Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
OilFilledPowerCable Catalog
Загружено:
mohannad87Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
OilFilledPowerCable Catalog
Загружено:
mohannad87Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
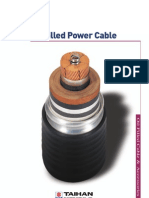
Oil Filled Power Cable
O
i
l
F
i
l
l
e
d
C
a
b
l
e
&
A
c
c
e
s
s
o
r
i
e
s
T
a
i
h
a
n
s
O
i
l
F
i
l
l
e
d
P
o
w
e
r
C
a
b
l
e
P4
T
a
i
h
a
n
s
O
i
l
F
i
l
l
e
d
P
o
w
e
r
C
a
b
l
e
Supply Records of Oil Filled Power Cable P4
Characteristics P5
System Design P6
Manufacturing Facilities and Checkpoints of Quality Control P9
Tests P13
Construction P14
Accessories P18
Installation P22
TAIHAN ELECTRIC WIRE
T
a
i
h
a
n
s
O
i
l
F
i
l
l
e
d
P
o
w
e
r
C
a
b
l
e
P4 P4
Started Supply and Installation of 154kV OF Cable to
KEPCO, Korea.
Contracted with TNB for Turnkey Project of 132kV OF
Cable Underground Network in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
Contracted with Dubai Electricity Company for Turnkey
Project of 132kV OF Cable Underground Network in
United Arab Emirates.
Contracted with TNB for Turnkey Project of 132kV OF
Cable Underground Network in kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
Contracted with PLN for 150kV OF Cable Underground
Network Project in Surabaya, Indonesia.
Contracted with Dubai Electricity Comapnay for Turnkey
Project of 132kV OF Cable Underground Network in
United Arab Emirates.
Started Supply and Installation of 345kV OF Cable to
KEPCO, Korea.
Contracted with PLN for 150kV OF Cable Underground
Network Project in Semarang, Indonesia.
Contracted with TNB for Turnkey Project of 132kV OF
Cable Underground Network in Malaysia.
Contracted with Meta-Epsi for Turnkey Project of 150kV
OF Cable Underground Network in Jakarta, Malaysia.
Contracted with TNB for Turnkey Project of 132kV OF
Cable Underground Network in Kuala Lumpur City
Center, Malaysia.
Contracted with SCECO-C for Turnkey Project of 132kV
OF Cable Underground Network in Riyadh, Saudi
Arabia.
Contracted with TNB for Turnkey Project of 275kV OF
Cable Underground Network in Malaysia.
Contracted with TPC for Turnkey Project of 161kV OF
Cable Underground Network in Taiwan.
Contracted with TPC for Turnkey Project of 161kV OF
Cable Underground Network in Taiwan.
1978
1983
1985
1986
1988
1991
1992
1994
1995
1996
1998
1999
2000
2002
Supply Records of Oil Filled Power Cable
T
a
i
h
a
n
s
O
i
l
F
i
l
l
e
d
P
o
w
e
r
C
a
b
l
e
T
a
i
h
a
n
s
O
i
l
F
i
l
l
e
d
P
o
w
e
r
C
a
b
l
e
P5
T
a
i
h
a
n
s
O
i
l
F
i
l
l
e
d
P
o
w
e
r
C
a
b
l
e
P5
Characteristics
Through incessant research and development, the excellent functions of oil filled cable has been
improved since 1924.
Among the many excellent characteristics, some typical ones can be listed as follows.
There is absolutely no void within insulation
and is stable electrically.
The insulation oil, whose air bubbles and humidity are
sufficiently removed by performing degassing treatment, is
impregnated in insulating paper layer which is fully dried
under high vacuum beforehand and kept under high
degree of vacuum, and the cable is made accordingly.
Since a definite positive pressure is always kept inside of
the finished cable, there is absolutely no void in the cable
insulation.
Operating potential gradient can be large.
Since no deterioration takes place in voids in the insulation
by ionizations as in the case with the solid-type cable, the
operating potential gradient can be large. Therefore, the
insulation thickness can be selected as thin.
Expansion and contraction of insulation oil
due to temperature change can be com-
pensated by the oil tanks.
Expansion and contraction of insulating oil, due to change
of load under use or due to change of the external
temperature, can be fully compensated by the oil tank
installed in a suitable position on the cable route.
Therefore, there can be no void in the insulation.
Possibility of cable self-monitoring
The inside of the cable is always kept at positive oil
pressure so that no humidity intrudes from the outside in
case damage occurs in the cable sheath, or in the joint
box. Further, in case the insulating oil leaks, the trouble is
detected earlier as the alarm device actuates and it is
possible to repair before occurrance of full-scale trouble in
the cable system.
T
a
i
h
a
n
s
O
i
l
F
i
l
l
e
d
P
o
w
e
r
C
a
b
l
e
P6
System Design
OF cable system can be derived from economical decision and maker s engineering capability about
super high tension engineering. The reason is that many sites, around the world, have their own
characteristics, for instances, swamp or desert, field or mountain, and inland or seaside. So pracrical route
survey can only give precise answer just suitable to its own geographical characteristics.
We, Taihan based upon the accumulated technical know-how, have the capability to design any kind
of cable system requried and install at any site under any circumstances.
By the calculation through computer, cable and accessories can be fixed to make a turn-key system
for OF cable.
Taihan manufactures oil filled cables according to the following specification and accomplishes design and manufacture of
oil filled cables which are suitable for using conditions to meet the following requirements.
1) Standard specification
IEC : International Electrotechnical Commission
BS : British Standard(U.K)
AEIC : Association of Edition Illuminating
Company(U.S.A)
Taihan Standard : Taihan Electric Wire Co., Ltd.
Others
2) Cable design parameters
a. Maximum Permissible Oil Pressure
b. Nominal Voltage and Conductor Sectional Area
c. Protective Cover
Note : Submarine cable is protected with steel tape and/or wire.
