Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Geothermal Power Generation
Загружено:
Syed Ameen MurtuzaАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Geothermal Power Generation
Загружено:
Syed Ameen MurtuzaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
GEOTHERMAL POWER GENERATION
AN OVERVIEW
Rajesh M Holmukhe
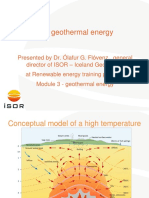
Electrical Bharati Vidyapeeth Assistant Professor Engineering Department, University, College of Engineering Pune, India e-mail:rajeshmholmukhe@hotmail.com Earth is made up of 3 layers namely, crust, mantle and metallic core. The crust, mainly composed of granites is split into 6 main plates which move away from each other at the rate of 2 to 20 cm per year. Relative motion of the plates occasionally gives rise to areas where internal heat of the earth reaches the surface and where most volcanoes and most of the world's geothermal fields are found. I) Water is the most important carrier of the energy in geothermal wells as it has a high heat capacity and latent heat of vaporization. 2) Impermeable rocks cover permeable layers which contain reservoir of hot water thereby preventing heat loss and maintaining water under pressure. Geothermal fields such as geysers require a combination of 3 geological factors-I) a natural underground source of water. 2) an impermeable layer that traps the water and permits formation of steam. 3) a mass of hot rock near the natural water system. Geothermal energy is derived from the hot interior of the earth. Crustal rock up to 70 km thick insulates it from earth's surface. Due to this insulation temperature at the surface is relatively cool but increases rapidly with growing depth inside the rock. A small portion of the rock is permeable so that over a long period of time it acquires a store of natural ground water which gets heated. In places where the heated water finds its way to the surface naturally, the geothermal energy can be extracted with relative ease. In other places it may be mined using deep bore holes. In Pacific Ocean lies the richest belt of geothermal energy known as 'RIM OF FIRE' stretching from New Zealand up through New Guinea, Philippines, Japan, Western Siberia and then down through Western United States, Mexico, Central America. Geothermal Gradient:- It is defined as the rate of increase of temperature with depth. In developing a program to use geothermal energy following factors need to be analyzedI. Variation of temperature with depths in different parts of the world. 2. Identification of location at convenient depths from which it is possible to approach water bearing rocks having water temperature higher than 50C.
ABSTRACTTHIS PAPER PRESENTS THE DEVELOPMENT, UTILISATION AND APPLICATION OF GEOTHERMAL POWER. THE FAST DEPLETING CONVENTIONAL RESOURCES HAVE COMPLETED US TO LOOK OUT FOR NEW AVENUES IN ENERGY GENERATION.THIS PAPER DISCUSSES IN GREATER DEPTHS DIFFERENT WAYS OF HARNESSING THIS NON-CONVENTIONAL ENERGY SOURCE. THE CLASSIFICATION AND OPERATION OF GEOTHERAMAL POWER PLANT AN LOG WITH SCHEMATIC DIAGRMS HAVE BEEN EXPLAINED IN DETAIL.IT GIVES AN OVERVIEW OF THE GEOTHERMAL POWER GENERATION IN INDIA AND ABROD AND ITS ECONIMIC FESIBILITY.FURTHER ACOMPARISION BETWEEN GEOTHERMAL POWER PLANT AND THERMAL POWER PLANT HAS BEEN MADE .WE HAVE TRIED OUR LEVEL BEST TO COVER ALL THE ASPECTS OF GEOTHERMAL POWER GENERATION IN THIS PAPER.
Keywords- geothermal powert ,. renewable energy
I.
INTRODUCTION
Non-Conventional Energy Source (NECS) which comprise both renewable and non renewable source should play an increasingly important role in the coming periods in view of fast depleting fossil fuel reserves and growing concerns for environment protection. Perennial energy shortages and resulting inflation have adversely affected the balance of payment position in energy scare economies of developing countries. Renewable energy sources occur in nature in the form of energy flows of indefinite duration as opposed to non-renewable conventional fuels of finite values. Here we shall see about Geothermal Power Plants as product of clean energy concept and geothermal energy resource which of 1 or 2 orders of magnitude larger than the recoverable energy from uranium and thorium in same volume of rocks.
II.
