Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Transient Tachypnea of The Newborn English
Загружено:
Dyan Friska Yanty Lbs0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
185 просмотров2 страницыTransient tachypnea (tak-ip-nee-ah) of the newborn, or TTN, is temporar y fast breathing. It is caused by leftover fluid in the lungs, which makes it harder for the baby to breathe. TTN affects between 1 and 9 out of ever y 1000 babies born.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn English
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документTransient tachypnea (tak-ip-nee-ah) of the newborn, or TTN, is temporar y fast breathing. It is caused by leftover fluid in the lungs, which makes it harder for the baby to breathe. TTN affects between 1 and 9 out of ever y 1000 babies born.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
185 просмотров2 страницыTransient Tachypnea of The Newborn English
Загружено:
Dyan Friska Yanty LbsTransient tachypnea (tak-ip-nee-ah) of the newborn, or TTN, is temporar y fast breathing. It is caused by leftover fluid in the lungs, which makes it harder for the baby to breathe. TTN affects between 1 and 9 out of ever y 1000 babies born.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
81915-TTN_81915-TTN 10/24/12 1:46 PM Page 1
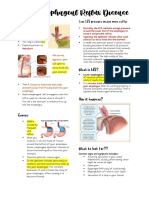
UNDERSTANDING
Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn
What is transient tachypnea of the newborn?
Transient tachypnea (tak-ip-nee-ah) of the newborn, or TTN, is temporar y fast breathing. It is sometimes called wet lungs.
Inhaled air
TTN
What causes TTN?
TTN is caused by leftover fluid in the lungs. Before bir th, a babys lungs are filled with fluid that helps them grow and develop. During labor and delivery, most of the fluid is removed. After bir th, breathing air helps remove the remaining fluid. In some babies, the fluid clears more slowly. The leftover fluid makes it harder for the baby to breathe, so the baby breathes faster (tachypnea) and less deeply. As soon as the fluid is gone, the baby can breathe normally (so the condition is transient, or temporar y).
Trachea
Alveoli (air sac)
Lung
Alveoli
Inhaled air
Fluid
What are the symptoms of TTN?
There are several symptoms of TTN. Your baby may not have all of them. Rapid breathing Flaring of the nostrils when breathing in Sharp pulling in of the chest muscles during breathing (retraction) Bluish skin color (cyanosis) around the nose and mouth
Babies with TTN have fluid in their lungs that makes it hard to breathe.
How common is TTN?
TTN affects between 1 and 9 out of ever y 1000 babies born. It is more common in babies who were delivered by C-section, especially if labor never star ted, and in babies born between 34 and 37 weeks' gestation.
81915-TTN_81915-TTN 10/24/12 1:46 PM Page 2
Treating Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn
How is TTN diagnosed?
The symptoms of TTN are very similar to several other breathing problems. The health care team may run tests to rule out these more serious problems. Tests may include: Chest X-rays to look for fluid in the lungs Blood tests to look for infection Constant monitoring of the babys oxygen level, breathing rate, and heart rate The diagnosis of TTN is often made after ruling out other causes.
Glossary
Antibiotics medicines that fight infections caused by bacteria CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) a treatment that uses mild, pressurized air to keep the lungs open Cyanosis bluish color of the skin Intravenous (IV) through a vein Mechanical ventilator a machine that helps your baby breathe by moving air in and out of the lungs Retraction sharp pulling in of the chest muscles during breathing Tachypnea fast breathing
What treatment will my baby receive?
Treatments for TTN depend on how much help your baby needs to breathe until the symptoms go away. Possible treatments include: Extra oxygen usually given through a nose tube or mask Help feeding rapid breathing can make feeding hard. Your baby may be given fluid and nutrients through an IV or a feeding tube until breathing is easier. Antibiotics until infection can be ruled out CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) a treatment that uses mild pressurized air to keep the lungs open Mechanical ventilator (in rare cases) a machine that helps your baby breathe using a tube. The tube goes through the baby's nose or mouth and into their throat
Ask the health care team when you have questionsthey are there to help.
What will happen next?
TTN usually goes away on its own within a few days of birth. In most cases, there are no long-term problems due to TTN. Talk to your health care team. They can answer any questions you have about your baby.
