Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Coordinate Geometry Problems
Загружено:
rajdeepghai5607Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Coordinate Geometry Problems
Загружено:
rajdeepghai5607Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Topic Coordinate Geometry
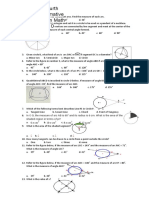
Class 10 1. Plot the following points in the rectangular coordinate system. (i) A (5, 4) (ii) B (-4, 3) (iii) C (-2, -3) (iv) D (3, -2) 2. Locate the points (i) (3, 5) and (5, 3) (ii) (-2, -5) and (-5, -2) in the rectangular coordinate system. 3. Plot the points (-1, 0), (2, 0), (-5, 0) and (4, 0) in the Cartesian plane. 4. Plot the points (0, 4), (0,-2), (0, 5) and (0,-4) in the Cartesian plane. 5. Plot the points (i) (-1, 2), (ii) (-4, 2), (iii) (4, 2) and (iv) (0, 2). What can you say about the position of these points? Identify the quadrants of the points 6. A (2, 3), 7. B (-2, 3), 8. C (-2, -3) 9. D (2, 3). Find the coordinates of the points shown in the Figure, where each square is a unit square. (Question 10 to 15)
10. A
11. B 12. C 13. D 14. E 15. F 16. G State whether the following statements are true / false. 17. (5, 7) is a point in the IV quadrant. 18. (2, 7) is a point in the III quadrant. 19. (8, 7) lies below the x-axis. 20. (5, 2) and (7, 2) are points on the line parallel to y-axis. 21. (5, 2) lies to the left of y-axis. 22. (0, 3) is a point on x-axis. 23. (2, 3) lies in the II quadrant. 24. (10, 0) is a point on x-axis. 25. (2, 4) lies above x-axis. 26. For any point on the x-axis its y coordinate is zero. Write down the abscissa for the following points. 27. (7, 2) 28. (3, 5) 29. (8, 7) 30. (5, 3) Write down the ordinate of the following points. 31. (7, 5) 32. (2, 9)
33. (5, 8) 34. (7, 4) 35. In a rectangle ABCD, the coordinates of A, B and D are (0, 0) (4, 0) (0, 3). What are the coordinates of C? 36. Find the distance between the points (-4, 0) and (3, 0) 37. Find the distance between the points (-7, 2) and (5, 2) 38. Find the distance between the points (-5, -6) and (-4, 2) 39. Find the distance between the points (0, 8) and (6, 0) 40. Find the distance between the points (3, -4), (5, -7) 41. Show that the three points A(4, 2), B(7, 5) and C(9, 7) lie on a straight line. 42. Determine whether the points are vertices of a right triangle A (-3, -4), B (2, 6) and C (-6, 10). 43. Show that the points (a, a), (a, a), and (a , a triangle. ) form an equilateral
44. Prove that the points (7, 3), (5, 10), (15, 8) and (3, 5) taken in order are the corners of a parallelogram. 45. Show that the following points (3, 2), (3, 2), (1, 2) and (1, 2) taken in order are vertices of a square. 46. Let P be a point on the perpendicular bisector of the segment joining (2, 3) and (6, 5). If the abscissa and the ordinate of P are equal, find the coordinates of P. 47. Show that (4, 3) is the centre of the circle which passes through the points (9, 3), (7, 1) and (1, 1). Find also its radius? 48. Show that S (4, 3) is the circum-centre of the triangle joining the points A (9, 3), B (7, 1) and C (1, 1) 49. If the point (a, b) is equidistant from (3, 4) and (8, 5), show that 5a b 32 = 0. Find the distance between the following pairs of points. 50. (7, 8) and (2, 3) 51. (6, 0) and (2, 4)
