Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Science F3 Yearly Plan 2012
Загружено:
Sunniez SunniezАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Science F3 Yearly Plan 2012
Загружено:
Sunniez SunniezАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
YEARLY PLAN OF SCIENCE FORM THREE 2012 THEME : MANAGEMENT AND CONTINUITY OF LIFE LEARNING AREA : 1.
RESPIRATION Week / Date 1 Lear ! " O#$e%t!&e' 1.1Analysing the human breathing mechanism. Lear ! " A%t!&!t!e' Observe models or computer software to identify the structure of the human respiratory system which consists of nasal cavity, trachea, bronchus, lungs, ribs, diaphragm and the intercostals muscles. Examine a model of a lung to identify the bronchus, bronchiole and alveolus. Build a functional model of the human respiratory system to show the relationship between the air pressure in the thoracic cavity and the process of inhalation and exhalation. Discuss the breathing mechanism. &iew a video or computer software then gather and interpret data on the following a. diffusion of oxygen from the alveoli into the blood capillaries and from the blood capillaries into the cells b. transport of oxygen by the red blood cells in the form of oxyhaemoglobin Lear ! " O(t%)*e' A student is able to identify the structure of the human respiratory system, identify the structure of the lung, describe the process of inhalation and exhalation, relate the changes of air pressure in the thoracic cavity to inhalation and exhalation, describe the breathing mechanism. A++r)a%, Strate"!onstructivism Discussion S%!e t!.!% Sk!//' Observing !ommunicating Re*ark' "he contraction and relaxation of the internal and external intercostals muscles are not re#uired.
1.$ %nderstanding the transport of oxygen in the human body.
A student is able to describe the diffusion of oxygen from the alveoli into the blood capillaries, describe the transport of oxygen by blood, describe the diffusion of oxygen from the blood capillaries into the cells.
'n#uiry discovery
Observing !ommunicating
1.( )eali*ing the importance of a healthy respiratory system.
!ollect and interpret data on the following a. substances that are harmful to the respiratory system ,i.e nicotine and tar +from the smo,e of cigarettes-, sulphur dioxide +from the smo,e of vehicles- and ha*e b. effect of harmful substances such as toxin and carcinogen on the respiratory system c. disease of the respiratory system. !arry out an activity to show the effects of smo,ing on the lungs. .old or visit an exhibition on the effect of smo,ing and disease of the lungs. Brainstorm ideas on how to improve air #uality and put these ideas into practice.
At the end of the lesson, students are able to / list the substances which are harmful to the respiratory system, explain the effects of pollutant on the respiratory system, list the diseases that affect the respiratory system, practice good habits to improve the #uality of air.
Experiment and discovery
Observing and Experimenting
LEARNING AREA: 2. 0LOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
Week / Date (
Lear ! " O#$e%t!&e' $.1 %nderstanding the transport system in humans.
Lear ! " A%t!&!t!e' Observe and study models, computer software or videos on the structure of the heart and types of blood vessels +i.e. artery, vein and capillaryin the blood circulatory system Examine a live specimen of a heart to identify its structure. Discuss the following a. functions of the heart b. characteristics of the blood vessels and their functions. !arry out an activity to compare and contrast oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. 0imulate the flow of blood in the circulatory system. Discuss the role of the blood circulatory system in the transport of substances. 'nvite a medical officer to give a tal, on 1"a,ing !are of 2our .eart3.
Lear ! " O(t%)*e' A student is able to describe the circulatory system as a system of tubes with a pump and valves that ensure one/ way flow of blood, state the function of the heart, identify the structure of the human heart compare and contrast the structure of arteries, veins and capillaries, relate the characteristics of the blood vessels to their functions compare and contrast oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, illustrate the path of blood flow in the circulatory system describe the role of the blood circulatory system in the transport of substances, explain the importance of maintaining a healthy heart
A++r)a%, Strate"'n#uiry/discovery
S%!e t!.!% Sk!//' Observing, !ommunicating, Analy*ing
Re*ark'
$.$ Analysing the human blood
$.( Analysing the transport system in plants.
'nvite a physician to give a tal, on the following a. the constituents of blood, i.e. plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets and their functions. b. "he blood groups, i.e. A, B, AB, and O. c. "he compatibility between the blood group of the donor and that of the recipient, d. "he importance of blood donation e. "he storage and handling of donated blood. Observe a wilted plant and discuss how it occurred. Examine the epidermis of a leaf under a microscope to identify the stomata. !arry out experiments to study the following a. transport of synthesi*ed food substances via the phloem b. transport of water from roots to the leaves via the xylem Examine cross/sections of root, stem and leaf to identify the location of xylem and phloem. Discuss the roles of transpiration in the transport of water and minerals.
A student is able to 0tate the constituents of blood and their functions 0tate the blood groups 4atch the blood group of the donor to that of the recipient 5ustify the importance of blood donation Describe how donated blood is stored and handled.
!ontextual
!lassifying 4a,ing inferences
%niversal donor and universal recipient should be included
A student is able to describe how wilting occurs describe what transpiration is describe the function of stomata identify the factors affecting the rate of transpiration describe how the factors affect the rate of transpiration describe the roles of transpiration investigate the pathway of water in a cut stem using a suitable stains identify the locations of xylem and phloem describe the functions of xylem and phloem
'n#uiry / discovery
Observing
"he transport of water and minerals in transpiration should be emphasi*ed
LEARNING AREA: 1. E2CRETION
Week / Date
Lear ! " O#$e%t!&e' (.1 %nderstanding human excretion
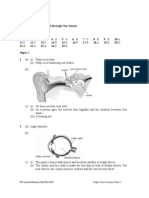
Lear ! " A%t!&!t!e' Discuss what excretion is. Examine models, charts or view computer software to identify the excretory organs, i.e. s,in, lungs and ,idneys. Discuss the excretory products of each excretory organ, i.e.water, carbon dioxide, minerals, salt and urea. Discuss the importance of excretion.
Lear ! " O(t%)*e' A student will be able to Explain what excretion is. 'dentify the excretory organs 0tate the excretory products of each excretory organ. Explain the importance of excretion.
