Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Appendices: Improving Steam System Performance: A Sourcebook For Industry
Загружено:
Nath Boyapati0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
27 просмотров3 страницыterms
Оригинальное название
Boiler Terms
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документterms
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
27 просмотров3 страницыAppendices: Improving Steam System Performance: A Sourcebook For Industry
Загружено:
Nath Boyapatiterms
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 3
APPENDICES
IMPROVING STEAM SYSTEM PERFORMANCE: A SOURCEBOOK FOR INDUSTRY | 53
Continuous blowdownThe process oI removing water,
on a continuous basis, from a boiler to remove high con-
centrations of dissolved solids, chlorides, and other prod-
ucts. Water is replaced by treated makeup water added to
the condensate return. The withdrawn blowdown water is
usually discharged to a sanitary drain.
DeaeratorA device that uses steam to strip Ieedwater oI
oxygen and carbon dioxide.
DesuperheaterA device used in steam systems to con-
trol the energy level and/or temperature of steam supplied
to an end use, typically by injecting a fne mist oI conden-
sate into the steam fow.
Dew pointThe temperature to which a vapor must be
cooled in order for saturation or condensation to occur.
Dissolved solidThe minerals and impurities in boiler
makeup water. These increase in concentration as water is
boiled into steam.
Distillation columnA device that separates components
of a compound relying on differences in boiling points.
DryerA device that removes moisture Irom a solid.
Duty cycleThe duration and periodicity oI the operation
of a device.
Excess airExcess air in a combustion process is that
amount of air present in excess of the theoretically
required air for complete combustion. Excess air absorbs
some of the heat of combustion and is carried away as
waste heat with the exhaust combusted gases.
EvaporatorA device that removes moisture Irom a liq-
uid, resulting in increased concentration of the remaining
compounds.
FeedwaterWater sent into a boiler or a steam generator.
Feedwater typically meets cleanliness criteria, contains
treatment chemicals, and has been stripped of oxygen.
Feedwater pumpA pump that suIfciently pressurizes
feedwater to supply a boiler or generator.
Full load efciencyThe stated eIfciency (in percent)
of a process in terms of energy or work output divided by
energy input at rated production (full load).
Greenhouse gas emissionsThose gases, such as water
vapor, carbon dioxide, tropospheric ozone, methane, and
low level ozone that are transparent to solar radiation, but
opaque to long wave radiation, and which are believed to
contribute to climate change.
Heat exchangerA device used to transIer heat Irom one
medium by either direct or indirect contact.
Heating, Ventilating and Air Conditioning (HVAC)
All the components of the appliance or system used to
condition the interior air of a facility.
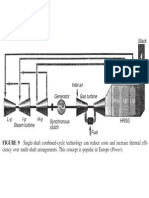
Heat Recovery Steam Generator (HRSG)A device
that captures the thermal energy in an exhaust stream or a
process stream and transfers it to water to generate steam.
Kilowatt hour (kWh)A unit oI measure oI electricity
supply or consumption of 1,000 Watts over the period of
one hour; equivalent to 3,412 Btu.
Latent heatThe change in heat content that occurs with
a change in phase and without change in temperature.
Changes in heat content that affect a change in tempera-
ture are called sensible heat changes.
Life Cycle Cost (LCC)The sum oI all the costs both
recurring and nonrecurring, related to a product, structure,
system, or service during its liIe span or specifed time
period.
Makeup waterWater brought into a boiler system Irom
outside to replace condensate not returned to the boiler
plant, water used in blowdown, steam lost through leaks,
or water lost through evaporation or mist.
MMBtuA unit oI one million British thermal units (Btu).
PaybackThe amount oI time required Ior positive cash
fows to equal the total investment costs. This is oIten used
to describe how long it will take for energy savings result-
ing Irom using more energy-eIfcient equipment to equal
the premium paid to purchase the more energy-eIfcient
equipment.
APPENDICES
54 | IMPROVING STEAM SYSTEM PERFORMANCE: A SOURCEBOOK FOR INDUSTRY
Potable waterWater that is suitable Ior drinking, as
defned by local health oIfcials.
Pounds per square inch gauge (psig)A unit oI pres-
sure in pounds force in comparison to local atmospheric
pressure (as measured by a gauge).
