Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Fruit Seed Dispersal
Загружено:
Lim Kew ChongАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Fruit Seed Dispersal
Загружено:
Lim Kew ChongАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Name:
Class:
Fruit and Seed Dispersal
Investigation 13.1 To examine wind-dispersed fruits and seeds
Procedure
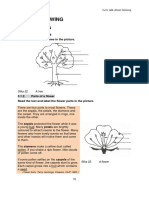
1. Make a large, labelled drawing of the fruits provided in the space below.
Angsana fruit Magnification = X
Shorea fruit (if available) Magnification = X
Tridex fruit Magnification = X
2.
(a)
State the common features of the fruits that make them suitable for wind dispersal.
(b)
What functions do these features play in dispersal?
(c)
State which part of the fruit and how it is modified to serve such functions:
Angsana Tridex Shorea
3.
.c.
Make a large, labelled drawing of the seeds provided.
Seed of Tecoma or African tulip Magnification = X
Lagerstroemia seed Magnification = X
4.
How are the seeds modified for wind dispersal?
5.
State 2 reasons for the dispersal of seeds.
(a) (b)
Name:
Class:
Investigation 13.2
To examine seeds dispersed by explosive mechanism
Procedure
1. Make a large, labelled drawing of the legume of Clitoria.
Legume of Clitoria (T.S.) Magnification = X
2.
Cut the long bean transversely in the region of the seed. You may need to cut a few times until you can see the whole seed with its stalk attached to the fruit. Make a large, labelled drawing of the cut surface.
Legume of long bean (T.S.) Magnification = X
3.
What would you consider to be the method of dispersal of the seeds of the legume you have drawn?
4.
What features of the legume of Clitoria make it suitable for this method of dispersal?
5.
Split a peanut fruit in half along its length. Remove one seed. Split the seed into its natural halves. Replace one half of the seed still with the plumule and radicle attached into the fruit. Make a large, labelled drawing of half the fruit (sectional view).
Sectional view of a peanut fruit
Questions
1. What is the main food substance stored in the peanut seed?
2.
List the functions of this food substance in the seed?
Name:
Class:
Investigation 13.3
To examine fruits and seeds dispersed by animals (I)
Procedure
1. Make a large, labelled drawing of the fruits provided in the spaces below.
T.S. of tomato Magnification = X
L.S. of tomato Magnification = X
T.S. of cucumber Magnification = X
T.S. of orangellime Magnification = X
2.
How are the seeds in the specimens you have drawn dispersed by animals?
3.
What features of the specimens indicate the method of dispersal?
4.
What features indicate that they are fruits?
5.
Cut the banana fruit transversely. Cover the cut surface with iodine solution and leave this aside for 5 minutes. Use the other cut surface and make a large, labelled drawing of it.
T.S. of banana fruit Magnification = X
6.
After at least 5 minutes examine the effect of the iodine solution on the cut surface of the banana fruit. Draw a sketch (not a detailed drawing) to show the effect of iodine (i.e., the distribution of colour) on the fruit.
Sketch of T.S. of banana fruit to show colour distribution
7.
Describe the effects of the iodine solution (i.e. the distribution of colour) on the cut surface of the banana fruit and say what this indicates.
8.
Investigation 4.3 shows that the banana fruit contains reducing sugars. How do the starch test and Benedict's test help you to understand the usefulness of banana fruit to Man?
Name:
Class:
Investigation 13.4
To examine fruits dispersed by animals (III
Procedure
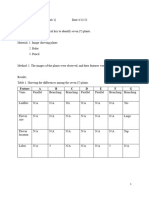
1. Make a large drawing of each of the fruits provided.
Spear grass/love grass Magnification = X
Urena fruit Magnification
=X
2.
How do you think the fruits are dispersed?
3.
In Investigations 13.3 and 13.4, we studied two groups of fruits.
(a)
How are these two groups alike?
(b)
How are they different?
