Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Diabetes Melitus
Загружено:
Indrii LestariiАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Diabetes Melitus
Загружено:
Indrii LestariiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1. Information about Diabetes : What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects over 150 million people in the world today. The percentage of people suffering from diabetes is increasing rapidly, to the point where many medical authorities are referring to it as an epidemic. So what is diabetes? Diabetes prevents your body from turning your food into energy. nstead glucose stays in your bloodstream, and left untreated can result in a range of complications. f you have recently been diagnosed as diabetic, don!t worry. "ith proper treatment and care, you will lead a normal and happy life. #ou may need to ma$e a few changes in your lifestyle % but then, if you are li$e me, you probably had plans to do that anyway and &ust never got round to it. 'ow is the time to $ic$ yourself into action. #ou cannot leave this up to your doctor alone % it needs you to ta$e responsibility for your own treatment, and that starts with understanding what you are dealing with. There are three types of Diabetes( ) Type 1 Diabetes ) Type * Diabetes ) +estational Diabetes 2. Diabetic Testing - blood glucose monitoring for diabetics Diabetic Testing - Knowledge is Power! ,egular diabetic testing is essential for proper management of diabetes. Depending on the severity of the diabetes, a diabetic may be instructed to test their blood sugar levels as often as every two hours. -ost of the medical complications associated with diabetes are caused by the long%term effects of high blood glucose, and low blood glucose must me controlled as well. Diabetic testing e.uipment is available from most medical supply stores and pharmacies. There are many options available in diabetic testing e.uipment. The oldest techni.ue still in use involves blood glucose testing strips that are compared against a color chart li$e ph testing paper. There are also many glucose monitors available that will electronically read glucose levels off their own type of testing strips. /ll of these diabetic testing techni.ues re.uire collecting blood for the test, most often by pric$ing the fingertip with a special lancet, and s.uee0ing a drop of blood out of the finger. The finger is then pressed against the diabetic testing strip, allowing measurement of blood glucose either with an electronic blood glucose meter or testing strip color chart. -any electronic diabetic testing glucose monitors are available with speech adapters, allowing diabetics with vision problems to hear their blood glucose test results. /nother 1recently 2D/ approved3 glucose monitor reads blood glucose levels through the s$in every *0 minutes, and only needs to be calibrated twice a day with a finger pric$ blood sample. 2or diabetics who are unable to obtain a large enough blood sample with a regular finger lancet, special lancets with integrated pump devices can be used to collect blood samples from other locations. There is a lot of current research into 4non%invasive! diabetic testing e.uipment, but no home blood glucose testing techni.ues available today have entirely eliminated the need for a lancet. 5ntil then, tal$ to your doctor about your best options for diabetic testing e.uipment, and find the testing techni.ue that will ma$e it easiest for you to control your blood glucose levels. 3. Sym toms of Diabetes - ho! to tell if you are diabetic What are the main Symptoms of Diabetes? The most consistent symptom of diabetes mellitus 1Type and 3 is elevated blood sugar levels. n Type 1insulin dependent 6 early onset3 diabetes, this is caused by the body not producing enough insulin to properly regulate blood sugar. n Type 1non insulin dependent6adult onset3 diabetes, it is caused by the body developing resistance to insulin, so it cannot properly use what it produces. 7owever, high blood sugar is not something you can see in the mirror at home, so it is useful to $now the side%effects of high blood sugar, which are commonly recogni0ed as the noticeable symptoms of diabetes. f you find yourself e8periencing many of these diabetes symptoms on a consistent, long term basis, you should visit a doctor to be tested for diabetes. gnoring 1or not recogni0ing3 the symptoms of diabetes can
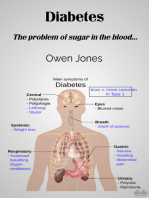
lead to long%term serious health ris$s and complications from untreated diabetes. Some of the common 4early warning! signs of diabetes are( ) The first symptom of diabetes is often e8cessive thirst 1unrelated to e8ercise, hot weather, or short% term illness3 ) 98cessive hunger 1you $now you!ve eaten :enough; but are still hungry all the time3 ) 2re.uent urination 1often noticed because you must wa$e up repeatedly during the night3 ) Tiredness and fatigue 1possibly severe enough to ma$e you fall asleep une8pectedly after meals3, one of the most common symptoms of diabetes. ) ,apid and6or sudden weight loss 1any dramatic change in weight is a sign to visit a doctor3 "hile many of the signs and symptoms of diabetes can also be related to other causes, testing for diabetes is very easy, and the constant6regular presence of one or more of these symptoms over an e8tended period of time should be cause for a visit to the doctor. f diabetes is suspected, tested for, and diagnosed when those symptoms first start appearing, other more serious symptoms of advanced diabetes can often be prevented or have their onset significantly delayed through diet, e8ercise and proper blood sugar management. 