52. (3, 2) and (2, 0) 53. (2, 8) and (4, 6) 54. (2, 3) and (3, 2) 55. (2, 2) and (3, 2) 56. (2, 2) and (3, 2) 57. (7, 0) and (8, 0) 58. (0, 17) and (0, 1) 59. (5, 7) and the origin. Show that the following points are collinear. 60. (3, 7), (6, 5) and (15, 1) 61. (3, 2), (2, 8) and (0, 4) 62. (1, 4), (3, 2) and (1, 10) 63. (6, 2), (2, 3) and (2, 8) 64. (4, 1), (5, 2) and (6, 5) Show that the following points form an isosceles triangle. 65. (2, 0), (4, 0) and (1, 3) 66. (1, 2), (5, 1) and (1, 4) 67. (1, 3), (2, 1) and (1, 1) 68. (1, 3), (3, -5) and (3, 0) 69. (2, 3), (5, 7) and (1, 4) Show that the following points form a right angled triangle. 70. (2, 3), (6, 7) and (8, 3) 71. (ii) (11, 13), (3, 1) and (4, 3) 72. (0, 0), (a, 0) and (0, b)
73. (10, 0), (18, 0) and (10, 15) 74. (5, 9), (5, 16) and (29, 9) Show that the following points form an equilateral triangle. 75. (0, 0), (10, 0) and (5, 5 ) 76. (a, 0), (a, 0) and (0, a ) 77. (2, 2), (- 2,- 2) and (2 , 2 ) 78. ( , 2), (0, 1) and (0, 3) 79. ( , 1), (2 , 2) and (2 , 4) Show that the following points taken in order form the vertices of a parallelogram. 80. (7, -5), (4, 3), (5, 6) and (2, 2) 81. (9, 5), (6, 0), (2, 3) and (1, 2) 82. (0, 0), (7, 3), (10, 6) and (3, 3) 83. (2, 5), (7, 1), (2, 4) and (7, 0) 84. (3, 5), (5, 4), (7, 10) and (15, 9) Show that the following points taken in order form the vertices of a rhombus. 85. (0, 0), (3, 4), (0, 8) and (3, 4) 86. (4, 7), (1, 2), (8, 5) and (5, 4) 87. (1, 0), (5, 3), (2, 7) and (2, 4) 88. (2, 3), (6, 5), (2, 1) and (6,7) 89. (15, 20), (3, 12), (11, -6) and (7, 2) 90. If the distance between two points (x, 7) and (1, 15) is 10, find x. 91. Show that (4, 1) is equidistant from the points (-10, 6) and (9, 13). 92. If two points (2, 3) and (6, 5) are equidistant from the point (x, y) , show that x + y + 3 = 0.
93. If the length of the line segment with end points (2, 6) and (2, y) is 4, find y. 94. Find the perimeter of the triangle with vertices (0, 8), (6, 0) and origin 95. Find the perimeter of the triangle with vertices (9, 3), (1, 3) and origin 96. Find the point on the y-axis equidistant from (5, 2) and (9, 2) (Hint: A point on the y-axis will have its x coordinate as zero). 97. Find the radius of the circle whose centre is (3, 2) and passes through (5, 6). 98. Prove that the points (0, -5) (4, 3) and (-4, -3) lie on the circle centered at the origin with radius 5. 99. In the Figure, PB is perpendicular segment from the point A (4,3). If PA = PB then find the coordinates of B.
100. Find the area of the rhombus ABCD with vertices A (2, 0), B (5, -5), C (8, 0) and D (5, 5) [Hint: Area of the rhombus ABCD = ] 101. Can you draw a triangle with vertices (1, 5) (5, 8) and (13, 14)? Give reason. 102. If origin is the centre of a circle with radius 17 units, find the coordinates of any four points on the circle which are not on the axes. (Use the Pythagorean triplets) 103. Show that (2, 1) is the circum-centre of the triangle formed by the vertices (3, 1), (2, 2) and (1, 1) 104. Show that the origin is the circum-centre of the triangle formed by the vertices (1, 0), (0, -1) and (
105. If the points A(6, 1), B(8, 2), C(9, 4) and D(p, 3) taken in order are the vertices of a parallelogram, find the value of p using distance formula. 106. The radius of the circle with centre at the origin is 10 units. Write the coordinates of the point where the circle intersects the axes. Find the distance between any two of such points.
