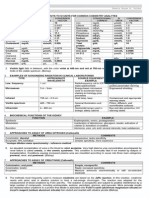
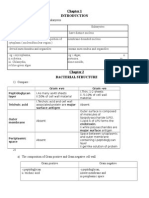
Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Blood Transfusion
Загружено:
Dennis Valdez0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
17 просмотров1 страница/.
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документ/.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
17 просмотров1 страницаBlood Transfusion
Загружено:
Dennis Valdez/.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
What is a blood transfusion?
A blood transfusion is when donated blood is given to you intravenously, directly into your bloodstream. Usually it is a component of blood which is given.
When is a blood transfusion necessary?
Blood transfusion is important in the treatment of many medical problems such as cancer and blood disorders, and in the treatment of some injuries and major surgical procedures when blood loss has occurred.
REASONS FOR BLOOD TRANSFUSION
Blood and blood products are used for a number of purposes, but the three main reasons for blood transfusion are: to correct anaemia (a low haemoglobin level) to replace blood lost by bleeding, either during surgery or because of an accident to replace other constituents of blood, such as coagulation factors.
IgM AND IgG (NATURALLY-OCCURRING AND IMMUNE) ANTI-A AND ANTI-B
All individuals, except those who are group AB, produce IgM anti-A and/ or anti-B. Some, particularly those who are group O, also produce IgG antibodies. It is thought that these are the result of stimulation by A- and B-like antigens commonly found in the environment, food, etc. When someone has IgG anti-AB, the amount of IgM anti-AB is usually high and the term high-titre anti-AB or high-titre O is used. The serum of these individuals will often lyse A and/or B cells in the reverse grouping. These hightitre antibodies are important in two situations: 1. Transfusion of group O blood or plasma to people who are not group O.If group O plasma containing high-titre anti-AB is transfused into an A or B person, there could be some red cell destruction a transfusion reaction. It is therefore preferable not to transfuse a person who is not group O with group O products. If it is unavoidable, select units from donors that do not lyse A and/or B cells in the serum group or remove the plasma aseptically from the red cells. 2. In pregnancy, when an O mother has an A or B infant. It is worth noting if the maternal serum lyses A and/or B cells as IgG anti-AB could have crossed the placenta and destroyed the fetal red cells. At birth, the baby could suffer from the effects of anaemia and jaundice as a result of the red cell destruction. However, haemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) of this sort is far less severe than that caused by anti-D, and tests for quantifying IgG anti-AB during pregnancy are of little value in predicting whether the baby will suffer. There is, therefore, no value in performing any further tests during pregnancy.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Blood Sample Blood + 0.30% Nacl Solution: Activity No. 2: Osmotic Behavior of Red Blood Cells Experimental PlatesДокумент1 страницаBlood Sample Blood + 0.30% Nacl Solution: Activity No. 2: Osmotic Behavior of Red Blood Cells Experimental PlatesDennis ValdezОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- Ti Bajssít Ajkáyo NaljjajjegénjДокумент8 страницTi Bajssít Ajkáyo NaljjajjegénjDennis ValdezОценок пока нет
- Mi..cr..o ...... Ans - Wer.s.h..eet....Документ67 страницMi..cr..o ...... Ans - Wer.s.h..eet....Dennis ValdezОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Grams: Allowable Actual Weight of Blood: 532 - 627Документ1 страницаGrams: Allowable Actual Weight of Blood: 532 - 627Dennis ValdezОценок пока нет
- Alcamo's Laboratory Fundamentals of Microbiology: by Jeffrey C. PommervilleДокумент2 страницыAlcamo's Laboratory Fundamentals of Microbiology: by Jeffrey C. PommervilleDennis ValdezОценок пока нет
- Prion Diseases: Primary StructuresДокумент4 страницыPrion Diseases: Primary StructuresDennis ValdezОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Erythropoiesis: Stages of MaturationДокумент3 страницыErythropoiesis: Stages of MaturationDennis ValdezОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Significance: Endothelial DysfunctionДокумент1 страницаSignificance: Endothelial DysfunctionDennis ValdezОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- CrazyДокумент1 страницаCrazyDennis ValdezОценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Q U Ota T Ion.p DFДокумент1 страницаQ U Ota T Ion.p DFDennis ValdezОценок пока нет