Вам также может понравиться
- Fruit and Seed Dissection LABДокумент3 страницыFruit and Seed Dissection LABCatherine JacksonОценок пока нет
- Science Fruit AdaptationsДокумент3 страницыScience Fruit Adaptationsapi-279826698Оценок пока нет
- Worksheet No. 12 - Angiosperm FruitsДокумент6 страницWorksheet No. 12 - Angiosperm FruitsRACHELLE DEMATERAОценок пока нет
- Env107l 6Документ12 страницEnv107l 6Jwc Fest2018Оценок пока нет
- Kwanza Bondar - 2020 Seed Germination Experiment Lab ReportДокумент3 страницыKwanza Bondar - 2020 Seed Germination Experiment Lab Reportapi-524255053Оценок пока нет
- Effect of Light and Water on Mung Bean GrowthДокумент21 страницаEffect of Light and Water on Mung Bean GrowthBaymax EatShowОценок пока нет
- ASESLE1 Teacher Made TestДокумент8 страницASESLE1 Teacher Made TestAlyana ContyОценок пока нет
- Plant Parts Lesson Plan 3rd GradeДокумент2 страницыPlant Parts Lesson Plan 3rd GradeROSARIO BARRIONОценок пока нет
- Bal Vaigyanik Class-6Документ143 страницыBal Vaigyanik Class-6sagonОценок пока нет
- The Story The Story of The Mouse With The (7 Tails)Документ6 страницThe Story The Story of The Mouse With The (7 Tails)YAn T. PaczОценок пока нет
- Fruits and Seeds ImradДокумент8 страницFruits and Seeds ImradJoses CalindasОценок пока нет
- Plants SurvivalДокумент27 страницPlants SurvivalChris TeoОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan Sir MarcosДокумент7 страницLesson Plan Sir MarcosJhon AgustinОценок пока нет
- Pineapple Micropropagation Lab Demonstrates Effective Vegetative PropagationДокумент5 страницPineapple Micropropagation Lab Demonstrates Effective Vegetative PropagationBobby AnoraОценок пока нет
- 12 Biology EMДокумент121 страница12 Biology EMSundara MoorthyОценок пока нет
- Fruit Types and StructuresДокумент8 страницFruit Types and StructuresUbaid Khan0% (1)
- Laboratory Manual Of Horticulture - With Illustrations Of Methods, Equipment, And ApparatusОт EverandLaboratory Manual Of Horticulture - With Illustrations Of Methods, Equipment, And ApparatusОценок пока нет
- Plant Unit TestДокумент4 страницыPlant Unit Testsmily_face15Оценок пока нет
- 2 Sem Unit Test-Exam AssihnmentДокумент3 страницы2 Sem Unit Test-Exam Assihnmentapi-233604231Оценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan in Science 3 - EscrimadoraДокумент8 страницLesson Plan in Science 3 - EscrimadoraMar Jen100% (1)
- Propagating Trees and Fruit-Bearing PlantsДокумент31 страницаPropagating Trees and Fruit-Bearing PlantsJC IsnainОценок пока нет
- Effect of citrus fruits on fruit fliesДокумент17 страницEffect of citrus fruits on fruit fliesAngelica Magdaraog0% (1)
- Fruit Dissection For SeedsДокумент4 страницыFruit Dissection For Seedsapi-248121250Оценок пока нет
- 2ND Term S3 BiologyДокумент25 страниц2ND Term S3 BiologyFGGC MINJIBIRОценок пока нет
- Bio100a Homework 2Документ11 страницBio100a Homework 2lucasaiu9409100% (1)
- CBSE Class 10 Science Lab Manual - StomataДокумент7 страницCBSE Class 10 Science Lab Manual - StomataSumit BissuОценок пока нет
- November Fruits Activity GuideДокумент2 страницыNovember Fruits Activity GuideMagali MadariagaОценок пока нет
- Plant Structures Quiz - Answer KeyДокумент2 страницыPlant Structures Quiz - Answer Keyapi-254428474Оценок пока нет
- TLE6 - AGRICULTURE - Q3 - Module1 (15pages)Документ15 страницTLE6 - AGRICULTURE - Q3 - Module1 (15pages)Jinky Gonzales GuevarraОценок пока нет
- Work - Book 2Документ14 страницWork - Book 2blonde hair jkОценок пока нет
