Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Experiment 6: Objective
Загружено:
djun033Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Experiment 6: Objective
Загружено:
djun033Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Experiment 6
Objective
Flip- Flops
-To become familiar with the input/output characteristics of several types of standard flip-flop devices and the conversion among them.
References
Donald P.Leach : Experimental in Digital Principles, 3rd Edition Malvino/Leach : Digital Principles and Applications Bartee : Digital Computer Fundamentals, 6th Edition John F.Wakerley : Digital Designs , Principle and Practice, 2nd Edition Ronald A Reis : Digital Electronics Through Project Analysis, 1st Edition
Component
1-74LS00 TTL IC 1-74LS74 TTL IC 1-74LS76 TTL IC
Introduction
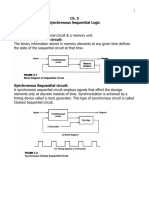
Logic circuit whose outputs depend upon circuit inputs as well as previous values of circuit outputs described as their present states are known as sequential logic circuits. A sequential system can be defined in terms of its inputs and present state. That is, the next state of the sequential system can be determined from these two quantities. The (clocked) RS, D, JK and T flip-flops are characterized by the following state tables.
SNI
11/17/2003
The ? in the RS flip-flop state table means that when R = 1 and S = 1 then the next state is not determined explicitly.
Procedure
1) Construct the cross-coupled NAND gate basic RS flip-flop depicted in fig 1 and verify its sequential operation by completing the timing diagram shown in fig 2.
Fig 1 : Basic RS flip flop
SNI
11/17/2003
R t S t Q t Q t Fig 2 : Timing Diagram
2) Construct the clocked RS flip flop of fig 3. Determine its state table. Use monostable circuit as your clock source.
Fig 3 : Clocked RS flip-flop
3) Simultaneously application of ones to R and S of the clocked RS flip flop, observe the outputs. 4) Since the constructed clocked RS flip flop is symmetric, we can change the position of R & S, and Q and Q. It is still a clocked RS flip flop.Repeat step 3, see what has happened. Give your conclusion.
SNI
11/17/2003
5) Using the 74LS74 dual D flip flop, investigate the operation of the D flip-flop (see fig 4). Compare your result with the state table given above.Pay attention to the change in state of the device as the clock signal is rising or falling. Compare the following timing diagram.
Fig 4 : D Flip Flop
Assume when t=0 , Q=0
CLK t D t Q t
Fig 5 : Timing Diagram
6) Let input R open, ground the input S, watch the output and then let S open, ground R, watch the output. Determine the usage of R and
SNI
11/17/2003
S.
7) Using the 74LS76 dual JK flip flop, determine its logical operation. The circuit diagram is shown in fig 6 . Pay attention to the change in state of the device as the clock signal is rising or falling. Compare the following timing diagram.
Fig 6 : JK Flip flop
assume when t=0 , y=0
CLK t K t J t Y t Fig 7 : Timing diagram
SNI
11/17/2003
8) The flip flop can simulate each other. Construct the circuit shown in fig 8. Verify its sequential operation as a D flip flop. Complete the following timing diagram. Compare it with the timing diagram of fig 5.
