Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Laboratory 8 - AGC
Загружено:
Ariana Ribeiro Lameirinhas0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
132 просмотров2 страницыThis experiment demonstrates one such system. Plot the input versus output characteristics for the AGC / AVC circuit. 8. Brief theory and motivation the reader will benefit from the recorded lectures at.
Исходное описание:
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThis experiment demonstrates one such system. Plot the input versus output characteristics for the AGC / AVC circuit. 8. Brief theory and motivation the reader will benefit from the recorded lectures at.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
132 просмотров2 страницыLaboratory 8 - AGC
Загружено:
Ariana Ribeiro LameirinhasThis experiment demonstrates one such system. Plot the input versus output characteristics for the AGC / AVC circuit. 8. Brief theory and motivation the reader will benefit from the recorded lectures at.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
experiment 8
Goal of the experiment
In the front-end electronics of a system, we may require that the gain of the amplifier be adjustable, since the amplitude of the input keeps varying. Such a system can be designed using feedback. This experiment demonstrates one such system.
8.3 Measurements to be taken
Transfer Characteristics - Plot the input versus output characteristics for the AGC/AVC.
8.4 What you should submit
1
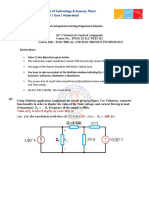
Simulate the circuit of Figure 8.1 and obtain the Transfer Characteristic of the system. Assume that the input comes from a function generator; use a sine wave input of a single frequency. Build the circuit shown on Figure 8.1. Plot/print the transfer characteristic using the oscilloscope and compare it with simulation results.
8.1 Brief theory and motivation
The reader will benefit from the recorded lectures at [25]. Another useful reference is the application note on Automatic Level Controller for Speech Signals using PID Controllers [2]. In the signal chain of an electronic system, the output of the sensor can vary depending on the strength of the input. To adapt to wide variations in the magnitude of the input, we can design an amplifier whose gain can be adjusted dynamically. This is possible when the input signal has a narrow bandwidth and the control system is called Automatic Gain Control or AGC. Since we may wish to maintain the output voltage of the amplifier at a constant level, we also use the term Automatic Volume Control (AVC). Figure 8.1 shows an AGC circuit. The typical I/O characteristics Vr Voutput ref of AGC/AVC circuit is shown in Figure 8.2. As shown in Figure 8.2, 2 the value of the system remains constant at 2Vr Vref beyond input voltage Vpi = 2Vr Vref . Vpi = 2Vr Vref
Figure 8.2: Input-Output Characteristics of AGC/AVC S.No. Input Voltage Output Voltage
VI =Vpisint VC
Figure 8.1: Automatic Gain Control (AGC)/Automatic Volume Control (AVC)
8.2 Specification
Design AGC/AVC system to maintain the peak amplitude of the sine wave at 2V. page 48
VC Vpisint VR
VCVpi 1 VR VR C Vref= VOP 2VR
2
1 2 3 4 Table 8.1: Transfer characteristic of the AGC circuit
Plot the output as a function of input voltage. Enter sufficient number of readings in Table 8.2. Does the output remain constant as the magnitude of the input is increased? Beyond what value of the input voltage does the gain begin to stabilize? We have included sample output waveform for the AGC circuit in Figure 8.3.
Analog System Lab Kit PRO
R3 +
VF2
R4 C1 U1 VXVY 10 U2 VXVY 10 + R1 R2 V1
Notes on Experiment 8:
V2 VF1
+ VG1
Figure 8.3: AGC circuit and its output
8.5 Exercise Set 8
Determine the lock range for the AGC, which is defined as the range of input values for which output voltage remains constant.
