Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Pspice For Thevenin and Norton Equivalents Pspice Review
Загружено:
Hanis HabidinИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Pspice For Thevenin and Norton Equivalents Pspice Review
Загружено:
Hanis HabidinАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
PSPICE for Thevenin and Norton Equivalents PSpice Review DC analysis is one of the standard analyses that we can
perform using PSpice. Other standard analyses include transient, AC, and Fourier. Under DC analysis, there are two kinds of simulation that PSpice can e ecute! DC nodal analysis and DC sweep. "n the pre#ious la$ we did DC nodal analysis, $ut now we will look at it in more detail. 1. DC Nodal Anal sis PSpice allows dc nodal analysis to $e performed on sources with an attri$ute of the form DC % #alue and pro#ides the dc #oltage at each node of the circuit and dc $ranch currents if re&uired. 'o #iew dc node #oltages and $ranch currents re&uires adding two kinds of additional parts, shown at right. 'he sym$ol (")*PO"+' is connected to each node at which the #oltage is to $e #iewed, while the sym$ol "P,O-) is connected in the $ranch where the current is to $e displayed. 'his necessitates modifying the schematic. For e ample, let us consider placing #oltage (")*PO"+'S and current "P,O-)S to the schematic shown.
'o add (")*PO"+'S, we take the following steps! .. Click Draw!"et New Part /or type 0Ctrl1234. 5. 'ype (")*PO"+' in the Part -rowser -asic $o . 6. Click O7 /or type 0)nter34. 8. DRA" to locate (")*PO"+' a$o#e (. and C#IC$#. 9. DRA" to locate (")*PO"+' a$o#e ,5 and C#IC$#. :. C#IC$R to end placement mode. 'he figure $elow shows the two #oltage (")*PO"+'S.
Since the "P,O-) sym$ol must $e connected in series with a $ranch element, we need to mo#e ,5 down $y clicking and dragging ,5 and the wires. Once this is done, we add "P,O-) as follows! .. Click Draw!"et New Part /or type 0Ctrl1234. 5. 'ype "P,O-) in the Part -rowser -asic $o . 6. Click %$ /or type 0)nter34. 8. DRA" to locate "P,O-) a$o#e ,5 and C#IC$#. 9. C#IC$R to end placement mode. :. Use wiring to ;oin all gaps.
*e are ready to simulate the circuit. At this point, we must sa#e the schematic. -efore running PSpice, note the following points! .. 'here must $e a reference node or ground connection in the schematic. Any node can $e used as ground, and the #oltages at other nodes will $e with respect to the selected ground. 5. Dependent sources are found in the Parts li$rary. O$tain them $y selecting Draw<2et +ew Part and typing the part name. 'hese are shown at right along with the part name for each type, with the gain. ) is a #oltage1controlled #oltage source with gain e= F is a current1controlled current source with gain f = 2 is a #oltage1 controlled current source with a transconductance gain g= and > is a current1controlled #oltage source with transresistance gain h. 6. -y con#ention, we assume in dc analysis that all capacitors are open circuits and all inductors are short circuits. *e run PSpice $y clicking Anal sis!Si&ulate. 'his in#okes the electric rule check /),C4, which generates the netlist. 'he ),C performs a connecti#ity check on the schematic $efore creating the netlist. 'he netlist is a list descri$ing the operational $eha#ior of each component in the circuit and its connections. )ach line in the netlist represents asingle component of the circuit. 'he netlist can $e e amined $y clicking Anal sis!E'a&ine Netlist from the Schematics window. "f there are errors in the schematic, an error window will appear. Click O7 /or type 0)nter34 to display the error list. After noting the errors, e it from the error list and go $ack to Schematics to correct the errors. "f no errors are found, the system automatically enters PSpice and performs the simulation /nodal analysis4. *hen the analysis is complete, the program displays (ias point calculated, and creates the result<output ?le with e tension .out. *e can also e amine the results of the simulation $y looking at the #alues displayed on the (")*PO"+'S and "P,O-)S parts of the schematics after the simulation is complete. 'he #alues displayed with (")*PO"+'S and "P,O-)S should $e the same as those in the output ?le. @our results should match what you o$tained $y manual calculation pre#iously. DC Sweep DC nodal analysis allows simulation for DC sources with ? ed #oltages or currents. DC sweep pro#ides more Ae i$ility in that it allows the calculation of node #oltages and $ranch currents of a circuit when a source is swept o#er a range of #alues. As in nodal analysis, we assume capacitors to $e open circuits and inductors to $e short circuits. Suppose we desire to perform a DC sweep of #oltage source (. in the figure at right from B to 5B #olts in .1#olt increments.