- Grade 11 Biology (Lab 18 - Investigative Proposal Part B The IMPLEMENTATION)Документ12 страницGrade 11 Biology (Lab 18 - Investigative Proposal Part B The IMPLEMENTATION)Ravin BoodhanОценок пока нет
- BIOLO001plants Parts and Function EditedДокумент18 страницBIOLO001plants Parts and Function EditedChristine angel mae BalsomoОценок пока нет
- 5 Aye Aye Thwe 1Документ11 страниц5 Aye Aye Thwe 1Kyaw Thu WinОценок пока нет
- Reproduction in PlantsДокумент10 страницReproduction in PlantsTIMEOFFICE KHARAGPURWORKSHOPОценок пока нет
- Fruit Growing 3.1. Fruit Trees: 3.1.1. Parts of A Tree Label The Parts of The Tree in The PictureДокумент8 страницFruit Growing 3.1. Fruit Trees: 3.1.1. Parts of A Tree Label The Parts of The Tree in The Pictureanggraini syaffitriОценок пока нет
- DNA Extraction Laboratory CompleteДокумент5 страницDNA Extraction Laboratory CompleteFrederick LoganОценок пока нет
- Biology Lab TemplateДокумент53 страницыBiology Lab TemplateTmickeltОценок пока нет
- Fruit Lab Fruit 2021Документ3 страницыFruit Lab Fruit 2021firsr goblОценок пока нет
- 1 Grade Plant Parts We EatДокумент4 страницы1 Grade Plant Parts We EatelwakilshaimaaОценок пока нет
- Roots and Stems and Leaves, Oh My!: TeksДокумент10 страницRoots and Stems and Leaves, Oh My!: TeksagapolusОценок пока нет
- Intro To Ecology and Plants TestДокумент5 страницIntro To Ecology and Plants Testapi-316047658Оценок пока нет
- PRACTICAL MODULE ONLY 60320 - Unit 3Документ5 страницPRACTICAL MODULE ONLY 60320 - Unit 3Cemerlang StudiОценок пока нет
- Cactus Jam 3MAДокумент17 страницCactus Jam 3MALK0% (1)
- Incomplete Ip PresentationДокумент25 страницIncomplete Ip PresentationGio Lorenzo Cadhit100% (1)
- 2nd Harvesting SeedsДокумент4 страницы2nd Harvesting Seedsapi-234861317Оценок пока нет
- Tle-Acp: Quarter 2 - Module 4 Interpret Plans and DrawingsДокумент18 страницTle-Acp: Quarter 2 - Module 4 Interpret Plans and DrawingsLester John Catapang100% (1)
- Natural Selection Foraging UneditedДокумент6 страницNatural Selection Foraging Uneditedvioly villegasОценок пока нет
- Seed Germination Experiment Lab ReportДокумент2 страницыSeed Germination Experiment Lab Reportapi-524483093Оценок пока нет
- Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and SeedsДокумент5 страницAngiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and SeedsAurora ÇizmjaОценок пока нет
- TLE6 Module5 Propagating Tress and Fruit-Bearing TreesДокумент29 страницTLE6 Module5 Propagating Tress and Fruit-Bearing TreesLorranne Maice D. Morano100% (1)
- Unit Ii-Week 7 Lesson 31: Modes Of: Reproduction of Flowering PlantsДокумент76 страницUnit Ii-Week 7 Lesson 31: Modes Of: Reproduction of Flowering PlantsLendel Mariz O. CepilloОценок пока нет
- Speight - Around The WorldДокумент23 страницыSpeight - Around The Worldapi-314126047Оценок пока нет
- Factors Affecting Plant GrowthДокумент5 страницFactors Affecting Plant GrowthBreckenwood100% (1)
- FUN SCIENCE 2: Reproduction of Non-Flowering Plants: A. ProceduresДокумент4 страницыFUN SCIENCE 2: Reproduction of Non-Flowering Plants: A. ProceduresSaldi Xaldz VitorilloОценок пока нет
- TLE Q2 W3 Online PresentationДокумент19 страницTLE Q2 W3 Online PresentationJean Paula SequiñoОценок пока нет
- Dna Extraction of Strawberries Lab Sheets Spring 2016 No RubricДокумент6 страницDna Extraction of Strawberries Lab Sheets Spring 2016 No Rubricapi-298247873Оценок пока нет
- Tle Agri 6 Week 3 Day 1 4Документ81 страницаTle Agri 6 Week 3 Day 1 4esmeralda.quezadaОценок пока нет
- Q.1 Multiple Choice Questions. 10x1Документ5 страницQ.1 Multiple Choice Questions. 10x1chhavi bhatnagarОценок пока нет