Oil Pressure Type
Normal Operation
Low-Pressure
Medium-Pressure
3
6 ~ 8
6
11 ~ 14
Maximum Permissible Oil Pressure ( / )
Transient Operation
Nominal Voltage
(KV)
110 ~ 154
Single
Three
Single 220 ~ 345
Number of
Core Sectional Area ( )
Upto 800
1,000 ~ 2,000
Upto 400
Upto 800
1,000 ~ 2,000
Hollow circular
Segmental hollow
Compact round
Hollow circular
Segmental hollow
Type
Conductor
Metalic Sheath Reinforcement Armor Anti-corrosion Layer
Stainless Steel
Steel Tape Compound Jute
PVC or Polyethylene
PVC or Polyethylene
Lead
Corrugated Aluminum - -
-
b. Nominal Voltage and Conductor Sectional Area
c. Protective Cover
a. Maximum permissible Oil Pressure
Cable Design
T
a
i
h
a
n
s
O
i
l
F
i
l
l
e
d
P
o
w
e
r
C
a
b
l
e
P7
Oil Feeding System
Single Core OF Cable
Outdoor Sealing End
Sealing End for SF6 Switchgear
Insulation Joint
Stop Insulation Joint
Straight Through Joint
Oil Pressure Tank
Gauge Panel
Link Box for Cross Bonding with Surge Diverter
Alarm Receiver
Oil Feeding Pipe
Control Cable
Selection of proper oil feeding system is one of the most important factors in the system design. We, Taihan OF cable
engineers, will design any kind of feeding system to meet the requirement of our customer. We will install our OF cable
system at any site whether normal or difficult.
The general principle of oil feeding system can be explained hereunder.
1) The minimum oil pressure should be above 0.2 / at any time and any position.
2) The distance necessary to feed the oil and the place to fix the oil feeding tank must be investigated first, and then the
kind and volume of oil tank can be fixed.
T
a
i
h
a
n
s
O
i
l
F
i
l
l
e
d
P
o
w
e
r
C
a
b
l
e
P8
System Design Flow Chart
Selection of Cable Route
and Laying Method
Power Capacity
Determination
Sheath Loss and Induced
Voltage Calculation
Route Profile
Selection of Stop
Joint Position
Selection of Oil Feeding
Tank Position
Determination of Oil
Feeding Method
Cable Manufacturing
Condition
Cable Pulling Tension
Calculation
Determination of Cable
Span
Fixing System Design
Transportation Condition
Off-set Calculation
Consideration of the
Space for Future
Consideration of
Electromagnetic
Inducement
Route Survey
Selection of Optimum
Size of Conductor
(Current Carrying Capacity)
T
a
i
h
a
n
s
O
i
l
F
i
l
l
e
d
P
o
w
e
r
C
a
b
l
e
P9
Manufacturing Facilities and
Checkpoints of Quality Control
With full automatic tension control apparatus, our paper lapping machine, made by Pirelli in Italy, can manufacture OF
cable up to 345kV by a single passage
Paper lapping tension
The lapping tension of paper is calculated by a
computer which considers the type of paper, the width
of paper, and the diameter on which the paper is
lapped.
Humidity control
Paper lapping machines are installed in an special
control room in order to keep the humidity in the room.
The room is kept at slightly higher than atmospheric
pressure so that the entry of dust, litter and fine
particles of metal which are detrimental to the insulation
of cable can be prevented.
Bending test immediately after paper lapping
When the leading end has passed the hauling ma-
chine, a sample in the length of several meters is
subjected to a bending test in order to ascertain that the
condition of paper lapping is suitable to working
standard.
The quality of a Taihan cable starts with select-ing and using only the best raw material. Be-fore
Taihan cables are manufactured the cop-per, aluminum, lead and lead alloy, paper, oil and
plastic etc. are all tested in raw mate-rial form. A fully equip-ped laboratory carries out
numerous tests, physical, analytical, chemical, electrical and mechanical. And throughout the
manu-facturing stages, further tests ensure that pro-duct quality is main-tained.
Paper Lapping Machine
T
a
i
h
a
n
s
O
i
l
F
i
l
l
e
d
P
o
w
e
r
C
a
b
l
e
P10
Cabler
Besides singe core, all kind of cables should be passed this machine for cabling. Smooth and clean pass lines for paper
core are essential to manufacture high quality cable.
Drying Tank
Dielectric power loss, one of the important characteristics of OF cable can be achieved by complete drying method.
Temperature control of drying tanks
The temperature of drying tank is measured at several
points, recorded continuously, and checked to make sure
that the temperature is held within the control limit.
Temperature control of conductor during heating
During the initial hours of drying, the cable is heated by
an electric current flowing directly through its conductor,
which is called the electric current drying method. In this
period, a program controller developed by our company
controls the speed of temperature rise automatically and
records the temperature.
Vacuum degree
The vacuum degree of a drying tank is measured at two
points, recorded continuously, and checked. Vacuum
pumps are in automatic operation and when something
goes wrong, they activate and alarm on the central
control panel.
Control of drying period
The manufacturing standard specifies the period of
drying according to the type of cable to avoid insufficient
or excessive drying. ln addition to that, the drop test and
leak test of drying tank utilizing the relationship between
the residual moisture content in paper and its equilibrium
vapor pressure tell us whether or not the operation is
within the contrl limit.
T
a
i
h
a
n
s
O
i
l
F
i
l
l
e
d
P
o
w
e
r
C
a
b
l
e
P11
Degasifying
Before degasifying, the oil is stored in a
low vacuum tank, the vacuum degree
being monitored, as the pretreatment.
During degasification, the vacuum
degree is continuously recorded, and
the rate of oil flow is automatically
controlled to the vacuum degree so as
to obtain a uniform degasification
degree.
After degasifying, the resistivity,
power factor, water content for all oil are
measured. In order to reduce moisture
infiltration, the oil is held under the
pressure of nitrogen during storage.