*e proceed as follows! .. Click Anal sis!Setup. 5. C#IC$# DC Sweep $utton. 6. Click +ame $o and type ( ..
8. Click Start (alue $o and type B. 9. Click )nd (alue $o and type 5B. :. Click "ncrement $o and type .. C. Click O7 to end the DC Sweep dialog $o and sa#e parameters. D. Click Close to end the Analysis Setup menu. 'he DC Sweep dialog $o is shown at right. +otice that the default setting is (oltage Source for the Swept (ar. 'ype, while it is Einear for Sweep 'ype. "f needed, other options can $e selected $y clicking the appropriate $uttons. 'o run DC sweep analysis, click Anal sis!Si&ulate. Schematics will create a netlist and then run PSpice if no errors are found. "f errors are found in the schematic, check for them in the )rror Eist and correct them as usual. "f no errors are found, the data generated $y PSpice is passed to Pro$e. 'he Pro$e window will appear, displaying a graph in which the F a is is $y default set to the DC sweep #aria$le and range, and the @ a is is $lank for now. 'o display some speci?c plots, click Trace!Add in the Pro$e menu to open the Add Traces dialog $o . 'he $o contains traces, which are the output #aria$les /node #oltages and $ranch currents4 in the data ?le a#aila$le for display. Select the traces to $e displayed $y clicking or typing them, and click O7. 'he selected traces will $e plotted and displayed on the screen. As many traces as you want may $e added to the same plot or on different windows. Select a new window $y clicking )indow!New. 'o delete a trace, click the trace name in the legend of the plot to highlight it and click Edit!Delete /or press 0Delete34. Thevenin and Norton Equivalents *e will use dc sweep analysis to ?nd the 'he#enin or +orton e&ui#alent at any pair of nodes in a circuit and the ma imum power transfer to a load.
'o ?nd the 'he#enin e&ui#alent of a circuit at a pair of open terminals using PSpice, we use the schematic editor to draw the circuit and insert an independent pro$ing current source, say, "p, at the terminals. 'he pro$ing current source must ha#e a part name "S,C. *e then perform a DC Sweep on "p, as discussed in Section D.6. 'ypically, we may let the current through "p #ary from B to . A in B..1A increments. After simulating the circuit, we use Pro$e to display a plot of the #oltage across "p #ersus the current through "p. 'he Gero intercept of the plot gi#es us the 'he#enin e&ui#alent #oltage, while the slope of the plot is e&ual to the 'he#enin resistance. 'o ?nd the +orton e&ui#alent in#ol#es similar steps e cept that we insert a pro$ing independent #oltage source /with a part name (S,C4, say, (p, at the terminals. *e perform a DC Sweep on (p and let (p #ary from B to . ( in B..1( increments. A plot of the current through (p #ersus the #oltage across
(p is o$tained using the Pro$e menu after simulation. 'he Gero intercept is e&ual to the +orton current, while the slope of the plot is e&ual to the +orton conductance. 'o ?nd the ma imum power transfer to a load using PSpice in#ol#es performing a dc parametric sweep on the component #alue of ,E in the figure and plotting the power deli#ered to the load as a function of ,E . According to the figure $elow, the ma imum power occurs when ,E % ,'h . Consider the circuit shown $elow. 'he schematic shown on the pre#ious page has $een redrawn so that the #oltage dependent #oltage source is connected as re&uired for PSpice. Use PSpice to ?nd the 'he#enin and +orton e&ui#alent circuits.
