Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
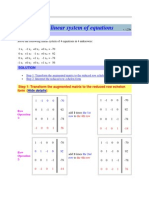
Problem: Step 1: Transform The Matrix To A Row Echelon Form
Загружено:
Juliette1987Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Problem: Step 1: Transform The Matrix To A Row Echelon Form
Загружено:
Juliette1987Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
PROBLEM
2 Calculate the determinant of the matrix 3 -7 -1 -1 2 -7 -2 2
SOLUTION
Step 1: Transform the matrix to a row echelon form Step 2: Calculate the determinant Comments
Step 1: Transform the matrix to a row echelon form
-1 Row Operation 1: 2 3 -7 -1 -1 2 -7 -2 2 multiply the 1st row by 1/2 the determinant is multiplied by 1/2 1 2 3 -7 -1 2 2 -2 2 -1 -1 Row Operation 2: 1 2 3 -7 -1 2 2 -2 2 -7 -1 -1 1 Row Operation 3: 2 1 0 2 -7 2 2 2 0 2 Row Operation 1 -1 -7 multiply the 2nd row by 2 the determinant is multiplied by 2 1 -1 -7 2 2 17 add 7 times the 1st row to the 3rd row the determinant does not change 0 2 -3 2 -45 -7 1 2 1 2 17 add -3 times the 1st row to the 2nd row the determinant does not change 0 2 2 2 2 -7 -7 1 2 1 2 17 -7 -7
4: 2 1 0 2 -3 0 2 -1 1 Row Operation 5: 2 0 0 2 -1 Row Operation 6: 1 2 0 0 1 0 2 17 3 multiply the 3rd row by 1/3 the determinant is multiplied by 1/3 2 -7 1 2 0 0 1 0 2 17 1 -1 -7 1 -3 2 17 -45 add 3/2 times the 2nd row to the 3rd row the determinant does not change 1 2 0 0 1 0 2 17 3 2 -7 -1 -7 2 -45 0 2 2 2 17 0 2 1 -3 2 17 -45
Step 2: Calculate the determinant
2 Let us denote the original matrix: A = 3 -7 -1 -1 2 -7 -2 2 -1 1 and the row echelon form obtained above: B = 0 0 We then have the following relationship: det(A) (1/2) (2) (1/3) = det(B). 2 1 0 2 17 1 -7
Since det(B) = 1 , we have, det(A) = 3
Luego se halla la inversa
PROBLEM
2 Find (if possible) the inverse of the matrix 3 -7 -1 -1 2 -7 -2 2
SOLUTION
Step 1: Adjoin the identity matrix to the given matrix Step 2: Transform the matrix to the reduced row echelon form Step 3: Interpret the reduced row echelon form Comments
Step 1: Adjoin the identity matrix to the given matrix
2 Adjoining I3 to the given matrix, we obtain the 3x6 matrix: 3 -7 -1 -1 2 -7 -2 2 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1
Step 2: Transform the matrix to the reduced row echelon form (Hide details)
2 Row Operation 1: 3 7 1 1 2 7 2 2 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 multiply the 1st row by 1/2 1 1 2 3 1 7 2 2 1 0 2 0 1 0 0
1 Row Operation 2:
- 1 7 2 2
1 0 2 0 0 1 0 0 1 add -3 times the 1st row to the 2nd row 0
1 2 1
-7 2 17 2 2
1 0 2 3 2 0 0 1 0
3 7
- 1 2 2 2
0 2 7 2
1 Row Operation 3:
1 2 1
-7 2 17 2 2
1 0 2 3 2 0 0 1 add 7 times the 1st row to the 3rd row 0
1 2 1
-7 2 17 2
1 0 2 3 2 7 0 2 1 0
0 2 3 45 2 2
0 2 7 2
1 2
-7 2 17 2 45 2
1 0 2 3 2 7 0 2 1 0 multiply the 2nd row by 2 0 1
1 2
-7 2 17 45 2
1 0 2 3 7 0 2 1 2 0 0
Row Operation 4:
1 0 2 3 2
1 3 2
1 Row Operation 5:
1 2
-7 2 17
1 0 2 3 7 0 2 1 0 2 0 add 3/2 times the 2nd row to the 3rd row 0 1
1 2
-7 2 17 3
1 0 2 3 1 2 3 0 1 0
1 0
3 45 2 2
1 Row Operation 6:
1 2
-7 2 17 3
1 0 2 3 1 2 3 0 1 multiply the 3rd row by 1/3 0
1 2
-7 2 17
1 0 2 3 1 3 2 0 1 1 3 0
0 0
1 0
1 Row Operation 7:
1 2
-7 2 17
1 0 0 2 3 1 3 2 0 1 1 3 add -17 times the 3rd row to the 2nd row
- 1 7 2 2 0
1 0 2 8 15 17 3 1 1 3 0
3 1 3
Row Operation 8:
- 1 7 2 2
1 0 2 0
add 7/2 times the 3rd row to the 1st row
1 2
2 3
7 2
7 6
- 17 15 3 3 8 1 3 1 1 3
- 17 15 3 3 8 1 3 1 1 3
1 2
2 3 8
7 2 15
7 1 6 17 3 1 add 1/2 times the 2nd row to the 1st row 0 1 0 0 0
2 -4 3 8
-5 3
Row Operation 9:
0 3 1 3
- 17 15 3 3 1 3 1 1 3
1 3
Step 3: Interpret the reduced row echelon form