Pressure Reducing Valve (PRV)A valve that regulates
the amount of steam allowed from a high-pressure service
to a low-pressure service.
Radiant energyEnergy (transIer oI heat through matter
or space by means of electromagnetic waves) that trans-
mits away from its source in all directions.
ReboilerA heat exchanger used in petroleum refning
and chemical manufacturing applications that adds heat to
a process stream.
ReformerA device that produces hydrogen Irom a
hydrocarbon compound such as methane, typically by
using steam.
Relative humidityA measure oI the percent oI moisture
actually in the air compared with what would be in it if it
were fully saturated at that temperature. When the air is
fully saturated, its relative humidity is 100 percent.
R-ValueA measure oI the capacity oI a material (or
assembly of materials) to resist heat transfer, sometimes
called thermal resistance. The R-Value is the reciprocal
oI the heat transIer coeIfcient (U-Value). The larger the
R-Value, the greater its insulating properties.
SensorA device that determines the operational param-
eter or status of a system or component such as tempera-
ture or harmonics within a steam trap to infer proper or
improper operational conditions.
SilicaThe concentration oI silica dioxide Iound in water
measured in parts per million. Silica forms a tenacious
scale with low thermal conductance. Silica is soluble in
steam and can carry over into steam where it can condense
on turbine blades or erode surfaces.
SludgeA general term applied to a relatively loose
accumulation of material that has settled to the bottom of
a boiler.
Stack heat lossSensible and latent heat contained in
combustion gases and vapor emitted to the atmosphere.
Stand-aloneA device that operates independent oI or is
not connected to other systems.
Standby lossesIn boiler systems, standby losses are
energy losses that are associated with natural draft through
a boiler in a standby operating mode.
Steam ejectorA device that uses a relatively high-
pressure motive steam fow through a nozzle to create a
low-pressure or suction effect.
Steam injectorA device that injects steam into a pro-
cess, often used in direct steam heating applications.
Steam trapAn automatic control valve that allows Ior
the release of condensate, air, CO
2
, and other non-con-
densable gases, yet keeps live steam in the system.
StripperA device that separates components Irom a
compound.
Surface blowdownBoiler blowdown taken Irom the
upper part of the boiler just below the water surface to
reduce the amount of dissolved solids.
Thermal conductivityThis is a positive constant, k,
that is a property of a substance and is used in the calcula-
tion of heat transfer rates for materials. It is the amount of
heat that fows through a specifed area and thickness oI
a material over a specifed period oI time when there is a
temperature difference of one degree between the surfaces
of the material.
Thermal load factorA term used to describe the rela-
tive stability of use of heating in a facility or a process.
Often used in cogeneration where a high factor denotes
a continuous use of steady heating.
ThermocompressorA device that uses high-pressure
steam to increase the pressure of a low-pressure steam
supply to generate a more useful steam service.
ThrottlingRegulating fow rate by closing a valve in
the system.
APPENDICES
IMPROVING STEAM SYSTEM PERFORMANCE: A SOURCEBOOK FOR INDUSTRY | 55
TurbineA device that converts the enthalpy oI steam
into mechanical work. See condensing turbine and back-
pressure turbine.
Vacuum breakerA device that responds to the Iorma-
tion of vacuum conditions in equipment such as a heat
exchanger by allowing in air which promotes condensate
drainage.
Variable Frequency Drive (VFD)A type oI variable
speed motor drive in which the motor is supplied with
electrical power at frequencies other than standard 60
Hertz through a converter.
Variable Air Volume (VAV)Variable air volume is a
term Ior changing the quantity oI air fow to meet heat-
ing, cooling, or exhaust loads rather than changing air
temperatures.
Waste heatHeat that is discharged Irom a mechanical
process, wastewater, or ventilation exhaust system that
could be reclaimed for useful purposes.
Water hammerA shock that results Irom the sudden
collapse of a steam pocket in a two phase line such as a
condensate return line. Also the impingement of a water
slug carried by relatively high velocity steam.
Wireless Sensor NetworkA combination oI sensors,
wireless data transmission, and reception technologies
commonly built upon standards such as ISA 100 that
results in data systems that reliably and securely moni-
tor eIfciency even in Radio Frequency noisy environ-
ments that are commonly found in industrial plants. These
systems allow plant personnel to improve the manage-
ment of energy systems by monitoring such parameters
as proper steam trap operation, or process heat exchanger
temperatures, or condensate or feedwater pump opera-
tion and performance, or boiler excess oxygen conditions.