'o ?nd the 'he#enin resistance ,'h and 'he#enin #oltage ('h at the terminals a1$ in the circuit, we ?rst use Schematics to draw the circuit as shown a$o#e. +otice that a pro$ing current source "5 is inserted at the terminals. Under Analysis<Setput, we select DC Sweep. "n the DC Sweep dialog $o , we select Einear for the Sweep 'ype and Current Source for the Sweep (ar. 'ype. *e enter "5 under the +ame $o , B as Start (alue, . as )nd (alue, and B.. as "ncrement. After simulation, we add trace (/"5! H 4 from the Pro$e menu and o$tain the plot shown.
From the plot, we o$tain ( 'h % Iero intercept % 5B (,
, 'h % Slope % /5: J 5B4 < . % : Ohms
'o ?nd the +orton e&ui#alent, we modify the schematic $y replacing the pro$ing current source with a pro$ing #oltage source (..
Again, in the DC Sweep dialog $o , we select Einear for the Sweep 'ype and (oltage Source for the Sweep (ar. 'ype. *e enter (. under +ame $o , B as Start (alue, . as )nd (alue, and B.. as "ncrement. *hen the Pro$e is running, we add trace "/(.4 and o$tain the plot.
From the plot, we o$tain "+ % Iero intercept % 6.669 A 2+ % Slope % 6.669 H 6..:9 % B..C S *a'i&u& Power Transfer Use PSpice to ?nd the ma imum power transfer to ,E in the circuit $elow!
*e need to perform a dc sweep on , E to determine when the power across it is ma imum. *e ?rst draw the circuit using Schematics as shown in. Once the circuit is drawn, we take the following three steps to further prepare the circuit for a dc sweep.
'he ?rst step in#ol#es de?ning the #alue of ,E as a parameter, since we want to #ary it. 'o do this! .. DC#IC$# the #alue .k of ,5 /representing , E 4 to open up the Set Attri$ute (alue dialog $o . 5. ,eplace .k with K ,E L and click %$ to accept the change. +ote that the curly $rackets are necessary. 'he second step is to de?ne parameter. 'o achie#e this! .. Select Draw!"et +ew Part<Ei$raries M M M <special.sl$. 5. 'ype PA,AN in the Part+ame $o and click O7. 6. DRA" the $o to any position near the circuit. 8. C#IC$# to end placement mode. 9. DC#IC$# to open up the Part+ame! PA,AN dialog $o .
:. C#IC$# on +AN). % and enter ,E /with no curly $rackets4 in the (alue $o , and CE"C7E Sa#e Attr to accept change. C. C#IC$# on (AEU). % and enter 5k in the (alue $o , and CE"C7E Sa#e Attr to accept change. D. Click %$. 'he #alue 5k in item C is necessary for a $ias point calculation= it cannot $e left $lank. 'he third step is to set up the DC Sweep to sweep the parameter. 'o do this! .. Select Anal sis!Setup to $ring up the DC Sweep dialog $o . 5. For the Sweep Type, select Einear /or Octa#e for a wide range of , E 4. 6. For the Sweep Var. Type, select 2lo$al Parameter. 8. Under the Name $o , enter ,E. 9. "n the Start Value $o , enter .BB. :. "n the End Value $o , enter 9k. C. "n the "ncrement $o , enter .BB. D. Click %$ and Close to accept the parameters. After taking these steps and sa#ing the circuit, we are ready to simulate. Select Anal sis!Si&ulate. "f there are no errors, we select Add 'race in the Pro$e menu and type H (/,5!54"/,54 in the 'race Command $o . O'he negati#e sign is needed since "/,54 is negati#e.P 'his gi#es the plot of the power deli#ered to , E as , E #aries from .BB Ohms to 9 kOhms. *e can also o$tain the power a$sor$ed $y , E $y typing (/,5!54 (/,5!54<,E in the 'race Command $o . )ither way, we o$tain the plot $elow.
"t is e#ident from the plot that the ma imum power is 59B Q*. +otice that the ma imum occurs when , E % . kOhm, as e pected analytically.
