Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Books Gate
Загружено:
Kapil TirodeАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Books Gate
Загружено:
Kapil TirodeАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
http://www.gatementor.com/viewtopic.php?
f=18
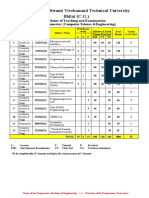
Compiler Design
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Compilers, Principles, Techniques and Tools by Alfred V. Aho, Ravi Sethi, Jeffery D. Ullman Modern Compiler Design by Dick Grune, H.E. Bal, C. Jacobs, K.G. Langendoen Optimizing Compilers for Modern Architectures: A Dependence-based Approach by Ken Kennedy, Randy Allen Compiler Construction: Principles and Practice, Kenneth C. Louden Engineering a Compiler by Deith D. Cooper, Linda Torczon and Morgan Kaufmann Compiler Construction: Principles and Practice, Kenneth C. Louden
Engg Maths
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Discrete mathematics & its applications, Kenneth H. Rosen Symbolic Logic, M. Copi Formal Logic, M. Copi Probability, Banerjee, De, Sen Statistics and probability, N.G. Das Higher Algebra, S.K. Mapa Modern Algebra, A.R. Vasistha Discrete Mathematical structure, Kolman, Busby, Ross Graph Theory, Narsingh Deo
10. Linear Algebra Hadley 11. Numerical Analysis & Computational procedure S.A.Mollah 12. Mathematical Analysis, Malik & Arora 13. Differential Calculus, Ghosh, Maity 14. Integral Calculus, Ghosh Maity
Theory of Computation
1. 2. 3. 4. Introduction to Automata Theory, Languages, and Computation, John E. Hopcroft, Jeffery D. Ullman An Introduction to Formal Languages and Automata, Peter Linz Theory of Computer Science (Automata, Languages and Computation), K.L.P. Mishra & N. Chandrasekaran Introduction to Computer Theory, Daniel I. A. Cohen
sbjoshi@cse.iitb.ac.in
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Discrete Mathematics by C L Liu (Nothing should be missed from the book) Introduction to Automata, Languages and Computation theory by John hopcroft, jeffery ullman and Rajiv Motwani (two books in GCET library, chapter 11 can be omitted ) Introduction to Compiler Design by Aho(first 7 chapters do not miss LALR parser) Linkers and Loaders by John R Levine(1 copy in GCET library- read only introductory chapters) Data structures( I dont remember the exact name) by Mark Allen Weiss (3 copies in GCET library) Some variants of data structures like splay trees can be omitted Computer Architechture by William Stallings (plz read RISC CISC and pipelining thoroughly) book by hamacher is also good. OS and Computer Networks by Tanenbaum (The things generally covered in the syllabus is sufficient) Propositional logic and first order logic (a must read , i dont have idea about any specific book but i can give some tutorial slides) this topic is much important from GATE point of view
9.
Digital Circuits by Morris Mano(contents covered in the syllabus is more than enough)
10. Sharpen your C, C++ skills before going for GATE.
Rajs Collection
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Databases: For Transaction management chapters refer book by Korth, Concurrency Control from Navathe, SQL Queries --- refer Raghuramkrishnan and Gerkhe. Network: Tanenbaum, Keith Ross { Both we have studied in our curriculum }. Operating system: Refresh Galvin and you can go for any other book where Synchronisation is covered in depth. Data Structure: Tanenbaum would serve the purpose. Algorithms : Introduction to algorithm -- By CORMEN and others { Good Book } , Refresh Levitin in case you wish to do. FAFL: Ullman is better book. You can even use Padmareddy for Quick revaisal. Logic Design: Moris mano,and even Givon { book of our syllabus } Computer Architecture: by Carl Hamacher { Study Caching in depth } Compiler Design: Aho, Ullman, Sethi { Prepare only selected topics; which are in the syllabus }
10. Discrete Mathematics & Graph Theory: --Grimaldi is best book {I have reaped its benefits}, But many refer to the book by Mott. --Only concentrate on [1] Matrix and determinants [2] Probability, Conditional Probability [3] Analytical Geometry.