Fig 8 : D flip flop ( constructed by JK FF)
assume when t=0 , Q=0
CLK t D t Q t
Fig 9 : Timing Diagram
SNI
11/17/2003
9) Wiring the circuit shown in fig 10, verify that it is a T flip flop
Fig 10 : T flip flop
SNI
11/17/2003
SNI
11/17/2003
SNI
11/17/2003
Вам также может понравиться
- Digital Electronics 2: Sequential and Arithmetic Logic CircuitsОт EverandDigital Electronics 2: Sequential and Arithmetic Logic CircuitsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- ExptДокумент7 страницExptM SHOAIB KHALIDОценок пока нет
- Advanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkОт EverandAdvanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkОценок пока нет
- Part A: Flip Flops: Sequential CircuitsДокумент18 страницPart A: Flip Flops: Sequential CircuitssuriantoОценок пока нет
- Lab 11 Digital JK FlipflopДокумент5 страницLab 11 Digital JK Flipflopzk7766100% (1)
- CounterДокумент22 страницыCounterMahesh MahiОценок пока нет
- Flip Flop Mealy and Moore ModelДокумент25 страницFlip Flop Mealy and Moore Modelsurajpb1989100% (1)
- Digital Design On Digital Works.Документ25 страницDigital Design On Digital Works.nileshchaurasiaОценок пока нет
- Lab 8 - LatchesДокумент5 страницLab 8 - LatchesSiegrique Ceasar A. JalwinОценок пока нет
- Report 1 (D2, Digital)Документ10 страницReport 1 (D2, Digital)Kian YingОценок пока нет
- Lecture 7: Memory: DOC112: Computer Hardware Lecture 7 1Документ4 страницыLecture 7: Memory: DOC112: Computer Hardware Lecture 7 1Taqi Shah0% (1)
- Digital LabДокумент51 страницаDigital LabBala SubramanianОценок пока нет
- Experiment 9 (Flip Flops)Документ7 страницExperiment 9 (Flip Flops)groupidb3100% (3)
- Lecture 7: Memory: DOC112: Computer Hardware Lecture 7 1Документ4 страницыLecture 7: Memory: DOC112: Computer Hardware Lecture 7 1rinobiОценок пока нет
- Synthesis of A Traffic Light Sequence CircuitДокумент19 страницSynthesis of A Traffic Light Sequence CircuitDino LigutanОценок пока нет
- Experiment 5 Monsoon, 2008 Latches and Flip-Flops: Digital Logic & ProcessorДокумент2 страницыExperiment 5 Monsoon, 2008 Latches and Flip-Flops: Digital Logic & ProcessorUtkar ShОценок пока нет
- Sequential CircuitsДокумент22 страницыSequential CircuitsBaeОценок пока нет
- The Clocked RS Flip-FlopДокумент4 страницыThe Clocked RS Flip-Flopabhisheksikka17Оценок пока нет
- Sample Questions - 3&4Документ2 страницыSample Questions - 3&4stevesequeira12Оценок пока нет
- DLC Unit 3 Part A - Q&aДокумент8 страницDLC Unit 3 Part A - Q&aVigneswaran VigneshОценок пока нет
- DSD-Unit 3Документ1 страницаDSD-Unit 3KeertanaОценок пока нет
- Java NotesДокумент37 страницJava NotesSandeep Kumar mehtaОценок пока нет
- Unit-1 - Digital ElectronicsДокумент50 страницUnit-1 - Digital ElectronicsVignesh VigneshОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 - Introduction To Sequential DevicesДокумент62 страницыChapter 6 - Introduction To Sequential DevicesSarath Chandra SОценок пока нет
- LogicDesign CHPT 10Документ31 страницаLogicDesign CHPT 10john juanОценок пока нет
- 4205+Course+Ch 5Документ19 страниц4205+Course+Ch 5RutaiaОценок пока нет
- Notes 326 Set8Документ16 страницNotes 326 Set8Bakshi AmitОценок пока нет
- Lab Session # 7 Flip-Flops: Figure 1: Block Diagram of A Sequential CircuitДокумент9 страницLab Session # 7 Flip-Flops: Figure 1: Block Diagram of A Sequential CircuitAhmad M. HammadОценок пока нет
- Expt08 - Latch, Flip-Flop and Ripple CounterДокумент2 страницыExpt08 - Latch, Flip-Flop and Ripple CounterRutvik NukalaОценок пока нет
- UNIT1Документ37 страницUNIT1Azliana Mohd Taib0% (1)
- Digital Electronics ProblemsДокумент3 страницыDigital Electronics Problemschintu333Оценок пока нет
- Latches and Flip-Flops: Experiment E10Документ9 страницLatches and Flip-Flops: Experiment E10Resy ApolinarioОценок пока нет
- Sequential CircuitsДокумент53 страницыSequential CircuitsbrsreddyОценок пока нет
- DIGITALASSIGN#2Документ4 страницыDIGITALASSIGN#2Dr-Tarun ParasharОценок пока нет