The matrix in reduced row echelon form obtained above can be interpreted as [ C | D ], where both C and D are 3x3 matrices. 1 Since C = 0 0 2 -4 3 then D = 8 -15 3 -1 1 3 1 3 -17 is the inverse of the original matrix. 0 1 0 0 0 1 -5 equals I3
Вам также может понравиться
- Linear Algebra ToolkitДокумент5 страницLinear Algebra ToolkitMauricio Cesar Molina ArtetaОценок пока нет
- Row Operation 1:: Add - 4 Times ToДокумент2 страницыRow Operation 1:: Add - 4 Times ToMartin RamosОценок пока нет
- Transforming Matrix To The Reduced Row Echelon FormДокумент2 страницыTransforming Matrix To The Reduced Row Echelon FormMuskaan FaheedОценок пока нет
- Row Operation 1:: Add - 3 Times ToДокумент4 страницыRow Operation 1:: Add - 3 Times ToMartin RamosОценок пока нет
- Solving A Linear System of Equations: ProblemДокумент3 страницыSolving A Linear System of Equations: ProblemDonald WilsonОценок пока нет
- Gauss JordanДокумент24 страницыGauss JordanJeanette Karen FaigalОценок пока нет
- Row Operation 1:: Multiply by 1/2Документ5 страницRow Operation 1:: Multiply by 1/2Martin RamosОценок пока нет
- Transforming Matrix To The Reduced Row Echelon FormДокумент3 страницыTransforming Matrix To The Reduced Row Echelon FormAnonymous dEfIaUОценок пока нет
- Math1314 Matrix Solutions To Linear EquationsДокумент10 страницMath1314 Matrix Solutions To Linear Equationsاحمد الشوافيОценок пока нет
- NotebookAL2021 2Документ7 страницNotebookAL2021 2Jaider Tellez . .Оценок пока нет
- Problem 1: Solve The Following System of Linear Equations.: R R R RДокумент3 страницыProblem 1: Solve The Following System of Linear Equations.: R R R RpennobulesugariОценок пока нет
- Module 1c Augmented Matrices 1Документ12 страницModule 1c Augmented Matrices 1ESTEBAN , BETHEL A.Оценок пока нет
- Engineering MathematicsДокумент74 страницыEngineering MathematicsAhmadMoaazОценок пока нет
- Row Operation 1:: Add - 1 Times ToДокумент3 страницыRow Operation 1:: Add - 1 Times ToMartin RamosОценок пока нет
- Crochet Tunic NizzaДокумент7 страницCrochet Tunic NizzaJoedy StevensОценок пока нет
- Gaussian Elimination MethodДокумент2 страницыGaussian Elimination MethodWaqar Aamir KatiarОценок пока нет
- Gauss Jordan MethodДокумент4 страницыGauss Jordan MethodDaus Firdaus BahariОценок пока нет
- Linearna Algebra: Glava 1Документ22 страницыLinearna Algebra: Glava 1Edin GlogicОценок пока нет
- Linear Algebra (PPT) UpdatedДокумент112 страницLinear Algebra (PPT) Updatedalwafi100% (1)
- W4 - The Simplex AlgorithmДокумент30 страницW4 - The Simplex AlgorithmadammarthenОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 4 - MatricesДокумент25 страницChapter 4 4 - Matricesapi-263209117Оценок пока нет
- Gauss Elimanation MethodДокумент3 страницыGauss Elimanation MethodRamzi YahyaОценок пока нет
- Bruinen EnglishДокумент7 страницBruinen Englishcherrie_ann_domingo100% (1)
- Hw8solutions PDFДокумент12 страницHw8solutions PDFLuize VasconcelosОценок пока нет
- Matrix Algebra Solution To Simultaneous Algebraic Equations - Gauss Elimination MethodДокумент11 страницMatrix Algebra Solution To Simultaneous Algebraic Equations - Gauss Elimination Methodvarshasdm1987Оценок пока нет
- Example of Gaussian EliminationДокумент4 страницыExample of Gaussian Eliminationloserboi101Оценок пока нет
- Ow Operation 1: Row Operation 2: Row Operation 3: Row Operation 4: Row Operation 5: Row Operation 6Документ5 страницOw Operation 1: Row Operation 2: Row Operation 3: Row Operation 4: Row Operation 5: Row Operation 6Leena AlbdraniОценок пока нет
- Operations Research 1 The Two-Phase Simplex Method: Dr. Özgür KabakДокумент16 страницOperations Research 1 The Two-Phase Simplex Method: Dr. Özgür KabakAshish RanjanОценок пока нет