- P-5 Unit 1Документ18 страницP-5 Unit 1Complete International Education ServiceОценок пока нет
- Affect of Detergent On Seed Germination LabДокумент5 страницAffect of Detergent On Seed Germination LabStefanie Loya WardОценок пока нет
- CamScanner Document TitleДокумент1 страницаCamScanner Document TitleLim Kew ChongОценок пока нет
- A Dedication-Prayer for the Mani Mantra that Brings Swift Realisation of Perfect BlissДокумент121 страницаA Dedication-Prayer for the Mani Mantra that Brings Swift Realisation of Perfect BlissLim Kew Chong100% (2)
- The Kinetic Model of Matter-Work Sheet AnswerДокумент3 страницыThe Kinetic Model of Matter-Work Sheet AnswerLim Kew ChongОценок пока нет
- Organic ChemistryДокумент37 страницOrganic ChemistryLim Kew ChongОценок пока нет
- Free Body Diagram AnswersДокумент4 страницыFree Body Diagram AnswersLim Kew ChongОценок пока нет
- Experience of SunyataДокумент5 страницExperience of SunyataLim Kew ChongОценок пока нет
- 4e3 A Maths Prelim Exam Paper 1Документ3 страницы4e3 A Maths Prelim Exam Paper 1ahmedzaki1234Оценок пока нет
- 2E Chemistry June Holiday HWДокумент4 страницы2E Chemistry June Holiday HWLim Kew ChongОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Matters Workbook Chapter 2 Experimental Chemistry AnswersДокумент2 страницыChemistry Matters Workbook Chapter 2 Experimental Chemistry AnswersLim Kew Chong83% (6)
- 1NT Finals 2006Документ10 страниц1NT Finals 2006Lim Kew ChongОценок пока нет
- Light Offering Prayer by AtishaДокумент3 страницыLight Offering Prayer by AtishanyomchenОценок пока нет
- Liberation WДокумент1 страницаLiberation WLim Kew ChongОценок пока нет
- The Kinetic Model of Matter-Work Sheet AnswerДокумент3 страницыThe Kinetic Model of Matter-Work Sheet AnswerLim Kew ChongОценок пока нет
- DHE Prayer of AspirationДокумент1 страницаDHE Prayer of AspirationLim Kew ChongОценок пока нет
- 3NA Common Test 1Документ5 страниц3NA Common Test 1Lim Kew ChongОценок пока нет
- Lu May Kön Chok Sum Gyi Ngo Wo Nyi: Prayer To Dudjom LingpaДокумент11 страницLu May Kön Chok Sum Gyi Ngo Wo Nyi: Prayer To Dudjom LingpaLim Kew ChongОценок пока нет
- 2011 Admiralty Sec SCH Final Exam Sec 2 Paper 2Документ14 страниц2011 Admiralty Sec SCH Final Exam Sec 2 Paper 2Lim Kew ChongОценок пока нет
- I Pray To Buddha AmitabhaДокумент1 страницаI Pray To Buddha AmitabhaLim Kew ChongОценок пока нет
- Exp FansДокумент4 страницыExp FansLim Kew ChongОценок пока нет
- The Manjushri PrayerДокумент3 страницыThe Manjushri PrayerEricson ChewОценок пока нет
- The Lama PrayerДокумент1 страницаThe Lama PrayerLim Kew ChongОценок пока нет
- 1 Exp SCДокумент20 страниц1 Exp SCLim Kew ChongОценок пока нет
- 3E Add Math SOWДокумент2 страницы3E Add Math SOWLim Kew ChongОценок пока нет
- 3na Add Math SowДокумент3 страницы3na Add Math SowLim Kew ChongОценок пока нет
- Second Semester Examination 2006 Secondary 1 Express: East Spring Secondary SchoolДокумент23 страницыSecond Semester Examination 2006 Secondary 1 Express: East Spring Secondary SchoolLim Kew ChongОценок пока нет
- 5129 w11 QP 22 PDFДокумент20 страниц5129 w11 QP 22 PDFJesús Eduardo Carbonó NieblesОценок пока нет
- Discovering Mathematics 3 Chapters 1-6 and 7-11 TopicsДокумент3 страницыDiscovering Mathematics 3 Chapters 1-6 and 7-11 TopicsFrancis Ho HoОценок пока нет
- 5054 w10 Ms 41Документ3 страницы5054 w10 Ms 41Ali RanaОценок пока нет
- 5054 w10 Ms 41Документ3 страницы5054 w10 Ms 41Ali RanaОценок пока нет