These systems provide a low-cost opportunity to improve
profts associated with optimum, real-time steam system
operation.
Вам также может понравиться
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesОт EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesОценок пока нет
- 1 HVAC IntroductionДокумент41 страница1 HVAC IntroductionAbdullah SendiОценок пока нет
- Recuperator - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент3 страницыRecuperator - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAvijit DasОценок пока нет
- Temperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemОт EverandTemperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemОценок пока нет
- Improve steam system efficiency with these energy conservation tipsДокумент29 страницImprove steam system efficiency with these energy conservation tipsareeb078Оценок пока нет
- Advanced Temperature Measurement and Control, Second EditionОт EverandAdvanced Temperature Measurement and Control, Second EditionОценок пока нет
- Semper Fi HVAC Glossary of Heating and A PDFДокумент13 страницSemper Fi HVAC Glossary of Heating and A PDFSmita SanjekarОценок пока нет
- Emulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingОт EverandEmulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- Hvac TermsДокумент65 страницHvac TermszebidiansОценок пока нет
- Heating Systems Troubleshooting & Repair: Maintenance Tips and Forensic ObservationsОт EverandHeating Systems Troubleshooting & Repair: Maintenance Tips and Forensic ObservationsОценок пока нет
- Deaerators in Industrial Steam Systems: Additional BenefitsДокумент5 страницDeaerators in Industrial Steam Systems: Additional BenefitsNaОценок пока нет
- HVAC Energy Saving and Clean Room TechniquesДокумент33 страницыHVAC Energy Saving and Clean Room Techniquesmanu guptaОценок пока нет
- Description of Useful HVAC TermsДокумент64 страницыDescription of Useful HVAC TermsShiyamraj Thamodharan100% (1)
- Steam: Dry and Wet SteamДокумент6 страницSteam: Dry and Wet SteamSyed Inamullah ShahОценок пока нет
- Power PlantДокумент3 страницыPower PlantangdelacruzОценок пока нет
- HVAC & Water SystemДокумент153 страницыHVAC & Water SystemSujan Bose100% (1)
- I-Mall Antipolo Supermarket Hvac DesignДокумент32 страницыI-Mall Antipolo Supermarket Hvac DesignCHRISTED ALJO BARROGAОценок пока нет
- Standard Operating Procedure - Cooling Tower - V01 - 05092010Документ6 страницStandard Operating Procedure - Cooling Tower - V01 - 05092010Karthik MandyaОценок пока нет
- HvacДокумент249 страницHvacengrjayasis20Оценок пока нет
- I-Mall Antipolo Supermarket Hvac DesignДокумент36 страницI-Mall Antipolo Supermarket Hvac DesignCHRISTED ALJO BARROGAОценок пока нет
- Hvac Prelim Finalspsychrometric PalangДокумент62 страницыHvac Prelim Finalspsychrometric PalangCHRISTED ALJO BARROGAОценок пока нет
- Script:-.Air Condition ScriptДокумент11 страницScript:-.Air Condition Scriptaimri_cochinОценок пока нет
- Steam Tip Sheet #18Документ2 страницыSteam Tip Sheet #18Muhammad NaeemОценок пока нет
- Calculate water and chemical usage for cooling towersДокумент11 страницCalculate water and chemical usage for cooling towersياسر نديمОценок пока нет
- Air Handler: Navigation SearchДокумент5 страницAir Handler: Navigation SearchNikhil KallaОценок пока нет
- Industrial Dehumidification Part 1Документ20 страницIndustrial Dehumidification Part 1Quora EarningОценок пока нет
- BU RESEARCH PDF Di Pa FinalДокумент26 страницBU RESEARCH PDF Di Pa FinalMichelle VillarandaОценок пока нет
- HVAC and Lighting Control PresentationДокумент52 страницыHVAC and Lighting Control PresentationEDUARD VI DANDAОценок пока нет