Control of vacuum degree of
cable before oil-impregnation
Usually, after the aluminum sheath
covering, vacuum degree of cables has
to be checked before being impreg-
nated with oil. This period is utilized to
measure the vacuum degree of the
cable just before oil-impregnation in
order to make sure the aluminum
sheath is no pinhole.
Inspection of oil before
oil-impregnation
The state of oil entering into a vacuum
bottle is oberved to ascertain if the oil
contains bubbles or foreign matter. A
sampling test for resistivity, power
factor, and water content is also carried
out.
Vacuum degree control during
oil- impregnation
The vacuum degree of the cable during
oil-impregnation is measured and
recorded by a worker every two hours.
Electromagnetic valves mounted on an
oil-impregnating panel automatically
close in case of failure of power supply
or abnormally low vacuum degree, thus
protecting the cable from the entrance
of air.
Completion of oil-impregnation
The judgement that oil-impregnation is
completed is made when the oil
pressure ceases to drop.
Insulating Oil Degasifier and Impregnating Panel
This equipments can degas and refine the insulating oil, alkylbenzene type synthetic oil,
to give and excellent insulating stability for cable.
Affer vacuum sheath process, degassed and refined oil can be put into cable.
T
a
i
h
a
n
s
O
i
l
F
i
l
l
e
d
P
o
w
e
r
C
a
b
l
e
P12
Vacuum Sheathing Equipment
To withstand inner oil pressure and prevent outer mechanical shock, OF cable should be made with metallic layer. To
maintain the low moisture contents of dried insulation paper while sheathing metal layer, OF cable should be made under
the vacuum continuously.
The manufacturing condition for Aluminum Press and Lead Extruder is almost same. For instance, working condition of
aluminum press is as follows.
Machine for Reinforced Tapes
After lead sheathing, non-magnetic tapes for example stainless tape, will be wrapped on the lead sheath to reinforce the
creep characteristics.
PE/PVC Extruder
As an anti-corrosion protection, in many cases underground cable is used with plastic outer sheathes.
Vacuum sheathing
After the completion of drying, the cable is covered with
an aluminum sheath while still being held in high vacuum
degree. Throughout this process, the vacuum degree in
the cable is monitored and recorded continuously, and
any abnormality in vacuum degree triggers and alarm.
Automatic operation
The aluminum press has fully automatic operation to
avoid human error and to obtain stablized quality.
Temperature control
The temperatures of the die-block, the ingot heating
furnace, and ingots are continuously recorded for
consistent operation.
Surface inspection
As the metallic sheath is one of the vital parts of oil filled
cables, its surface is inspected continuously in order to
confirm that surface damage, pinhole, and other defects
do not exist.
T
a
i
h
a
n
s
O
i
l
F
i
l
l
e
d
P
o
w
e
r
C
a
b
l
e
P13
Tests
Routine Test
The tests are carried out on all supplied lengths and the
results are recorded. The scope of the test is mainly
based on IEC 141-1.
Type Tests
Each new type of cable is submitted to a type approval
test that is executed in our high voltage research
laboratory. A type tests on short cable lenghs may be
agreed. If proof is provided that type tests have
previously been carried out on cables of similar
construction, no further test needs to be carried out.
The scope of the test is mainly based on IEC 141-1.
Site Tests
The scope of the tests after installation is mainly based
on IEC 141-1.
Before the cables leave factory for their destinations all over the world, a thorough program of
extensive testing is carried out.
Construction
Single Core
Rated
Voltage
(
BIL =
+,ookV
;
BIL =
+,ookV
kV mm
mm mm mm mm mm mm mm
Nominal
Area
Oil Passage
Conductor Insulation Aluminum Sheath
Approx.
O.D
Material Thickness
Thickness
of
Sheath
Thickness
of
Jacket
Approx.
Overall
Dia.
of Cable
I.D
Thickness
of
Steel Sprial
600
800
1200
1400
1600
1800
2000
600
800
1200
1400
1600
1800
2000
600
800
1200
1400
1600
1800
2000
600
800
1200
1400
1600
1800
2000
37.9
42.0
47.2
50.3
53.3
56.1
58.8
37.9
42.0
47.2
50.3
53.3
56.1
58.8
35.6
40.6
45.7
48.9
51.9
54.8
57.5
35.6
40.6
45.7
48.9
51.9
54.8
57.5
2.3
2.4
2.5
2.6
2.6
2.7
2.8
2.2
2.3
2.4
2.4
2.5
2.5
2.6
2.1
2.2
2.4
2.4
2.5
2.5
2.6
2.0
2.1
2.3
2.3
2.4
2.4
2.5
118
122
129
133
136
140
143
107
114
120
124
127
130
134
106
112
118
122
126
129
132
99
105
114
117
121
124
128
18.0
18.0
18.0
18.0
18.0
18.0
18.0
18.0
18.0
18.0
18.0
18.0
18.0
18.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
23.4
23.4
23.4
23.4
23.4
23.4
23.4
19.5
19.5
19.5
19.5
19.5
19.5
19.5
19.5
19.5
19.5
19.5
19.5
19.5
19.5
17.5
17.5
17.5
17.5
17.5
17.5
17.5
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
Kraft
Paper
PPLP
Kraft
Paper
PPLP
T
a
i
h
a
n
s
O
i
l
F
i
l
l
e
d
P
o
w
e
r
C
a
b
l
e
P14
kg/km Ir/km mm mm mm kg/km Ir/km /km, o /km, o
Lead Sheath
Approx.
Cable
Weight
Approx.
Cable
Weight
Maximum
Conductor
Resistance
Maximum
Electrostatic
Capacity
Thickness
of
Sheath
Thickness
of
Jacket
Approx.
Volume
of Cable
Oil
Approx.
Volume
of Cable
Oil
Approx.