107. Find a point on x-axis which is equidistant from the points (7, 6) and (3, 4). 108. Determine the equation of the straight line whose slope is 2 and y-intercept is 7. 109. Determine the equation of the straight line passing through ( 1, 2) and having slope . 110. Determine the equation of the straight line passing through the points (1, 2) and (3, 4). 111. Find the equation of the straight line passing through the point (1, 2) and making intercepts on the co-ordinate axes which are in the ratio 2 : 3. 112. Find the length of the perpendicular from (2, 3) to the line 2x y + 9 = 0 . 113. Find the co-ordinates of the points on the straight line y = x + 1 which are at a distance of 5 units from the straight line 4x 3y + 20 = 0 114. Find the equation of the straight line, if the perpendicular from the origin makes an angle of 120 with x-axis and the length of the perpendicular from the origin is 6 units. 115. Find the points on y-axis whose perpendicular distance from the straight line 4x 3y 12 = 0 is 3. 116. Determine the equation of the straight line passing through the point ( 1, 2) and having slope . 117. Determine the equation of the line with slope 3 and y-intercept 4. 118. A straight line makes an angle of 45 with x-axis and passes through the point (3, 3). Find its equation. 119. Find the equation of the straight line joining the points (3, 6) and (2, 5). 120. Find the equation of the straight line passing through the point (2, 2) and having intercepts whose sum is 9. 121. Find the equation of the straight line whose intercept on the x-axis is 3 times its intercept on the y-axis and which passes through the point ( 1, 3). 122. Find the equations of the medians of the triangle formed by the points (2, 4), (4, 6) and ( 6, 10). 123. Find the equations of the medians of the triangle formed by the points (2, 4), (4, 6) and ( 6, 10).
124. Find the length of the perpendicular from (3, 2) to the straight line 3x + 2y + 1=0. 125. The portion of a straight line between the axes is bisected at the point ( 3, 2). Find its equation. 126. Find the equation of the diagonals of a quadrilateral whose vertices are (1, 2), ( 2, 1), (3, 6) and (6, 8). 127. Find the equation of the straight line, which cut off intercepts on the axes whose sum and product are 1 and 6 respectively. 128. Find the intercepts made by the line 7x + 3y 6 = 0 on the co -ordinate axis. 129. What are the points on x-axis whose perpendicular distance from the straight line is 4? 130. Find the distance of the line 4x y = 0 from the point (4, 1) measured along the straight line making an angle of 135 with the positive direction of the x-axis. 131. Find the angle between the straight lines 3x 2y + 9 = 0 and 2x + y 9 = 0. 132. Show that the straight lines 2x + y 9 = 0 and 2x + y 10 = 0 are parallel. 133. Show that the two straight lines whose equations are x + 2y + 5 = 0 and 2x + 4y 5 = 0 are parallel. 134. Find the distance between the parallel lines 2x + 3y 6=0 and 2x + 3y + 7 = 0. 135. Show that the straight lines 2x + 3y 9 = 0 and 3x 2y + 10 = 0 are at right angles. 136. Find the equation of the straight line parallel to 3x + 2y = 9 and which passes through the point (3, 3). 137. Find the equation of the straight line perpendicular to the straight line 3x + 4y + 28 = 0 and passing through the point ( 1, 4). 138. Show that the triangle formed by straight lines 4x 3y 18 = 0, 3x 4y + 16 = 0 and x + y 2 = 0 is isosceles. 139. Find the point of intersection of the straight lines 5x + 4y 13 = 0 and 3x + y 5=0 140. Find the equation of the straight line passing through the intersection of the straight lines 2x + y = 8 and 3x y = 2 and through the point (2, 3)