Вам также может понравиться
- How To Work On Cadence PspiceДокумент46 страницHow To Work On Cadence PspiceDhruv AgrawalОценок пока нет
- Learn C Programming through Nursery Rhymes and Fairy Tales: Classic Stories Translated into C ProgramsОт EverandLearn C Programming through Nursery Rhymes and Fairy Tales: Classic Stories Translated into C ProgramsОценок пока нет
- 220 PSPICE BJTamp Curve TraceДокумент3 страницы220 PSPICE BJTamp Curve Tracetipo_de_incognitoОценок пока нет
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10От EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10Оценок пока нет
- LTSpice Ac AnalysisДокумент5 страницLTSpice Ac AnalysisJuan PerezОценок пока нет
- Projects With Microcontrollers And PICCОт EverandProjects With Microcontrollers And PICCРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Project Name: Calculator (Algorithm Based)Документ5 страницProject Name: Calculator (Algorithm Based)Amber YounasОценок пока нет
- PSpiceTutorialHKN UMNДокумент15 страницPSpiceTutorialHKN UMNwinowich5813Оценок пока нет
- Even Parity Bit GeneratorДокумент18 страницEven Parity Bit GeneratorKeith FernandesОценок пока нет
- Cse230 s14 h05Документ3 страницыCse230 s14 h05Heather MarshallОценок пока нет
- Advanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionОт EverandAdvanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionОценок пока нет
- Exam 1 EE 371 Summer 2000: University of Washington Department of Electrical EngineeringДокумент6 страницExam 1 EE 371 Summer 2000: University of Washington Department of Electrical EngineeringngeievyiОценок пока нет
- 08a 02 Description-Flood Profile Modeling With A Bridge WorkДокумент3 страницы08a 02 Description-Flood Profile Modeling With A Bridge WorkDragos SalageanОценок пока нет
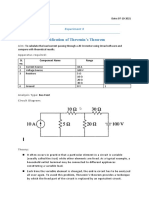
- NAME: - EXPERIMENT 3: Basic TTL Logic Gates (1 Week)Документ7 страницNAME: - EXPERIMENT 3: Basic TTL Logic Gates (1 Week)Melody ArandelaОценок пока нет
- Shaft Alignment - Solved ExamplesДокумент12 страницShaft Alignment - Solved Examplesmane1976100% (3)
- Experiment Guide: RC Filters and Simulation/Instrumentation Software Description and BackgroundДокумент12 страницExperiment Guide: RC Filters and Simulation/Instrumentation Software Description and BackgroundNik Fikrie Nik HusseinОценок пока нет
- Designing An ALU: 2.1 Operations of Our ALUДокумент8 страницDesigning An ALU: 2.1 Operations of Our ALUdarklord338Оценок пока нет
- 211-5OperationalAmplifiers 05Документ10 страниц211-5OperationalAmplifiers 05Kumar ReadarОценок пока нет
- Project Ideas: 1. What Is A PLD?Документ27 страницProject Ideas: 1. What Is A PLD?محمد فصیح آفتابОценок пока нет
- Vlsi Lab Manual FinalДокумент26 страницVlsi Lab Manual FinalAshish SharmaОценок пока нет
- WindTunnelLab Assignment and Laboratory 2012 13 NewДокумент8 страницWindTunnelLab Assignment and Laboratory 2012 13 NewwaleedashrafОценок пока нет
- ADC ConfigurationДокумент4 страницыADC ConfigurationSaritechОценок пока нет
- Designing A Class A Power Amplifier Using The Load-Pull MethodДокумент15 страницDesigning A Class A Power Amplifier Using The Load-Pull MethodNguyen Duc TaiОценок пока нет
- Buku Kerja Praktikal Ej501 PW1-PW3 - JUN 2014 StudentДокумент17 страницBuku Kerja Praktikal Ej501 PW1-PW3 - JUN 2014 StudentAL HxqОценок пока нет
- B.Tech (Computer Engineering) 5th Semester COT-311, ALGORITHM (PR) HandoutsДокумент13 страницB.Tech (Computer Engineering) 5th Semester COT-311, ALGORITHM (PR) HandoutsNehaNehaОценок пока нет
- Linear and Non Linear On PspiceДокумент11 страницLinear and Non Linear On PspiceAseem GhimireОценок пока нет