NOTES: ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________
Signature: __________________________________________ Date:__________________ Time: ____________
2012 Ikaria, Inc. IMK111-01516 November 2012
Вам также может понравиться
- Transient Tachypnea of The NewbornДокумент2 страницыTransient Tachypnea of The Newbornjulesubayubay5428Оценок пока нет
- Abdominal Distention inДокумент45 страницAbdominal Distention inArif Rahman DmОценок пока нет
- Patent Ductus ArteriosusДокумент3 страницыPatent Ductus ArteriosusMika SaldañaОценок пока нет
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: What Is LES?Документ3 страницыGastroesophageal Reflux Disease: What Is LES?Irish Eunice Felix100% (1)
- Henoch Schonlein Purpura REVДокумент42 страницыHenoch Schonlein Purpura REVBayu Kurniawan100% (1)
- SHOCKДокумент26 страницSHOCKArif Zulfian MubarokОценок пока нет
- Diabetic Foot: by Myrna Rita PMRДокумент33 страницыDiabetic Foot: by Myrna Rita PMRDianNurlitaAnggrainiОценок пока нет
- Airway Management I. Airway 1. Causes of Airway ObstructionДокумент1 страницаAirway Management I. Airway 1. Causes of Airway ObstructionDelicateDogОценок пока нет
- Airway ManagementДокумент63 страницыAirway ManagementGilang GumilangОценок пока нет
- Urinary Tract Infections: Dr. Shweta Naik Assistant ProfessorДокумент62 страницыUrinary Tract Infections: Dr. Shweta Naik Assistant ProfessorMeenakshisundaram CОценок пока нет
- Postpartum HemorrhageДокумент8 страницPostpartum HemorrhageMazlina MaidinОценок пока нет
- Cholecystitis Cholelithiasis PresentationДокумент21 страницаCholecystitis Cholelithiasis PresentationDe WiqОценок пока нет
- Case Report MTH HydroceleДокумент9 страницCase Report MTH Hydrocelesamuel_hildaОценок пока нет
- Submandibular Phlegmon - Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentДокумент1 страницаSubmandibular Phlegmon - Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentTri Sakti Sunda RomdhoniОценок пока нет
- Transposition of The Great ArteriesДокумент29 страницTransposition of The Great ArteriesbookwormMD100% (1)
- Urosepsis: Dr. Tameem Mohammed Department of Anesthesia and Intensive Care San Fernando General HospitalДокумент22 страницыUrosepsis: Dr. Tameem Mohammed Department of Anesthesia and Intensive Care San Fernando General HospitalRicky AliОценок пока нет
- Cholecystitis Cholelithiasis PresentationДокумент21 страницаCholecystitis Cholelithiasis PresentationPrincess Meinny JeanОценок пока нет
- Abnormal OBДокумент34 страницыAbnormal OBLawrence NemirОценок пока нет
- Acute Pulmonary Edema - NEJMДокумент4 страницыAcute Pulmonary Edema - NEJMSuzika Dewi0% (1)
- DRUG ERUPTION GUIDEДокумент46 страницDRUG ERUPTION GUIDESyahDikaОценок пока нет
- WHO Dengue Classification and Case Management-FlyerДокумент2 страницыWHO Dengue Classification and Case Management-FlyerKathleen DyОценок пока нет
- Dr. Sunatrio - Management Hypovolemic ShockДокумент59 страницDr. Sunatrio - Management Hypovolemic ShockArga Putra SaboeОценок пока нет
- FIXED PPT Case Report EsterДокумент39 страницFIXED PPT Case Report Esterririn esterinaОценок пока нет
- Pediatric History Taking and Clinical ExaminationДокумент6 страницPediatric History Taking and Clinical ExaminationSamdiSutantoОценок пока нет
- Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)Документ7 страницIdiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)Rizqka PertiwiОценок пока нет
- GastroenteritisДокумент24 страницыGastroenteritisMomogi ForeverhappyОценок пока нет
- Surgery Case AppendicitisДокумент30 страницSurgery Case AppendicitisSarahОценок пока нет
- Isotonic Saline (0.9%Nacl-Normal Saline) IndicationДокумент3 страницыIsotonic Saline (0.9%Nacl-Normal Saline) IndicationJared AllenОценок пока нет