141. Find the equation of the straight line passing through the intersection of the straight lines 2x + y = 8 and 3x 2y + 7 = 0 and parallel to 4x + y 11 = 0 142. Find the equation of the straight line which passes through the intersection of the straight lines 5x 6y = 1 and 3x + 2y + 5 = 0 and is perpendicular to the straight line 3x 5y + 11 = 0 143. Find the co-ordinates of orthocentre of the triangle formed by the straight lines x y 5 = 0, 2x y 8 = 0 and 3x y 9 = 0 144. For what values of a, the three straight lines 3x + y + 2 = 0, 2x y + 3 = 0 and x + ay 3 = 0 are concurrent? 145. Find the angle between the straight lines 2x + y = 4 and x + 3y = 5 146. Find the equation of the straight line passing through the point (1, 2) and parallel to the straight line 3x + 2y 7 = 0 147. Find the equation of the straight line passing through the point (2, 1) and perpendicular to the straight line x + y = 9 148. Find the point of intersection of the straight lines 5x + 4y 13 = 0 and 3x + y 5=0 149. If the two straight lines 2x 3y + 9 = 0, 6x + ky + 4 = 0 are parallel, find k 150. Find the distance between the parallel lines 2x + y 9 = 0 and 4x + 2y + 7 = 0
Answer Key:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5. 6. I 7. II 8. III 9. IV 10. A(3, 2) 11. B(3, 2) 12. C(2, 2) 13. D(2, 1) 14. E(5, 3) 15. F(3, 4) 16. G(3, 1) 17. False 18. True 19. False 20. False 21. True 22. False 23. True 24. True 25. False 26. True 27. 7 28. 3 29. 8 30. 5 31. 5
32. 9 33. 8 34. 4 35. (4, 3) 36. 7 37. 12 38. 39. 10 40. 41. AB + BC = 3 +2 =5 = AC. The points A, B, and C are collinear. 42. AB2 + BC2 = 125 + 80 = 205 = CA2 43. AB = BC = CA = 2a 44. The opposite sides are equal. ( 45. AB = BC = CD = DA = 4 46. (4, 4) 47. CP2 = CQ2 = CR2 = 25, The points P, Q, R are on the circle. and radius = 5 units. 48. SA = SB = SC = 5 49. Hint: (a 3)2 + (b + 4)2 = (a 8)2 + (b + 5)2 50. 51. 4 52. 53. 2 54. 5 55. 1 56. 5 57. 15 58. 18 59. 60. (Question 60 to 89, are proofs using the distance between two points formula) 90. (7, 5) 91. Proof 92. Proof )
93. 10, 2 94. 24 95. 10 + 4 96. (0, 7) 97. 4 98. Proof 99. (4, 3) 100. 101. 102. 103. 104. 105. 106. 107. 108. 109. 110. 111. 112. 113. 114. 115. 116. 117. 118. 119. 120. 121. 122. 123. 124. 30 No Collinear points (8, 15) (8, 15) (8, 15) (8, 15) Proof Proof 11, 7 20 ( )
2x 7y + 16 = 0 y = 2x + 7 2x 7y + 16 = 0 3x + y = 5 3x + 2y = 7
(8, 9) and ( 42, 41) x - y + 12 = 0 (0, 1) and (0, 9). 4x 7y 10 = 0 y = 3x + 4 xy=6 11x y = 27 2x + y = 6 ; x + 2y = 6 x + 3y = 8 3x 2y = 0 ; 2x y = 0 and 5x 3y = 0
units
125. 126. 127. 128. 129. 130. 131. 132.
2x 3y + 12 = 0 9x 8y + 10 = 0 ; 2x y = 0 2x 3y = 6; 3x 2y = 6 x intercept ; y intercept 2 (8, 0) and ( 2, 0) 3 ( ) m1 = m2 = 2 and therefore they are
133. The coefficients of x and y are proportional since = parallel. 134. 135. 136. 137. 138. 139. 140. 141. 142. 143. 144. 145. 146. 147. 148. 149. 3x + 2y + 1 = 0 xy1=0 (1, 2) k=9 m1 = units and m2 =
3x + 2y 3 = 0 4x 3y + 16 = 0 Proof (1, 2) x=2 28x + 7y 74 = 0 5x + 3y + 8 = 0 (2, 3), (3, 2), ( 6, 1) a=4
150.