Rajs Tips
Dont invest much time on Mathematics { there will be least no. of Questions on them } Database: Generally SQL queries will be confusing to understand and may even be time consuming. o So Avoid them {dont attempt} in case they start to bother you in exam. LD: Concentrate on Registers, Flip-flops, Counters, mod-counters, K-map simplifications. FAFL : Concentrate on CFG, CFL, Ambiguous grammars......etc Discrete Mathematics and GT: We can score in these subjects, and there will be many no. of questions on them. {Prepare well} OS: Concentrate on Synchronizations, and CPU scheduling algorithms. { and you will see good no. of questions on them } Compiler Design: Concentrate on Parsing Methods {very very important} like LALR, SLR... blah blah.... :) CO: Concentrate on Interrupt processing like Daisy chain, Central Interrupt Resolution. ADA: Concentrate on analysis of Algorithms and Master theorems usage and compute complexity.
Gate 2008 Computer Science Syllabus
ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Mathematical Logic: Propositional Logic; First Order Logic. Probability: Conditional Probability; Mean, Median, Mode and Standard Deviation; Random Variables; Distributions; uniform, normal, exponential, Poisson, Binomial. Set Theory & Algebra: Sets; Relations; Functions; Groups; Partial Orders; Lattice; Boolean Algebra. Combinatorics: Permutations; Combinations; Counting; Summation; generating functions; recurrence relations; asymptotic. Graph Theory: Connectivity; spanning trees; Cut vertices & edges; covering; matching; independent sets; Colouring; Planarity; Isomorphism. Linear Algebra: Algebra of matrices, determinants, systems of linear equations, Eigen values and Eigen vectors. Numerical Methods: LU decomposition for systems of linear equations; numerical solutions of non-linear algebraic equations by Secant, Bisection and Newton-Raphson Methods; Numerical integration by trapezoidal and Simpsons rules.
8.
Calculus: Limit, Continuity & differentiability, Mean value Theorems, Theorems of integral calculus, evaluation of definite & improper integrals, Partial derivatives, Total derivatives, maxima & minima.
COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Theory of Computation: Regular languages and finite automata, Context free languages and Push-down automata, Recursively
enumerable sets and Turing machines, Undecidability; NP-completeness.
Digital Logic: Logic functions, Minimization, Design and synthesis of combinational and sequential circuits; Number representation and
computer arithmetic (fixed and floating point).
Computer Organization and Architecture: Machine instructions and addressing modes, ALU and data-path, CPU control design,
Memory interface, I/O interface (Interrupt and DMA mode), Instruction pipelining, Cache and main memory, Secondary storage.
Programming and Data Structures: Programming in C; Functions, Recursion, Parameter passing, Scope, Binding; Abstract data
types, Arrays, Stacks, Queues, Linked Lists, Trees, Binary search trees, Binary heaps.
Algorithms: Analysis, Asymptotic notation, Notions of space and time complexity, Worst and average case analysis; Design: Greedy
approach, Dynamic programming, Divide-and-conquer; Tree and graph traversals, Connected components, Spanning trees, Shortest paths; Hashing, Sorting, Searching.
6. 7. 8. 9.
Compiler Design: Lexical analysis, Parsing, Syntax directed translation, Runtime environments, Intermediate and target code
generation, Basics of code optimization.
Operating System: Processes, Threads, Inter-process communication, Concurrency, Synchronization, Deadlock, CPU scheduling,
Memory management and virtual memory, File systems, I/O systems, Protection and security.
Databases: ER-model, Relational model (relational algebra, tuple calculus), Database design (integrity constraints, normal forms),
Query languages (SQL), File structures (sequential files, indexing, B and B+ trees), Transactions and concurrency control.
Computer Networks: ISO/OSI stack, LAN technologies (Ethernet, Token ring), Flow and error control techniques, Routing algorithms,
Congestion control, TCP/UDP and sockets, IP(v4), Application layer protocols (icmp, dns, smtp, pop, ftp, http); Basic concepts of hubs, switches, gateways, and routers.