ORIGIN AND DISTRIBUTION GEOTHERMAL ENERGY
OF
Geothermal energy is present over the entire extent of the earth's surface. It varies only in its ease and cost of extraction. The need for developing the least expensive resource first has resulted in the exploration of geothermal resources primarily in these areas which have associated volcanic activity. However, by no means is the resource restricted only to volcanic areas.
3.
Identification of rocks that are sufficiently hot and impermeable which render extraction of heat and economically viable proposition.
IV. VAPOUR DOMINATED (STEAM) GEOTHERMAL ELECTRIC POWER PLANT: The geothermal fluid for such plants is dry steam at temperature between 180 C to 240 C with low content of particulate impurities and dissolved solid impurities. Mass flow rate per well is around 10 kg/see with power rating per well at rate of 6 MWe. SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM: Figure (3) gives a typical schematic of a vapour dominated geothermal power plant. Dry steam from the geothermal reservoir I) flows upwards through the production well (2) and is admitted in the centrifugal separator (4) The temperature and pressure of the steam at the bottom of the well are 280 C and 35 bar. As steam flows towards the ground surface, it expands and cools. Temperature and pressure at the well head is about 250 C and 8 bar. The centrifugal separator (4) removes particulate matter (13) from the steam. The steam is admitted into the steam turbine (5) The steam expands in the turbine buckets producing rotary kinetic energy. The low pressure steam at the exhaust of the turbine is condensed in condenser (8) the condensated is reinjected into the earth via the reinjection wall. (9) Cooling water for condensing the steam is circulated through the cooling tower (12) by means of cooling water pump. (13) The synchronous generator (6) generate electrical power at high voltage 50 Hz A.C. The turbine and generator form one unit. Complete power plants has several units. Geothermal energy in the form of dry steam (1) is converted into mechanical energy by the turbine (5) The mechanical energy is converted to electrical energy by the generator. The electrical power is transmitted by electrical transmission system and fed to 30 AC supply network. Steam geothermal power plant are grid connected and operated continuously as base load power plants. PRODUCTION WELL: Are located at a distance of about05. km. Life of a steam power production well is 6 to 15 years. Thereafter new well should be used. Steam production from a well declines by about 20% in about 6 years. REINJECTION WELLS: The reason for reinjection of condensate into the earth are :1) To ensure supply of fresh water from production well for several years. The earth acts as a steam generator. 2) To prevent environmental pollution. The condensate contains certain pollutants for e.g. The steam at the geysers contains Hydrogen Sulphide up to 200 ppm. If condensate is let out on ground level, it causes environmental hazard. V. COMPARISION BETWEEN GEOTHERMAL POWER PLANT AND STEAM THERMAL POWER PLANT: The main difference between conventional steam thermal power plant and geothermal power plant are:-
III. CLASSIFICAITON OF TYPES OF GEOTHERMAL POWER PLANTS: Geothermal Power Plants are of several types. They are classified on basis of Geothermal fluid used Thermodynamic cycle adopted I. STEAM GEOTHERMAL POWER PLANT: It is called vapour dominated geothermal power plant. Geothermal fluid is steam. PETRO THERMAL GEOTHERMAL POWER PLANT: It is also called Hot Dry Rock geothermal power plant. Thermal energy in hot dry geological rock is extracted by circulating water through artificial fracture in hot dry rock. Steam turbine is used as prime mover. FLASHED STEAM GEOTHERMAL POWER PLANT:- It is a type of Liquid Dominated geothermal power plant. Production well produces mixture of water and steam at temperature more than 180 C and with low content of dissolved minerals. Steam turbine is the prime mover. Geothermal fluid is flashed to obtain steam. BINARY LIQUID DOMINATED GEOTHERMAL POWER PLANT: The geothermal fluid is mixture of water and steam at temperature less than 150 C. The geothermal fluid cycle is different from the working fluid cycle. The geothermal heat is exchanged with the working fluid of low boiling point in a heat exchanger gas turbine drives the generator shaft. BINARY CYCLE GEOTHERMAL POWER PLANT WITH HOT BRlNE: When geothermal fluid is liquid with high mineral content, binary cycle similar to (4) is preferred. TOTAL FLOW GEOTHERMAL POWER PLANT" The entire geothermal fluid is passed through the special turbine. Such system is used when the geothermal fluid has very high content of mud, dissolved minerals etc.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Geothermal Power Plants are operated continuously as base load power plants. Production wells require a few hours from start to reach the rated level of delivery. Thermal equipment are loaded gradually. In the beginning, the geothermal fluids contain excessive particulate and dirt. After a few hours the quality of production fluid is improved. Hence frequent restarts must be avoided.