units
Вам также может понравиться
- CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Worksheet - Coordinate GeometryДокумент2 страницыCBSE Class 10 Mathematics Worksheet - Coordinate GeometrySandya100% (1)
- IB Math SL Arithmetic Geometric Sequences Series ReviewДокумент8 страницIB Math SL Arithmetic Geometric Sequences Series ReviewDiana Oblitas Zanabria100% (1)
- CBSE Class 11 Mathematics Worksheet - Sequences and SeriesДокумент1 страницаCBSE Class 11 Mathematics Worksheet - Sequences and SeriesOmprakash BanshiwalОценок пока нет
- Implicit DifferentiationДокумент8 страницImplicit Differentiationjake8837Оценок пока нет
- SL Practice For Exp Logs Key PDFДокумент8 страницSL Practice For Exp Logs Key PDFLeo DennisОценок пока нет
- Venn Diagram Probability ProblemsДокумент40 страницVenn Diagram Probability Problemstaimoor2Оценок пока нет
- Permutaions and CombinationsДокумент25 страницPermutaions and CombinationsamithbaluОценок пока нет
- Mathematical Induction and Complex Number ProblemsДокумент2 страницыMathematical Induction and Complex Number ProblemsMaged SamuelОценок пока нет
- Chandu Numerical Abilities - IДокумент12 страницChandu Numerical Abilities - Ichandumicrocosm1986Оценок пока нет
- Level 6 (Quiz 1)Документ3 страницыLevel 6 (Quiz 1)Ml PhilОценок пока нет
- Sub-Mathematics, Class-Ix Chapter - Linear Equation in Two Variables WorksheetДокумент2 страницыSub-Mathematics, Class-Ix Chapter - Linear Equation in Two Variables WorksheetKilaparthi KeertikaОценок пока нет
- Math IB QuestionsДокумент11 страницMath IB QuestionsFei TengОценок пока нет
- Solving Square and Cube Root ProblemsДокумент3 страницыSolving Square and Cube Root Problemsneomatrix70Оценок пока нет
- Albert Town High School Maths Matrix WorksheetДокумент1 страницаAlbert Town High School Maths Matrix WorksheetRosemary ReynoldsОценок пока нет
- ISMO PreviousPaper 5Документ13 страницISMO PreviousPaper 5kalthebal1029Оценок пока нет
- CBSE Class 11 Mathematics Worksheet - Conic SectionsДокумент1 страницаCBSE Class 11 Mathematics Worksheet - Conic SectionsRanjitha SabapathyОценок пока нет
- LCM & HCFДокумент5 страницLCM & HCFArockia RajОценок пока нет
- Maths Class 8 Annual-2Документ4 страницыMaths Class 8 Annual-2Satpreet DhanjalОценок пока нет
- Exercise 5 Sequence and SeriesДокумент5 страницExercise 5 Sequence and SeriesNurul SamsuddinОценок пока нет
- IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Документ5 страницIB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Ayush MunotОценок пока нет
- Logs and Exponents Review 1 PDFДокумент2 страницыLogs and Exponents Review 1 PDFMatematika SsvОценок пока нет
- MENTAL ABILITY PRACTICE TESTДокумент3 страницыMENTAL ABILITY PRACTICE TESTAshin ShamsuОценок пока нет
- Surd PDFДокумент3 страницыSurd PDFChai Usajai UsajaiОценок пока нет
- Unit 5: Permutation and Combination Grade 11 MathДокумент2 страницыUnit 5: Permutation and Combination Grade 11 MathRobel YacobОценок пока нет
- Quadratic EquationДокумент1 страницаQuadratic EquationEmyRaОценок пока нет
- Binomial Theorem Explainedtepsq ≠ 1.IIT - 98ySДокумент17 страницBinomial Theorem Explainedtepsq ≠ 1.IIT - 98ySHimanshu GuptaОценок пока нет
- 2004 AMC 12B SolutionsДокумент6 страниц2004 AMC 12B SolutionsjabagaweeОценок пока нет
- Add Maths F4 Topical Test 6 (E)Документ4 страницыAdd Maths F4 Topical Test 6 (E)HANIFAHОценок пока нет