Вам также может понравиться
- Essential Algorithms: A Practical Approach to Computer AlgorithmsОт EverandEssential Algorithms: A Practical Approach to Computer AlgorithmsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Course Outlines-SemesterДокумент7 страницCourse Outlines-SemesterZara TariqОценок пока нет
- Gate Computer Science TopicsДокумент6 страницGate Computer Science TopicsNaveed TawargeriОценок пока нет
- CS: Computer Science and Information Technology: Discrete MathematicsДокумент1 страницаCS: Computer Science and Information Technology: Discrete Mathematicsrifat iqbalОценок пока нет
- GATE CS Computer Science and Information Technology SyllabusДокумент2 страницыGATE CS Computer Science and Information Technology SyllabusShrinidhi KRОценок пока нет
- Gate Study MaterialsДокумент22 страницыGate Study MaterialsnehanirmalОценок пока нет
- MCA R13 SyllabusДокумент121 страницаMCA R13 SyllabusRanjith KumarОценок пока нет
- CS Computer Science and Information Technology: Section 1: Engineering MathematicsДокумент2 страницыCS Computer Science and Information Technology: Section 1: Engineering MathematicsPratiksha GaikwadОценок пока нет
- Syllabus 4th SemДокумент17 страницSyllabus 4th SemROHIT SHARMAОценок пока нет
- Section 1: Engineering MathematicsДокумент2 страницыSection 1: Engineering MathematicsNava ReenaОценок пока нет
- Gujarat Technological University: Masters in Computer Application Year - 3 (Semester - V) (W.E.F. JUNE 2017)Документ2 страницыGujarat Technological University: Masters in Computer Application Year - 3 (Semester - V) (W.E.F. JUNE 2017)Anonymous 4TUYfgmpОценок пока нет
- Changes in GATE-2021 Syllabus From GATE-2020 Syllabus ForДокумент2 страницыChanges in GATE-2021 Syllabus From GATE-2020 Syllabus ForsaurabhОценок пока нет
- Syllabus of GateДокумент3 страницыSyllabus of Gatemohammad shahnawazОценок пока нет
- Gate ItДокумент6 страницGate ItVICASRVERMAОценок пока нет
- C V V VVVVVVVVVДокумент5 страницC V V VVVVVVVVVAjmal KhanОценок пока нет
- Gate Syllabus - Computer Science and EngineeringДокумент2 страницыGate Syllabus - Computer Science and EngineeringAmit JhaОценок пока нет
- Computer Science Syllabus UG-1Документ7 страницComputer Science Syllabus UG-1lkОценок пока нет
- Algo Syllabus NewДокумент2 страницыAlgo Syllabus NewRaj EinsteinОценок пока нет
- CS Syllabus 2021Документ2 страницыCS Syllabus 2021CОценок пока нет
- Preface of AlgorithmsДокумент8 страницPreface of AlgorithmsAMIT RADHA KRISHNA NIGAM100% (1)
- GatesyllabusДокумент2 страницыGatesyllabusEr Nikita BansalОценок пока нет
- Gate-Cs: Section1: Engineering MathematicsДокумент4 страницыGate-Cs: Section1: Engineering MathematicsviddusagarОценок пока нет
- GATE 2024 Computer Science and Information Technology CS SyllabusДокумент2 страницыGATE 2024 Computer Science and Information Technology CS SyllabusSINIGI RAMYA SRIОценок пока нет
- GATE Syllabus Computer Science and Information TechnologyДокумент3 страницыGATE Syllabus Computer Science and Information TechnologyLalit jadhavОценок пока нет
- Syllabus For TestДокумент2 страницыSyllabus For Testdipa112Оценок пока нет
- CS Computer Science and Information Technology: Section1: Engineering MathematicsДокумент4 страницыCS Computer Science and Information Technology: Section1: Engineering MathematicsanubhooticbsОценок пока нет
- Algorithm (From Subjects Find and Chat GPT Generate)Документ19 страницAlgorithm (From Subjects Find and Chat GPT Generate)Scholarship LetterОценок пока нет
- Final CSE V Semester New SyllabusДокумент13 страницFinal CSE V Semester New Syllabussaurabh303Оценок пока нет
- Mca I Year Syllabus 9-9-2011Документ21 страницаMca I Year Syllabus 9-9-2011Priya AggarwalОценок пока нет
- CSE & AI SyllabusДокумент2 страницыCSE & AI SyllabusjanakОценок пока нет