A++r)a%, Strate"Discussion !ontextual
S%!e t!.!% Sk!//' 7redicting Defining operationally !ommunicating
Re*ark'
(.$ Analysing the %rinary system in human
Examine models, charts or view computer software of the urinary system to identify the locations of ,idneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra. !ollect and interpret data on the functions of the ,idney. Examine a live specimen of a ,idney to a. describe the shape of the ,idney. b. 'dentify the components of the ,idney, i.e. the cortex, medulla and pelvis
A student is able to identify the location of ,idneys and other parts of the urinary system. Describe the shape of the ,idneys. 'dentify the structures of the ,idneys Describe the functions of the ,idney Explain the importance of maintaining healthy ,idneys
!onstructivism Discussion
Observing 4a,ing inferences 7redicting !ommunicating "hin,ing s,ills )elating 4a,ing inferences
Describe briefly how a dialysis machine wor,s
Discuss the following a. "he importance of the ,idneys b. 9iving with ,idney failure (.( Analysing excretion in plants !ollect and interpret data on the following a. "he ways plants eliminate their excretory products, b. "he excretory products of plants, i.e. carbon dioxide, water and complex waste products A student is able to Describe the ways plants eliminate their excretory products 'dentify the excretory products of plants !ontextual 'nterpreting data
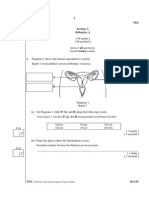
LEARNING AREA: 3. REPRODUCTION Week / Date Lear ! " O#$e%t!&e' 6.1 %nderstanding sexual and asexual reproduction Lear ! " A%t!&!t!e' Discuss the following a. the importance of reproduction b. the similarities and differences between sexual and asexual reproduction %sing charts, diagrams, videos or computer software to study the following fertili*ation a. internal and external fertili*ation b. the various ways of asexual reproduction, i.e. binary fission, budding, spore formation, Lear ! " O(t%)*e' 0tudents are able to 0tate the importance of reproduction 0tate the types of reproduction 0tate what fertilisation is Describe internal and external fertili*ation !ompare and contrast sexual and asexual reproduction !lassify animals and plants according to their ways of reproduction A++r)a%, Strate"Discussions 'n#uiry/discovery !onstructivism !ontextual 9earning S%!e t!.!% Sk!//' !lassifying Observing !ommunicating 'dentifying Re*ark' )eproduction
vegetative reproduction and re;uvenation Discuss and classify animals and plants according to how they reproduce 6.$ Analysing the male reproductive system 'dentify the following parts of the male reproductive system with the help of charts, models, videos or computer software a. the sexual organs, i.e. testes and penis, b. the other related parts, i.e. the scrotum, urethra, sperm duct and prostate gland Discuss the following a. the functions of the different parts of the male reproductive system b. the role of sperm in reproduction c. the physical, physiological and emotional changes in male during puberty 6.( Analysing the female reproductive system 'dentify the following parts of the female reproductive system with the help of diagrams, models, videos or computer software a. the sexual organs, i.e ovaries and uterus b. the other related parts, e.i fallopian tube, vagina and cervix A student is able to 'dentify the parts of the male reproductive system Describe the functions of the different parts of the male reproductive system 0tate the role of sperm in reproduction Describe the changes in male during puberty Discussion !ommunicating
A student is able to identify the parts of the female reproductive system. Describe the functions of the different parts of the female reproductive system. 0tate the role of an ovum in reproduction.
!ontextual
Observing, classifying, communicating, interpreting data
<
Discuss the following a. the functions of the different parts of the female reproductive system b. the role of an ovum in reproduction c. the physical, physiological and emotional changes in female during puberty 0imulate the differences between male and female gametes in terms of si*e, numbers and mobility. 6.6 Analysing the menstrual cycle. Discuss the following a. menstruation and the menstrual cycle, b. the changes in uterus wall during menstrual cycle, c. the relationship between the fertile phase and the menstrual cycle and fertili*ation d. the importance of personal hygiene during menstruation. Discuss the following with the help of diagrams, charts, models, videos or computer software a. the location of implantation of embryo, b. the development of *ygote into an embryo and subse#uently into a foetus until birth.
Describe the changes in female during puberty. !ompare and contrast male and female gametes in terms of si*e, numbers and mobility.
6.8 Analysing fertili*ation and pregnancy. .
A student is able to Describe the meaning of menstruation, Describe the menstrual cycle, Describe the changes in uterus wall during the menstrual cycle, )elate the fertile phase of the menstrual cycle to fertili*ation, Explain the importance of personal hygiene during menstruation. A student is able to identify the location of implantation of embryo describe the development of a *ygote into an embryo in subse#uently into a foetus until birth.
Brainstorming
!omunicating
"he description of the menstrual cycle should not include hormones.
!ontextual
Observing, communicating, interpreting data
"he concept of fertili*ation in human should include tracing the pathway of sperm and oyum until they meet and fuse.
6.: %nderstanding the importance of pre/natal care
Organise an exhibition or a multimedia presentation on the following a. the importance of ta,ing nutritious food during pregnancy b. the effects of smo,ing and the ta,ing of certain substances such as drugs and alcohol on the embryo and feotus !ollect and interpret data on the following a. the meaning of sterility, b. ways to overcome sterility, i.e. nutrition, hormone treatment, surgery, and in/vitro fertili*ation +'&>c. birth control, i.e rhythm method, the use of condom, contraceptive device +'%!D-, spermicides, vasectonomy and ligation. Debate on birth control and its effects on society Discuss the importance of research on human reproduction.
A student is able to )elate the imprtance of ta,ing nutritious food to the health of both mother and feotus during pregnancy. explain the importance of avoiding the inta,e of substances that are harmful to the feotus A student is able to state the meaning of sterility, describe ways to overcome sterility, describe the methods of birth control, present argument against the abuse of birth control ad its effects on the community, explain the importance of research on human reproduction
4astery/9earning
Observing, classifying, ma,ing inferences, predicting, communicating interpreting data
6.< Evaluating the importance of research in human reproduction.
4astery/9earning
Observing, classifying, ma,ing inferences, predicting, communicating interpreting data
Birth control methods to be included natural, chemical, mechanical, hormonal and surgical
6.= Analysing the sexual reproductive system of flowering plants
Examine flowers to identify the following parts a. petal and sepal. b. the male part, i.e. the stamen which consists of the filament, anther
A student is able to 'dentify the different parts of a flower 'dentify the male and female reproductive parts of a flower
Brainstorming, experiment, observation, identification, group discussion.
Observing, classifying, defining operationally, experimenting.
c.
and pollen grains. "he female parts, i.e. the pistil which consists of the stigma, style, ovary and ovules.
%se microscope or hand lens to observe the following a. cross/section and longitudinal section of an ovary to identify the ovules, b. pollen grains. Discuss the functions of the following a. flowers in reproduction, b. male reproductive parts of the flower c. female reproductive parts of the flowers. 6.? Analysing pollination Discuss the following with the help of models, charts, videos or computer software a. pollination b. types of pollination c. similarities and differences of self/ pollination and cross/ pollination d. advantages of cross/ pollination e. uses of cross/pollination in agriculture. !arry out an activity to study the various types of flowers to identify their pollinating
'dentify the male and female gametes Describe the functions of the male and female reproductive parts of a flower in sexual reproduction.