- LTSpice Tutorial PDFДокумент43 страницыLTSpice Tutorial PDFRasoul Gmdri100% (1)
- BEEE (Experiment 3 and 4)Документ13 страницBEEE (Experiment 3 and 4)Surjosnath Guha ThakurtaОценок пока нет
- DC Analysis Using Orcad CaptureДокумент3 страницыDC Analysis Using Orcad CaptureMatt ImriОценок пока нет
- SPICEДокумент91 страницаSPICESiva YellampalliОценок пока нет
- Exercise4 Using NfSenДокумент31 страницаExercise4 Using NfSenAngel LopezОценок пока нет
- 06 CSL38 Manual LDДокумент68 страниц06 CSL38 Manual LDSwathi N SudarshanОценок пока нет
- EEE111 Multisim ManualДокумент14 страницEEE111 Multisim ManualSHADOW manОценок пока нет
- DISCUSSIONДокумент2 страницыDISCUSSIONMuhd FaizОценок пока нет
- 1998 Robert Woudsma, Upper Canada TechnologiesДокумент11 страниц1998 Robert Woudsma, Upper Canada Technologiesjocansino4496Оценок пока нет
- Nodeb Creation ScriptДокумент14 страницNodeb Creation ScriptMENANI ZineddineОценок пока нет
- Short Tutorial On PSpiceДокумент14 страницShort Tutorial On PSpiceHuỳnh Thanh DưОценок пока нет
- Parallel Port InterfacingДокумент6 страницParallel Port InterfacingYasir AmmarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ23 страницыChapter 1CarolineОценок пока нет
- Logic GatesДокумент15 страницLogic GatesRoland RamirezОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Pspice PDFДокумент7 страницIntroduction To Pspice PDFAseem GhimireОценок пока нет
- Lab1 - Pspce Tutorial and CS AmplifierДокумент15 страницLab1 - Pspce Tutorial and CS AmplifierAdnan HossainОценок пока нет
- Smith ChartsДокумент11 страницSmith ChartsNarayanBadigerОценок пока нет
- ZigbeeДокумент11 страницZigbeeAlexandre MeloОценок пока нет
- Digital Electronics - Logic CircuitsДокумент58 страницDigital Electronics - Logic CircuitsgunapalshettyОценок пока нет
- Ex1 PDFДокумент7 страницEx1 PDFHabib KhanОценок пока нет
- The University of Asia PacificДокумент4 страницыThe University of Asia PacificsabitavabiОценок пока нет
- Statistics 350 Sample Midterm 1: Do Not Turn This Page Until You Are Told To Do So!Документ7 страницStatistics 350 Sample Midterm 1: Do Not Turn This Page Until You Are Told To Do So!ArtificialTruthОценок пока нет
- EE124 Web Site - Introduction To PSPICE: Analyzing The AC Characteristics of The Example CircuitДокумент9 страницEE124 Web Site - Introduction To PSPICE: Analyzing The AC Characteristics of The Example CircuitTonderayi MangaraОценок пока нет
- Digital Circuits: Experiment 2 2012-13/I Combinational Circuits For Binary AdditionДокумент2 страницыDigital Circuits: Experiment 2 2012-13/I Combinational Circuits For Binary AdditionSidhartha Sankar RoutОценок пока нет
- Ieee Pspice - Transient Analysis: Parts Used School Version Student Version Description Name Library Part Name LibraryДокумент9 страницIeee Pspice - Transient Analysis: Parts Used School Version Student Version Description Name Library Part Name LibraryAnonymous eWMnRr70qОценок пока нет
- Lab 1 Introduction and Top-SPICE DemoДокумент10 страницLab 1 Introduction and Top-SPICE Demochrisdp23Оценок пока нет
- Experiment # 01: Introduction To Pspice: Eee 110: Electrical Circuit Simulation LaboratoryДокумент11 страницExperiment # 01: Introduction To Pspice: Eee 110: Electrical Circuit Simulation LaboratoryArifuzzamanFaisalОценок пока нет
- Circuit Analysis Lab TaskДокумент19 страницCircuit Analysis Lab Taskhanif ur rehmanОценок пока нет
- Simulating DC Circuits Using Pspice SoftwareДокумент8 страницSimulating DC Circuits Using Pspice SoftwareAhmar KhanОценок пока нет
