7. Wang J. G. Z. Q and J. K Tim Law , Siting in Earthquake zones, A. A. Balkema, 1994.
8. Ferrito, J. M, Seismic design criteria for soil liquefaction, Tech. Report of Naval Facilities service centre, Port Hueneme, 1997.
ROCK ENGINEERING
CE-823
3(3-0-0)
Pre-requisites: Nil Geological formation of rocks, Structural Geology, Classification of rocks, Physicomechanical properties of rocks, Laboratory and field tests, Stress-strain behaviour, Failure criteria for intact rock and rock masses, Fracture mechanism, Analysis and design of underground openings, Instrumentation in tunnels, Rock support and reinforcement, Foundations on rock, Rock blasting. Textbooks/References 1. Mukerjee, P. K.,A text book of Geology, World Press, 1995. 2. Brady, B. H. G. and Brown, E. T, Rock Mechanics for Underground Mining, Chapman & Hall, 1993. 3. Brown, E. T, Rock Characterisation, Testing and Monitoring, Pergamon Press, 1986. 4. Herget, G, Stresses in Rock, Balkema, 1988. 5. Hoek, E. and Brown, E. T, Underground Excavation in Rock, Institution of Mining and Metallurgy, 1982.. 6. Goodman, R. E, Introduction to Rock Mechanics, John Wiley & Sons, 1989. 7. Bieniawski, Z. T, Engineering Rock Mass Classification, John Wiley and Sons, 1989. 8. Coates, D. F, Rock Mechanics Principles, Canada Centre for Mineral and Energy Technology, 1981. 9. Jaeger, J. C. and Cook, N. G. W, Fundamentals of Rock Mechanics, Champman and Hall, 1976. 10. Wyllie, D. C, Foundations on Rock, E & FN Spon. 2nd Edition,1992.
ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF PAVEMENT
CE-824
3(3-0-0)
Philosophy of design of flexible and rigid pavements, analysis of pavements using different analytical methods, selection of pavement design input parameters traffic loading and volume, material characterization, drainage, failure criteria, reliability, design of flexible and rigid pavements using different methods, comparison of different pavement design approaches, design of overlays and drainage system. Textbooks/References 1. Yang H. Huang, Pavement Analysis and Design, Pearson Prentice Hall, 2004. 2. Yoder and Witzech, Pavement Design, McGraw-Hill, 1982. 3. Sharma and Sharma, Principles and Practice of Highway Engg., Asia Publishing House, 1980. 4. Teng, Functional Designing of Pavements, McGraw- Hill, 1980.
CLAY MINERALOGY AND EXPANSIVE SOIL
CE-826
3(3-0-0)
Origin and occurrence, Weathering and soil formation, clay minerals, composition, classification and nomenclature, non-clay and organic constituents, isomorphism substitution, cation exchange capacity, structure of clay mineral, Kaolinite, Illite and montmorillonite groups, identification by X-ray diffraction, electron microscope, chemical, DT A methods. Clay water relationships, structure of soils effect of cations, Thixotropy, Electrical effects, Electro osmosis and electrophoresis, streaming potentials. Effects of clay minerals on engg. properties of soils, introduction to rheological properties of clay soils. Classification of expansive soils, free swells index property tests, swelling potential, measurement and prediction. Theories of swelling, mechanical concepts, physico chemical and electro chemical theories swell calculation for simple systems. Earth pressure and slope stability, code of practice, stabilization of expansive soils. 1. Foundation on expansive soils-Chen, F.H. 2. Clay mineralogy - Grim R. E. 3. Applied clay mineralogy- Grim R. E. GROUND MODIFICATION AND LAND RECLAMATION CE-827 1. Introduction: Objectives, classification and options of ground improvement 2.Mechanical modification: Introduction, principles of soil densification, properties of compacted soil and compaction control specifications for quality controls. 3.Hydraulic modification: Introduction, objectives, techniques, Dewatering methods, soil 8water relationship, Types of aquifer, Design of Dewatering systems, filtration, drainage and seepage, control, preloading and vertical drains, electro kinetic dewatering and stabilization. 4.Physical and chemical Modification: Modification by admixtures, grouting, and thermal modification. 5. Modification by inclusions and confinement: Soil reinforcement, ground anchorage, and rock bolting soil nailing, crib walls, and gabions. 3(3-0-0)
6. Land reclamation: Hydraulic fills, colliery discard lagoons. Land affected by old mines and open cast mining. Land fill sites of industrial mining, chemical and domestic waste. Derelict sites of former industries. Soft or loose natural soils.