- ASHRAE Terminology of Heating VentilatinДокумент249 страницASHRAE Terminology of Heating VentilatinAnggaОценок пока нет
- Steam BasicsДокумент7 страницSteam BasicsNirmal CoolОценок пока нет
- Engg CE Subject PUSCP Semester 6th PUSCP 1st UnitДокумент15 страницEngg CE Subject PUSCP Semester 6th PUSCP 1st UnitrohanОценок пока нет
- Atmospheric Water Generator: Anurag Tripathi, Samir Tushar, Saurabh Pal, Shoumik Lodh, Shashank TiwariДокумент4 страницыAtmospheric Water Generator: Anurag Tripathi, Samir Tushar, Saurabh Pal, Shoumik Lodh, Shashank TiwariJade AusteroОценок пока нет
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Systems ExplainedДокумент6 страницRefrigeration and Air Conditioning Systems ExplainedYash TewariОценок пока нет
- A Z GlossaryДокумент47 страницA Z Glossaryhijasdayamahal hijasОценок пока нет
- Me 451 - 1Документ35 страницMe 451 - 1Edrees AldreesОценок пока нет
- Poultry Housing Environmental Control Using Radiant System Coupled To A Solar-Driven Liquid Desiccant Evaporative Water Cooler, by Soliman AbdallaДокумент9 страницPoultry Housing Environmental Control Using Radiant System Coupled To A Solar-Driven Liquid Desiccant Evaporative Water Cooler, by Soliman AbdallaDavid BroadfootОценок пока нет
- Air Conditioning SystemsДокумент3 страницыAir Conditioning SystemsArman Ul NasarОценок пока нет
- AFBC BoilerДокумент12 страницAFBC BoilerNaman Sharma0% (1)
- Optimizing Steam Boiler Efficiency for Laundry OperationsДокумент57 страницOptimizing Steam Boiler Efficiency for Laundry OperationsMcilwaine Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- Cooling Tower Efficiency ManualДокумент26 страницCooling Tower Efficiency ManualSyed Alwi AlattasОценок пока нет
- Cooling TowersДокумент40 страницCooling Towers1000 Subscribers Without a Video100% (2)
- Industrial DehumidificationДокумент16 страницIndustrial Dehumidificationdax18003904100% (1)
- 2009-08 EMOs For Cooling SystemsДокумент4 страницы2009-08 EMOs For Cooling Systemsnikola ilicОценок пока нет
- Air Conditioning Plant (BSME 5B)Документ128 страницAir Conditioning Plant (BSME 5B)Marvin ArnaizОценок пока нет
- BME Refrigeration and Air ConditioningДокумент6 страницBME Refrigeration and Air ConditioningalysonmicheaalaОценок пока нет
- Class-1-HVAC GLOSSARYДокумент7 страницClass-1-HVAC GLOSSARYAmrit BaniyaОценок пока нет
- Components of Coal-Fired Steam Power PlantДокумент5 страницComponents of Coal-Fired Steam Power PlantDanBenedictAcuzarОценок пока нет
- IntroductionДокумент2 страницыIntroductionAli ImranОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ12 страницChapter 2Mohammad Muawya Nouri HijaziОценок пока нет
- Elements of Energy Systems 2Документ21 страницаElements of Energy Systems 2Marcial Jr. MilitanteОценок пока нет
- Intelligent Adiabatic Evaporative SystemДокумент6 страницIntelligent Adiabatic Evaporative SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Control and condition air with an air handler unitДокумент10 страницControl and condition air with an air handler unitSreekanth MadakaОценок пока нет
- AAtheroysДокумент10 страницAAtheroysBisob MannaОценок пока нет
- HavcДокумент14 страницHavcSharique AliОценок пока нет
- Utility SystemДокумент15 страницUtility SystemprasadparulekarОценок пока нет
- PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF INTERNAL HEAT EXCHANGERДокумент39 страницPERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF INTERNAL HEAT EXCHANGERNeal Christian ParatoОценок пока нет
- Heating Coil in The Main Air Handling UnitДокумент15 страницHeating Coil in The Main Air Handling UnitMohsinShaikh100% (2)