- Pyothorax Treatment & StagesДокумент22 страницыPyothorax Treatment & StagesAnkan Dey100% (1)
- Tinea CorporisДокумент23 страницыTinea CorporisDita lewaherillaОценок пока нет
- Cme Acs 2. Stemi (Izzah)Документ36 страницCme Acs 2. Stemi (Izzah)Hakimah K. SuhaimiОценок пока нет
- Hipertiroid HarrisonДокумент8 страницHipertiroid HarrisonravenskaОценок пока нет
- Type B (Hib) Vaccine: Haemophilus InfluenzaeДокумент2 страницыType B (Hib) Vaccine: Haemophilus InfluenzaeEnce MalatambanОценок пока нет
- Transient Tachypnea of NewbornsДокумент16 страницTransient Tachypnea of NewbornsSelena Marie0% (1)
- Fever of Unknown OriginДокумент26 страницFever of Unknown OriginFiona Yona Sitali100% (1)
- 06prof. Riwanto-Abdominal Compartment SyndromeДокумент41 страница06prof. Riwanto-Abdominal Compartment SyndromeTanujaa Venugopal100% (1)
- Diarrhea 2016Документ37 страницDiarrhea 2016oli garkiОценок пока нет
- Responsi HemoroidДокумент26 страницResponsi HemoroidJessica Alexandria WuОценок пока нет
- SURGICAL PROCEDURE SUFFIXESДокумент3 страницыSURGICAL PROCEDURE SUFFIXESgrgicosОценок пока нет
- CM Extravasation: Signs, Risks, Prevention & TreatmentДокумент19 страницCM Extravasation: Signs, Risks, Prevention & Treatmentzainab sawanОценок пока нет
- Acute Gastroenteritis (AGE)Документ37 страницAcute Gastroenteritis (AGE)Sari HariyaniОценок пока нет
- INTUSSUSCEPTIONДокумент3 страницыINTUSSUSCEPTIONS GОценок пока нет
- Roseola PDFДокумент1 страницаRoseola PDFLili PredescuОценок пока нет
- UrethritisДокумент11 страницUrethritisgreggy_rebel17Оценок пока нет
- Meconium AspirationДокумент23 страницыMeconium AspirationWitneyGraceОценок пока нет
- Orchitis Vs Testicular Torsion Urology ReportДокумент13 страницOrchitis Vs Testicular Torsion Urology ReportRem AlfelorОценок пока нет
- Abnormal Midwifery: by Gladys M. BSN, KRCHNДокумент352 страницыAbnormal Midwifery: by Gladys M. BSN, KRCHNMercy KeruboОценок пока нет
- Description: Kawasaki Disease (Mucocutaneous Lymph Node Syndrome) Is A Form of VasculitisДокумент4 страницыDescription: Kawasaki Disease (Mucocutaneous Lymph Node Syndrome) Is A Form of VasculitishamporkОценок пока нет
- Rheuamatic Heart DiseaseДокумент28 страницRheuamatic Heart DiseaseNITHA KОценок пока нет
- Clinical Evaluation of DehydrationДокумент5 страницClinical Evaluation of DehydrationEricka Lyn Arenas MonzonОценок пока нет
- HypertensionДокумент6 страницHypertensionTj Kevin P-DoctorОценок пока нет
- Cardiorespiratory ArrestДокумент51 страницаCardiorespiratory ArrestIrham KhairiОценок пока нет
- Renal Tumors Classification GuideДокумент38 страницRenal Tumors Classification GuideMim Rashed0% (1)
- Gastric CancerДокумент7 страницGastric CancerMicah PingawanОценок пока нет
- Missed AbortionДокумент5 страницMissed AbortionDesta MarpaungОценок пока нет
- HepatomegalyДокумент2 страницыHepatomegalyFuyumi RiaОценок пока нет
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Gastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandGastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- TTN en PDFДокумент2 страницыTTN en PDFAmin RoyОценок пока нет
- TTNДокумент3 страницыTTNMarhina Asarabi MukimОценок пока нет
- Jurnal MataДокумент3 страницыJurnal MataAsiah AbdillahОценок пока нет
- Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis UveitisДокумент5 страницJuvenile Idiopathic Arthritis UveitisDyan Friska Yanty LbsОценок пока нет
- JIA Eye Risks and TreatmentsДокумент5 страницJIA Eye Risks and TreatmentsDyan Friska Yanty LbsОценок пока нет
- JIA Eye Risks and TreatmentsДокумент5 страницJIA Eye Risks and TreatmentsDyan Friska Yanty LbsОценок пока нет
- IgE-Mediated Soy Protein Sensitizatin in Children Allergy Cow MilkДокумент5 страницIgE-Mediated Soy Protein Sensitizatin in Children Allergy Cow MilkEssaLoyalLitaLestariОценок пока нет