Geothermal power plants have smaller units sizes (S MW, 10 MW, IS MW) whereas the thermal steam power plants have large unit sizes (200MW, SOO MW,800MW) A Variety of systems are used in geothermal power plant for extraction of steam from geothermal energy source. geothermal power plants need a large flow of geothermal fluids (due to lesser temperature and pressure) Geothermal power plants need a large flow of geothermal fluids (due to lesser temperature and pressure) Geothermal power plants are located on geothermal field. it is not technically feasible to transport hot geothermal fluid over long distance due to drop in pressure and temperature. the energy conversion sequence in vapour dominated geothermal power cycle is as following:-
VI. SCOPE FOR GEOTHERMAL ENERGY SYSTEM IN INDIA: India has I SO known geothermal sites having geothermal fluid
of moderate and low temperature that is <160 C. the geothermal fields in India are in the form of hot water springs (40 C to 98 C) and shallow water reservoir temperatures are less than 160 C. The important hydro-geothermal resource locations are:-
FIELD PUGAJ&K
DRY STEAM GENERATOR SEPERA TOR
CENTRIFUGAL CONSUMER TURBINE
STEAM STEAM
WEST COAST MAHARASHTRA GUJARAT FIELDS, AND
Geothermal power plant requires much larger flow of steam per kWh of electrical energy generated. Power available per well is relatively small.
VAPOUR DOMINATED GEOTHERMAL POWER PLANT UNIT SIZE OF TURBINE GENERATOR STEAM TEMPERA TURE STEAM PRESSURE STEAM PER kWh (relative) VOLUME OF STEAM ( relative) SMW-IOMW
COAL FIRED STEAM THERMAL POWER PLANT IOOMW-600 MW
AND PARTICULARS LlKEL Y APPLICATIONS -Geo-hydrothermal -I IS springs SO to 80 C - total discharge 18 kllh - field area 3 sq. meter -Appl ications -green house cultivation - space heating - drying of wool -binary cycle power plant -geo-hydrothermal - 18 springs 34 to 72 C - locations with water at 120 C at 200 to SOO m depths -Applications -mushroom farming -animal husbandry -biogas production -drvinz of sea fish PARTICULARS AND LlKEL Y APPLICATIONS -geo-hydrothermal - 23 springs, SO to 98 C - total discharge 3600llh -Applications -silver culture -drying of timber - drying of cotton - drying of fruits
FIELD T ATT APANI FIELDS - MP
270C 8 Bar
SOOC
30 BAR X
2.SX SOY
The working fluid in conventional steam thermal coal fired power plant is high temperature high pressure steam produced from lean water with very low particulate and dissolved solid matter. Geothermal steam has highest content of particulate and dissolved impurities. Additional equipments are necessary in geothermal power plant for production of clean steam suitable for admitting into the steam turbines. The configuration of power plant and equipment is influenced by the temperature pressure solid particulate and dissolved impurities in geothermal steam water produced by production well.
Due to moderate and low temperature of geothermal fluids, the prospects of such plants in India are very low. However geothermal energy is likely to have several applications in temperature range of 30 C to 190 C.
VII. GEOTHERMAL ELECTRICAL POWER PLANTS IN THE WORLD:
About 20 nations in the world have known geothermal resources. total installed capacity of geothermal power plants in the world is around 10,000 MW.
HISTORIC PLANTS:-
REVIEW
OF
GEOTHERMAL
POWER
VIII.