Overall
Dia.
of Cable
19,500
22,000
26,900
29,500
31,900
34,500
37,200
17,200
20,000
24,600
27,000
29,600
32,000
34,500
16,700
19,800
24,200
26,800
29,300
31,700
34,300
15,400
18,400
23,100
25,600
28,100
30,400
32,900
3,900
4,250
4,640
4,920
5,160
5,420
5,680
2,580
2,990
3,270
3,450
3,070
3,850
4,070
2,940
3,320
3,630
3,880
4,110
4,320
4,560
2,070
2,500
2,770
2,940
3,140
3,310
3,500
29,500
32,900
38,600
41,800
45,100
47,900
51,100
26,100
29,300
34,800
38,000
41,000
43,800
47,000
24,800
28,700
34,400
37,500
40,300
43,300
46,600
23,100
26,900
32,500
35,600
38,400
41,400
44,500
0.0299
0.0227
0.0151
0.0131
0.0114
0.0102
0.00915
0.0299
0.0277
0.0151
0.0131
0.0114
0.0102
0.00915
0.0299
0.0227
0.0151
0.0131
0.0122
0.0102
0.00915
0.0299
0.0277
0.0151
0.0131
0.0122
0.0102
0.00915
0.27
0.29
0.31
0.33
0.34
0.36
0.37
0.25
0.27
0.30
0.31
0.33
0.34
0.35
0.28
0.31
0.35
0.37
0.39
0.40
0.42
0.26
0.29
0.32
0.33
0.35
0.36
0.38
3,100
3,360
3,660
3,870
4,080
4,280
4,470
1,750
2,210
2,400
2,560
2,720
2,870
3,020
2,290
2,600
2,830
3,020
3,190
3,370
3,550
1,600
1,840
2,000
2,150
2,290
2,440
2,570
3.7
3.8
3.9
4.0
4.1
4.1
4.2
3.5
3.6
3.7
3.8
3.9
3.9
4.0
3.4
3.5
3.7
3.8
3.8
3.9
4.0
3.3
3.4
3.6
3.7
3.7
3.8
3.9
111
115
121
125
128
131
134
103
107
113
116
119
123
125
100
105
111
115
118
121
124
96
101
107
110
114
117
120
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
T
a
i
h
a
n
s
O
i
l
F
i
l
l
e
d
P
o
w
e
r
C
a
b
l
e
P15
T
a
i
h
a
n
s
O
i
l
F
i
l
l
e
d
P
o
w
e
r
C
a
b
l
e
P16
Rated
Voltage
Rated
Voltage
Nominal
Area
Approx.
O.D
Material Thickness
Thickness
of
Sheath
Thickness
of
Jacket
Approx.
Overall
Dia.
of Cable
Approx.
Cable
Weight
o
BIL =
,ookV
+(
BIL =
;okV
+(
kV
kV mm
mm mm mm mm mm kg/km
mm
mm mm mm mm mm mm mm
Nominal
Area
Oil Passage
Conductor
Conductor Insulation Aluminum Sheath
Insulation Aluminum Sheath
Approx.
O.D
Material Thickness
Thickness
of
Sheath
Thickness
of
Jacket
Approx.
Overall
Dia.
of Cable
I.D
Thickness
of
Steel Sprial
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
1500
2000
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1500
2000
150
200
250
325
14.7
17.0
19.0
21.7
2.5
2.5
2.6
2.7
126
129
131
134
18,300
19,200
21,000
24,100
4.5
4.5
4.5
4.5
14.0
13.0
12.5
12.5
24.4
30.6
35.6
40.6
42.2
45.7
48.9
50.4
57.5
24.4
30.6
35.6
40.6
42.2
45.7
50.4
57.5
1.9
2.0
2.1
2.2
2.2
2.3
2.4
2.4
2.5
1.7
1.8
1.8
2.0
2.1
2.2
2.2
2.4
97
104
110
115
119
123
126
127
136
83
87
93
96
102
106
111
119
14.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
14.0
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
18.0
18.0
18.0
18.0
18.0
18.0
18.0
18.0
18.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
4.5
4.5
4.5
4.5
4.5
4.5
4.5
4.5
14.0
13.0
12.5
12.5
13.5
13.5
13.5
13.5
Kraft
Paper
Kraft
Paper
Kraft
Paper
Three Core
Construction
T
a
i
h
a
n
s
O
i
l
F
i
l
l
e
d
P
o
w
e
r
C
a
b
l
e
P17
kg/km Ir/km mm mm mm kg/km Ir/km /km, o /km, o
Lead Sheath
Approx.
Cable
Weight
Approx.
Cable
Weight
Maximum
Conductor
Resistance
Maximum
Electrostatic
Capacity
Thickness
of
Sheath
Thickness
of
Jacket
Approx.
Volume
of Cable
Oil
Approx.
Volume
of Cable
Oil
Approx.
Overall
Dia.
of Cable
Approx.
Volume
of Cable
Oil
Thickness
of
Sheath
Thickness
of
Jacket
Approx.
Overall
Dia.
of Cable
Approx.
Cable
Weight
Approx.
Volume
of Cable
Oil
Maximum
Conductor
Resistance
Maximum
Electrostatic
Capacity
4.5
4.5
4.5
4.5
Ir/km mm mm mm kg/km Ir/km /km, o /km, o
Lead Sheath
3.9
3.9
3.9
4.0
123
124
125
128
32,400
33,700
35,500
38,300
4,480
4,120
4,290
4,650
0.1210
0.0906
0.0732
0.0563
0.19
0.23
0.25
0.28
6,000
5,530
5,740
5,920
10,400
13,400
16,100
19,000
19,400
23,400
26,200
27,900
34,100
7,600
9,900
12,100
14,800
17,300
19,800
23,000
29,100
2,230
2,610
2,890
3,250
3,310
3,470
3,680
3,800
4,270
1,480
1,640
1,820
2,050
2,220
2,380
2,630
3,140
15,000
19,200
22,200
26,100
27,900
30,800
33,700
37,100
43,200
12,700
15,800
18,900
22,300
26,100
28,900
33,700
40,700
0.0889
0.0441
0.0299
0.0227
0.0181
0.0151
0.0131
0.0122
0.00915
0.0131
0.0122
0.0102
0.00915
0.0181
0.0151
0.0122
0.00915
0.23
0.26
0.29
0.32
0.34
0.36
0.38
0.39
0.43
0.27
0.34
0.39
0.43
0.43
0.45
0.51
0.57
1,440
1,680
1,890
2,120
2,200
2,310
2,410
2,490
2,750
1,150
1,270
1,390
1,600
1,720
1,850
1,980
2,240
3.0
3.2
3.3
3.4
3.5
3.6
3.7
3.7
3.9
2.8
2.9
3.0
3.1
3.3
3.3
3.5
3.6
79
87
92
97
100
103
106
108
113
73
78
83
88
94
97
102
110
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
6.0
4.5
4.5
4.5
4.5
4.5
4.5
4.5
4.5
T
a
i
h
a
n
s
O
i
l
F
i
l
l
e
d
P
o
w
e
r
C
a
b
l
e
P18
As oil filled cable accessories, there are sealing ends(EB-A, EB-G, EB-O), joint boxes(IJ, NJ, SJ,
SIJ), oil feeding and alarm equipments.