- Design and Analysis of Algorithms: Course ObjectivesДокумент2 страницыDesign and Analysis of Algorithms: Course ObjectivesRISHABH CHAURASIAОценок пока нет
- 1-B - SC - SyllabusДокумент10 страниц1-B - SC - SyllabusBhargava PrasadОценок пока нет
- Indicative Syllabus of Information Technology: Section 1: Engineering MathematicsДокумент2 страницыIndicative Syllabus of Information Technology: Section 1: Engineering MathematicsAbhilasha ThakurОценок пока нет
- Teaching and Examination Scheme For Second Year Computer Science & Engineering (W.e.f. Academic Year 2009-10)Документ10 страницTeaching and Examination Scheme For Second Year Computer Science & Engineering (W.e.f. Academic Year 2009-10)VISION GAMINGОценок пока нет
- Course Titlesand DescriptionsДокумент2 страницыCourse Titlesand DescriptionsUltimate AltruistОценок пока нет
- Description of Courses2015 PDFДокумент11 страницDescription of Courses2015 PDFwerrick pharmaОценок пока нет
- Analysis and Design of Algorithms - ADA - Elective IДокумент3 страницыAnalysis and Design of Algorithms - ADA - Elective IDebashish MahapatraОценок пока нет
- Detailed syllabus-MCA-2019-2020Документ34 страницыDetailed syllabus-MCA-2019-2020Total FunОценок пока нет
- A o AДокумент2 страницыA o Aprad280589Оценок пока нет
- DAA SyllabusДокумент2 страницыDAA Syllabussushankreddy0712Оценок пока нет
- Week Wise Syllabus 1st SemesterДокумент7 страницWeek Wise Syllabus 1st SemesterRehman Ahmad ChОценок пока нет
- CS Computer Science and Information TechnologyДокумент2 страницыCS Computer Science and Information TechnologyAmit TiwariОценок пока нет
- 132 Numerical Analysis MethodsДокумент12 страниц132 Numerical Analysis Methodshadi13shsОценок пока нет
- Subject Code Subject Name Credits: Overview of Computer Architecture & OrganizationДокумент4 страницыSubject Code Subject Name Credits: Overview of Computer Architecture & Organizationanon_71491248Оценок пока нет
- Cucet Technical Syllabus PGДокумент3 страницыCucet Technical Syllabus PGMeenakshi VermaОценок пока нет
- GATE CS SyllabusДокумент4 страницыGATE CS SyllabusdennisfrancisОценок пока нет
- Gate Computer Science and Information Technology SyllabusДокумент3 страницыGate Computer Science and Information Technology SyllabusharshitaОценок пока нет
- Se 2Документ10 страницSe 2Sushrit PoudelОценок пока нет
- 2nd SemДокумент18 страниц2nd SemSuman Raj SharmaОценок пока нет
- Cse PDFДокумент55 страницCse PDFNikhil PhulОценок пока нет
- Mca153201 Web Technologies Credits: 3 Total: 60 Hours ObjectivesДокумент7 страницMca153201 Web Technologies Credits: 3 Total: 60 Hours ObjectivesashwiniОценок пока нет
- SyllabusДокумент2 страницыSyllabusrishabhtak16Оценок пока нет
- Fifth Semester: BTCS 501 Computer Networks - IIДокумент6 страницFifth Semester: BTCS 501 Computer Networks - IIPrincess deepikaОценок пока нет
- CS Computer Science and Information TechnologyДокумент2 страницыCS Computer Science and Information TechnologyprofBalamuruganОценок пока нет
- Syllabus of B.Sc. (Computer Science)Документ7 страницSyllabus of B.Sc. (Computer Science)Shishir MishraОценок пока нет
- Bachelor / Master of Technology (Dual Degree) : Computer Science & EngineeringДокумент7 страницBachelor / Master of Technology (Dual Degree) : Computer Science & EngineeringtarunjainusitОценок пока нет
- CS Computer Science and Information Technology: Section1: Engineering MathematicsДокумент2 страницыCS Computer Science and Information Technology: Section1: Engineering Mathematicsnitin kumarОценок пока нет
- Cse Odd Syllabus 2023-24Документ19 страницCse Odd Syllabus 2023-24Satyam GuptaОценок пока нет
- Essential MATLAB for Engineers and ScientistsОт EverandEssential MATLAB for Engineers and ScientistsРейтинг: 2 из 5 звезд2/5 (2)
- 06.14.20 Biblical Parenting in A Digital Age Part 1Документ2 страницы06.14.20 Biblical Parenting in A Digital Age Part 1Anjelica OtañesОценок пока нет