GEOINFORMATICS
CE-829
3(3-0-0)
Remote Sensing Physics of remote sensing, Remote sensing satellites and their data products, Sensors and orbital Characteristics, Spectral reflectance curves for earth surface features, Methods of remotely sensed data interpretation Visual interpretation and Digital image processing, Application of remote sensing in natural resources management Geographic Information System (GIS) Basic concepts of geographic data, GIS and its components, Data acquisition, Raster and Vector formats, Data editing, Spatial modeling, Data output, GIS Applications
Photogrammetry Aerial Photographs Basic terms & Definitions, scales, relief displacements, Flight Planning, Stereoscopy, Characteristics of photographic images, Fundamentals of aerial photointerpretation. Global Positioning System (GPS) Introduction, Satellite navigation System, GPS- Satellite constellation, Space segment, Control segment, User segment, GPS satellite signals, Receivers, Static, Kinematic and Differential GPS
PILE FOUNDATIONS
CE-830
3(3-0-0)
1. PILE CLASSIFICATIONS Function classification of piles Factors governing choice of pile foundation Load transfer principles piling equipments and methods changes in soil condition during installation of piles requirement of code of practice responsibility of engineer and contractor. 2. AXIALLY LOADED PILES AND PILE GROUPS Allowable load evaluation of piles and pile groups Static method cohesive cohesion less soil time effects Dynamic method pile driving formulae Wave equation application modeling theoretical analysis Interpretation of field test results and pile load test results
Settlement of Piles and Pile groups. 3. LATERAL AND UPLIFT LOAD EVALUATION Piles subjected to Lateral loads Broms method, elastic p-y curve analyses Batter piles response to moment pile subjected to uplift loads load deformation behaviour Lateral and uplift load test data interpretation. Foundation on weak compressible collapsible soil case studies. 4. STRUCTURAL DESIGN OF PILE AND PILE GROUPS Pile foundation structural design pile cap analysis, pile raft system basic interactive analysis pile and pile groups subjected to vibrations fundamental solutions.
REFERENCES : 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Das, B.M., Principles of Foundation Engineering, Design and Construction, PWS., Publishing, 1999 (Fourth Edition) Cernica, J.N. Geotechnical Engineering Foundation Design, John Wiley and Sons, Inc. 1995. Poulos, H.G., Davis, E.H., Pile foundation analysis and design, John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1980. Tomlinson, M.J. Foundation engineering, ELBS, Longman Group, U.K. Ltd., England 1995. Bowles, J.E., Foundation Analysis and Design, McGraw Hill book Company, 1996. Winterkorn, H.F. and Fang, H.Y Foundation Engineering Handbook, Von Nostrand Reinhold, 1994. Tomlinson, M.J., Pile design and construction practice, Cement and concrete association, 1977 CE-831 3(3-0-0)
STABILITY OF SLOPES
Natural and manmade slopes, types of slope movements and landslides, Nature of soil and rock progressive failure of slopes. Limit equilibrium methods, Planar Failure surface and slip surface of arbitrary shape. Some special aspects of slope analysis i.e., Earthquakes, Creep, Anisotropy, initial stresses. Probabilistic approach in slope analysis. Centrifuge model testing. References: 1. Slope stability-Chaudary, R. N.
2. Earth and Earth rock dams-Sherard, Woodward, Gizienski & Cleverages. 3. Earth and rockfill dam Engineering - Sowers G.F. and Sally. H.N.
ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA FOR THE M. TECH PROGRAMME: Candidates must have consistently good academic record and minimum of first class or equivalent in B.E./B.Tech in Civil Engineering.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- NEC Work Information GuidanceДокумент38 страницNEC Work Information Guidancethadikkaran100% (2)
- Directional DrillingДокумент24 страницыDirectional DrillingRanjith Premadasan100% (5)
- Earthquakes PresentationДокумент18 страницEarthquakes PresentationDeepak Lalwani100% (1)
- Bored Pile Installation RecordДокумент1 страницаBored Pile Installation RecordthadikkaranОценок пока нет
- GeogridBridge1 1Документ5 страницGeogridBridge1 1thadikkaranОценок пока нет
- Incheon-A4 World Record TestДокумент2 страницыIncheon-A4 World Record TestthadikkaranОценок пока нет
- Subsurface Conditions and Canal Stability BollesДокумент9 страницSubsurface Conditions and Canal Stability BollesthadikkaranОценок пока нет