Accessories
Sealing Ends
Indoor and outdoor sealing end (EB-A)
Sealing end is sends and takes electric power into and
out of cable. Porcelain bushings are needed to be
insulated between the earth potential parts and the high
voltage parts, and this sealing end has stress relief cone
formed of wide paper or a condenser cone formed of
insulating paper layers and metal foil for inside
reinforcement according to the voltage uesd. Connector
is fastened to the cable conductor by compression
method and a flexible terminal lug is placed between the
conductor and the lead wire to avoid applying
unnecessary external force against the sealing end.
SF6 gas immersed sealing end (EB-G)
Sealing end is used for terminating the cable for the
SF6 gas switch gear. Epoxy bushings are needed to
be insulated between the earth potential parts and the
high voltage parts. The inner construction of this
sealing end is similar to that of an indoor and outdoor
sealing end except that the sealing end is completely
encl osed and i mmersed i n gas to the hi gher
i nsul ati on strength and to prevent dust from
collecting, etc.
Nominal
Voltage
(kV) A B C D E
Dimension(mm)
1,480
1,830
2,940
3,350
3,975
110
154
220
275
345
1,725
2,075
3,290
3,700
4,250
435
435
500
500
600
360
360
480
480
550
315
315
470
470
510
Nominal
Voltage
(kV) A B C D E F
Dimension(mm)
80
110
110
112
202
252
220
480
540
298
559
617
320
582
640
757
960
1,400
110~161
220~300
330~420
T
a
i
h
a
n
s
O
i
l
F
i
l
l
e
d
P
o
w
e
r
C
a
b
l
e
P19
Oil immersed type sealing end (EB-O)
This construction of this sealing end is similar to the of an
indoor and outdoor sealing end except that the sealing
end is completely enclosed and immersed in oil to prevent
dust from collecting, and the size of EB-O is much smaller
than the one of EB-A, this type of sealing end is for
connecting cable with transformer
Joint Box
Straight through joint (NJ)
This joint is used for jointing cables, and electrical jointing
and oil passage are part of its function or structure. And
this joint has same quality as, or better than cable itself,
and is free from any electrical and mechanical defects due
to the trouble developed by the power transmission
system.
Rated
Voltage
(kV)
Nominal Area
of Conductor
(mm
) L D
Dimension(mm)
110 ~ 161
less than 1,000
1,200 ~ 2,000
less than 2,000
less than 2,000
220 ~ 300
330 ~ 420
1,300
1,530
2,000
2,400
130
180
200
240
Rated
Voltage
(kV) A B C D E F G H I
Dimension(mm)
990
1,350
1,170
1,550
1,260
1,700
585
900
450
640
375
420
340
390
320
420
380
550
110 ~ 161
220 ~ 345
T
a
i
h
a
n
s
O
i
l
F
i
l
l
e
d
P
o
w
e
r
C
a
b
l
e
P20
Insulation joint (IJ)
The structure of this joint is almost same as straight
through joint box, and the difference between them is to
put an insulator flange at the center of copper casing.
This box is used for jointing cables and at the same
time for insulating on metal sheath from the other metal
sheath to get a sheath voltage reducing under safety
level.
Oil stop joint (SJ)
This joint is used for dividing the oil feeding section in
case that route length is too long or oil pressure change
is too excessive at static or transient operation. Also
this joint is used for connecting the cables electrically,
and at any time for stopping the oil passage to separate
the oil feeding section of both cables.
Rated
Voltage
(kV)
Nominal Area
of Conductor
(mm
) L D
Dimension(mm)
110 ~ 161
less than 1,000
1,200 ~ 2,000
less than 2,000
less than 2,000
220 ~ 300
330 ~ 420
1,300
1,530
2,000
2,400
130
180
200
240
Rated
Voltage
(kV)
Nominal Area
of Conductor
(mm
) L D
Dimension(mm)
110 ~ 161 less than 2,000
less than 2,000
less than 2,000
220 ~ 300
330 ~ 420
2,900
3,400
4,100
250
350
350
T
a
i
h
a
n
s
O
i
l
F
i
l
l
e
d
P
o
w
e
r
C
a
b
l
e
P21
Oil feeding tank
The inner oil of oil filled cables expands or shrinks automatically, and enough oil has to be kept in the oil feeding tank to
supply oil to the cables for a significant length of time even if the oil should be out. There are many kinds of oil feeding
tanks, for example, pressure tank(inner and outer gas type) and special oil feeding tank, etc.
Valve panel
The valve panel(guage panel) shall be installed at the intermediate of
pressure tank and sealing end or oil stop joint and have such a function
as to sense and indicate the oil pressure. If necessary, the pressure
guage shall be provided with the electrical contacts which shall make the
electric cirucit for the oil pressure alarm.
Other Accessories
Cross bond link box
The cross bonding link box shall be used for connecting the bonding
wire properly and be provided with surge diverters to discharge at the
suitable for installation in joint handholes and manholes and be fully
watertight.