- Step 2:: Enter The Values For Your Matrix, and Press The "Solve" ButtonДокумент3 страницыStep 2:: Enter The Values For Your Matrix, and Press The "Solve" ButtonRahmawati NurfitriaОценок пока нет
- 5 Dual Decomposition ExampleДокумент8 страниц5 Dual Decomposition ExampleFateme OzgoliОценок пока нет
- 07 Inverse and EROДокумент5 страниц07 Inverse and EROgolam habibОценок пока нет
- Practice Questions Lecture 7 and 8 With SolutionДокумент8 страницPractice Questions Lecture 7 and 8 With SolutionmmlmОценок пока нет
- GaussElim PDFДокумент15 страницGaussElim PDFMuhammad Tariq SadiqОценок пока нет
- Bus Impedance MatrixДокумент17 страницBus Impedance MatrixFayez BaigОценок пока нет
- EPPC102 Module IIIДокумент26 страницEPPC102 Module IIIElizabeth GomezОценок пока нет
- PracticeДокумент6 страницPracticemmlmОценок пока нет
- Zeros Below The Diagonal: Row I Column I I NДокумент4 страницыZeros Below The Diagonal: Row I Column I I NরোদেলাদুপুরেরফুলОценок пока нет
- Section 2.2. Elementary Row OperationsДокумент6 страницSection 2.2. Elementary Row OperationsJason LeeОценок пока нет
- Linear Algebra HW1Документ4 страницыLinear Algebra HW1Gomi9kОценок пока нет
- hw1 SolnsДокумент7 страницhw1 SolnssiddiquentcОценок пока нет
- Ero Matrix Group2Документ22 страницыEro Matrix Group2izzuddinzamri98Оценок пока нет
- Lecture 5Документ21 страницаLecture 5AhmedОценок пока нет
- Linear Eqtn 2Документ77 страницLinear Eqtn 2Sittie Sorjanna DimaampaoОценок пока нет
- Determinan MapleДокумент12 страницDeterminan MaplerallyОценок пока нет
- Simplex Method ExamplesДокумент21 страницаSimplex Method ExamplesAnonymous HEzOOydОценок пока нет
- Algorithm, Is Used To Solve Such ModelsДокумент42 страницыAlgorithm, Is Used To Solve Such ModelshrithikroyОценок пока нет
- Microsoft Power Point History of MathematicsДокумент11 страницMicrosoft Power Point History of MathematicsZetroc JessОценок пока нет
- Topic 2 System of Linear EquationsДокумент59 страницTopic 2 System of Linear EquationsThinesh SubramaniОценок пока нет
- 101 Crochet Stitch Patterns & EdgingsОт Everand101 Crochet Stitch Patterns & EdgingsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- Rank of A MatrixДокумент36 страницRank of A MatrixAditya AndhaleОценок пока нет
- Crochet Halter Top Free PatternДокумент7 страницCrochet Halter Top Free PatternVasi Chrys100% (2)
- International Islamic University ChittagongДокумент3 страницыInternational Islamic University ChittagonghasunrajjaОценок пока нет
- Mypicot - Crochet Patterns: Uk / Us Crochet TermДокумент9 страницMypicot - Crochet Patterns: Uk / Us Crochet TermSzonja DocОценок пока нет
- Solution of The Linear Algebraic SystemДокумент17 страницSolution of The Linear Algebraic Systemsad birdОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2 Linear SystemДокумент12 страницLecture 2 Linear SystemEbrahim Abdullah HanashОценок пока нет
- Solving Systems of Equations: P P P P PДокумент5 страницSolving Systems of Equations: P P P P PMalcolmОценок пока нет
- Course Code and Title: Lesson Number: Topic:: Solve LP Problems Using Simplex Maximization MethodДокумент10 страницCourse Code and Title: Lesson Number: Topic:: Solve LP Problems Using Simplex Maximization MethodJessaОценок пока нет
- Lecture10 BclemmaДокумент4 страницыLecture10 BclemmaNancy NayakОценок пока нет
- Solving Exponential Equations Using Logarithms - ChiliMathДокумент6 страницSolving Exponential Equations Using Logarithms - ChiliMathMelanie AbaldeОценок пока нет
- Logical Reasoning Number SeriesДокумент26 страницLogical Reasoning Number SeriesHeather Holmes100% (1)
- Probability Notes Part 2Документ51 страницаProbability Notes Part 2brijotheОценок пока нет
