Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Hormones and Their Roles During Pregnancy
Загружено:
Bella IsananАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Hormones and Their Roles During Pregnancy
Загружено:
Bella IsananАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
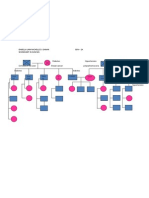
HORMONES AND THEIR ROLES DURING PREGNANCY Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) secreted by syncitial trophoblast cells derived
d from a fertilized ovum, and is first detectable 8-9 days after ovulation. Prevent degradation of the corpus luteum, therefore allowing the corpus luteum to maintain progesterone levels mainly responsible for the early pregnancy symptoms ranging from missed period to nausea, vomiting and fatigue. Estrogen secreted by the placenta mainly aims to stimulate the production of progesterone in the ninth month of pregnancy. An important role of estrogen is to facilitate the maturation of lungs, kidneys, adrenal gland, liver and bone density of the unborn baby. it also aids the flow of blood to fetus Estrogen also protects the female baby from the masculine effects of androgen Progesterone major pregnancy hormone that is primarily produced by the placenta. hormone maintains the functionality of placenta and prevents sudden movement and contraction of the uterus As the pregnancy progresses, the hormonal level of progesterone also rises. Its increased level affects the muscles thus leading to a bloated feeling, heartburn and acid flux, particularly in the later stages of pregnancy. also responsible for hip and pubic bone pain and breast does not allow lactation during pregnancy, only post delivery. Oxytocin produced in the hypothalamus and is secreted into the bloodstream by the posterior pituitary gland. stimulates the uterine muscles to contract and also increases production of prostaglandins which increase the contractions further facilitates the delivery process by helping in the contraction of uterus. promotes the movement of milk into the breast, allowing it to be excreted by the nipple Human chorionic somatomammotropin hormone hCS is a protein hormone produced by the placenta from approximately the 5th week of pregnancy Believed to be involved in breast development and lactation. This action of hCS has been proven in animal models, but has not been shown to cause lactation in humans. Due to this function, hCS was initially known as human placental lactogen (HPL).
closely related to prolactin and GH Similar functions to growth hormone (GH). Both have similar structures, and both cause protein tissue formation via similar mechanisms. However, much more hCS is required to produce the same growth as GH.
Anti-insulin effects and decreased insulin sensitivity in the mother. This avails larger quantities of glucose to the developing fetus, which uses glucose as its major substrate for growth
increases levels of free fatty acids in the mother, providing an alternative source of energy during pregnancy. Due to this effect, hCS might be involved in the development of insulin resistance seen in pregnancy
Вам также может понравиться
- Nonoperative Management Techniques for FracturesДокумент11 страницNonoperative Management Techniques for FracturesBella IsananОценок пока нет
- Transactional AnalysisДокумент3 страницыTransactional AnalysisBella Isanan100% (1)
- AppendectomyДокумент39 страницAppendectomyBella IsananОценок пока нет
- Cebu Doctors' University Hospital: Summary Nursing Care Plan Date: Total Census: Area & Shift: Charge NurseДокумент2 страницыCebu Doctors' University Hospital: Summary Nursing Care Plan Date: Total Census: Area & Shift: Charge NurseBella IsananОценок пока нет
- Trigger FingerДокумент1 страницаTrigger FingerBella IsananОценок пока нет
- Fields of Specialization in NursingДокумент6 страницFields of Specialization in NursingBella IsananОценок пока нет
- EpisiotomyДокумент2 страницыEpisiotomyBella IsananОценок пока нет
- GeneticsДокумент1 страницаGeneticsBella IsananОценок пока нет