Alarm device
It is advisable to have an alarm device to notify the guard when the
cables are out of order or damaged.
Usually a transmitter is located at the oil tank and a receiver is placed in the control room. We manufacture three
kinds of alarm devices; one alarm device operates when the minimum pressure or volume is reached. Another
continuously indicates the pressure or volume, and the third has an indicator and a recorder. The proper one should be
chosen after duly considering the functional importance of the cable and the maintenance system adopted for the line.
Oil feeding pipe
The oil feeding pipes used for connecting the cables to the oil tank lead are made of armored lead, copper and etc. We
will choose the most suitable one for your particular system.
Terminal box for control cable
The alarm transmitter and receiver are connected with control cables. Since many alarm transmitters are generally
used, this terminal box is placed near the transmitters to allow the circuits to be opened or checked.
Piping Indication Panel
PT BPT
T
a
i
h
a
n
s
O
i
l
F
i
l
l
e
d
P
o
w
e
r
C
a
b
l
e
P22
Installation
Direct Burial
Where the road is narrow, the construction of conduit
under the road is usually not permitted.
Where the number of cables is few and no future
increase is expected.
Where the road digging is easy.
Underground Duct
In case of a main underground transmission line where
the number of cables are many or expected to be
increased in near future.
In case of hard pavement or where hard pavement will
be constructed in future.
Where digging is difficult due to heavy traffic.
Special Laying
In case cables are installed in special places where there
are bridges or railways, special laying methods are
employed as follows ;
When a cable crosses a river or canal, cables are
attached to the bridge. If there is no suitable bridge in the
neighborhood, an exclusive bridge should be buit or a
method of submarine laying should be adopted.
As long as the strengh and space of the bridge
permits, it is best to attach the cables to the bridge.
Whether it is better to build an exclusive bridge or to lay
submarine cable depends on the cost and difficulty of
construction.
In case of crossing a railway, there are two methods; one
is digging through the railway bed, and the other is
piercing from the side of the railway by using an
excavator. When the cable crosses many tracks like a
surface from railroad or suburban railway, digging the
railway bed is usually adopted. Except for the above
case, piercing by using an excavator is adopted.
Taihan has many achievements and excellent techniques, relative to cable installation work and
is making performance doubly sure in regard to safety of operations, besides vigorously
promoting development, rationalization and speedy installation. And also Taihan is performing its
work consistently, from planning to testing after installation, including laying of oil filled cables,
sealing ends assembly, construction of joints, and oil feeding equipment. There are the following
methods in laying of oil filled cables and special features are as follows.
T
a
i
h
a
n
s
O
i
l
F
i
l
l
e
d
P
o
w
e
r
C
a
b
l
e
P23
Looking to the Future
In order to provide all the requirement of a world market that asks for ever higher voltages, Taihan
hace a dedicated policy of high investment into research.
Its this policy which keeps Taihan at the front of thier field-innovating, testing new tecniques and
incorporating the latest technological advancements.
Large conductor size
ELECTRIC WIRE CO., LTD.
Head Office
Insong Building, 194-15,
1-ga, Hoehyeon-dong,
Jung-gu, Seoul, Korea
Tel. 82-2-316-9114
Fax. 82-2-757-2942
R & D Center
996, Siheung-dong,
Geumcheon-gu,
Seoul, Korea
Tel. 82-2-890-9504
Fax. 82-2-806-0186
Anyang Plant
785, Gwanyang-dong,
Dongan-gu, Anyang,
Gyeonggi-do, Korea
Tel. 82-31-420-9114
Fax. 82-31-423-2685
Siheung Plant
113-119, Siheung-dong,
Geumcheon-gu,
Seoul, Korea
Tel. 82-2-890-9114
Fax. 82-2-808-6320
Ansan Plant
603, Seonggok-dong,
Ansan, Gyeonggi-do,
Korea
Tel. 82-31-490-5114
Fax. 82-31-491-3721
Kuala Lumpur
Office
15th Floor, Kenanga
International, JL. Sultan
lsmail, 50250 Kuala
Lumpur, Malaysia
Tel. 60-3-2161-8017
Fax. 60-3-2161-3628
Singapore Office
629 Aljunied Road
#05-19, Cititech
Industrial Building,
Singapore 389838,
Singapore
Tel. 65-842-5069
Fax. 65-842-5076
Riyadh Office
Al Akariyah Shopping
Center 2, Room No.
726, Olaya Road,
P.O.Box 201, Riyadh,
Saudi Arabia
Tel. 966-1-419-0227
Fax. 966-1-419-0262
Skytel Co., Ltd.
4th Floor of the Montel
Building, Chingeltel
District 1st. Horoo,
Ulaanbaatar-13,
Mongolia
Tel. 976-1-318488
Fax. 976-1-318487
Malesela Taihan
Electric Cable (Pty) Ltd.
Vereeniging 1930,
Steel Road, Peacehaven
Vereeniging 1939,
Gauteng, South Africa
Tel. 27-16-450-8333
Fax. 27-16-450-8266
Telecom & Energy
Cables Corp.