Analog System Lab Kit PRO
page 49
experiment 8
Вам также может понравиться
- Laboratory in Automatic Control: Lab 1 Matlab BasicsДокумент23 страницыLaboratory in Automatic Control: Lab 1 Matlab BasicsnchubcclОценок пока нет
- Linear Control TCДокумент46 страницLinear Control TCjibranbaladiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Signal Conditioning CircuitДокумент30 страницChapter 3 Signal Conditioning CircuittcsОценок пока нет
- Temperature Sensing/Monitoring Using Lm35 & Atmega8Документ6 страницTemperature Sensing/Monitoring Using Lm35 & Atmega8Suket75% (4)
- Thermal Diode ModelДокумент23 страницыThermal Diode ModelAzxctybv VpolmОценок пока нет
- Interfacing Programs For 8085Документ37 страницInterfacing Programs For 8085archankumarturagaОценок пока нет
- Ventilador - Neumático y ElectricoДокумент39 страницVentilador - Neumático y ElectricoCastillo CarolinaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 12 (ADC) Rv01Документ47 страницLecture 12 (ADC) Rv01Amirul HaqimieОценок пока нет
- EMBEDDED BASED Automatic AUDITORIUM CONTROLLER 0TH REVДокумент36 страницEMBEDDED BASED Automatic AUDITORIUM CONTROLLER 0TH REVspringsource100% (1)
- Notes04 ADCДокумент9 страницNotes04 ADCHosam BendaryОценок пока нет
- Lab 5: Design Single Stage and Telescopic Differential AmplifiersДокумент13 страницLab 5: Design Single Stage and Telescopic Differential AmplifiersTamilinbaaОценок пока нет
- Electrical and Electronics Lab Manual For Mechanical EngineeringДокумент21 страницаElectrical and Electronics Lab Manual For Mechanical EngineeringSreerag Kunnathu SugathanОценок пока нет
- ADC (Analog-To-Digital Converter)Документ11 страницADC (Analog-To-Digital Converter)Abdullah Muzammil0% (1)
- Ei-2406 Isd Lab Manual (2013)Документ47 страницEi-2406 Isd Lab Manual (2013)Rahul GRОценок пока нет
- Cs2252 - MPMC 16 M With Answers Upto 2Документ40 страницCs2252 - MPMC 16 M With Answers Upto 2archumeenabaluОценок пока нет
- Frequency Response PlotsДокумент8 страницFrequency Response PlotsMOHAMED IBRAHIM0% (1)
- Home Task:: Lab No. 8 - PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) ProgrammingДокумент3 страницыHome Task:: Lab No. 8 - PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) Programminganon_781544752Оценок пока нет
- 5W USB Flyback Design ReviewApplication ReportДокумент21 страница5W USB Flyback Design ReviewApplication ReportleechulmiuОценок пока нет
- ECE 271 Lab 1 An Introduction To Modeling, Verilog, and Real World Digital PartsДокумент20 страницECE 271 Lab 1 An Introduction To Modeling, Verilog, and Real World Digital PartsBin BinОценок пока нет
- Software button debouncing in 40 charactersДокумент11 страницSoftware button debouncing in 40 charactersEmanuel CrespoОценок пока нет
- Esp32 Wroom 32d - Esp32 Wroom 32u - Datasheet - enДокумент28 страницEsp32 Wroom 32d - Esp32 Wroom 32u - Datasheet - enFranco Rivadeneyra100% (1)
- Atmel-Code Lock With 4x4 Keypad and I2C™ LCDДокумент9 страницAtmel-Code Lock With 4x4 Keypad and I2C™ LCDkaran_vistaОценок пока нет
- Simulation and Arduino Hardware Implementation of DC Motor Control Using Sliding Mode ControllerДокумент6 страницSimulation and Arduino Hardware Implementation of DC Motor Control Using Sliding Mode Controllermiftah fadhliОценок пока нет
- Jump, Loop and Call Instructions: University of Engineering and Technology TaxilaДокумент93 страницыJump, Loop and Call Instructions: University of Engineering and Technology TaxilaPraneetha InumarthiОценок пока нет
- STM32F30xx-31xx Standard Peripheral Library UM1581Документ584 страницыSTM32F30xx-31xx Standard Peripheral Library UM1581John LeungОценок пока нет
- Automatic Fan Speed Control Circuit Using PIC16F877A MicrocontrollerДокумент5 страницAutomatic Fan Speed Control Circuit Using PIC16F877A MicrocontrollerPramillaОценок пока нет
- Connect ATmega328P Xplained Mini to Arduino IDEДокумент5 страницConnect ATmega328P Xplained Mini to Arduino IDEphuceltnОценок пока нет
- Lab 1-9Документ36 страницLab 1-9HassanAhmed124Оценок пока нет