A students is able to describe what pollination is relate the characteristics of flowers to their agents of pollination. 0tate the types of pollination !ompare and contrast self/pollination and cross/pollination Explain the advantages of cross/pollination Explain with examples the uses of cross/ pollination in agriculture.
0imulation Discussion
Observing 7redicting !ommunicating 'nterpreting data .ypothesising Experimenting
1@
agents.
11
6.1@ %nderstanding the development of fruits and seeds in plants
%se a microscope to observe the development of pollens tubes in different percentage of sucrose solution +8A/1@A-. Draw annotated diagrams of the following a. "he fertili*ation process in plants b. "he formation of fruits and seeds. Discuss the following a. the location where fertilisation occurs in flower b. fertilisation in plants c. formation of fruits and seeds
A student is able to identify the location where fertilisation occurs in flower describe fertilisation in plants describe the formation of fruits and seeds.
Discussion and !ontextual
Observing communicating
6.11 0ynthesising the concept of germination of seeds
Dissect a seed longitudinally and identify its structure using hand lens or microscope. !ollect and interpret data on the following a. functions of the different parts of a seed, i.e. the embryo +radicle, plumule and cotyledons- and testa, protected by the prericarp +fruit wallb. physical changes of seddlings in terns of the development of radicle, plumule and cotyledon. !arry out small group discussions to a. identify the variables related to the
A student is able to identify the structure of a seed explain the functions of the different parts of a seed describe the physical changes of seddlings during germination ma,e hypotheses on the conditions re#uired for the germination of seeds design an experiment to study the conditions re#uired for the germination of seeds carry out the experiment to study
Discussion and identify
Observing, !ommunicating,
1$
b.
germination of sedds, formulate hypotheses about the conditions re#uired for the germination of seeds.
Design and carry out experiments to determine the conditions re#uired for the germination of seeds. 6.1$ Application of vegetative reproduction in flowering plants !arry out a study of the vegetative reproduction of various plants in a nursery to identify the types of vegetative reproduction. Discuss what vegetative reproduction is. Discuss the application of research carried out in vegetative reproduction in agricuture.
the conditions re#uired for the germination of seeds draw conclusions on the conditions re#uired for the germination of seeds
A student is able to explain with examples the meaning of vegetative reproduction, state the parts of the plants that can reproduce vegetatively, classify flowering plants according to the parts that can reproduce vegetatively, describe the application of research carried out on vegetative reproduction in agricuture
'n#uiry/Discovery
Observing !lassifying !ommunicating 'nterpreting data
Biotechnology can be introduced. Example of vegetative reproduction is plant tissue culture. Details of plants tissue culture are not re#uired.
1(
LEARNING AREA: 4. GROWTH
Week / Date
Lear ! " O#$e%t!&e' 8.1 Analysing the pattern of human growth
Lear ! " A%t!&!t!e' Discuss the following a. characteristics used to measure growth rate such as height and weight b. meaning of growth c. growth pattern in male and female d. effect of nutrition on the development of physical and mental well being of children !arry out activities to interpret the growth curve for male and female infancy to adulthood
Lear ! " O(t%)*e' A student is able to Describe what growth is 'dentify the characteristic used to measure growth rate Analyse the growth curve for male and female !ompare and contrast between growth rate in male and female Describe the effects of nutrition on the growth in children
A++r)a%, Strate"!ommunicating, interpreting data
S%!e t!.!% Sk!//'
Re*ark'
16
THEME: MATTER IN NATURE LEARNING AREA: 1. LAND AND ITS RESOURCES Week / Date Lear ! " O#$e%t!&e' 1.1 Analysing the various minerals found in the Earth crust. Lear ! " A%t!&!t!e' Discuss what a mineral is. !ollect and interpret data on the various types of minerals that exist in the Earth crust a. Batural elements, i.e. gold and silver b. Batural compounds, i.e. oxides, carbonates, sulphides and silicates. Discuss and identify the elements in a few natural compounds. !arry out activities to study the following a. .ardness of minerals b. 0olubility of minerals in water c. "he effect of heat on some metal carbonates, oxides and sulphides 1.$ %nderstanding the reactions between metal and non metal Brainstorm and discuss the following a. examples of metals. b. examples of non/metal !arry out activities to study the reaction of some metals , i.e magnesium, aluminium, *inc and iron with the following non/metals a. 0ulphur b. Oxygen A student is able to state examples of metals and non/metals describe the reactions between metals and non/ metals write e#uations in words for the reaction between metals and non/metals. 0tate that metals react with non/metals at different rate. 4astery learning !ommunicating "he reactivity series need not be introduced. Lear ! " O(t%)*e' A student is able to Describe what a mineral is. Explain through examples that minerals exist in the form of natural elements or natural compounds. 'dentify the elements in naturals compounds Describe the properties of minerals Crite e#uations in words to show the effect of heat on the minerals. A++r)a%, Strate"4astery learning S%!e t!.!% Sk!//' Observing 4a,ing inferences Re*ark'
18
1.( %nderstanding silicon compounds
!ollect and interpret data on silicon compounds that exist in the form of silica and silicate !arry out activities to study the properties of silica and silicates as follows a. 0olubility in water b. )eaction with hydrochloric acid c. Effects of heat &isit factories to learn about the process of ma,ing glass, ceramic, electronic chips and fibre optics. Discuss the uses of silicon compounds in our daily life.
A student is able to state the different forms of silicon compounds state examples of silica state examples of silicate relate the properties of silicon compounds to their stability explain through examples the uses of silicon compounds in our daily life.
Discussion &isits
!ommunicating Observing
1.6 Analysing calcium compounds.
!ollect and interpret data on calcium carbonate. !arry out activities to study the following a. the properties of calcium carbonates in terms of its reaction with acid, solubility in water and the effects of heat. b. "he formation of calcium oxide +#uic,lime- and calcium hydroxide +sla,ed lime-. Discuss the following a. %ses of calcium
A student is able to 0tate the elements in calcium carbonate. 'dentify the various forms of calcium carbonate Describe the properties of calcium carbonate. Crite e#uations in words for the reaction of calcium carbonate. Describe the formation of calcium oxide and calcium hydroxide )elate the properties of calcium compounds to their uses
Experiments !ontextual learning
Observing !ommunicating !lassifying
1:
b.
compounds, i.e. calcium carbonate, calcium oxide and calcium hydroxide 7roperties of calcium compounds with reference to their uses. A student is able to 9ist the natural fuel resources Explain the formation of natural fuel resources Describe the fraction distillation of petroleum Describe the characteristic of the various fractions from the fractional Describe the uses of the various fractions of petroleum Explain the contributions of petroleum and natural gas industry to the economic development of our country Denerate ideas on how to use natural fuel resources efficiently. !onstructivism 4a,ing inferences
1.8 Analy*ing natural fuel resources and their importance
Access websites or visit 7E")O0A'B0, Bational 0cience !entre or an oil refinery to collect information on the formation of natural fuel resources found in 4alaysia. !arry out an activity to study fractional distillation of petroleum. Discuss the following a. !haracteristics and uses of the various fractions of petroleum b. !ontributions of petroleum and natural gas industry to the economic development of our country. c. Efficient ways of using petroleum and other natural fuel resources.