- PHP FrameworkДокумент6 страницPHP FrameworkNurul Salkinah KamaruddinОценок пока нет
- Revised Part I & IiДокумент14 страницRevised Part I & IiRosario BacaniОценок пока нет
- Bootstrap Cheat Sheet: If You Plan To Pick Up Some Coding Skills, Bootstrap 4 Is A Solid Choice!Документ50 страницBootstrap Cheat Sheet: If You Plan To Pick Up Some Coding Skills, Bootstrap 4 Is A Solid Choice!BL Pipas100% (2)
- Development of A Web-Based Water Supply ComplaintДокумент12 страницDevelopment of A Web-Based Water Supply ComplaintMattew OlawumiОценок пока нет
- IP Address ManagementДокумент4 страницыIP Address ManagementVo TinhОценок пока нет
- 18 R80 REST API LabДокумент40 страниц18 R80 REST API Labcharlyv3Оценок пока нет
- KДокумент54 страницыKGood Mesho0% (1)
- Shashi Shekhar: Work Experience SkillsДокумент1 страницаShashi Shekhar: Work Experience Skillsshashi shekharОценок пока нет
- Implementationof AcunetixДокумент13 страницImplementationof AcunetixPaul BenОценок пока нет
- Gantt Chart DoneДокумент3 страницыGantt Chart DoneNorihanMohamadSabdinОценок пока нет
- Adobe Photoshop Cs5 Extended - Mac Osx + Serial and Hack - XsellizeДокумент4 страницыAdobe Photoshop Cs5 Extended - Mac Osx + Serial and Hack - XsellizeMuhamad Zuzariff Kamaruzaman33% (3)
- Syllabus 245 JRДокумент15 страницSyllabus 245 JRSAMIKSHA GHOSHALОценок пока нет
- Opatach DBДокумент4 страницыOpatach DBMurali BodapatiОценок пока нет
- PR2 Module 4 Design Research in Daily LifeДокумент11 страницPR2 Module 4 Design Research in Daily LifeJohn Francis O. TañamorОценок пока нет
- Mindanao State University at NaawanДокумент10 страницMindanao State University at NaawanHamot KentОценок пока нет
- HP 15-J 15CRU 6050A2548201-MB-A01 PV 2012-12-06 Schematic DiagramДокумент58 страницHP 15-J 15CRU 6050A2548201-MB-A01 PV 2012-12-06 Schematic DiagramGerman ValenciaОценок пока нет
- Software IEC60870-5 Master Slave enДокумент7 страницSoftware IEC60870-5 Master Slave endivaОценок пока нет
- CV - Aisyah Lisana ChoiryДокумент2 страницыCV - Aisyah Lisana ChoiryLisana ChoiryОценок пока нет
- Aras Innovator 9.3 - Installation GuideДокумент66 страницAras Innovator 9.3 - Installation GuidevisokotОценок пока нет
- Selenium Installation GuideДокумент14 страницSelenium Installation GuideaujadhavОценок пока нет
- Tutorial J5Документ6 страницTutorial J5helllooОценок пока нет
- DreamweaverДокумент14 страницDreamweavermike ngwereОценок пока нет
- Upload 1 Document To Download: CISSP All-In-One Exam Guide 9th EditionДокумент3 страницыUpload 1 Document To Download: CISSP All-In-One Exam Guide 9th EditionnobodyОценок пока нет
- Computer Networks (Universität Paderborn)Документ3 страницыComputer Networks (Universität Paderborn)Mike MikkelsenОценок пока нет
- Ndpi - Quick Start Guide: Open and Extensible Lgplv3 Deep Packet Inspection LibraryДокумент15 страницNdpi - Quick Start Guide: Open and Extensible Lgplv3 Deep Packet Inspection LibraryLinh Nguyễn VănОценок пока нет
- Date / Day: REVIEW TEST 5 (Advanced) Paper 1 - (12:00 PM To 3:00 PM) Paper 2 - (04:00 PM To 07:00 PM)Документ26 страницDate / Day: REVIEW TEST 5 (Advanced) Paper 1 - (12:00 PM To 3:00 PM) Paper 2 - (04:00 PM To 07:00 PM)Priti tiwariОценок пока нет
- Make $100 Daily, Weekly or Monthly Using Ecoin With Payment Proof - Make Money Online PDFДокумент22 страницыMake $100 Daily, Weekly or Monthly Using Ecoin With Payment Proof - Make Money Online PDFEli AbofuorОценок пока нет
- We Can Already Define Social Media According To The TermsДокумент2 страницыWe Can Already Define Social Media According To The TermsOpa ChenkualОценок пока нет
- How To Do This in Flutter?: Flutter and Dart Cheat SheetДокумент18 страницHow To Do This in Flutter?: Flutter and Dart Cheat SheetMaaz AdreesОценок пока нет