- DAQ, Simulation and Control in MATLAB and SimulinkДокумент21 страницаDAQ, Simulation and Control in MATLAB and SimulinkHammerly Mamani ValenciaОценок пока нет
- 8279 Keyboard and Display ControllerДокумент33 страницы8279 Keyboard and Display Controllergutzz0079197100% (1)
- Matlab Basics Tutorial: VectorsДокумент52 страницыMatlab Basics Tutorial: VectorsMohit Bathla MontyОценок пока нет
- MATLAB & Simulink IntroductionДокумент17 страницMATLAB & Simulink IntroductionBharat BehlОценок пока нет
- Final Review DSPДокумент17 страницFinal Review DSPKota Krishna DheerajОценок пока нет
- Analysis and Design of Combinational Logic CirciutsДокумент74 страницыAnalysis and Design of Combinational Logic CirciutsMS RahilОценок пока нет
- How To Interfacing Sensor With LPC2148 ARMДокумент8 страницHow To Interfacing Sensor With LPC2148 ARMSubir MaityОценок пока нет
- Ldmicro ChangesДокумент4 страницыLdmicro ChangesPandu Milik MuОценок пока нет
- Clap CounterДокумент2 страницыClap CounterRiddhi Hiren KakkaОценок пока нет
- 54124-mt - CPLD & Fpga Architecture & ApplicationsДокумент1 страница54124-mt - CPLD & Fpga Architecture & ApplicationsSRINIVASA RAO GANTAОценок пока нет
- 8085 Microproceesor - PPTДокумент59 страниц8085 Microproceesor - PPTShanagonda Manoj KumarОценок пока нет
- Program For Interfacing 8279: 1. 8085 Microprocessor Kit 2. 8279 Interfacing Module 3. Power SupplyДокумент21 страницаProgram For Interfacing 8279: 1. 8085 Microprocessor Kit 2. 8279 Interfacing Module 3. Power SupplySubhashini MurugesanОценок пока нет
- Laboratory2 Marking SchemeДокумент12 страницLaboratory2 Marking SchemeAmna EhtshamОценок пока нет
- Timer Counter in ARM7 (LPC2148) : Aarav SoniДокумент26 страницTimer Counter in ARM7 (LPC2148) : Aarav SoniMatthew BattleОценок пока нет
- Demo Program From Lecture #1: RegistersДокумент15 страницDemo Program From Lecture #1: RegistersNaresh BopparathiОценок пока нет
- Adders and MultipliersДокумент59 страницAdders and Multipliersdbanbumani_501791840Оценок пока нет
- Ecad & Vlsi LabДокумент98 страницEcad & Vlsi LabbitseceОценок пока нет
- Intro To Embedded Systems - AMIT - NewДокумент73 страницыIntro To Embedded Systems - AMIT - NewOmar EzzОценок пока нет
- Statement List InstructionsДокумент50 страницStatement List InstructionsMiladShahabiОценок пока нет
- Embedded Lab: Kgisl Institute of Technology Department of Electronics and CommunicationДокумент111 страницEmbedded Lab: Kgisl Institute of Technology Department of Electronics and CommunicationJeeva NatarajanОценок пока нет
- Tiva C Series LaunchPadДокумент13 страницTiva C Series LaunchPadVivek ShrigiriОценок пока нет
- MPS-2100 Pressure Sensors Competitive Prices Wide Temp RangeДокумент3 страницыMPS-2100 Pressure Sensors Competitive Prices Wide Temp RangeAhmed ShadeedОценок пока нет
- Development of ARM Architecture and its ProcessorsДокумент40 страницDevelopment of ARM Architecture and its ProcessorsDwaraka OrugantiОценок пока нет
- SMS Based Energy Meter MonitoringДокумент6 страницSMS Based Energy Meter MonitoringNarayan Singh WaraichОценок пока нет
- Embedded Systems With 8051 CДокумент190 страницEmbedded Systems With 8051 CPayal SinghОценок пока нет
- EI6702-Logic and Distributed Control System PDFДокумент15 страницEI6702-Logic and Distributed Control System PDFlionelprakzy100% (1)
- LAB 02 ControlДокумент20 страницLAB 02 Controlfiaz023Оценок пока нет
- ANALOG MULTIPLIERS: KEY COMPONENTS AND APPLICATIONSДокумент17 страницANALOG MULTIPLIERS: KEY COMPONENTS AND APPLICATIONSMarykutty CyriacОценок пока нет
- Multisim Unsolved Questions BITS PilaniДокумент2 страницыMultisim Unsolved Questions BITS Pilanimanish_genus100% (1)
- Active Disturbance Rejection Control for Nonlinear Systems: An IntroductionОт EverandActive Disturbance Rejection Control for Nonlinear Systems: An IntroductionОценок пока нет
- Simulink 8.3 - Release 2014a - ElectronicsДокумент87 страницSimulink 8.3 - Release 2014a - ElectronicsAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasОценок пока нет
- Torque Control Guide: Tightening Torque and Tensile LoadДокумент2 страницыTorque Control Guide: Tightening Torque and Tensile LoadAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasОценок пока нет