- 01 - Sets, Relations and FunctionsДокумент6 страниц01 - Sets, Relations and Functionsjitender8Оценок пока нет
- Polynomial and Rational FunctionsДокумент11 страницPolynomial and Rational Functionsoana_brincoveanuОценок пока нет
- Matrices MCQДокумент7 страницMatrices MCQsMОценок пока нет
- IB Math SL Statistics ReviewДокумент11 страницIB Math SL Statistics ReviewJorgeОценок пока нет
- SAT Math Level 1 Subject Test Practice Questions 1Документ32 страницыSAT Math Level 1 Subject Test Practice Questions 1Yb Andik Adi CahyonoОценок пока нет
- Summative Test 2.4Документ2 страницыSummative Test 2.4Jaymar SarvidaОценок пока нет
- Ib Maths ST Number HW 1Документ6 страницIb Maths ST Number HW 1Shiny Nivolya100% (2)
- Workshop DPP's NTSE - Stage-2 - With PDFДокумент40 страницWorkshop DPP's NTSE - Stage-2 - With PDFUmang PatelОценок пока нет
- Surds pdf1 PDFДокумент5 страницSurds pdf1 PDFANGELINE MaduОценок пока нет
- Quadratic - Equation Hints and SolutionДокумент38 страницQuadratic - Equation Hints and SolutionNEWS ONLINEОценок пока нет
- C2 Logarithms Assignment With AnswersДокумент2 страницыC2 Logarithms Assignment With AnswersKothakonda Praveen KumarОценок пока нет
- IB REVIEW - Vectors Review 2012Документ13 страницIB REVIEW - Vectors Review 2012makunjap100% (1)
- Rounding and Estimating NumbersДокумент3 страницыRounding and Estimating NumbersjosephchengОценок пока нет
- Math IB Revision MatricesДокумент2 страницыMath IB Revision Matricesmykiri79100% (1)
- Solving Quadratic Equations from SPM 2003-2007 ExamsДокумент1 страницаSolving Quadratic Equations from SPM 2003-2007 ExamsRosmizar AhmadОценок пока нет
- Longman - Grammar Practice For Elementary (Longman)Документ5 страницLongman - Grammar Practice For Elementary (Longman)Sơn NguyễnОценок пока нет
- Sequence 1Документ5 страницSequence 1yashshri singhОценок пока нет
- Hkimo Mock Exam ReviewerДокумент16 страницHkimo Mock Exam ReviewerRonel SanicoОценок пока нет
- Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsДокумент8 страницExponential and Logarithmic FunctionsJas Dhillon0% (1)
- Test 1. SequencesДокумент3 страницыTest 1. SequencessohamОценок пока нет
- Number System Practice QuestionsДокумент12 страницNumber System Practice QuestionsAshok SanОценок пока нет
- SUB: Algebra (Math-I) STD: 10 Marks: 40 Time: 2 HrsДокумент3 страницыSUB: Algebra (Math-I) STD: 10 Marks: 40 Time: 2 HrsZiya Shaikh0% (1)
- Metrobank-MTAP-DepEd Math Challenge 2017 Elimination RoundДокумент2 страницыMetrobank-MTAP-DepEd Math Challenge 2017 Elimination RoundSunshine MaisoОценок пока нет
- CBSE Class 8 Maths Sample Paper Set 2 PDFДокумент3 страницыCBSE Class 8 Maths Sample Paper Set 2 PDFHRS originalОценок пока нет
- IOQM 2023 Solution 03092023Документ22 страницыIOQM 2023 Solution 03092023AKANKSHA DIXIT100% (1)
- Cayley Contest: Canadian Mathematics CompetitionДокумент6 страницCayley Contest: Canadian Mathematics CompetitioneilycОценок пока нет
- Pre RMO 1 PDFДокумент3 страницыPre RMO 1 PDFTanmay SagarОценок пока нет
- Parametric CurvesДокумент16 страницParametric CurvesSayan PalОценок пока нет
- Maths 4Документ10 страницMaths 4raghav_pcb6700Оценок пока нет
- Co OrdinateДокумент2 страницыCo OrdinateVarshith VОценок пока нет
- Excel Formatting ManualДокумент8 страницExcel Formatting Manualrajdeepghai5607Оценок пока нет
- Easy ExcelДокумент17 страницEasy ExcelKristine ReyesОценок пока нет