ECONOMICS
FOR POWER GENERATION:
1904
LARDERDLLO,
IT AL Y
1914
LARDERDLLO,
IT AL Y
1944
LARDERDLLO,
ITALY
1958
JAPAN, MEXICO
1960 1982 1979
THE GEYSERS, THE GEYSERS,
USA USA
1987 1988
USA, ITALY, NEW MEXICO, ZEALAND, USSR USA THE WORLD
electricity from generated geothermal energy for first time - 8.5 MW power plant with steam turbine generators - 127 MW steam geothermal power plant geothermal energy electric power plants - II MW steam turbine generator - 109 steam turbine generator -total installed capacity 1900 MW - 70 MW binary cycle power plant -total installed capacity 3500 MW -total installed capacity 8000 MW
Factors affecting economic growth of geothermal energy based power generation are the well head temperature, well flow rate and the cost of wells. Optimum plant size is in 50 to 100MW range. Scope of cost reduction in large plants through economics of scale is limited and hence geothermal power plants are more appropriate for supplying power to public buildings and commercial establishments. Total cost of geothermal plant can be divided in 3 categories: 1. Power Plant capital costs 2. Operating cost 3. Energy supply cost Power plant costs mainly cover the initial capital required to build it with operating cost forming a small proportion. As the proportion of operating costs in total costs is low, uncertainties in operating costs would not have a significant impact on power costs. Geothermal power generation is thus capital intensive with 75% of generating costs as fixed costs pertaining to capital investment.
CONCLUSION
Geothermal power can become a valuable source of energy if properly harnessed. Continued energy shortages have created added interest in geothermal energy for both power generation 2000 THE WORLD and direct applications. The technology is expensive and it is necessary that for real breakthrough the cost be reduced , substantially. GEOTHERMAL ELECTRIC POWER PLANTS IN THE Development of geothermal energy has some li tiIons on the environment. Environmental problems WORLD imouca COUNTRY AND TOTAL GEOTHERMAL TEMPRA TURlissociated g eothermal development are physical disturbance LOCATION INSTALLED FLUID C of site, noi e, brine, disposal, ground water contamination, by CAPACITY fluids and air pollution especially by hydrogen v USA,THE IIOOMW STEAM 285 sulphide. GEYSERS ITALY, 406MW STEAM+ 260 A ditional and often less manageable problems relate LARDERELLO WATER to serious social, economic and institutional impacts that ccompany large scale geothermal development. o 'J NEWZEALAND, 290MW STEAM+WATER 260 This could be compounded by the effects of new industrial WEIRAKAI wrucn roup ws as a result of low cost geothermal power JAPAN IIOMW STEAM+WATER 280 CHILE,ELTATIO 15MW STEAM+WATER 280 developmehi t plans should include careful ground work to mitigate irrp act on areas with geothermal resources.
,......
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
"
MEXICO, CERRO PRlETO TURKEY, KIZILDEE FORMERUSSR ICELAND
150MW 10MW 7MW 2.5 MW
STEAM+ WATER STEAM+ WATER STEAM+ WATER STEAM+ WATER
370 210
Bharati Vidyapeeth Pune-43.
University College of
Engineering,
REFERENCES
200 280
I.
,
3. 4.
EI' ERGY TECHNOLOGY-S.Rao and Dr. B.B. Parulekar(26730 pp) N-CONVENTlONAL ENERGY SYSTEMS -K.M. Mittal " (4 0-420 pp) E ECTRICAL ENGINEERING HANDBOOK 2nd EDITION. II 02-1315P) STANDARDHANDBOOKFORELECTRICAL ENGINEERING 13th EDITION(11-2to I 1-6)
Вам также может понравиться
- Geothermal Heat Pump: User ManualДокумент16 страницGeothermal Heat Pump: User ManualEgorОценок пока нет
- Schwarzman Scholars Sample Application 2019Документ17 страницSchwarzman Scholars Sample Application 2019Waqas AhmadОценок пока нет