1<
THEME: LEARNING AREA:
ENERGY IN LIFE 1. ELECTRICITY
Week / Date
Lear ! " O#$e%t!&e' 1.1 understanding electrostatics
Lear ! " A%t!&!t!e' !arry out following activities a. 7roducing static electrical charges in materials through friction b. Detecting static electrical charges using an electroscope c. Observing what happens when two ob;ects with the same or opposite charges are brought near to each other and ma,ing conclusions about static electrical charges. Discuss the following a. Chat electrostatic is b. "ypes of static electrical charges c. 7roperties of static electrical charges d. Examples of material that are easily charged, i.e. acetate and polythene e. Everyday phenomena related to static electrical charges, e.g. lighting f. 0afety measures to be ta,en when dealing with electrical charges, e.g. the use of lighting conductor.
Lear ! " O(t%)*e' A student is able to Describe what electrostatics is 0tate the types of static electrical charges 0tate the properties of static electrical charges Describe how static electrical charges can be produced in some materials Describe ways to detect static electrical charges Explain everyday phenomena caused by static electrical charges 0tate the safety measures to be ta,en when dealing with static electricity.
A++r)a%, Strate"!ontextual
S%!e t!.!% Sk!//' Observing 4a,ing inferences
Re*ark'
1=
1.$ %nderstanding electricity
!ollect and interpret data on the sources of electrical energy used in everyday life. !arry out activity to observe the flow of electric current using a &an de Draff generator and a galvanometer. Discuss the following a. electricity b. current c. voltage d. resistance e. directions of current and electron flow in an electric circuit
A student is able to give examples of sources electrical energy used everyday life state what electricity , state what voltage is, state what resistance is describe the directions current and electron flow an electric circuit
of in
!ontextual, Discussion
Observing, communicating, interpreting data
of in
1.( Applying the understanding of measuring electricity
!ollect information and carry out a multimedia presentation on the discovery of the unit for a. current, i.e. ampere b. voltage, i.e. volt c. resistance, i.e. ohm examine the instruments and discuss its use for measuring a. current b. voltage Assemble an electric circuit and measure its current and voltage
A student is able to identify the instrument for measuring current identify the instrument for measuring voltage state the unit for current state the unit for voltage state the unit for resistance measure current in an electric circuit measure voltage in an electric curcuit
!ontextual
4easuring and using numbers
1.6 0ynthesising the relationship between current, voltage and resistance.
Design and carry out an experiment to study the following a. effects of the change in resistance on current b. effects of the change in voltage on current
A student is able to Design and carry out experiments to study the relationship between resistance and current Describe the effects of the change in resistance on current
!onstructivism
Experimenting !ontrolling the variables 4a,ing hypothesis 'nterpreting data
'nterpretation of graphs should be emphasi*ed.
1?
Discuss the following a. relationship between voltage, current and resistance b. OhmEs 9aw
1.8 0ynthesising the concept of parallel and series circuit.
4atch the components found in an electric circuit to their symbols. Draw the following circuit diagrams and assemble the circuits a. a complete circuitF b. a series circuitF c. a parallel circuit. Discuss the similarities and differences between a series circuit and a parallel circuit with the help of illustration.
Design and carry out experiment to study the relationship between voltage and current Describe the effect of the change in voltage on current 0tate OhmEs 9aw A student is able to identify the components of an electric circuit and their symbolsF draw a diagram of a complete circuitF build a complete electric circuitF build a series circuitF build a parallel circuitF compare and contrast the arrangement of components in a series circuit and a parallel circuit.
4astery 9earning
Observing, experimenting, communicating,
1.: Analysing current, voltage and resistance in a series circuit.
!arry out activities to study current, voltage and resistance in a series circuit. Discuss the advantage and disadvantage of a series circuit.
1.< Analysing current, voltage and resistance in parallel circuit.
!arry out activities to study current, voltage and resistance in a parallel circuit. Discuss the following
A student is able to describe the current flowing through the components in a series circuit describe the voltages across the components in a series circuit describe the resistance in a series circuit explin the advantage and the disadvantage of a series circuit. A student is able to describe the current flowing through the components in a parallel circuit describe the voltage across
!ontextual
Experimenting
0imple calculations can be introduced
!ontextual
Observing
0imple calculations can be introduced.
$@
a. b.
advantage and disadvantage of a parallel circuit similarities and differences between series and parallel circuits in terms of current, voltage and resistance.
the components in a parallel circuit describe the resistance in a parallel circuit explain the advantage and the disadvantage of a parallel circuit compare and contrast a series circuit and a parallel circuit in terms of current, voltage and resistance !ontextual Experimenting
"he differences between a series circuit and a parallel circuit should be demonstrated using meters and brightness of bulbs.
1.= %nderstanding magnetism
!arry out the following activities a. use iron fillings to study the magnetic field of a bar magnet b. use compass to plot the directions of the magnetic field. Discuss the following a. magnetic field b. relationship between magnetic field lines and strength of magnetic field. 0tudy and discuss the use of a magnet in a compass.
A student is able to describe what a magnetic field is draw the magnetic field of a bar magnet draw the directions of the magnetic field relate magnetic field lines and strength of magnetic field explain the use of a magnet in a compass
1.? %nderstanding electro/magnetism
!arry out an activity to study the magnetic field produced by a straight wire carrying electric current. Discuss the meaning of a. electromagnetism b. electromagnet
A student is able to relate the current flow through a conductor with magnetism describe what an electromagnet is
!ontextual
Experimenting
$1
LEARNING AREA: 2. GENERATION OF ELECTRICITY
Week / Date
Lear ! " O#$e%t!&e' $.1 %nderstanding of generation of electrical energy
Lear ! " A%t!&!t!e' Explore website or visit a power station to collect and interpret data on the following a. various types of generators, i.e, thermal, hydro electric, diesel, nuclear and gas turbine b. generation of electrical energy in various types of power stations c. alternative sources of energy e.g solar energy and biomass Discuss the similarities and differences in the generation of electrical energy in various types of power stations. !arry out activity on the utili*ation of solar energy using devices such as solar box or solar cell +photovoltaic cell-.