- AO Jan 2010 Paper 2Документ10 страницAO Jan 2010 Paper 2rajdeepghai5607Оценок пока нет
- LocusДокумент29 страницLocusTayeb Abdul Rahman MohdОценок пока нет
- IB Math BookДокумент290 страницIB Math Bookrajdeepghai56070% (1)
- Mathematics: Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationДокумент8 страницMathematics: Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationigcsepapersОценок пока нет
- IB Math BookДокумент314 страницIB Math Bookrajdeepghai5607Оценок пока нет
- Excel BasicsДокумент42 страницыExcel Basicsrajdeepghai5607Оценок пока нет
- IB Maths BookДокумент382 страницыIB Maths Bookrajdeepghai5607100% (1)
- AO January 2008 Paper 1Документ28 страницAO January 2008 Paper 1rajdeepghai56070% (2)
- Functions 1Документ7 страницFunctions 1rajdeepghai5607Оценок пока нет
- 6320 - 01a 4PM0 Paper 1 - June 2011Документ28 страниц6320 - 01a 4PM0 Paper 1 - June 2011rajdeepghai5607Оценок пока нет
- Igcse Maths 580 - 2003 - QP - 1Документ12 страницIgcse Maths 580 - 2003 - QP - 1Hassan mahmud100% (1)
- 2012 Paper 21Документ12 страниц2012 Paper 21rajdeepghai5607Оценок пока нет
- 2000 Paper 2 NovДокумент12 страниц2000 Paper 2 Novrajdeepghai5607Оценок пока нет
- MAths IGCSE PAper 2 May 2002Документ12 страницMAths IGCSE PAper 2 May 2002shalin_hitter60% (5)
- 2001 Paper 2 NovДокумент12 страниц2001 Paper 2 Novrajdeepghai5607Оценок пока нет
- Mathematics: Paper 2Документ12 страницMathematics: Paper 2nshoulyОценок пока нет
- 2001 Paper 2 JunДокумент12 страниц2001 Paper 2 Junrajdeepghai5607Оценок пока нет
- 2000 Paper 4 NovДокумент8 страниц2000 Paper 4 Novrajdeepghai5607Оценок пока нет
- Countries With Capital and CurrienciesДокумент15 страницCountries With Capital and CurrienciesPrateek MathurОценок пока нет
- 2000 Paper 2 NovДокумент12 страниц2000 Paper 2 Novrajdeepghai5607Оценок пока нет
- Igcse 2005Документ12 страницIgcse 2005rajdeepghai5607Оценок пока нет
- 1999 Paper 4 NovДокумент12 страниц1999 Paper 4 Novrajdeepghai56070% (3)
- Countries With Capital and CurrienciesДокумент15 страницCountries With Capital and CurrienciesPrateek MathurОценок пока нет
- Higher QA 2008 With SolutionsДокумент36 страницHigher QA 2008 With Solutionsrajdeepghai5607Оценок пока нет
- IGCSE Maths exam paper with questions on decimals, fractions, percentages, equations, geometry, trigonometry and graphsДокумент12 страницIGCSE Maths exam paper with questions on decimals, fractions, percentages, equations, geometry, trigonometry and graphsMichelle Hsieh100% (1)
- IGCSE Math 2006Документ8 страницIGCSE Math 2006rajdeepghai5607Оценок пока нет
- P5 Intensive Maths Drill AnswersДокумент29 страницP5 Intensive Maths Drill Answersrajdeepghai560750% (4)
- Higher QA 2009 With SolutionsДокумент36 страницHigher QA 2009 With Solutionsrajdeepghai5607Оценок пока нет
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFДокумент2 страницыGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFAditya MoreОценок пока нет
- Lecture 18 General Equation of 2nd DegreeДокумент17 страницLecture 18 General Equation of 2nd Degreegoutam sanyalОценок пока нет
- Medieval Islamic World: The Compendious Book On Calculation by Completion and BalancingДокумент2 страницыMedieval Islamic World: The Compendious Book On Calculation by Completion and BalancingRonaldОценок пока нет
- CirclesДокумент26 страницCirclesNeha ThakurОценок пока нет
- In This Case: in This Case:: Construction of BoxesДокумент4 страницыIn This Case: in This Case:: Construction of BoxesGaurav SethiaОценок пока нет