- Geothermal Power Plant: Wesleyan University-Philippines Mabini Extension, Cabanatuan CityДокумент10 страницGeothermal Power Plant: Wesleyan University-Philippines Mabini Extension, Cabanatuan CityRoss Sonny CruzОценок пока нет
- Geothermal: Exploration and ExploitationДокумент18 страницGeothermal: Exploration and ExploitationPrakhar SarkarОценок пока нет
- AbstractДокумент3 страницыAbstractsreeramyadingariОценок пока нет
- A Review On The Prospect of Geothermal Energy in BangladeshДокумент8 страницA Review On The Prospect of Geothermal Energy in BangladeshInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Geothermal ExplorationДокумент40 страницGeothermal ExplorationPhan Trong HuanОценок пока нет
- Metode Seismik Bias: Refraction SeismicДокумент30 страницMetode Seismik Bias: Refraction SeismicDimas PermanaОценок пока нет
- Seismic RefractionДокумент74 страницыSeismic RefractionAdrian Liviu BugeaОценок пока нет
- Pertrophysics-00List of Abbreviations PDFДокумент6 страницPertrophysics-00List of Abbreviations PDFOlaoluwa OlatonaОценок пока нет
- JoomlaДокумент7 страницJoomlamythygpbhuОценок пока нет
- 02 Acquisition Processing Basics 02Документ56 страниц02 Acquisition Processing Basics 02HarshОценок пока нет
- Apt For Geologist & Pet EngrsДокумент4 страницыApt For Geologist & Pet EngrsOlawale Whales ArowoloОценок пока нет
- Lecture4 - Fluvial Processes and LandformsДокумент70 страницLecture4 - Fluvial Processes and LandformsAniket KannoujiyaОценок пока нет
- MSC Petroleum Geoscience SMTДокумент43 страницыMSC Petroleum Geoscience SMTSean YiyangОценок пока нет
- Deep Learning Applied To Seismic Facies Characterization SEG WKSHP PDFДокумент3 страницыDeep Learning Applied To Seismic Facies Characterization SEG WKSHP PDFkusbarotoОценок пока нет
- Eugene Island Submerged Geological OilДокумент117 страницEugene Island Submerged Geological OilVincent J. CataldiОценок пока нет
- Application Student 2018Документ1 страницаApplication Student 2018GisheilaОценок пока нет
- 04 Segy FormatДокумент7 страниц04 Segy FormatPhạm NamОценок пока нет
- Data Conditioning and ReprocessingДокумент13 страницData Conditioning and ReprocessingWindy D AОценок пока нет
- John Castagna CV PDFДокумент9 страницJohn Castagna CV PDFMark MaoОценок пока нет
- Refraction Seismic IIДокумент30 страницRefraction Seismic IIabuobidaОценок пока нет
- Erth3021 Seismic Refraction PracДокумент3 страницыErth3021 Seismic Refraction PracDhaffer Al-MezhanyОценок пока нет
- Sampling Theory: Double Sampling (Two Phase Sampling)Документ12 страницSampling Theory: Double Sampling (Two Phase Sampling)andriyesОценок пока нет
- Geothermal Energy Used in Buildings Heating and CoolingДокумент22 страницыGeothermal Energy Used in Buildings Heating and CoolingAdvanced Research PublicationsОценок пока нет
- Velocity Analysis ProcessingДокумент24 страницыVelocity Analysis ProcessingLilyОценок пока нет
- What Defines A Reflection: Refraction (First Arrival)Документ17 страницWhat Defines A Reflection: Refraction (First Arrival)usjpphysicsОценок пока нет
- Shallow Seismic Refraction InterpretationДокумент33 страницыShallow Seismic Refraction InterpretationYong PrazОценок пока нет
- Basin ModellingДокумент6 страницBasin ModellingMartin OviedoОценок пока нет
- Facies Classification-ML PDFДокумент4 страницыFacies Classification-ML PDFkmilo04Оценок пока нет
- Seismic Attributes and AVO Analysis by Ahmed Hafez: January 2018Документ30 страницSeismic Attributes and AVO Analysis by Ahmed Hafez: January 2018omoba solaОценок пока нет
- MSc. Geology Syllabus (Pune University)Документ37 страницMSc. Geology Syllabus (Pune University)SangitaОценок пока нет