Lear ! " O(t%)*e' A student is able to list the various types of generators describe the generation of electrical energy in various types of power stations compare and contrast the generation of electrical energy in various types of power stations give examples of alternatives source of energy
A++r)a%, Strate"!ontextual
S%!e t!.!% Sk!//' Observing !lassifying !ommunicating
Re*ark'
$.$ %nderstanding "ransformer
Build a simple transformer and study its physical structure !arry out an activity to show the function of the simple transformer !ollect and interpret data on the wor,ing principle of a step/up transformer and a step/down transformer
A student is able to 'dentify the different parts of a transformer Describe how a transformer wor,s Describe the roles of transformer in the transmission and distribution of electricity !ompare and contrast a step/ up transformer and step/down transformer
!onstructivism
'nferring 'nterpreting Data !lassifying
$$
Discuss step/up and step/down transformers in terms of a. similarities and differences b. their uses in the transmission and distribution of electricity $.( Analysing the electricity transmission and distribution system Discuss the electrical transmission and distribution system which includes the Bational Drid Betwor,, transformer stations, switch *one, main sub/station and its branches !ollect and interpret data on the Bational Drid Betwor, in 4alaysia. A student is able to arrange in order the components in the electricity transmission and distribution system describe the functions of the components in the electricity transmission and distribution system describe how electricity is transmitted and distributed from power stations to consumers. A student is able to state the value of the main voltage. state the types of current identify the type of electric current supplied to home state the type of electrical wiring, identify the parts in an electrical wiring system describe the functions of the parts of an electrical wiring system describe the wiring in a (/pin plug. Discussion 'n#uiry/Discovery !lassifying 'nterpreting data
$.6 %nderstanding the electrical supply and wiring system at home
!ollect and interpret data on electrical energy supply at home. 0tudy and discuss the following a. electrical wiring system at home include fuse box, mains switch, circuit brea,er, live wire neutral wire, earth wire and electric meter, b. international colour code. !arry out an activity to a. study the structure and design of a (/pin plug b. complete the wiring of a (/ pin plug
!ontextual
Experimenting
$(
$.8 Analysing the cost of electrical energy usage
Examine various home appliances to collect and interpret data on the power, voltage and current ratings !alculate the amount of current flowing through home electrical appliances Discuss the relationship between electrical energy usage, power and time. !arry out the home electrical energy usage audit to determine the cost of electrical energy use per month
A student is able to 0tate the power and voltage rating of home electrical appliances !alculate the amount of current flowing through an electrical appliances )ecall the relationship between electrical energy usage, power and time 0olve problem by calculating the cost of electricity use
!ontextual
!lassifying 4easuring and using numbers 'nterpreting data
'ntroduce the following formulae 7ower G &oltage H !urrent 7G&H' Energy + ,ChG 7ower+,CH "ime+h-
$.: %nderstanding the function of fuse and earth wire
Discuss the following a. types of fuses b. ratings of fuses c. function of fuse in electrical wiring system d. the role of earth wire in electrical wiring system !arry out an activity to study the occurrence of a short circuit. !arry out activities to determine the suitable ratings of fuses for different electrical appliances.
A student is able toF identify the types of fuses state the ratings of fuses describe the function of fuse in electrical wiring system determine the suitable rating of a fuse for an electrical appliances describe the role of earth wire in electrical wiring system
!ontextual
Observing, classifying, communicating, 'nterpreting data and inferring
$6
$.< Evaluating the importance of safety precautions in the use of electricity.
!ollect and interpret data on the following a. causes of electrical accidents, b. steps to be ta,en if electrical accidents occur, c. safety features at home to prevent electrical accidents. Discuss the need to ta,e safety precautions when using electricity.
A student is able to state the safety measures to be ta,en when using electricity, describe the steps to be ta,en when accidents involving electricity occur, ;ustify the need for having safety precautions and safety features at home to prevent electrical accidents.
!ontextual 9earning 4a,ing decisions
4easuring and using number
4ention the following safety features '. 4iniature !ircuit Brea,er +4!B''. Earth 9ea,age !ircuit Brea,er +E9!B'ntroduce energy labeling of appliances to improve energy efficiency.
$.= Evaluating the importance of conserving electricity.
!ollect and interpret data about activities that cause electricity wastage. Discuss the ways to conserve electricity. !arry out a pro;ect on energy efficiency. Discuss and ;ustify the needs for conserving electricity. Brainstorm the problems faced by the country if there was a shortage of electricity.
A student is able to identify the activities that cause electricity wastage, describe ways to conserve electricity, ;ustify the needs for conserving electricity predict problems our country would face if there was a shortage of electricity.
Discussion
7redicting
$8
THEME: ASTRONOMY AND SPACE E2PLORATION LEARNING AREA: 1. STARS AND GALA2IES
Week / Date
Lear ! " O#$e%t!&e' 1.1 Analysing the sun
Lear ! " A%t!&!t!e' !ollect and interpret data on the following a. characteristics of the sun i.e. si*e, mass, density relative to the earth and surface temperature. b. 0tructures of the sun, i.e. the corona, chromosphere and photosphere. c. 7henomena occurring at the surface at the surface of the sun i.e. prominences, flares and sunspots. d. Effects of the phenomena on the surface of the 0un on Earth e. Deneration of energy by the sun Discuss the following a. the definition of star, b. the 0un as a star. &isit the Bational 7lanetarium or Bational 0cience !entre to collect and interpret data on the following a. bright stars such as the 0irius and )igel, b. the 0un as a star, c. various types of stars based on temperature, si*e and brightness, d. formation of stars, e. death of stars leaving behind the white dwarf,
Lear ! " O(t%)*e' A student is able to Describe the characteristics of the sun 'dentify the structures of the sun 'dentify the phenomena occurring on the surface of the 0un Explain the effects of the phenomena on the sun on the Earth 0tate how energy is generated by the sun
A++r)a%, Strate"!onstructivism
S%!e t!.!% Sk!//' Observing , classifying, communicating, ma,ing inferences
Re*ark' Aurorae, fre#uently associated with flares should be introduced.
1.$ understanding the stars and the galaxies in the %niverse.
A student is able to define what a star is, identify the 0un as a star, identify the bright stars in the s,y, compare and compare and contrast the stars based on certain characteristics, describe the formation of stars, describe the death of stars, state the types of galaxies, describe the 4il,y Cay, describe the %niverse, state the position of the 0olar 0ystem in the %niverse.