- EST II - Math Level 1 - December 2020Документ16 страницEST II - Math Level 1 - December 2020Hazem ShehabОценок пока нет
- 2 Basic Properties of Circles ReviewДокумент49 страниц2 Basic Properties of Circles Reviewandylai0923Оценок пока нет
- Notes For HKCEE Mathematics Trigonometry: DefinitionДокумент7 страницNotes For HKCEE Mathematics Trigonometry: DefinitionCarlos TorresОценок пока нет
- Addis Ababa City Administration Education Bureau Grade Eight Model Exam Examination 2012/ 2020Документ13 страницAddis Ababa City Administration Education Bureau Grade Eight Model Exam Examination 2012/ 2020शिवम् सुनील कुमार100% (2)
- Comp2025 Btest-5 Maths PaperДокумент6 страницComp2025 Btest-5 Maths Papershrekyy9507Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 Prisms and Cylinders: Multiple Choice QuestionsДокумент15 страницChapter 6 Prisms and Cylinders: Multiple Choice QuestionsLilianLeeОценок пока нет
- Grade 9 Sept Test 2023.Документ12 страницGrade 9 Sept Test 2023.mapulacatherine33Оценок пока нет
- Moment of InertiaДокумент10 страницMoment of InertiasenthilcaeОценок пока нет
- Angles, parallel lines, and geometric relationships guideДокумент13 страницAngles, parallel lines, and geometric relationships guideGodisGood AlltheTimeОценок пока нет
- Department of Mathematics: Indian Institute of Technology, BombayДокумент16 страницDepartment of Mathematics: Indian Institute of Technology, BombayMridul ChhipaОценок пока нет
- CevaДокумент3 страницыCevaChuotcon TrầnОценок пока нет
- A4 Tracing Book TEMPLATE COVER AND PAGESДокумент51 страницаA4 Tracing Book TEMPLATE COVER AND PAGESangelinemaelagua04Оценок пока нет
- MATRIX AND DETERMINANTS ONE MARK QUESTIONSДокумент21 страницаMATRIX AND DETERMINANTS ONE MARK QUESTIONSSu SiОценок пока нет
- Review in TrigoДокумент5 страницReview in TrigoJohnMichaelM.ManaloОценок пока нет
- Trigonometry Identities and ConceptsДокумент93 страницыTrigonometry Identities and ConceptsKayzel Joyce De RoxasОценок пока нет
- Find the Radius of a Circle Given Tangent LengthsДокумент2 страницыFind the Radius of a Circle Given Tangent LengthspiyushОценок пока нет
- 50 Counting Figures Practice Questions: For Bank, SSC, Railway & Government ExamsДокумент26 страниц50 Counting Figures Practice Questions: For Bank, SSC, Railway & Government ExamsDoddy FeryantoОценок пока нет
- USA Mathematical Talent Search Solutions To Problem 5/2/19Документ4 страницыUSA Mathematical Talent Search Solutions To Problem 5/2/19ArsyОценок пока нет
- Autolisp ProgramsДокумент43 страницыAutolisp ProgramsAmit MishraОценок пока нет
- Spheres and HemispheresДокумент6 страницSpheres and HemispherescapableconsultantsОценок пока нет
- 06 - Trigonometric Identities - 15Документ15 страниц06 - Trigonometric Identities - 15Shah RukhОценок пока нет
- Cbiemasu 04Документ5 страницCbiemasu 04Shalini MishraОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9 Solid GeometryДокумент12 страницChapter 9 Solid GeometryNur Fatihah Abdullah Eno100% (1)
- 13 Triangle ConstructionsДокумент6 страниц13 Triangle ConstructionsAnwar HossainОценок пока нет
- Aces Review Center: Ree Online Review Refresher Math 7 by Engr. Jimmy L. Ocampo 0920 - 644 - 6246Документ6 страницAces Review Center: Ree Online Review Refresher Math 7 by Engr. Jimmy L. Ocampo 0920 - 644 - 6246Jr TrinidadОценок пока нет