- PSPICEДокумент29 страницPSPICEnainaОценок пока нет
- Design Entry CIS-Allegro To Xpedition Design Translation GuideДокумент39 страницDesign Entry CIS-Allegro To Xpedition Design Translation Guidealexandr.k.stuОценок пока нет
- A Where To Learn MoreДокумент8 страницA Where To Learn MoreAmarnath M DamodaranОценок пока нет
- Pspice NotesДокумент123 страницыPspice NotesKeane Foo100% (1)
- Linear and Non Linear On PspiceДокумент11 страницLinear and Non Linear On PspiceAseem GhimireОценок пока нет
- Pe Using PspiceДокумент39 страницPe Using Pspicesujith100% (1)
- 0601pcdm DigitalДокумент69 страниц0601pcdm DigitalJanis KlavinsОценок пока нет
- DC DCconverters 2016Документ9 страницDC DCconverters 2016aaqibОценок пока нет
- Embedded System Industrial TrainingДокумент75 страницEmbedded System Industrial TrainingTechTerms_YoutubeОценок пока нет
- Unit 5 - Simulation of HVDC SystemДокумент24 страницыUnit 5 - Simulation of HVDC Systemkarthik60% (10)
- Choosing A Simulation Tool, 1998.Документ10 страницChoosing A Simulation Tool, 1998.Ali H. NumanОценок пока нет
- Information On Some of The Parts in PSpice LibrariesДокумент8 страницInformation On Some of The Parts in PSpice Librarieshamza abdo mohamoudОценок пока нет
- Appendix F BibliographyДокумент2 страницыAppendix F BibliographySIDDHARTHA SARKARОценок пока нет
- Lab 5: Computer Simulation of RLC Circuit Response Using PspiceДокумент8 страницLab 5: Computer Simulation of RLC Circuit Response Using PspiceRudra MishraОценок пока нет
- Cadence OrCAD 17 - 2 Installation Guide PDFДокумент8 страницCadence OrCAD 17 - 2 Installation Guide PDFRoberto MartinezОценок пока нет
- Competency Demonstration ReportДокумент38 страницCompetency Demonstration ReportTommy Bui57% (7)
- PSPICEДокумент9 страницPSPICEdurgendra100% (2)
- Tina v12 ManualДокумент443 страницыTina v12 ManualYeferson Mauricio Rodriguez RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Ic LM Op Amp PDFДокумент2 страницыIc LM Op Amp PDFAdyPajuraОценок пока нет
- Design Xor Gate in SchematicДокумент5 страницDesign Xor Gate in SchematicAnish BansalОценок пока нет
- Learning MapsДокумент13 страницLearning MapsVinay DMОценок пока нет
- Fresh Graduate Resume SampleДокумент2 страницыFresh Graduate Resume Samplenazira_alias33% (3)
- Dm00064632 Spice Model Tutorial For Power Mosfets StmicroelectronicsДокумент24 страницыDm00064632 Spice Model Tutorial For Power Mosfets Stmicroelectronicsjoao pedro pasconОценок пока нет
- EGR260 - Introduction To PSPICEДокумент14 страницEGR260 - Introduction To PSPICEJai BaluniОценок пока нет
- SanketShinde 4885793 - 11 00 - 1 2022-08-08T14 01 35.159Документ6 страницSanketShinde 4885793 - 11 00 - 1 2022-08-08T14 01 35.159Ajay WanjareОценок пока нет
- Simulaciones de Electrónica de Potencia en PspiceДокумент63 страницыSimulaciones de Electrónica de Potencia en PspiceCarlos Iván RuedaОценок пока нет
- (Book - Review) Analog - Design - and - Simulation - Using - OrCAD - Capture - and - PSpiceДокумент11 страниц(Book - Review) Analog - Design - and - Simulation - Using - OrCAD - Capture - and - PSpiceBambang W. PambudiОценок пока нет
- Installation Procedure of Orcad PSPICE 9.2: April 2014Документ50 страницInstallation Procedure of Orcad PSPICE 9.2: April 2014ChAmirShokatGujjarОценок пока нет
- Introduction To PSpiceДокумент15 страницIntroduction To PSpiceUmera Anjum100% (1)
- SrajanДокумент15 страницSrajanBhargav ChaitanyaОценок пока нет
- Wireless Radio Frequency Module Using PIC Microcontroller.Документ74 страницыWireless Radio Frequency Module Using PIC Microcontroller.Abhi Sharma100% (16)