- Schwarzman Scholars 2017 Application InstructionsДокумент4 страницыSchwarzman Scholars 2017 Application InstructionsnhlhОценок пока нет
- Principles of AVO Cross PlottingДокумент6 страницPrinciples of AVO Cross PlottingRiki RisandiОценок пока нет
- Seismic Facies and Hydrocarbon Potential of Carbonate Reservoirs in Ramp SettingsДокумент13 страницSeismic Facies and Hydrocarbon Potential of Carbonate Reservoirs in Ramp SettingsRuth Santos NaranjoОценок пока нет
- Palmer.03.Digital Processing of Shallow Seismic Refraction Data PDFДокумент23 страницыPalmer.03.Digital Processing of Shallow Seismic Refraction Data PDFAirОценок пока нет
- If You Want To Be A FulbrighterДокумент3 страницыIf You Want To Be A FulbrighteryOtAhОценок пока нет
- Lab 7Документ4 страницыLab 7郭佳靇Оценок пока нет
- A Review of AVO Analysis PDFДокумент24 страницыA Review of AVO Analysis PDFMohamed Abdel-FattahОценок пока нет
- Rock Physics Coures - Lect#5Документ19 страницRock Physics Coures - Lect#5dvarma_6Оценок пока нет
- Basics of Sequence StratДокумент119 страницBasics of Sequence StratMohamed Hataba0% (1)
- Seistomopy: Fast Visualization, Comparison, and Calculations in Global Tomographic ModelsДокумент11 страницSeistomopy: Fast Visualization, Comparison, and Calculations in Global Tomographic ModelsAdexa PutraОценок пока нет
- N. (Geophysics) : Seismic Record Noise FoldДокумент84 страницыN. (Geophysics) : Seismic Record Noise FoldRazi AbbasОценок пока нет
- Pitfalls in Seismic InterpretationДокумент71 страницаPitfalls in Seismic InterpretationAmmad Ali QureshiОценок пока нет
- GG09 - Geothermal FluidsДокумент37 страницGG09 - Geothermal FluidsMichelle MilleniaОценок пока нет
- Turbidite Systems, Part 1Документ6 страницTurbidite Systems, Part 1Angel SaldañaОценок пока нет
- Geophysical Applications Mine Waste Piles: Bruce D. Smith, USGSДокумент30 страницGeophysical Applications Mine Waste Piles: Bruce D. Smith, USGSBha Bha SieteОценок пока нет
- 2019 Geoteric Overview Brochure PDFДокумент9 страниц2019 Geoteric Overview Brochure PDFolaseyeОценок пока нет
- Seismic Reflection Data: What It Is, How It Can Be Used, & An Application at Elk Hills, CAДокумент25 страницSeismic Reflection Data: What It Is, How It Can Be Used, & An Application at Elk Hills, CAvishnurajОценок пока нет
- Manual WaveletДокумент626 страницManual Waveletjulio gamboaОценок пока нет
- EAGE Minus CO2 ChallengeДокумент5 страницEAGE Minus CO2 ChallengeabuobidaОценок пока нет
- Field QC With VISTA (Houston)Документ9 страницField QC With VISTA (Houston)LiliОценок пока нет
- Seismic Imaging Toolbox For PythonДокумент16 страницSeismic Imaging Toolbox For PythonSupriyo ChakrabortyОценок пока нет
- Dix - 55 - Seismic Velocities From Surface MeasurementsДокумент15 страницDix - 55 - Seismic Velocities From Surface MeasurementsHoidi Shitakwa Zacharia100% (2)
- StructuralGeologyLabManual PDFДокумент194 страницыStructuralGeologyLabManual PDFmariocb1103Оценок пока нет
- Deepwater Sedimentary Systems: Science, Discovery, and ApplicationsОт EverandDeepwater Sedimentary Systems: Science, Discovery, and ApplicationsJon R. RotzienОценок пока нет
- Modeling The Earth For Oil Exploration: Final Report of the CEC's Geoscience I Program 1990-1993От EverandModeling The Earth For Oil Exploration: Final Report of the CEC's Geoscience I Program 1990-1993Оценок пока нет
- Advances in Subsurface Data AnalyticsОт EverandAdvances in Subsurface Data AnalyticsShuvajit BhattacharyaОценок пока нет
- Innovative Exploration Methods for Minerals, Oil, Gas, and Groundwater for Sustainable DevelopmentОт EverandInnovative Exploration Methods for Minerals, Oil, Gas, and Groundwater for Sustainable DevelopmentA. K. MoitraОценок пока нет