- Grade 4 Project An Assessment Tool No AnswerДокумент2 страницыGrade 4 Project An Assessment Tool No AnswerJocelyn ElegadoОценок пока нет
- 2015 RMW QuestionsДокумент2 страницы2015 RMW QuestionsJohnRocelPerezОценок пока нет
- Finite Element Analysis of Thin-Walled Structures-Dr John W. Bull - CRC Press (1988)Документ264 страницыFinite Element Analysis of Thin-Walled Structures-Dr John W. Bull - CRC Press (1988)Anonymous 1rLNlqUОценок пока нет
- 3-Points in The Co-Ordinate PlaneДокумент4 страницы3-Points in The Co-Ordinate PlaneBlack Ink Tutorials & ServicesОценок пока нет
- 9X MNCERT - A - Number System (Sol)Документ10 страниц9X MNCERT - A - Number System (Sol)ShdriveОценок пока нет
- Engineering Mathematics 4E MatreciesДокумент23 страницыEngineering Mathematics 4E Matreciesأحمد كرارОценок пока нет
- Modern Crypto 18 Homework 2 SolutionДокумент5 страницModern Crypto 18 Homework 2 Solutionعبدالله بحراويОценок пока нет
- ELEMENTARY SCHOOL: No. of Days Level of UnderstandingДокумент4 страницыELEMENTARY SCHOOL: No. of Days Level of Understandingnorvel_19Оценок пока нет
- Survival Analysis in R PDFДокумент16 страницSurvival Analysis in R PDFmarciodoamaralОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Olympiad: National Board For Higher MathematicsДокумент52 страницыMathematics Olympiad: National Board For Higher MathematicsAakashParanОценок пока нет
- Wakali 1Документ5 страницWakali 1fjswalala100% (1)
- M. Thirumaleshwar - Fundamentals of Heat & Mass Transfer Includes Mathcad-Based Solutions To Problems-Pearson Education (2014)Документ800 страницM. Thirumaleshwar - Fundamentals of Heat & Mass Transfer Includes Mathcad-Based Solutions To Problems-Pearson Education (2014)Shailesh Singh Sikarwar100% (7)
- 10th Maths Public Important QuestionsДокумент2 страницы10th Maths Public Important QuestionsLAKSHMI BОценок пока нет
- Examples S-Convex FunctionsДокумент7 страницExamples S-Convex Functionstradutora100% (2)
- PIC, PID Control 2Документ8 страницPIC, PID Control 2Ermias NigussieОценок пока нет
- Geomanist SpecimenДокумент12 страницGeomanist SpecimenAdal2Оценок пока нет
- Stage 1 Mathematics MethodДокумент10 страницStage 1 Mathematics Methodyolanda Sitepu100% (3)
- Assessment 3: Graph Algorithms, Algorithm Analysis, Finite State MachinesДокумент9 страницAssessment 3: Graph Algorithms, Algorithm Analysis, Finite State MachinesCybercrime AndhraPradeshОценок пока нет
- Io Journal - Inaugural Issue 2q 2009Документ40 страницIo Journal - Inaugural Issue 2q 2009shakes21778Оценок пока нет
- Virtual Lab Report Vectors and Scalars Guide Two Astronauts On AДокумент8 страницVirtual Lab Report Vectors and Scalars Guide Two Astronauts On ALevi AckermannОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Is The Art of Patterns and Connections Embedded in Nature and in Our EnvironmentДокумент4 страницыMathematics Is The Art of Patterns and Connections Embedded in Nature and in Our EnvironmentJasmine TeaОценок пока нет
- 2-1 Guided NotesДокумент2 страницы2-1 Guided Notesapi-294399143Оценок пока нет
- (David Pisinger) Where Are The Hard Knapsack ProblemsДокумент14 страниц(David Pisinger) Where Are The Hard Knapsack Problemswalrod22Оценок пока нет
- Yr 11 Specialist - Complex NumbersДокумент6 страницYr 11 Specialist - Complex Numbersapi-372267775Оценок пока нет
- (6.3) Solving Systems EliminationДокумент29 страниц(6.3) Solving Systems Eliminationgtan@icacademy.orgОценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes For HCF and LCM: Some Properties of Prime NumbersДокумент18 страницLecture Notes For HCF and LCM: Some Properties of Prime NumbersUTKARSH TRIPATHI (RA1811004010394)Оценок пока нет