- Creating A Symbol For A Part: Figure 1: Download The ModelsДокумент9 страницCreating A Symbol For A Part: Figure 1: Download The ModelsAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasОценок пока нет
- Chip Inductor (Chip Coil) : Power Inductor (Wire Wound Type) LQH55P Series (2220 Size)Документ2 страницыChip Inductor (Chip Coil) : Power Inductor (Wire Wound Type) LQH55P Series (2220 Size)Ariana Ribeiro LameirinhasОценок пока нет
- Part 4Документ31 страницаPart 4jagadees21Оценок пока нет
- Introduction ElectromagneticsДокумент96 страницIntroduction ElectromagneticsAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasОценок пока нет
- Tea 5764Документ68 страницTea 5764Ariana Ribeiro LameirinhasОценок пока нет
- Series: Inductors For Standard CircuitsДокумент13 страницSeries: Inductors For Standard CircuitsAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasОценок пока нет
- Tea 5777Документ47 страницTea 5777Ariana Ribeiro LameirinhasОценок пока нет
- Tea 5767Документ40 страницTea 5767Ariana Ribeiro LameirinhasОценок пока нет
- A Dimensions: (MM) B Recommended Land Pattern: (MM) : WE-PD SMD Shielded Power InductorДокумент6 страницA Dimensions: (MM) B Recommended Land Pattern: (MM) : WE-PD SMD Shielded Power InductorAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasОценок пока нет
- XiangYong ZhouДокумент8 страницXiangYong ZhouAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 - Analog Integrated Circuit Design by John ChomaДокумент99 страницChapter 2 - Analog Integrated Circuit Design by John ChomaAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasОценок пока нет
- Spru889 - High Speed DSP Systems DesignДокумент77 страницSpru889 - High Speed DSP Systems DesignAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasОценок пока нет
- Part 5Документ36 страницPart 5Ariana Ribeiro LameirinhasОценок пока нет
- 108104011Документ2 страницы108104011Raja ReddyОценок пока нет
- SCAA048 - Filtering TechniquesДокумент7 страницSCAA048 - Filtering TechniquesAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 - Analog Integrated Circuit Design by John ChomaДокумент95 страницChapter 5 - Analog Integrated Circuit Design by John ChomaAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasОценок пока нет
- ACS800 Manual For Laboratory WorksДокумент16 страницACS800 Manual For Laboratory WorksAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasОценок пока нет
- BJT Models and Biasing Circuits ExplainedДокумент125 страницBJT Models and Biasing Circuits ExplainedAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Analog Integrated Circuit Design by John ChomaДокумент87 страницChapter 1 - Analog Integrated Circuit Design by John ChomaAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 - Analog Integrated Circuit Design by John ChomaДокумент92 страницыChapter 4 - Analog Integrated Circuit Design by John ChomaAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 - Analog Integrated Circuit Design by John ChomaДокумент134 страницыChapter 6 - Analog Integrated Circuit Design by John ChomaAriana Ribeiro Lameirinhas100% (1)
- Nice Contact Headquarters LocationsДокумент1 страницаNice Contact Headquarters LocationsAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasОценок пока нет
- Anderson Final ETD VersionДокумент492 страницыAnderson Final ETD VersionAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasОценок пока нет
- Multi Level Open End WindingДокумент6 страницMulti Level Open End WindinglohitashriyaОценок пока нет
- AMS ThesisДокумент85 страницAMS ThesisAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasОценок пока нет
- 2008 - Space Vector Based Hybrid PWM Techniques For Reduced Current Ripple by Gopalaratnam Narayanan and Di ZhaoДокумент14 страниц2008 - Space Vector Based Hybrid PWM Techniques For Reduced Current Ripple by Gopalaratnam Narayanan and Di ZhaoAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasОценок пока нет
- Telit LE70-868Документ41 страницаTelit LE70-868Ariana Ribeiro LameirinhasОценок пока нет