'n#uiry / discovery
Observing, communicating
$:
f. g. h.
neutron star and the blac, hole, types of galaxies, i.e. elliptical, spiral and irregular, the 4il,y Cay, the %niverse.
"a,e part in star ga*ing activities. &iew computer software or videos to gather information about the topics in this learning area. 1.( "han,ful for the existence of the %niverse as a gift from Dod Crite a poem or hai,u about the uni#ueness, orderliness, beauty and harmony of the %niverse as sign of the glory of god. Discuss the following a. the expanse of the %niverse b. all that exists in the %niverse is not permanent c. the importance of the 0un and the 4oon to life on Earth A student is able to Appreciate the uni#ueness, orderliness, beauty and harmony in the %niverse as a sign of the glory of Dod. Describe the expanse of the %niverse compared to Earth, 0tate that all the exists in the %niverse is not permanent, Explain the importance of the 0un and the 4oon to life on Earth. !ontextual !ommunicating .ai,u is a 5apanese poem that comprise of three lines. "he first and third is made up of five syllables while the second line is made up of seven syllables. "he theme and message of the poem is often associated with nature. >or example Up the sky I stare, I look up and wish Im there, Beautiful and rare.
$<
"his learning ob;ective +1.(should be intergrated with the other learning ob;ectives when relevant.
LEARNING AREA : 2. SPACE E2PLORATION
Week / Date
Lear ! " O#$e%t!&e' $.1 %nderstanding developments in the field of astronomy and space exploration.
Lear ! " A%t!&!t!e' 0urf the 'nternet, visit the 7lanetarium or the Bational 0cience !entre to collect and interpret data on the following a. Developments in the field of astronomy, b. Applications of technology related to space exploration and astronomy, e.g. remote sensing, c. Developments in space exploration, e.g launching the roc,ets, satellites, probes as well as manEs landing on the moon. Debate on the need to continue space exploration. !arry out a multimedia presentation on the developments in the field of astronomy and space exploration.
Lear ! " O(t%)*e' A student is able to describe the developments in the field of astronomy, describe the developments in space exploration, explain with examples the applications of technology related to space exploration and astronomy, ;ustify the need to continue space exploration.
A++r)a%, Strate"Discussion
S%!e t!.!% Sk!//' 7redicting !ommunicating Observing
Re*ark' 'nclude the applications of remote sensing, e.g. in geology, agriculture, forestry, disaster management, national security management, etc. 4alaysian !entre for )emote 0ensing +4A!)E0- is responsible for the romote sensing pro;ects in the country.
$=
$?
Вам также может понравиться
- Squirting For DummiesДокумент31 страницаSquirting For DummiesGustavoCalderin75% (4)
- AMA Manual 10th Edition PDFДокумент1 014 страницAMA Manual 10th Edition PDFKannan Fangs S100% (1)
- The Eight Extraordinary Qi Vessels and The Twelve Primary Qi ChannelsДокумент25 страницThe Eight Extraordinary Qi Vessels and The Twelve Primary Qi ChannelsJaffer Aftab100% (9)
- Wendy Carlin & David Soskice - Macroeconomics - Imperfections, Institutions & Policies-Oxford University Press (2006)Документ828 страницWendy Carlin & David Soskice - Macroeconomics - Imperfections, Institutions & Policies-Oxford University Press (2006)shashaОценок пока нет
- AMA Manual 10th Edition PDFДокумент1 014 страницAMA Manual 10th Edition PDFKannan Fangs S100% (2)
- Possible Essay Questions For The Physiology Final ExamДокумент3 страницыPossible Essay Questions For The Physiology Final ExamSalman Majid100% (1)
- Adolescent HealthДокумент19 страницAdolescent Healthhou1212!67% (3)
- Cambridge Secondary 1 Science Curriculum FrameworkДокумент14 страницCambridge Secondary 1 Science Curriculum Frameworkapi-217350410100% (3)
- Experimental Hydrodynamics of Fast-Floating Aquatic AnimalsОт EverandExperimental Hydrodynamics of Fast-Floating Aquatic AnimalsОценок пока нет
- Ovarian Cyst Types, Symptoms, Diagnosis & TreatmentДокумент19 страницOvarian Cyst Types, Symptoms, Diagnosis & TreatmentMuhammad AbeeshОценок пока нет
- Asking Effective QuestionsДокумент8 страницAsking Effective Questionsjrogenski9000Оценок пока нет
- Scheme of Work Science Stage 7.v1Документ45 страницScheme of Work Science Stage 7.v1gkawsar22100% (2)
- Cervical Cancer Awareness StudyДокумент67 страницCervical Cancer Awareness StudyPriyanshi DhankarОценок пока нет
- RPH Biologi TG4Документ28 страницRPH Biologi TG4lilyraj100% (1)
- Emergencias ReproductivasДокумент24 страницыEmergencias ReproductivasYami SuperОценок пока нет
- Chordate Origins and Evolution: The Molecular Evolutionary Road to VertebratesОт EverandChordate Origins and Evolution: The Molecular Evolutionary Road to VertebratesОценок пока нет
- Science F3 Yearly PlanДокумент35 страницScience F3 Yearly Plankiey_02Оценок пока нет
- HSP Science Form 3Документ30 страницHSP Science Form 3Rafizal ShafieeОценок пока нет
- Yearly Plan Science Form 3Документ17 страницYearly Plan Science Form 3lccjane8504Оценок пока нет
- Scheme F3Science 2010 (BARU)Документ35 страницScheme F3Science 2010 (BARU)Roziah RamliОценок пока нет
- Sow Science s3 2011Документ32 страницыSow Science s3 2011Salmah YunusОценок пока нет
- SMK Sinar Bintang, Segambut Kuala Lumpur Yearly Plan Science Form 3Документ16 страницSMK Sinar Bintang, Segambut Kuala Lumpur Yearly Plan Science Form 3Azie HarunОценок пока нет
- RPT Sains Ting. 3 2016Документ20 страницRPT Sains Ting. 3 2016NorSafarien RahimОценок пока нет