- Unit 5 Sequential CircuitДокумент21 страницаUnit 5 Sequential CircuitAnurag GoelОценок пока нет
- Assignment EDES232CДокумент3 страницыAssignment EDES232CPrakash DasОценок пока нет
- D Flip-FlopДокумент35 страницD Flip-FlopSwati Kasht100% (1)
- Flip FlopsДокумент11 страницFlip FlopsZakaria JubarnОценок пока нет
- Experiment 1 SALAZARДокумент8 страницExperiment 1 SALAZARgerand salazarОценок пока нет
- Chp1 - Latches and Flip-FlopsДокумент44 страницыChp1 - Latches and Flip-FlopsAbnen OngОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Flip Flop-ROBIAHДокумент50 страницChapter 4 Flip Flop-ROBIAHKelvin YipОценок пока нет
- Flip FlopДокумент5 страницFlip Flopwala alabedОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Flip Flop-ROBIAHДокумент50 страницChapter 4 Flip Flop-ROBIAHIqmal Shah Putra50% (2)
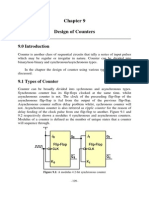
- Counters DesignДокумент12 страницCounters DesignSuresh Bharath100% (1)
- Expt 12Документ5 страницExpt 12Dhrrishith VikalОценок пока нет
- DE Module 03Документ20 страницDE Module 03Rishabh TiwariОценок пока нет
- Project ReportДокумент11 страницProject Reportamiethurgat100% (2)
- Digital Design ExamplesДокумент29 страницDigital Design ExampleshumnaharoonОценок пока нет
- Digital Electronics 8Документ12 страницDigital Electronics 8Tapas BanerjeeОценок пока нет
- Arithmetic and Logic (Cont) : 2.3 Build Sequential Logic CircuitДокумент22 страницыArithmetic and Logic (Cont) : 2.3 Build Sequential Logic CircuitBadrul Afif ImranОценок пока нет
- D and JK FFДокумент22 страницыD and JK FFRawan AyyoubОценок пока нет
- Unit 3Документ24 страницыUnit 3Raja BenitaОценок пока нет
- Dflipfop Easy Problem Marvin JavierДокумент9 страницDflipfop Easy Problem Marvin JavierAngelica FangonОценок пока нет
- Synchronous Sequential LogicДокумент18 страницSynchronous Sequential LogicDucnguyenОценок пока нет
- DS - Expt 10Документ6 страницDS - Expt 10Aditya SalunkheОценок пока нет
- SN1-2223-Lab3 1-2 EngДокумент4 страницыSN1-2223-Lab3 1-2 EngBoualem MestafaОценок пока нет
- JK Flip Flop Experiment 9Документ5 страницJK Flip Flop Experiment 9Nev Callejo50% (2)
- Flip-Flop Electronics) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopedДокумент16 страницFlip-Flop Electronics) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopednatcutОценок пока нет
- Complete Power SupplyДокумент13 страницComplete Power Supplydjun033Оценок пока нет
- Am Quiz 2Документ1 страницаAm Quiz 2djun033Оценок пока нет
- MCQ Midter 2Документ2 страницыMCQ Midter 2djun033Оценок пока нет
- MMДокумент2 страницыMMdjun033Оценок пока нет
- PART A (50 PTS) Submit in Class.: ECE 502 Quiz 2Документ1 страницаPART A (50 PTS) Submit in Class.: ECE 502 Quiz 2djun033Оценок пока нет
- Probset 13Документ1 страницаProbset 13djun033Оценок пока нет
- Qi Midterms PrincommДокумент1 страницаQi Midterms Princommdjun033Оценок пока нет
- Qi Midterms PrincommДокумент1 страницаQi Midterms Princommdjun033Оценок пока нет
- Lecture NoteДокумент12 страницLecture Notedjun033Оценок пока нет
- Miller ch03Документ28 страницMiller ch03Vipul TyagiОценок пока нет
- Solution QuizДокумент3 страницыSolution Quizdjun033Оценок пока нет
- Find Also The Am Voltage Equation For #5 and #6Документ1 страницаFind Also The Am Voltage Equation For #5 and #6djun033Оценок пока нет
- VisitДокумент20 страницVisitdjun033Оценок пока нет
- Take HomeДокумент2 страницыTake Homedjun033Оценок пока нет
- Activity 1Документ1 страницаActivity 1djun033Оценок пока нет
- MCQДокумент1 страницаMCQdjun033Оценок пока нет
- Quiz1 PcomДокумент1 страницаQuiz1 Pcomdjun033Оценок пока нет
- Radio Wave AssignmentДокумент1 страницаRadio Wave Assignmentdjun033Оценок пока нет
- MMDDДокумент2 страницыMMDDdjun033Оценок пока нет
- Quiz1 PcomДокумент1 страницаQuiz1 Pcomdjun033Оценок пока нет
- Activity TemplateДокумент1 страницаActivity Templatedjun033Оценок пока нет
- Assignment 1Документ1 страницаAssignment 1djun033Оценок пока нет
- Assignment 2Документ5 страницAssignment 2djun033Оценок пока нет