- Pivas 2018Документ46 страницPivas 2018Denny PaatОценок пока нет
- Excerpt: "Unaccountable: What Hospitals Won't Tell You and How Transparency Can Revolutionize Health Care" by Marty MakaryДокумент4 страницыExcerpt: "Unaccountable: What Hospitals Won't Tell You and How Transparency Can Revolutionize Health Care" by Marty Makarywamu885Оценок пока нет
- Planes Systems OrganizationДокумент36 страницPlanes Systems OrganizationR. EssoОценок пока нет
- How To Avoid Medication ErrorsДокумент2 страницыHow To Avoid Medication ErrorsLorenn AdarnaОценок пока нет
- Cephalometric Evaluation and Measurement of The Upper Airway PDFДокумент13 страницCephalometric Evaluation and Measurement of The Upper Airway PDFSoe San KyawОценок пока нет
- Hand Hygiene: Protocol For UWS ClinicsДокумент8 страницHand Hygiene: Protocol For UWS ClinicsOliaОценок пока нет
- The JFK AutopsyДокумент6 страницThe JFK AutopsysithusoemoeОценок пока нет
- Monnal t75 Air Liquide Ventilator PDFДокумент10 страницMonnal t75 Air Liquide Ventilator PDFFederico DonfrancescoОценок пока нет
- Nextier - Pharma 101 - 29-Jun-2016Документ28 страницNextier - Pharma 101 - 29-Jun-2016Ammar ImtiazОценок пока нет
- What Type of Resistance Training Program Can Help Increase Muscle MassДокумент75 страницWhat Type of Resistance Training Program Can Help Increase Muscle Massyokimura dimaunahanОценок пока нет
- BSN 4A Group 5 Nigerian AmericanДокумент39 страницBSN 4A Group 5 Nigerian AmericanAngelie PantajoОценок пока нет
- Hospital Floor Plan Checklist ReviewДокумент5 страницHospital Floor Plan Checklist Reviewjherica baltazarОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular Physiology Case 9Документ50 страницCardiovascular Physiology Case 9Kim AcostaОценок пока нет
- Anvisa National Health Surveillance AgencyДокумент52 страницыAnvisa National Health Surveillance AgencyVimarsha HSОценок пока нет
- Staph and Strep Lab Report BMS 501Документ2 страницыStaph and Strep Lab Report BMS 501aruiz93Оценок пока нет
- Head and Neck PDFДокумент274 страницыHead and Neck PDFRakesh Jadhav100% (1)
- Biology Contents - RPSC FSO by Food TecKnowДокумент35 страницBiology Contents - RPSC FSO by Food TecKnowRahul JainОценок пока нет
- Presenter: Dervin Ariansyah Supervisor: DR. Dr. Abdul Hakim Alkatiri SP - JP (K)Документ12 страницPresenter: Dervin Ariansyah Supervisor: DR. Dr. Abdul Hakim Alkatiri SP - JP (K)mcvuОценок пока нет
- CasestudynervoussystemДокумент2 страницыCasestudynervoussystemapi-265854240Оценок пока нет
- Implants Session I Revised 21 Sept 2012Документ17 страницImplants Session I Revised 21 Sept 2012Norman AjxОценок пока нет
- Zocor (Simvastatin)Документ3 страницыZocor (Simvastatin)E100% (1)
- ENTEROBACTERIACEAEДокумент13 страницENTEROBACTERIACEAEStephen Jao Ayala Ujano100% (1)
- Hydralazine For Severe PIHДокумент4 страницыHydralazine For Severe PIHYwagar YwagarОценок пока нет
- Akupuntur 7Документ9 страницAkupuntur 7Ratrika SariОценок пока нет
- Medical DeviceДокумент8 страницMedical DeviceHarshvardhan ChoudharyОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 PsychДокумент12 страницChapter 3 Psychred_gyrl9282Оценок пока нет
- Large Volume Parenterals: Guidelines and Quality Control TestsДокумент36 страницLarge Volume Parenterals: Guidelines and Quality Control TestsRákêsh MãttàОценок пока нет
- Grievously: News Item 9: EARTHQUAKE 2Документ2 страницыGrievously: News Item 9: EARTHQUAKE 2roxana_boraОценок пока нет
- The Role Ultrasound in Early PregnancyДокумент167 страницThe Role Ultrasound in Early PregnancyCordova ArridhoОценок пока нет
- Presentations Sux ApnoeaДокумент18 страницPresentations Sux ApnoeaalishbaОценок пока нет