85, Denton Avenue,
New Hyde Park,
NY 11040, U.S.A
Tel. 1-718-347-6030
Fax. 1-718-347-6045
www.taihan.com
Вам также может понравиться
- Marine Electrical Practice: Marine Engineering SeriesОт EverandMarine Electrical Practice: Marine Engineering SeriesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (8)
- 16th Edition IEE Wiring Regulations: Design and Verification of Electrical InstallationsОт Everand16th Edition IEE Wiring Regulations: Design and Verification of Electrical InstallationsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Xlpe CableДокумент18 страницXlpe CableSandipNanawareОценок пока нет
- Radio Stations: Installation, Design and PracticeОт EverandRadio Stations: Installation, Design and PracticeРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- R1-External Electrical BOQ - ComparativeДокумент8 страницR1-External Electrical BOQ - ComparativeyogeshОценок пока нет
- Gas Springs1Документ32 страницыGas Springs1GLADWIN PAUL SIM 16-18Оценок пока нет
- Transformer PDFДокумент35 страницTransformer PDFjiguparmar1516100% (2)
- List of IEC Standards - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент7 страницList of IEC Standards - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediamohannad87Оценок пока нет
- Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook: A Manual of Quick, Accurate Solutions to Everyday Pipeline Engineering ProblemsОт EverandPipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook: A Manual of Quick, Accurate Solutions to Everyday Pipeline Engineering ProblemsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (10)
- Cat-CMP Cable GlandДокумент64 страницыCat-CMP Cable GlandSyahirul Alim100% (1)
- Octane NumberДокумент4 страницыOctane NumberMm AbdulaОценок пока нет
- Method Statement: Conbextra GP2Документ5 страницMethod Statement: Conbextra GP2diwakar1978Оценок пока нет
- Project ReportДокумент63 страницыProject ReportPramit ChhabraОценок пока нет
- Kobelco FillerДокумент24 страницыKobelco FillerRamzi Dol Abdul WahidОценок пока нет
- Ee Construction MethoologyДокумент5 страницEe Construction MethoologyFennelyn JusayanОценок пока нет
- Arial Bunch ConductorДокумент10 страницArial Bunch Conductorbbakari2000Оценок пока нет
- Wire and CableДокумент5 страницWire and CablejosemartinpenatorresОценок пока нет
- Crusher Bearings Technical White PaperДокумент6 страницCrusher Bearings Technical White PaperApna BharatОценок пока нет
- Total Losses in Power Distribution and Transmission Lines 1Документ7 страницTotal Losses in Power Distribution and Transmission Lines 1mohannad87Оценок пока нет
- Instrument TransformersДокумент16 страницInstrument Transformersnitinatp1978Оценок пока нет
- Methods, Processes, and Equipment in Size Reduction of Solids - 5ME2Документ35 страницMethods, Processes, and Equipment in Size Reduction of Solids - 5ME2Ana Marie Baysa100% (3)
- 1127 Raceway System TrainingДокумент50 страниц1127 Raceway System Training54045114Оценок пока нет
- Waste Heat Boiler: YoshimineДокумент12 страницWaste Heat Boiler: Yoshimineamits4uОценок пока нет
- Sa P 041Документ5 страницSa P 041Haleem Ur Rashid BangashОценок пока нет
- HendrixACS - 4. Restoration GuideДокумент14 страницHendrixACS - 4. Restoration GuideMarilyn ChimarroОценок пока нет
- OETC-74 - 400kV Tower Design Inputs To AL-BABTAINДокумент146 страницOETC-74 - 400kV Tower Design Inputs To AL-BABTAINMohamed Gad67% (3)
- PDF HT-XLPEДокумент36 страницPDF HT-XLPEKvj SrinivasaraoОценок пока нет
- BushingДокумент8 страницBushingrasheed313Оценок пока нет
- 600 MW Stator Bar Training ReportДокумент21 страница600 MW Stator Bar Training ReportHimanshu SharmaОценок пока нет
- 1.5 LEADER XLPE Cable - Catalogue PDFДокумент62 страницы1.5 LEADER XLPE Cable - Catalogue PDFGan SAIK NGAIОценок пока нет
- Lecture 7-8Документ37 страницLecture 7-8usamaОценок пока нет
- Station Service TransformerДокумент13 страницStation Service TransformerpvenkyОценок пока нет
- NORSOK U CR 006r1 - Subsea Production Control UmbilicalДокумент14 страницNORSOK U CR 006r1 - Subsea Production Control UmbilicalNils Antoine FreundОценок пока нет
- EHV XLPE Cable & AccessoriesДокумент40 страницEHV XLPE Cable & AccessoriesgurusamyperumalОценок пока нет
- Technical Service Pits Specification KEOДокумент18 страницTechnical Service Pits Specification KEOVijay BarreyОценок пока нет
- OilFilledPowerCable Catalog PDFДокумент24 страницыOilFilledPowerCable Catalog PDFsamsungloverОценок пока нет
- Polycab HT XlpeДокумент36 страницPolycab HT XlpePravin NarkhedeОценок пока нет
- Electrical Tests Uncured RR CoilsДокумент2 страницыElectrical Tests Uncured RR CoilsTiagoFaleiros100% (1)
- Summer Training Presentation Crompton GreavesДокумент43 страницыSummer Training Presentation Crompton GreavesKanhaiya Kumar60% (5)
- Tuty Court Genset ESTIMATES NewДокумент42 страницыTuty Court Genset ESTIMATES NewRajaDurai RamakrishnanОценок пока нет
- Catalog 1.0Документ24 страницыCatalog 1.0Dax Xenos ArenasОценок пока нет
- Cap Ngam 24KV-1x500mm2Документ10 страницCap Ngam 24KV-1x500mm2Minh VienОценок пока нет
- Cable JointsДокумент22 страницыCable JointsRajОценок пока нет
- TCJДокумент12 страницTCJThilina Dhanushka GuluwitaОценок пока нет
- MU038 KRT HighVoltage-catalog-lowres PDFДокумент24 страницыMU038 KRT HighVoltage-catalog-lowres PDFgerrzen64Оценок пока нет