- Final Project Grade: Logic Circuits and Switching Theory Final Project Guidelines Target CosДокумент3 страницыFinal Project Grade: Logic Circuits and Switching Theory Final Project Guidelines Target Cosdjun033Оценок пока нет
- Basic Logic Gates Experiment 2Документ1 страницаBasic Logic Gates Experiment 2djun033Оценок пока нет
- Clampers PDFДокумент1 страницаClampers PDFdjun033Оценок пока нет
- Technological Institute of The Philippines: JK Flip Flop and ApplicationДокумент3 страницыTechnological Institute of The Philippines: JK Flip Flop and ApplicationBernabeth PlancoОценок пока нет
- Resistor-Diode-Transistor Logic Experiment No.1 Data and ResultsДокумент4 страницыResistor-Diode-Transistor Logic Experiment No.1 Data and Resultsdjun033Оценок пока нет
- Basic Logic Gates Experiment 2Документ1 страницаBasic Logic Gates Experiment 2djun033Оценок пока нет
- PRELIM EXAM - Solution CPE 004: PART II. Find The Radix RДокумент5 страницPRELIM EXAM - Solution CPE 004: PART II. Find The Radix Rdjun033Оценок пока нет
- Argillon Insulators EnglishДокумент8 страницArgillon Insulators EnglishHillary McgowanОценок пока нет
- Power Distribution Systems and Its Characteristics IДокумент16 страницPower Distribution Systems and Its Characteristics IMohammedSaadaniHassani100% (1)
- Manual Allem BradleyДокумент212 страницManual Allem BradleyKaaberОценок пока нет
- QuadCopter FlightДокумент60 страницQuadCopter Flightasso2412100% (1)
- Reference Guide To Fiber Optic Testing: Second EditionДокумент172 страницыReference Guide To Fiber Optic Testing: Second EditionJoao Silva100% (1)
- Is.10118.3.1982 0 PDFДокумент33 страницыIs.10118.3.1982 0 PDFBhalsingh JangraОценок пока нет
- PSS Lab Manual - 18EEL76Документ60 страницPSS Lab Manual - 18EEL76Rohan J EEE-2019-23100% (1)
- User Manual For Wireless Controller HAMA SCORPAD 00051838 PS3Документ3 страницыUser Manual For Wireless Controller HAMA SCORPAD 00051838 PS3Victor GheorgheОценок пока нет
- Publison InfernalДокумент2 страницыPublison InfernalShane SandersОценок пока нет
- FC22 Bundle Transport For RadimatДокумент40 страницFC22 Bundle Transport For Radimatpk cfctkОценок пока нет
- Green Mode Power Switch FSDH321, FSDL321: DescriptionДокумент16 страницGreen Mode Power Switch FSDH321, FSDL321: DescriptionJosue Rafael BorjasОценок пока нет
- J1939 Datalink CommunicationДокумент16 страницJ1939 Datalink CommunicationNgoc Nguyen100% (1)
- Ieee STD 1547Документ19 страницIeee STD 1547Hoang Tran The100% (1)
- RDE10.1 Datasheet enДокумент8 страницRDE10.1 Datasheet enReparatii CncОценок пока нет
- Product Specifications: CharacteristicsДокумент3 страницыProduct Specifications: Characteristicseslam salmonyОценок пока нет
- ConneXium TCSESM Installation Manual V6Документ36 страницConneXium TCSESM Installation Manual V6Vinicius Mello AlmeidaОценок пока нет
- Manual Instalacion RTUДокумент25 страницManual Instalacion RTUlmbkn2013Оценок пока нет
- LPWAN Research PaperДокумент17 страницLPWAN Research PaperthijsОценок пока нет
- High Voltage CoilsДокумент20 страницHigh Voltage CoilsMarco SussuaranaОценок пока нет
- NE556 Linear Integrated Circuit: Dual TimerДокумент4 страницыNE556 Linear Integrated Circuit: Dual TimerJim LiebОценок пока нет
- CAT ParalelingДокумент68 страницCAT ParalelingGabriel Paco LunaОценок пока нет
- Plugs and Sockets PosterДокумент1 страницаPlugs and Sockets PostersybonОценок пока нет
- Scully ST-47C Groundhog Technical ManualДокумент32 страницыScully ST-47C Groundhog Technical ManualOscar Moreno100% (1)
- Profile of HTGD EPCДокумент31 страницаProfile of HTGD EPCAgung RahinoОценок пока нет
- Model BETA 87A User Guide: Application and PlacementДокумент12 страницModel BETA 87A User Guide: Application and PlacementMHEP_DANIELОценок пока нет
- DAF CF65/75/85 Series 0E621376Документ712 страницDAF CF65/75/85 Series 0E621376Dan Birkenhead95% (21)
- PLC Report TimerДокумент5 страницPLC Report TimersadmanОценок пока нет
- Neuron II Elgi CompressorДокумент42 страницыNeuron II Elgi CompressorOswaldo69% (16)