- Datasheet Atmega32Документ346 страницDatasheet Atmega32Mas NyamОценок пока нет
- Occurrence of Black Soldier Fly HermetiaДокумент2 страницыOccurrence of Black Soldier Fly HermetiaMarcelo Geraldo TeixeiraОценок пока нет
- Eaton: Medium Duty Piston PumpДокумент25 страницEaton: Medium Duty Piston PumprazvanОценок пока нет
- ZRO List 3.17Документ4 страницыZRO List 3.17Com22Оценок пока нет
- International Journal of Computer Science and Innovation - Vol 2015-n1 - Paper1Документ6 страницInternational Journal of Computer Science and Innovation - Vol 2015-n1 - Paper1sophiaОценок пока нет
- International Capital Structure and Cost of CapitalДокумент20 страницInternational Capital Structure and Cost of CapitalQuoc AnhОценок пока нет
- Ahmad Hassan Textile MillsДокумент52 страницыAhmad Hassan Textile Millsmakymakymaky007100% (4)
- Tutorial Question 4 TORTДокумент2 страницыTutorial Question 4 TORTNBT OOОценок пока нет
- Gobenciong v CA ruling on preventive suspensionДокумент3 страницыGobenciong v CA ruling on preventive suspensionBambi GumbanОценок пока нет
- Extreme Ware Command Ref 78Документ2 652 страницыExtreme Ware Command Ref 78sol9159Оценок пока нет
- ATTДокумент3 страницыATTforu_kkkОценок пока нет
- North American Series 4762 Immersion Tube Burners 4762 - BULДокумент4 страницыNorth American Series 4762 Immersion Tube Burners 4762 - BULedgardiaz5519Оценок пока нет
- Marty Schwartz Blues TipsДокумент25 страницMarty Schwartz Blues TipsEuCelNouОценок пока нет
- Impact of Digitalisation Online FinalДокумент72 страницыImpact of Digitalisation Online FinalBanon KekeОценок пока нет
- Business Math - QuizДокумент2 страницыBusiness Math - QuizHannah Giezel MalayanОценок пока нет
- ERP ImplementationДокумент47 страницERP Implementationattarjaved100% (1)
- Brightspot Training ManualДокумент97 страницBrightspot Training ManualWCPO 9 NewsОценок пока нет
- Machine Learning: MACHINE LEARNING - Copy Rights Reserved Real Time SignalsДокумент56 страницMachine Learning: MACHINE LEARNING - Copy Rights Reserved Real Time SignalsLohith Ds BangloreОценок пока нет
- The Structural Engineer - August 2022 UPDATEDДокумент36 страницThe Structural Engineer - August 2022 UPDATEDES100% (1)
- Catalogue: See Colour in A Whole New LightДокумент17 страницCatalogue: See Colour in A Whole New LightManuel AguilarОценок пока нет
- Mipspro™ Assembly Language Programmer'S Guide: Document Number 007-2418-001Документ129 страницMipspro™ Assembly Language Programmer'S Guide: Document Number 007-2418-001mr_silencioОценок пока нет
- Jameson 2000 The Journal of Prosthetic DentistryДокумент4 страницыJameson 2000 The Journal of Prosthetic DentistryKarthikmds ElangovanОценок пока нет
- IAS Physics SB1 Practs CP1 Student SheetДокумент3 страницыIAS Physics SB1 Practs CP1 Student Sheethussain azizОценок пока нет
- Best Practices in Non-Revenue Water en FinalДокумент96 страницBest Practices in Non-Revenue Water en FinalEddiemtonga100% (1)
- Assignment: Name: Armish Imtiaz Roll No: 37: TopicДокумент3 страницыAssignment: Name: Armish Imtiaz Roll No: 37: TopicKhubaib ImtiazОценок пока нет
- Over 20 free and paid Pathfinder 2E character sheet optionsДокумент1 страницаOver 20 free and paid Pathfinder 2E character sheet optionsravardieresudОценок пока нет
- Self-Certification and Medical Examiner's Certificate ReportingДокумент2 страницыSelf-Certification and Medical Examiner's Certificate ReportingcatrutterОценок пока нет
- The Puppet Masters: How The Corrupt Use Legal Structures To Hide Stolen Assets and What To Do About ItДокумент284 страницыThe Puppet Masters: How The Corrupt Use Legal Structures To Hide Stolen Assets and What To Do About ItSteve B. SalongaОценок пока нет
- Playlist ArchacДокумент30 страницPlaylist ArchacMartin JánošíkОценок пока нет
- Nanotechnology Applications in Viscoelastic Surfactant Stimulation FluidsДокумент10 страницNanotechnology Applications in Viscoelastic Surfactant Stimulation FluidsNircarlomix OrtegaОценок пока нет
- Brother Electric Sewing xr9550prwДокумент2 страницыBrother Electric Sewing xr9550prwVenkatОценок пока нет