- LV SWBD Design ProblemДокумент15 страницLV SWBD Design ProblemkggganiОценок пока нет
- Cable JointsДокумент22 страницыCable Jointsmrb88Оценок пока нет
- Oil Filled Cables TerminalsДокумент8 страницOil Filled Cables TerminalsGabriel SantiagoОценок пока нет
- WMS For Cable Laying & TerminationДокумент5 страницWMS For Cable Laying & Terminationeiplstaff.nav2Оценок пока нет
- Bushing Selection - Making The Right ChoiceДокумент9 страницBushing Selection - Making The Right ChoiceManojОценок пока нет
- 220KV CVT 0 2 Metering AccuracyДокумент12 страниц220KV CVT 0 2 Metering AccuracyJAY PARIKHОценок пока нет
- Well Intervention Coiled Tubing Course 6 10 Nov 2023 1699741620Документ65 страницWell Intervention Coiled Tubing Course 6 10 Nov 2023 1699741620136. Iqbal ipmawan YogatamaОценок пока нет
- VAHLEДокумент28 страницVAHLEAdrian M FahriОценок пока нет
- Testing of Distribution CablesДокумент11 страницTesting of Distribution CablesHashimi JuniОценок пока нет
- CMP TMCX Installation Fitting Instructions FI280 Issue 6 0210Документ18 страницCMP TMCX Installation Fitting Instructions FI280 Issue 6 0210raviОценок пока нет
- Materials and ComponentsДокумент121 страницаMaterials and ComponentskishoreОценок пока нет
- Transformers Manufacturing Process - Electrical Controls & Switchgear LTDДокумент8 страницTransformers Manufacturing Process - Electrical Controls & Switchgear LTDRaghavendra M RОценок пока нет
- Thermoplastic Composite PipeДокумент11 страницThermoplastic Composite PipeRenanОценок пока нет
- Electrical Safety Inspection Report: A & B Outerwear LTDДокумент12 страницElectrical Safety Inspection Report: A & B Outerwear LTDAkula VeerrajuОценок пока нет
- The Norms Set For Discharge of Its Function: Manual 4Документ30 страницThe Norms Set For Discharge of Its Function: Manual 4SandipNanawareОценок пока нет
- Indian Standard 3637Документ10 страницIndian Standard 3637Aman DeepОценок пока нет
- Off-Line Partial Discharge Testing of A Nuclear Reactor Coolant Pump MotorДокумент10 страницOff-Line Partial Discharge Testing of A Nuclear Reactor Coolant Pump MotorjuarozОценок пока нет
- Busduct System T-BuswayДокумент26 страницBusduct System T-BuswayFernando LoteroОценок пока нет
- Product Catalogue ERTG-LresДокумент12 страницProduct Catalogue ERTG-LrescocoricorОценок пока нет
- Training ReportДокумент20 страницTraining ReportAbhishek SinghОценок пока нет
- How to prepare Welding Procedures for Oil & Gas PipelinesОт EverandHow to prepare Welding Procedures for Oil & Gas PipelinesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- HV CablesДокумент14 страницHV Cablesmohannad87Оценок пока нет
- المصنف 5Документ1 страницаالمصنف 5mohannad87Оценок пока нет
- المصنف 4Документ1 страницаالمصنف 4mohannad87Оценок пока нет
- المصنف 3Документ1 страницаالمصنف 3mohannad87Оценок пока нет
- المصنف2Документ1 страницаالمصنف2mohannad87Оценок пока нет
- Impulse TestДокумент2 страницыImpulse Testmohannad87Оценок пока нет
- ChapterДокумент14 страницChaptermohannad87Оценок пока нет
- Dem 60 CДокумент3 страницыDem 60 Cmohannad87Оценок пока нет
- Danfoss TP4:TP5 Thermostat PDFДокумент84 страницыDanfoss TP4:TP5 Thermostat PDFABW35Оценок пока нет
- United States Patent (19) : Fisher, Both of Chester, All of VaДокумент4 страницыUnited States Patent (19) : Fisher, Both of Chester, All of VaCh PrasadОценок пока нет
- PNGF Rooftop 048 350 R410aДокумент32 страницыPNGF Rooftop 048 350 R410aRayhan Sayeed100% (1)
- ATS2018 Installation ManualДокумент28 страницATS2018 Installation ManualJohnny BravooОценок пока нет
- Replacing Downdraft Kiln With Chamber Kiln in A Refractory IndustryДокумент2 страницыReplacing Downdraft Kiln With Chamber Kiln in A Refractory IndustryKauser ImamОценок пока нет
- Sales Territory & CodeДокумент9 страницSales Territory & Codeaktaruzzaman bethuОценок пока нет
- Product Catalogue (ARZTECH SOLUTION) PDFДокумент5 страницProduct Catalogue (ARZTECH SOLUTION) PDFAzizy YusofОценок пока нет
- GFNДокумент19 страницGFNAl Amin ZubirОценок пока нет
- Grand VivaДокумент12 страницGrand VivaAbhishek PadmasaleОценок пока нет
- Large Engine Lubricants: OutlineДокумент17 страницLarge Engine Lubricants: OutlineJahmia CoralieОценок пока нет
- CFBC Boiler Bed MaterialДокумент2 страницыCFBC Boiler Bed MaterialmkoelrealОценок пока нет
- Coolant DatasheetДокумент2 страницыCoolant DatasheetTerminal TruckОценок пока нет
- Gestra Check ValveДокумент4 страницыGestra Check Valvetilakthakar1Оценок пока нет
- 01 Catalog Mesin - MV-01 Vertical Winding Machine Range 1.2inch - 10inchДокумент2 страницы01 Catalog Mesin - MV-01 Vertical Winding Machine Range 1.2inch - 10inchSUPPORT GTE100% (1)
- Ventilation: Plant RoomДокумент3 страницыVentilation: Plant RoomggrapsasОценок пока нет
- EHB - en - File - 9.7.3 Equivalent ASME EN Materials PDFДокумент3 страницыEHB - en - File - 9.7.3 Equivalent ASME EN Materials PDFks2000n1Оценок пока нет
- 1 Toth Opt SecДокумент12 страниц1 Toth Opt SeccoolerthanhumphreyОценок пока нет
- Spheroidal Graphite (SG) Acicular / MartensiticДокумент2 страницыSpheroidal Graphite (SG) Acicular / MartensiticTarun ChakrabortyОценок пока нет
- MSDS - Fuel-Protect, Keep Clean Solution, For Diesel InjectorДокумент5 страницMSDS - Fuel-Protect, Keep Clean Solution, For Diesel InjectorDaniel OlanoОценок пока нет
- LG wd-1457rd 1458rdДокумент42 страницыLG wd-1457rd 1458rdGlen CastlemanОценок пока нет