- Module 1Документ121 страницаModule 1Soniya KadamОценок пока нет
- Osiprox - Inductive Proximity Sensors Catalogue 2004.06 PDFДокумент14 страницOsiprox - Inductive Proximity Sensors Catalogue 2004.06 PDFSarah RichardОценок пока нет
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyОт EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (227)
- Chip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyОт EverandChip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (82)
- iPhone 14 Guide for Seniors: Unlocking Seamless Simplicity for the Golden Generation with Step-by-Step ScreenshotsОт EverandiPhone 14 Guide for Seniors: Unlocking Seamless Simplicity for the Golden Generation with Step-by-Step ScreenshotsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102От EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- CompTIA Security+ All-in-One Exam Guide, Sixth Edition (Exam SY0-601)От EverandCompTIA Security+ All-in-One Exam Guide, Sixth Edition (Exam SY0-601)Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- iPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]От EverandiPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- iPhone X Hacks, Tips and Tricks: Discover 101 Awesome Tips and Tricks for iPhone XS, XS Max and iPhone XОт EverandiPhone X Hacks, Tips and Tricks: Discover 101 Awesome Tips and Tricks for iPhone XS, XS Max and iPhone XРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (2)
- How to Jailbreak Roku: Unlock Roku, Roku Stick, Roku Ultra, Roku Express, Roku TV with Kodi Step by Step GuideОт EverandHow to Jailbreak Roku: Unlock Roku, Roku Stick, Roku Ultra, Roku Express, Roku TV with Kodi Step by Step GuideРейтинг: 1 из 5 звезд1/5 (1)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam Core 1 220-1001 and Exam Core 2 220-1002От EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam Core 1 220-1001 and Exam Core 2 220-1002Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Interview Questions and AnswersОт EverandAmazon Web Services (AWS) Interview Questions and AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- Programming with STM32: Getting Started with the Nucleo Board and C/C++От EverandProgramming with STM32: Getting Started with the Nucleo Board and C/C++Рейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (3)
- Hacking With Linux 2020:A Complete Beginners Guide to the World of Hacking Using Linux - Explore the Methods and Tools of Ethical Hacking with LinuxОт EverandHacking With Linux 2020:A Complete Beginners Guide to the World of Hacking Using Linux - Explore the Methods and Tools of Ethical Hacking with LinuxОценок пока нет
- iWoz: How I Invented the Personal Computer and Had Fun Along the WayОт EverandiWoz: How I Invented the Personal Computer and Had Fun Along the WayРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (317)
- Mastering IoT For Industrial Environments: Unlock the IoT Landscape for Industrial Environments with Industry 4.0, Covering Architecture, Protocols like MQTT, and Advancements with ESP-IDFОт EverandMastering IoT For Industrial Environments: Unlock the IoT Landscape for Industrial Environments with Industry 4.0, Covering Architecture, Protocols like MQTT, and Advancements with ESP-IDFОценок пока нет
- Windows 10 Mastery: The Complete User Guide to Learn Windows 10 from Beginner to ExpertОт EverandWindows 10 Mastery: The Complete User Guide to Learn Windows 10 from Beginner to ExpertРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (6)
- Amazon Echo Manual Guide : Top 30 Hacks And Secrets To Master Amazon Echo & Alexa For Beginners: The Blokehead Success SeriesОт EverandAmazon Echo Manual Guide : Top 30 Hacks And Secrets To Master Amazon Echo & Alexa For Beginners: The Blokehead Success SeriesОценок пока нет





























































































































![iPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/audiobook_square_badge/728318688/198x198/f3385cbfef/1714829744?v=1)