- Safety in Power Plants: Preventing Electrical, Fire, and Chemical HazardsДокумент53 страницыSafety in Power Plants: Preventing Electrical, Fire, and Chemical HazardsAntony Chacha GatiОценок пока нет
- Istilah Istilah Yang Sering Di Temukan Dalam Kamus PendinginДокумент9 страницIstilah Istilah Yang Sering Di Temukan Dalam Kamus PendinginFriget RusiantoОценок пока нет
- Fastener Handouts (Screw)Документ34 страницыFastener Handouts (Screw)cluchavezОценок пока нет
- Measurement of Bearing Clearance - Turbomachinery MagazineДокумент3 страницыMeasurement of Bearing Clearance - Turbomachinery MagazineNath BoyapatiОценок пока нет
- 6000 en 06 SRBДокумент84 страницы6000 en 06 SRBSuphi YükselОценок пока нет
- CFBCДокумент1 страницаCFBCNath BoyapatiОценок пока нет
- Second Amendment On CSS OrderДокумент2 страницыSecond Amendment On CSS OrderNath BoyapatiОценок пока нет
- Dunlop Technical ManualДокумент41 страницаDunlop Technical ManualGonzalo AriasОценок пока нет
- Capacitor Bank ProtectionДокумент17 страницCapacitor Bank ProtectionskisakОценок пока нет
- 1la8 SeimennДокумент8 страниц1la8 SeimennNath BoyapatiОценок пока нет
- Motor Spare 2Документ2 страницыMotor Spare 2Nath BoyapatiОценок пока нет
- BRGДокумент2 страницыBRGNath BoyapatiОценок пока нет
- Instruction ScreenДокумент1 страницаInstruction ScreenNath BoyapatiОценок пока нет
- Supp Screen (IC)Документ2 страницыSupp Screen (IC)Nath BoyapatiОценок пока нет
- STD UploadДокумент1 страницаSTD UploadNath BoyapatiОценок пока нет
- Belt ConveyorДокумент12 страницBelt ConveyorNath Boyapati100% (1)
- Moody's Friction Factor Chart Represented by Cole Brook EquationДокумент1 страницаMoody's Friction Factor Chart Represented by Cole Brook EquationNath BoyapatiОценок пока нет
- Comparison-R407c and R410aДокумент5 страницComparison-R407c and R410aKartik PrabhakarОценок пока нет
- Energy Loss When Moving Water Between Copper TubesДокумент1 страницаEnergy Loss When Moving Water Between Copper TubesNath BoyapatiОценок пока нет
- AДокумент1 страницаANath BoyapatiОценок пока нет
- Ideal Gas-Turbine Cycle T-S Diagram With The Same Processes As in Fig. 6 Complete-Cycle Gas Turbine Shown Below The T-S DiagramДокумент1 страницаIdeal Gas-Turbine Cycle T-S Diagram With The Same Processes As in Fig. 6 Complete-Cycle Gas Turbine Shown Below The T-S DiagramNath BoyapatiОценок пока нет
- Gas PowerДокумент1 страницаGas PowerNath BoyapatiОценок пока нет
- Claim FormДокумент3 страницыClaim FormMorgan ThomasОценок пока нет
- 155-MW Natural-Gas-Fired Gas Turbine Featuring A Dry Low NO Combustor (Power)Документ1 страница155-MW Natural-Gas-Fired Gas Turbine Featuring A Dry Low NO Combustor (Power)Nath BoyapatiОценок пока нет
- Ì Iêv Êãõ Ià I Ìiàê Vviàãê Ià Ì Êv Iý L Ìþê 'Ê V Ê I Ê Àiûi Ìê' ) Iêì Êãõ Ià I ÌiàêìõliãДокумент1 страницаÌ Iêv Êãõ Ià I Ìiàê Vviàãê Ià Ì Êv Iý L Ìþê 'Ê V Ê I Ê Àiûi Ìê' ) Iêì Êãõ Ià I ÌiàêìõliãNath BoyapatiОценок пока нет
- NOTIS - Basic Theory: Basic Types of ScalesДокумент1 страницаNOTIS - Basic Theory: Basic Types of ScalesNath BoyapatiОценок пока нет
- 27 Nakshatra PadasДокумент13 страниц27 Nakshatra PadasAstrologer in Dubai Call 0586846501Оценок пока нет
- Recommended Fluid Velocities in Piping: Determine The Pipe Schedule NumberДокумент1 страницаRecommended Fluid Velocities in Piping: Determine The Pipe Schedule NumberNath BoyapatiОценок пока нет
- Sources of Textile Fibers: Solar Energy Is The Basis of LifeДокумент1 страницаSources of Textile Fibers: Solar Energy Is The Basis of LifeNath BoyapatiОценок пока нет
- Inspect and Repair Desuperheater Nozzle AssemblyДокумент1 страницаInspect and Repair Desuperheater Nozzle AssemblyNath BoyapatiОценок пока нет