- Blood and Tissue FlafellatesДокумент4 страницыBlood and Tissue FlafellatesDennis ValdezОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- Food Preferences of Dmmmsu Laboratory High Schoolstudents: Their Implications To Nutrition EducationДокумент1 страницаFood Preferences of Dmmmsu Laboratory High Schoolstudents: Their Implications To Nutrition EducationDennis ValdezОценок пока нет
- Dennis Bryan A. ValdezДокумент58 страницDennis Bryan A. ValdezDennis ValdezОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Antibodies Produced Against RH AntigensДокумент1 страницаAntibodies Produced Against RH AntigensDennis ValdezОценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- DTT PDFДокумент2 страницыDTT PDFJack WyattОценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Reviewer - Immunohematology - Part 1Документ16 страницReviewer - Immunohematology - Part 1Joshua TrinidadОценок пока нет
- Immunology and Serology NotesДокумент171 страницаImmunology and Serology NotesMa Loidette Rull Guanlao-Serrano67% (3)
- Cal Bio Chem Human IgG Booklet CB0051Документ66 страницCal Bio Chem Human IgG Booklet CB0051Alok PandeyОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Pathophysiology Test Bank CH 6-9Документ33 страницыPathophysiology Test Bank CH 6-9Joyy86% (7)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Capillarys ImmunotypingДокумент62 страницыCapillarys ImmunotypingAbdel Razzak Mikati100% (1)
- BHRC Rates 01.04Документ87 страницBHRC Rates 01.04nishant00032Оценок пока нет
- HarrisДокумент35 страницHarrisMariel AbatayoОценок пока нет
- Blood Bank TrainingДокумент82 страницыBlood Bank TrainingMohamed Elmasry0% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- 130 Immunology Questions and AnswersДокумент46 страниц130 Immunology Questions and Answers成失92% (13)
- QUIZ 8-Gen - PathДокумент27 страницQUIZ 8-Gen - PathDrbee10Оценок пока нет
- Compare Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes: Gram +ve Gram - Ve Peptidoglycan Layer Teichoic Acid Surface AntigenДокумент12 страницCompare Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes: Gram +ve Gram - Ve Peptidoglycan Layer Teichoic Acid Surface AntigenAamir BugtiОценок пока нет
- 08-0923 FinaldДокумент5 страниц08-0923 FinaldAndri YansyahОценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- ImmunoglobulinДокумент41 страницаImmunoglobulinFarlogyОценок пока нет
- Interpretation of Serology Tests in Selected InfectionsДокумент35 страницInterpretation of Serology Tests in Selected InfectionsAnees AdamsОценок пока нет
- 13fk10 Hav Igg-Igm (D) Ins (En) CeДокумент2 страницы13fk10 Hav Igg-Igm (D) Ins (En) CeCrcrjhjh RcrcjhjhОценок пока нет
- Agility & TestLine SmartKits - AN - 210x210mm - 3Документ5 страницAgility & TestLine SmartKits - AN - 210x210mm - 3Abdalazeez AlsayedОценок пока нет
- Kit Insert - Anti-SARS-CoV-2Документ5 страницKit Insert - Anti-SARS-CoV-2Yosua Butar ButarОценок пока нет
- España Boulevard, Sampaloc, Manila, Philippines 1015 Tel. No. 406-1611 Loc. 8241 Telefax: 731-5738 Website: WWW - Ust.edu - PHДокумент4 страницыEspaña Boulevard, Sampaloc, Manila, Philippines 1015 Tel. No. 406-1611 Loc. 8241 Telefax: 731-5738 Website: WWW - Ust.edu - PHsteffiОценок пока нет
- Immunology QuestionsДокумент41 страницаImmunology QuestionsNazima Nasrullah100% (1)
- Laughter Is The Best MedicineДокумент9 страницLaughter Is The Best MedicineGaurav GautamОценок пока нет
- Immunoglobulins: Structure and FunctionДокумент31 страницаImmunoglobulins: Structure and FunctionbuscacomicОценок пока нет
- Immunoglobulins: Structure and Function Immunoglobulins (Ig) - Glycoprotein Molecules Which Are Produced by Plasma Cells inДокумент14 страницImmunoglobulins: Structure and Function Immunoglobulins (Ig) - Glycoprotein Molecules Which Are Produced by Plasma Cells inCristina GeorgianaОценок пока нет
- GENEDIA W ONE COVID-19 IgM - IgG BrochureДокумент2 страницыGENEDIA W ONE COVID-19 IgM - IgG BrochureBPG ServiceОценок пока нет
- Serum Protein ElectrophoresisДокумент33 страницыSerum Protein Electrophoresiskiedd_04100% (7)
- Rapid Test CovidДокумент2 страницыRapid Test CovidYuzia Birthdie C UОценок пока нет
- PreciControl Anti-HAV IgM - Ms - 11876368122.V14.EnДокумент2 страницыPreciControl Anti-HAV IgM - Ms - 11876368122.V14.EnARIF AHAMMED PОценок пока нет
- Bioline Rapid. Urinalysis Test PDFДокумент34 страницыBioline Rapid. Urinalysis Test PDFGail IbanezОценок пока нет
- Antigen and Antibody InteractionДокумент17 страницAntigen and Antibody InteractionSaumya PothukuchiОценок пока нет
- A Brief History of The Discovery of The ImmunoglobДокумент6 страницA Brief History of The Discovery of The ImmunoglobVentanucoОценок пока нет
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)От EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Рейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)