- Bella Health Ass PresentationДокумент20 страницBella Health Ass PresentationBella IsananОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- 4 Common Thyroid Disorders ExplainedДокумент5 страниц4 Common Thyroid Disorders ExplainedAnggunNMОценок пока нет
- Endocrine System: Chapter 13. Control and Response Cambridge IGCSE Biology Grade 9Документ12 страницEndocrine System: Chapter 13. Control and Response Cambridge IGCSE Biology Grade 9laila RamlanОценок пока нет
- Performance Task 1Документ3 страницыPerformance Task 1Jellie May RomeroОценок пока нет
- Calcium Salts Calcitonin and CA RegulatorsДокумент40 страницCalcium Salts Calcitonin and CA RegulatorsSudhakar LakavathОценок пока нет
- HipertiroidДокумент42 страницыHipertiroidCoass XII BonamОценок пока нет
- HypothyroidismДокумент54 страницыHypothyroidismagakshat23Оценок пока нет
- Human Reproductive System GuideДокумент25 страницHuman Reproductive System GuidePhoeberly SabadoОценок пока нет
- Luteinizing HormoneДокумент8 страницLuteinizing HormoneNTA UGC-NETОценок пока нет
- Week 13 Endocrine 2 1 PPДокумент57 страницWeek 13 Endocrine 2 1 PPJoy KОценок пока нет
- LH Assay InsertДокумент8 страницLH Assay InsertYogaswara AdiputroОценок пока нет
- Hypothalamus and Pituitary GlandДокумент39 страницHypothalamus and Pituitary GlandGish KioiОценок пока нет
- European Society of Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guidelines On The Management of Adrenal Incidentalomas, in Collaboration With The European Network For The Study of Adrenal TumorsДокумент42 страницыEuropean Society of Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guidelines On The Management of Adrenal Incidentalomas, in Collaboration With The European Network For The Study of Adrenal TumorsLaura Marina IlincaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy & Assessment of The Endocrine System - HandoutДокумент12 страницAnatomy & Assessment of The Endocrine System - HandoutGil Raphael Ganiban0% (2)
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Di WenДокумент17 страницPolycystic Ovary Syndrome: Di WenSalam AlmudarrisОценок пока нет
- Anatomy & Physiology of The Endocrine System (Pancreas & Thyroid Gland)Документ5 страницAnatomy & Physiology of The Endocrine System (Pancreas & Thyroid Gland)Joanna DuapaОценок пока нет
- Praktikum Endokrin Activity 1 Kelompok 2Документ8 страницPraktikum Endokrin Activity 1 Kelompok 2kuanlins crushОценок пока нет
- Hyperthyroidism Causes and SymptomsДокумент26 страницHyperthyroidism Causes and Symptomskriti kaushalОценок пока нет
- Immunology Report: Test Is Carried Out by Maglumi-2000 PlusДокумент1 страницаImmunology Report: Test Is Carried Out by Maglumi-2000 PlusKH. A. H. M. SAYEF 1706024Оценок пока нет
- Hormones and the Reproductive SystemДокумент5 страницHormones and the Reproductive SystemDionil CabilanОценок пока нет
- Pancreas Structure and FunctionsДокумент11 страницPancreas Structure and FunctionsCheng XinvennОценок пока нет
- Oet Online - Reading Test 4 A4: 9-If A Hashimoto's Patient Has High Blood Pressure, What Does It Usually Indicate?Документ2 страницыOet Online - Reading Test 4 A4: 9-If A Hashimoto's Patient Has High Blood Pressure, What Does It Usually Indicate?Vistaa SunnyОценок пока нет
- Pathology of Thyroid DiseasesДокумент5 страницPathology of Thyroid DiseasesGerardLum100% (2)
- Canine Hypothyroidism, An OverviewДокумент6 страницCanine Hypothyroidism, An OverviewISABELSSBОценок пока нет
- Understanding Multinodular Non-Toxic GoiterДокумент58 страницUnderstanding Multinodular Non-Toxic GoiterSeff CausapinОценок пока нет
- Science 10 - Learning Module 3QДокумент86 страницScience 10 - Learning Module 3QJovanni SimbulanОценок пока нет
- Vphy 143 Lab Experiment 4Документ12 страницVphy 143 Lab Experiment 4Regulus Fidelis SevillaОценок пока нет
- Fluid Deprivation TestДокумент3 страницыFluid Deprivation TestsakuraleeshaoranОценок пока нет
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) Diagnosis and TreatmentДокумент25 страницPolycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) Diagnosis and Treatmenting_claudia100% (3)
- Thyroid Case StudyДокумент68 страницThyroid Case Studyshadydogv5Оценок пока нет
- Salivation PDFДокумент5 страницSalivation PDFmehdi mafakheri100% (1)