- Yearly Plan 2008Документ22 страницыYearly Plan 2008rickysuОценок пока нет
- Secondary Science Curriculum Guide for Form 3Документ37 страницSecondary Science Curriculum Guide for Form 3mohd_junaid19Оценок пока нет
- Yearly Plan - Biology Form 4: Pupils Will Be Able ToДокумент47 страницYearly Plan - Biology Form 4: Pupils Will Be Able ToVeronica FrancisОценок пока нет
- Scheme of Work - 2013Документ21 страницаScheme of Work - 2013pemikiranОценок пока нет
- Form 5 Biology Scheme of Work - Transport and Locomotion SystemsДокумент52 страницыForm 5 Biology Scheme of Work - Transport and Locomotion SystemsSyakirah Abdullah100% (1)
- 20 - Appendix e PDFДокумент47 страниц20 - Appendix e PDFShilpaОценок пока нет
- RPT SC F3Документ20 страницRPT SC F3Missz WazeeОценок пока нет
- Yearly Lesson Plan SC f4Документ36 страницYearly Lesson Plan SC f4Gula MelakaОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Pengajaran Tahunan Bio Form 4Документ50 страницRancangan Pengajaran Tahunan Bio Form 4Cik NanaОценок пока нет
- Yearly Plan Bio Form5Документ30 страницYearly Plan Bio Form5maieyОценок пока нет
- 9th Grade Science Lesson on the Cardiovascular SystemДокумент5 страниц9th Grade Science Lesson on the Cardiovascular SystemOliver VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- RPT Science FRM 3Документ14 страницRPT Science FRM 3Ashlan AdamОценок пока нет
- Science 6 Lesson Plan (First Grading)Документ59 страницScience 6 Lesson Plan (First Grading)Sonny MatiasОценок пока нет
- RPT: Science Form 3Документ14 страницRPT: Science Form 3Hajar Norasyikin Abu BakarОценок пока нет
- RPT Biology Form4Документ50 страницRPT Biology Form4Nadiah BorhanОценок пока нет
- Scheme of Work BIOLOGY FORM 5, 2012Документ46 страницScheme of Work BIOLOGY FORM 5, 2012sitnorsyahidah100% (2)
- RPT: SCIENCE TOPICS FOR FORM 3 STUDENTSДокумент14 страницRPT: SCIENCE TOPICS FOR FORM 3 STUDENTSSo HannaОценок пока нет
- RPT Bio T5 2013Документ50 страницRPT Bio T5 2013Nyne NaaОценок пока нет
- Learning Area: 1.0 Respiration: Theme: Management and Continuity of LifeДокумент2 страницыLearning Area: 1.0 Respiration: Theme: Management and Continuity of LifeMusliza Rashid Noir IpohОценок пока нет
- RPT: Science Form 3Документ14 страницRPT: Science Form 3Safwan AzizulОценок пока нет
- Week e Stage 4 ScienceДокумент50 страницWeek e Stage 4 SciencesallynourlbОценок пока нет
- Science Project Based Learning (PBL) Form 3 2022: No Theme Management and Continuity of LifeДокумент8 страницScience Project Based Learning (PBL) Form 3 2022: No Theme Management and Continuity of LifeCrosty DfafraurОценок пока нет
- Scheme of Work Biology Form 4 2013Документ33 страницыScheme of Work Biology Form 4 2013Sitinorsyahidah JantanОценок пока нет
- Curriculum Map 2013-2014Документ18 страницCurriculum Map 2013-2014api-233653042Оценок пока нет
- BSC 2085 Final Exam Study Guide RevisedДокумент3 страницыBSC 2085 Final Exam Study Guide RevisedReymon SalvadorОценок пока нет
- Biology Notes Form 2 - Form Two Biology by The End of Form Two Work, The Learner Should Be Able ToДокумент71 страницаBiology Notes Form 2 - Form Two Biology by The End of Form Two Work, The Learner Should Be Able ToKehmoka TimothyОценок пока нет
- OPP 101 Fall 2010 Syllabus1Документ3 страницыOPP 101 Fall 2010 Syllabus1ferry7765Оценок пока нет
- Blood Circulation and TransportДокумент3 страницыBlood Circulation and TransportSselvi SubramoniamОценок пока нет
- Biology Form 5 Yearly Teaching Plan 2016Документ15 страницBiology Form 5 Yearly Teaching Plan 2016FidaОценок пока нет
- Form Two Biology1Документ62 страницыForm Two Biology1Mail MamaОценок пока нет
- Bio GR 10Документ4 страницыBio GR 10api-253466750Оценок пока нет
- Ac Year Level Icu Scope and Sequence Term 4 FinalДокумент16 страницAc Year Level Icu Scope and Sequence Term 4 FinalS TANCREDОценок пока нет
- Understanding the Physiology of Living ThingsДокумент13 страницUnderstanding the Physiology of Living ThingsMasitah AmzalОценок пока нет
- Ota Go 730857Документ9 страницOta Go 730857Super sonicОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Tahunan BIO T5Документ38 страницRancangan Tahunan BIO T5riyashreeОценок пока нет
- Reproductio ENДокумент5 страницReproductio ENtexasrepublican1976Оценок пока нет
- General ObjectivesДокумент23 страницыGeneral ObjectivesSamuel BlessОценок пока нет
- YEARLY BIOLOGY TEACHING PLANДокумент13 страницYEARLY BIOLOGY TEACHING PLANChe Mahani HussainОценок пока нет
- Edexcel Biology: ClassificationДокумент14 страницEdexcel Biology: Classificationeyheth100% (1)
- Ap Biology Syllabus 2014-2015 - ShhsДокумент21 страницаAp Biology Syllabus 2014-2015 - Shhsapi-262235970Оценок пока нет
- CellsДокумент20 страницCellsppttppОценок пока нет
- RES7 BiocontentchecklistДокумент12 страницRES7 Biocontentchecklistkruthasan12345Оценок пока нет
- AS Biology Syllabus 9700 Unit 4: Transport and Gas ExchangeДокумент21 страницаAS Biology Syllabus 9700 Unit 4: Transport and Gas Exchangefairy56Оценок пока нет
- Sains Menengah Rendah: Bahan Sumber Pengajaran Dan PembelajaranДокумент6 страницSains Menengah Rendah: Bahan Sumber Pengajaran Dan PembelajaranSunniez SunniezОценок пока нет
- Structure of The Ear (2A2)Документ1 страницаStructure of The Ear (2A2)Sunniez SunniezОценок пока нет
- Science Paper 2Документ23 страницыScience Paper 2Sunniez SunniezОценок пока нет
- SMK Segambut Jaya students' 1 Malaysia anti-drug storyboardДокумент1 страницаSMK Segambut Jaya students' 1 Malaysia anti-drug storyboardSunniez SunniezОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology RespiratoryДокумент52 страницыAnatomy and Physiology Respiratorytaslim3Оценок пока нет