- 9-30-12 - Praises To 21 TarasДокумент4 страницы9-30-12 - Praises To 21 TarasLim Kew Chong100% (1)
- IPA Report Copper Velocity and Temperature April 2015 PDFДокумент13 страницIPA Report Copper Velocity and Temperature April 2015 PDFasastreОценок пока нет
- Antioxidant Enzyme EvaluationДокумент14 страницAntioxidant Enzyme EvaluationArpit JainОценок пока нет
- Hardsurfacing HandbookДокумент24 страницыHardsurfacing HandbookscribdphinОценок пока нет
- Polyurea Resistance ChartДокумент1 страницаPolyurea Resistance ChartTanmay GorОценок пока нет
- Tool Makers MicroscopeДокумент13 страницTool Makers MicroscopeLokesh LokiОценок пока нет
- Electricity PowerPoint-0Документ34 страницыElectricity PowerPoint-0Ryan P. YapОценок пока нет
- Design of Fatigue StrengthДокумент21 страницаDesign of Fatigue StrengthRaviteja VgaОценок пока нет
- Solubility of Titanium Dioxide in Cosmetic FormulationsДокумент10 страницSolubility of Titanium Dioxide in Cosmetic FormulationsMeiОценок пока нет
- Plain Concrete FootingДокумент6 страницPlain Concrete FootingAnonymous mcHqIfbnV1Оценок пока нет
- Welding Guide For Rina-EngДокумент75 страницWelding Guide For Rina-EngReaz UddinОценок пока нет
- Three Dimensional Numerical Simulation of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers Part I Foundation and Fluid Mechanics PDFДокумент19 страницThree Dimensional Numerical Simulation of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers Part I Foundation and Fluid Mechanics PDFAltamash MunirОценок пока нет
- Interpreting Spectra for Organic CompoundsДокумент4 страницыInterpreting Spectra for Organic CompoundsIván SalazarОценок пока нет
- Vertical forces-WPS OfficeДокумент2 страницыVertical forces-WPS OfficeJesusa EstradaОценок пока нет
- Hardtop XP (Azad)Документ5 страницHardtop XP (Azad)Anonymous f1NlMPnОценок пока нет
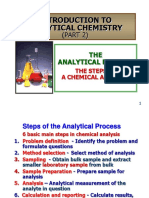
- Topic 1.2 Analytical ProcessДокумент52 страницыTopic 1.2 Analytical ProcessEyzah75% (8)
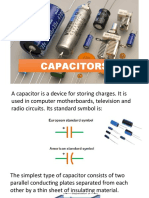
- CapacitorsДокумент25 страницCapacitorsAlbert Rosete0% (1)
- Astm 2Документ5 страницAstm 2carlos salinasОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Chemical Reactor Engineering - Problems PDFДокумент75 страницIntroduction To Chemical Reactor Engineering - Problems PDFJojie-Ann Alabarca100% (1)
- 3-11-8 - Pressure Vessel Cs - UopДокумент31 страница3-11-8 - Pressure Vessel Cs - UopSean Davis100% (1)
- Experiment No. 1 Rockwell Hardness Group 1 Final - PaperДокумент3 страницыExperiment No. 1 Rockwell Hardness Group 1 Final - PaperThomas Jefferson AntonioОценок пока нет
- VFD Pumping SystemsДокумент22 страницыVFD Pumping Systemsrajurajangam100% (1)
- CH CH CH - CH CL CL N N: PolymerizationДокумент40 страницCH CH CH - CH CL CL N N: PolymerizationAkash YadavОценок пока нет
- 442-032 PDF PDFДокумент12 страниц442-032 PDF PDFCalОценок пока нет
- Factors of Safety for Cuttings in Normally Consolidated ClaysДокумент5 страницFactors of Safety for Cuttings in Normally Consolidated ClaysAnonymous GnfGTwОценок пока нет
- DentinДокумент133 страницыDentindentistry24100% (1)
- M20Документ54 страницыM20Mijail Pérez Miranda100% (1)
- GaN HEMTs - Advantages Opportunities and Challenges PDFДокумент60 страницGaN HEMTs - Advantages Opportunities and Challenges PDFghatakp2069Оценок пока нет
- Scotch Tape Method: Producing Graphene FlakesДокумент3 страницыScotch Tape Method: Producing Graphene Flakestaniya balochОценок пока нет
- API 2H Grade 50 Steel Plate SpecificationДокумент3 страницыAPI 2H Grade 50 Steel Plate SpecificationJym GensonОценок пока нет