- Abbreviations Abbreviations Abbreviations Abbreviations AbbreviationsДокумент3 страницыAbbreviations Abbreviations Abbreviations Abbreviations AbbreviationsNath BoyapatiОценок пока нет
- PPG Loss CalДокумент1 страницаPPG Loss CalNath BoyapatiОценок пока нет
- ASTM C1609 - C1609M - 19a Standard Test Method For Flexural Performance of Fiber-Reinforced Concrete (Using Beam With Third-Point Loading)Документ5 страницASTM C1609 - C1609M - 19a Standard Test Method For Flexural Performance of Fiber-Reinforced Concrete (Using Beam With Third-Point Loading)ming_zhu10Оценок пока нет
- Solenoid Operated Deluge Valve: - UL Listed / ULC Listed Main Valves - 3 - 12 Inch SizesДокумент2 страницыSolenoid Operated Deluge Valve: - UL Listed / ULC Listed Main Valves - 3 - 12 Inch Sizeseng_poohОценок пока нет
- Auto Trans Removal and Install 97-98 PDFДокумент8 страницAuto Trans Removal and Install 97-98 PDFxstyle123Оценок пока нет
- How VVT and Variable Lift Improve Engine PerformanceДокумент32 страницыHow VVT and Variable Lift Improve Engine PerformanceumairОценок пока нет
- Chapter 71 - Power Plant: BHT-412-CR&O-6Документ40 страницChapter 71 - Power Plant: BHT-412-CR&O-6252nd PAS100% (1)
- FEA Answers by Professor GuruprasadДокумент146 страницFEA Answers by Professor GuruprasadManendra SaiОценок пока нет
- Machine Tool DrivesДокумент21 страницаMachine Tool DrivesChaitanyaSrivastava100% (1)
- Downtime BD TyreДокумент127 страницDowntime BD TyreRidhani IqbalОценок пока нет
- P730 Brochure ENДокумент2 страницыP730 Brochure ENVictor GalarzaОценок пока нет
- HR2470TДокумент3 страницыHR2470TRosângela O. Santos0% (1)
- ITP For Nuts & Bolts - R22Документ7 страницITP For Nuts & Bolts - R22Hamid Taghipour ArmakiОценок пока нет
- Design of An Electronic Stability Program For Vehicle Simulation SoftwareДокумент25 страницDesign of An Electronic Stability Program For Vehicle Simulation SoftwarepmaznikerОценок пока нет
- REE 6031 Tutorial 1Документ5 страницREE 6031 Tutorial 1Eng Maboshe Charles Namafe0% (1)
- Strengthening Mechanisms ExplainedДокумент74 страницыStrengthening Mechanisms ExplainedRyan TorresОценок пока нет
- Section 5 - Relief SystemsДокумент22 страницыSection 5 - Relief Systemslulis171Оценок пока нет
- Mechanical, Physical and Wear Properties of PP-SCF CompositesДокумент11 страницMechanical, Physical and Wear Properties of PP-SCF CompositesHarriJunaediОценок пока нет
- Vdocuments - MX - Caterpillar Cat 320l Track Excavator Prefix 8lk Service Repair Manual 8lk00001 and Up 1586311769Документ30 страницVdocuments - MX - Caterpillar Cat 320l Track Excavator Prefix 8lk Service Repair Manual 8lk00001 and Up 1586311769Ikeo100% (1)
- General Online QuestДокумент80 страницGeneral Online QuestPankaj PooniaОценок пока нет
- DP09toc PDFДокумент1 страницаDP09toc PDFNerio CanadellОценок пока нет
- MeasurIT Flexim Fastening Parts 0910Документ5 страницMeasurIT Flexim Fastening Parts 0910cwiejkowskaОценок пока нет
- BMW 2 - M5 - Engine - S62B50 PDFДокумент26 страницBMW 2 - M5 - Engine - S62B50 PDFkukumarcic0% (1)
- Hydraulic Accumulator (High Pressure) - Test and Charge: Pruebas y AjustesДокумент16 страницHydraulic Accumulator (High Pressure) - Test and Charge: Pruebas y AjustesBrayan Sánchez ParedesОценок пока нет
- Buckling Analysis: The Theory of BucklingДокумент6 страницBuckling Analysis: The Theory of BucklingKing Everest100% (2)
- Aprilia Parts CatalogДокумент126 страницAprilia Parts CatalogyokoОценок пока нет
- PROSIS Part Information: 8/3/2011 1020038 20060 EC700B LC Volvo 10001-212/100 Cylinder Block 8279230Документ3 страницыPROSIS Part Information: 8/3/2011 1020038 20060 EC700B LC Volvo 10001-212/100 Cylinder Block 8279230Power MobileОценок пока нет