- Foundation EQ Design Requirements C7Документ28 страницFoundation EQ Design Requirements C7thadikkaranОценок пока нет
- Case Study Delayed Failure of A Deep Cutting in Lodgement TillДокумент10 страницCase Study Delayed Failure of A Deep Cutting in Lodgement TillthadikkaranОценок пока нет
- Moisture in Pavements and Design SA EmeryДокумент83 страницыMoisture in Pavements and Design SA EmerythadikkaranОценок пока нет
- Weldgrip: Double Twisted Hexagonal PVC Coated MeshДокумент0 страницWeldgrip: Double Twisted Hexagonal PVC Coated MeshthadikkaranОценок пока нет
- Career ExplorerДокумент82 страницыCareer Explorerthadikkaran100% (1)
- CR and Galvanized Steel PDFДокумент6 страницCR and Galvanized Steel PDFthadikkaranОценок пока нет
- Piles Supported Embankment PDFДокумент20 страницPiles Supported Embankment PDFthadikkaran100% (1)
- FBE Coating PDFДокумент12 страницFBE Coating PDFthadikkaran100% (1)
- Embankments On Organic Soils SurchargeДокумент9 страницEmbankments On Organic Soils SurchargethadikkaranОценок пока нет
- Pv1202-Soil Test ReportДокумент51 страницаPv1202-Soil Test Reportgohilnarendra0% (1)
- Oedometer Test: Soil Mechanics 2 CE PC 504Документ26 страницOedometer Test: Soil Mechanics 2 CE PC 504SumanHaldarОценок пока нет
- Advance Foundation Engineering Design Principles PDFДокумент61 страницаAdvance Foundation Engineering Design Principles PDFmamoun_hammad7917Оценок пока нет
- Evaluation of Static Liquefaction Potential of SiltyДокумент19 страницEvaluation of Static Liquefaction Potential of SiltyCarlos Francisco Gutiérrez DavilaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8Документ268 страницChapter 8Matthew B. PolingОценок пока нет
- Group 1 Geotech FinalДокумент13 страницGroup 1 Geotech FinalTakudzwa Calvin ChibudaОценок пока нет
- 3 Shallow Foundations-Bearing Capacity-1Документ34 страницы3 Shallow Foundations-Bearing Capacity-1YIAN ZENGОценок пока нет
- 175X175 RC Piles PDFДокумент2 страницы175X175 RC Piles PDFSiva JaseОценок пока нет
- Rock Foundations EM-1110!1!2908Документ120 страницRock Foundations EM-1110!1!2908Maria ValleОценок пока нет
- Clay Mineral of SabahДокумент10 страницClay Mineral of SabahBandilung TzОценок пока нет
- GP - Flyer - Dam MonitoringДокумент2 страницыGP - Flyer - Dam MonitoringOktarianWisnuLusantonoОценок пока нет
- Module 1 Overview of Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering Practice Guidelines Version 1Документ52 страницыModule 1 Overview of Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering Practice Guidelines Version 1Agus Setyo MuntoharОценок пока нет
- Lab Open Ended Dry Sieve AnalysisДокумент9 страницLab Open Ended Dry Sieve Analysiskhairul hisyamОценок пока нет
- Earthquake TheoryДокумент26 страницEarthquake TheoryMaanvendra KholiyaОценок пока нет
- Sample of Geotechnical ReportДокумент17 страницSample of Geotechnical ReportyassinaОценок пока нет
- FoundationДокумент43 страницыFoundationNel PaganaОценок пока нет
- GEO Publication No. 1 - 2009Документ78 страницGEO Publication No. 1 - 2009Gunnar KumarОценок пока нет
- Advanced Offshore EngineeringДокумент8 страницAdvanced Offshore EngineeringVikas KatiyarОценок пока нет
- Lecture 31Документ13 страницLecture 31alfredomotaОценок пока нет
- ENGR 340 - Foundations 3 - Ashlock - SchaeferДокумент36 страницENGR 340 - Foundations 3 - Ashlock - SchaeferSnaz_nedainОценок пока нет
- Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering: Suresh R. Dash, L. Govindaraju, Subhamoy BhattacharyaДокумент14 страницSoil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering: Suresh R. Dash, L. Govindaraju, Subhamoy BhattacharyaKuntal GhoshОценок пока нет
- Underground Structures During Earthquac Failure Mechanisms ofДокумент13 страницUnderground Structures During Earthquac Failure Mechanisms ofIntishar RahmanОценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes - URM UARMДокумент54 страницыLecture Notes - URM UARMAragon Palac BacquianoОценок пока нет
- Naeim y Kelly 1999 (026-034) Word CorregidoДокумент9 страницNaeim y Kelly 1999 (026-034) Word CorregidoAndreGalvezVillenaОценок пока нет
- Geologist Petrophysicist Geotechnical Engineer in Tulsa OK Resume Elizabeth DickinsonДокумент3 страницыGeologist Petrophysicist Geotechnical Engineer in Tulsa OK Resume Elizabeth DickinsonElizabethDickinsonОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Soil CompositionДокумент15 страницChapter 1 Soil CompositionJemuel Flores100% (1)
- Sheet PileДокумент14 страницSheet PileSara BookerОценок пока нет