- Form 5 Bio SummaryДокумент3 страницыForm 5 Bio SummarySunniez SunniezОценок пока нет
- Biology Form 5 Sdjzvbkwetyuip: Curriculum SpecificationДокумент1 страницаBiology Form 5 Sdjzvbkwetyuip: Curriculum SpecificationSunniez SunniezОценок пока нет
- Scheme of Work BIOLOGY FORM 5 - 2012Документ48 страницScheme of Work BIOLOGY FORM 5 - 2012Sunniez SunniezОценок пока нет
- s1 PDFДокумент4 страницыs1 PDFZouk9696Оценок пока нет
- 2013 10OctHCfree PDFДокумент0 страниц2013 10OctHCfree PDFSunniez SunniezОценок пока нет
- Scheme of Work BIOLOGY FORM 4 - 2012Документ28 страницScheme of Work BIOLOGY FORM 4 - 2012Sunniez SunniezОценок пока нет
- Yearly Plan 2013 Biology Form 5Документ2 страницыYearly Plan 2013 Biology Form 5Sunniez SunniezОценок пока нет
- s1 PDFДокумент4 страницыs1 PDFZouk9696Оценок пока нет
- Biology Scoring Check List Student's Name: Class: Instrument: TitleДокумент16 страницBiology Scoring Check List Student's Name: Class: Instrument: TitleazszahОценок пока нет
- SC F2 - AnswersДокумент16 страницSC F2 - AnswersSunniez SunniezОценок пока нет
- Biology Scoring Check List Student's Name: Class: Instrument: TitleДокумент16 страницBiology Scoring Check List Student's Name: Class: Instrument: TitleazszahОценок пока нет
- 1.2 Sense of TouchДокумент15 страниц1.2 Sense of TouchSunniez SunniezОценок пока нет
- s1 PDFДокумент4 страницыs1 PDFZouk9696Оценок пока нет
- 1Документ1 страница1Sunniez SunniezОценок пока нет
- ExerciseДокумент5 страницExerciseSunniez SunniezОценок пока нет
- Sains Menengah Rendah: Bahan Sumber Pengajaran Dan PembelajaranДокумент6 страницSains Menengah Rendah: Bahan Sumber Pengajaran Dan PembelajaranSunniez SunniezОценок пока нет
- Receptor in The Skin Type of Stimulus DetectedДокумент2 страницыReceptor in The Skin Type of Stimulus DetectedSunniez SunniezОценок пока нет
- 1.5 Sense of HearingДокумент15 страниц1.5 Sense of HearingSunniez SunniezОценок пока нет
- BioF4 ModuleДокумент72 страницыBioF4 ModuleEva Mayse50% (2)
- Understanding support and locomotionДокумент29 страницUnderstanding support and locomotionSunniez SunniezОценок пока нет
- Understanding support and locomotionДокумент29 страницUnderstanding support and locomotionSunniez SunniezОценок пока нет
- FridayДокумент1 страницаFridaySunniez SunniezОценок пока нет
- LPДокумент1 страницаLPSunniez SunniezОценок пока нет
- Unification Theory Debate Under 40 CharactersДокумент2 страницыUnification Theory Debate Under 40 CharactersiruleyouОценок пока нет
- Study Questions 2Документ10 страницStudy Questions 2CGОценок пока нет
- Pulex IrritansДокумент3 страницыPulex IrritansSuha AbdullahОценок пока нет
- TestesДокумент39 страницTestesImadShaheen50% (2)
- Women's Sexual Dysfunction Revised and Expanded DefinitionsДокумент7 страницWomen's Sexual Dysfunction Revised and Expanded DefinitionsjoaomartinelliОценок пока нет
- Bee Propolis May Improve Fertility in Women With en Dome Trios IsДокумент2 страницыBee Propolis May Improve Fertility in Women With en Dome Trios Isapi-3723677Оценок пока нет
- Management of Monochorionic Twin Pregnancy: Green-Top Guideline No. 51Документ13 страницManagement of Monochorionic Twin Pregnancy: Green-Top Guideline No. 51indra_strongОценок пока нет
- Review Lessons: What is a nervous system and endocrine glands? (39Документ28 страницReview Lessons: What is a nervous system and endocrine glands? (39Kizyanah Palanas Bentic100% (1)
- Sexed Oral CommДокумент8 страницSexed Oral CommJhozane SiagaОценок пока нет
- CNS and PNS Test for Science 10Документ3 страницыCNS and PNS Test for Science 10Ron Adrian Sarte SebastianОценок пока нет
- TAHBSO surgical procedure overviewДокумент1 страницаTAHBSO surgical procedure overviewKristofer Karlo Cabrera CastilloОценок пока нет
- Estrous Cycle in The Bitch and QueenДокумент9 страницEstrous Cycle in The Bitch and QueenSandrine WoolcockОценок пока нет
- BIOC19 Midterm 3Документ16 страницBIOC19 Midterm 3idk manОценок пока нет
- 01 Introduction To Clinical ParasitologyДокумент5 страниц01 Introduction To Clinical ParasitologyKaye Angel VillonОценок пока нет
- 7/23/2016 Cristina S. Nebres Mindanao State University at Naawan 1Документ32 страницы7/23/2016 Cristina S. Nebres Mindanao State University at Naawan 1Laila UbandoОценок пока нет
- Child Sexual Abuse A Medico-Legal AnalysisДокумент8 страницChild Sexual Abuse A Medico-Legal AnalysisYogi Ardhi IrafaniОценок пока нет
- 2012rh CommunitymidwiferyguidelinesДокумент43 страницы2012rh Communitymidwiferyguidelinesgeorgeloto12100% (1)
- AbortionДокумент27 страницAbortionVlynОценок пока нет
- Ergasilus ArgulusДокумент6 страницErgasilus ArgulusChen VasquezОценок пока нет
- Morphology and Anatomy of EarthwormДокумент30 страницMorphology and Anatomy of Earthwormlearn easyОценок пока нет
- FAMILY PLANNING Action Plan For 2011-12 (For Workshop 20th)Документ46 страницFAMILY PLANNING Action Plan For 2011-12 (For Workshop 20th)keshabnОценок пока нет
- Maternal Positions and Mobility During First Stage Labour - Annemarie Lawrence, Lucy Lewis, G Justus Hofmeyr, Therese Dowswell & Cathy StylesДокумент2 страницыMaternal Positions and Mobility During First Stage Labour - Annemarie Lawrence, Lucy Lewis, G Justus Hofmeyr, Therese Dowswell & Cathy StylesPujianti LestarinaОценок пока нет
- Ectopic Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentДокумент15 страницEctopic Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentPrincess Huey GreyОценок пока нет
- JADWAL 8-10 JULI 2019Документ12 страницJADWAL 8-10 JULI 2019Hartanto LieОценок пока нет
- CBQДокумент6 страницCBQCarlos BaysaОценок пока нет