- Integrated Control of Braking and SteeringДокумент10 страницIntegrated Control of Braking and SteeringakkkkОценок пока нет
- 101 FA08 HE2SolvedДокумент12 страниц101 FA08 HE2SolvedJulio César Macías ZamoraОценок пока нет
- User Instructions MOD 110SH: Warning!Документ2 страницыUser Instructions MOD 110SH: Warning!Jhon Fabio ParraОценок пока нет
- Gallic 16 Engels Hld23 TornoДокумент47 страницGallic 16 Engels Hld23 TornoAdrian Macaya100% (1)
- Eni Blasia S 220Документ2 страницыEni Blasia S 220Fajar EkoОценок пока нет
- You Can't Joke About That: Why Everything Is Funny, Nothing Is Sacred, and We're All in This TogetherОт EverandYou Can't Joke About That: Why Everything Is Funny, Nothing Is Sacred, and We're All in This TogetherОценок пока нет
- Lessons from Tara: Life Advice from the World's Most Brilliant DogОт EverandLessons from Tara: Life Advice from the World's Most Brilliant DogРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (42)
- Sexual Bloopers: An Outrageous, Uncensored Collection of People's Most Embarrassing X-Rated FumblesОт EverandSexual Bloopers: An Outrageous, Uncensored Collection of People's Most Embarrassing X-Rated FumblesРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (7)
- The Importance of Being Earnest: Classic Tales EditionОт EverandThe Importance of Being Earnest: Classic Tales EditionРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (43)
- Welcome to the United States of Anxiety: Observations from a Reforming NeuroticОт EverandWelcome to the United States of Anxiety: Observations from a Reforming NeuroticРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (10)
- The House at Pooh Corner - Winnie-the-Pooh Book #4 - UnabridgedОт EverandThe House at Pooh Corner - Winnie-the-Pooh Book #4 - UnabridgedРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (5)
- The Asshole Survival Guide: How to Deal with People Who Treat You Like DirtОт EverandThe Asshole Survival Guide: How to Deal with People Who Treat You Like DirtРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (60)
- Other People's Dirt: A Housecleaner's Curious AdventuresОт EverandOther People's Dirt: A Housecleaner's Curious AdventuresРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (104)
- The Smartest Book in the World: A Lexicon of Literacy, A Rancorous Reportage, A Concise Curriculum of CoolОт EverandThe Smartest Book in the World: A Lexicon of Literacy, A Rancorous Reportage, A Concise Curriculum of CoolРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (14)
- Tidy the F*ck Up: The American Art of Organizing Your Sh*tОт EverandTidy the F*ck Up: The American Art of Organizing Your Sh*tРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (99)
- Humorous American Short Stories: Selections from Mark Twain, O. Henry, James Thurber, Kurt Vonnegut, Jr. and moreОт EverandHumorous American Short Stories: Selections from Mark Twain, O. Henry, James Thurber, Kurt Vonnegut, Jr. and moreОценок пока нет
- The Best Joke Book (Period): Hundreds of the Funniest, Silliest, Most Ridiculous Jokes EverОт EverandThe Best Joke Book (Period): Hundreds of the Funniest, Silliest, Most Ridiculous Jokes EverРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (4)




































































































































![The Inimitable Jeeves [Classic Tales Edition]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/audiobook_square_badge/711420909/198x198/ba98be6b93/1712018618?v=1)