- Contrastive Linguistics - D2019 (Ms. Yen)Документ134 страницыContrastive Linguistics - D2019 (Ms. Yen)Lan Anh ChuОценок пока нет
- Geothermal Reservoir Simulation in Hot Sedimentary Aquifer System Using FeflowДокумент1 страницаGeothermal Reservoir Simulation in Hot Sedimentary Aquifer System Using FeflowImmanuel Lumban GaolОценок пока нет
- XiGo Note 112 Pharma and The Acorn AreaДокумент3 страницыXiGo Note 112 Pharma and The Acorn Areaprakush01975225403Оценок пока нет
- Design and Construction LandscapingДокумент162 страницыDesign and Construction LandscapingShah Tulsi100% (3)
- The Secrets of The SoilДокумент2 страницыThe Secrets of The SoilOmar CespedesОценок пока нет
- 11 Solutions KTPДокумент22 страницы11 Solutions KTPAdiya AshimovaОценок пока нет
- PR2 Questionnaire FinalДокумент4 страницыPR2 Questionnaire FinalGevin DuetchОценок пока нет
- Recognition of Idle Resources in Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing and Resource Consumption Accounting ModelsДокумент15 страницRecognition of Idle Resources in Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing and Resource Consumption Accounting ModelsBassel JaberОценок пока нет
- Bruggolite - FF6M Low Temperature Redox Polymerization PDFДокумент7 страницBruggolite - FF6M Low Temperature Redox Polymerization PDFLin NiuОценок пока нет
- Abhijit MuhuratДокумент7 страницAbhijit MuhuratAbi Abilash100% (1)
- Are Animals Getting Smarter?Документ1 страницаAre Animals Getting Smarter?Bismi IqbalОценок пока нет
- Guide To The Pallet Specification Sheet: Pallet Design System PDSДокумент6 страницGuide To The Pallet Specification Sheet: Pallet Design System PDSirtaza324197Оценок пока нет
- Technical Seminar ReportДокумент21 страницаTechnical Seminar ReportManoj MОценок пока нет
- SOAL + JAWAB BHS Inggris HAL 1-15Документ15 страницSOAL + JAWAB BHS Inggris HAL 1-15Nor JanahОценок пока нет
- 02 LMS Test IntroductionДокумент33 страницы02 LMS Test IntroductionKimi KononОценок пока нет
- The LargestДокумент3 страницыThe Largestsh_shi2003Оценок пока нет
- SEAD - Solution Manual - 2019-2020 EditionДокумент37 страницSEAD - Solution Manual - 2019-2020 EditionYokaОценок пока нет
- ERIKS - Y Filter 1610 - Data SheetДокумент1 страницаERIKS - Y Filter 1610 - Data SheetNoparit KittisatitОценок пока нет
- Lucas Buchaillot 1ere3Документ2 страницыLucas Buchaillot 1ere3buchaillotlucas1Оценок пока нет
- Application of Derivatives: FactsДокумент11 страницApplication of Derivatives: FactsJayant SinghОценок пока нет
- CH 5 RCC SlabДокумент76 страницCH 5 RCC SlabAmanGargОценок пока нет
- Automated Blood Culture SystemДокумент2 страницыAutomated Blood Culture SystemAltruist AcharyaОценок пока нет
- Pre - Historic ArchitectureДокумент4 страницыPre - Historic ArchitecturemoodyОценок пока нет
- Montoya NGM SB Nse 2021 ThesisДокумент76 страницMontoya NGM SB Nse 2021 ThesisSupeR StaRОценок пока нет
- Webinar MacDrain ENGДокумент45 страницWebinar MacDrain ENGIrcil Rey QuiblatОценок пока нет
- Irc SP81 Micro-Surfacing - An - Eco-Friendly - Bailout PDFДокумент9 страницIrc SP81 Micro-Surfacing - An - Eco-Friendly - Bailout PDFAmit Prasad100% (1)
- Bugreport Fog - in SKQ1.211103.001 2023 04 10 19 23 21 Dumpstate - Log 9097Документ32 страницыBugreport Fog - in SKQ1.211103.001 2023 04 10 19 23 21 Dumpstate - Log 9097chandrakanth reddyОценок пока нет
- Reading Material Lecture 04Документ12 страницReading Material Lecture 04Muqeem MahmoodОценок пока нет
- Culture Communication and SilenceДокумент20 страницCulture Communication and SilencerogarhiОценок пока нет
- Language Paper 1 - Q SДокумент8 страницLanguage Paper 1 - Q Ssaumya.pardeshiОценок пока нет