7owever, often the 4minor! symptoms of diabetes go unrecogni0ed, and physical and neurological problems may arise, resulting in some of the following symptoms( ) <lurred vision 1diabetes can lead to macular degeneration and eventual blindness3 ) 'umbness and6or tingling in the hands and feet 1peripheral neuropathy, a symptom of diabetes, causes nerve damage in the e8tremities3 ) Slow healing of minor scratches and wounds 1diabetes often leads to impaired immune system function3 ) ,ecurrent or hard%to%treat yeast infections in women 1another sign of impaired immune function3 ) Dry or itchy s$in 1peripheral neuropathy also affects circulation and proper sweat gland function3 f you are e8periencing any of these symptoms on a regular basis, or you recogni0e these symptoms in a child or relative, they may be signs of untreated diabetes. / doctor!s appointment should be made as soon as possible, so the individual e8periencing the symptoms can = if diabetes is diagnosed = ta$e the steps needed to prevent more serious health problems. ". What is Ty e 1 Diabetes? Type 1 Diabetes, 1sometimes called >uvenile Diabetes3 is usually found in young children and teenagers, but can also occur later in life. n Type 1 Diabetes, your body is not producing insulin, a hormone needed to convert blood sugar into energy. 'ormally this hormone is produced by cells in your pancreas, but for some reason this is not happening as it should. /s the glucose in your blood can!t be converted into energy and absorbed by your cells, it builds up causing high blood sugar. ?eft untreated, high blood sugar can cause serious long%term health problems. The normal treatment for people with type 1 diabetes is daily in&ections of insulin which $eeps the blood sugar level within normal ranges. 2inding out you have diabetes can be upsetting, but it should not prevent you from living a long and happy life. f you thin$ this condition will prevent you leading an active life, consider Sir Steve ,edgrave, one of the "orld!s greatest @lympic athletes. Sir Steve battled type 1 diabetes to win his record%brea$ing fifth @lympic +old medal at the Sydney games in the co8less fours rowing eventA #. What is Ty e 2 Diabetes? Type * diabetes 1sometimes called mature onset diabetes3 is the most common form of diabetes. /s with Type 1 Diabetes, the problem is related to insulin, a hormone needed to convert sugar into energy.
"ith Type * diabetes your body might be producing too little insulin, or it might not be reacting to the insulin correctly. 9ither way, the end result is that glucose builds up in the bloodstream instead of going into the cells. ?eft untreated, high blood sugar can cause serious long%term health problems. Type * diabetes usually appears later in life, often between the ages of B5%C5 years. /s it often develops slowly, many people may not recognise the symptoms, and may have diabetes without $nowing it. f you have recently been diagnosed with type * diabetes, you are one of the luc$y ones. -any people have diabetes without $nowing it, and are at much greater ris$ of long term medical complications. 2inding out you have diabetes can be upsetting, but it should not prevent you from living a long and happy life. #ou may need to ma$e a few changes in your lifestyle, but these changes are also good advice for non% diabetics, so probably a good idea anyway. $. What is %estational Diabetes? +estational diabetes is a type of diabetes, that is only suffered by pregnant women. n +estational diabetes, a woman!s blood sugar is higher than normal because of the other hormones pridcued during preganancy interfere with the insulin that is produced naturally. +estational diabetes usually becomes apparent during the *Cth to *Dth wee$s of pregnancy, and, in most cases, disappears of its own accord once the baby is born. "omen with gestational diabetes usually do '@T have an increased ris$ of having a baby with birth defects. +enerally, sufferers of gestational diabetes have normal blood sugar levels during the critical first stages of the preganancy. "hilst there can be complications caused by gestational diabetes, these can usually be managed by careful attention to nutrition and blood sugar levels. /ppro8imately B to 5 percent of all pregnant women in the developed world suffer from gestational diabetes. &. Diabetes 'anagement What is Diabetes Management, the how! and why! Eroper diabetes management is critical in preventing serious long%term complications arising from high blood sugar. 5nmanaged 1or poorly managed3 diabetes can lead to medical complications as serious as blindness, emergency amputations, or permanent damage to internal organs. @bviously, diabetes management is something every diabetic must ta$e very seriously. The cornerstone of diabetes management is $eeping your blood sugar as regular, and within healthy levels, as possible. /ll of the other effects of diabetes stem from the effects of high blood sugar. ?uc$ily, today!s diabetic has a wide variety of home e.uipment available for regularly monitoring blood sugar levels. <y $eeping close trac$ of your blood sugar throughout the day, you can learn your 4normal! responses to your medications, different foods and eating schedules, trac$ the effects of a regular e8ercise program, and discuss these patterns with your doctor, to adapt the management of your diabetes even more effectively. The basis of blood sugar management is usually a combination of medication and diet. Type diabetics must ta$e insulin because their body does not produce it properly. -anagement of Type diabetes needs to be very precise, so the diabetic!s need for insulin matches the dose they are ta$ing, preventing both high blood sugar and dangerous drops in blood sugar as well 1hypoglycemia3. n Type diabetes the body gradually becomes resistant to insulin over a span of many years. /lthough insulin is still produced, the body cannot use it effectively. Type diabetics may ta$e pills to help their body become more receptive to insulin.
n either case becoming familiar with the +lycemic nde8, which shows which foods cause blood sugar levels to rise faster than others, is an important part of proper dietary management of diabetes. 2oods with a high +lycemic nde8 will ma$e blood sugar rise very rapidly, and should be avoided. Sugars and refined carbohydrates 1!white! pasta, white bread, etc.3 are among the things at the top of the list, while whole grains 1comple8 carbohydrates3 are lower on the inde8, and proteins are near the bottom. <ecoming familiar with the +lycemic nde8, and finding which foods you li$e are safest for management of your blood sugar can ma$e overall management of your diabetes much easier. ,egular e8ercise is an important part of long term management of diabetes. Since peripheral neuropathy often has serious effects on muscle mass and control in the arms and legs, muscle%building e8ercises can be an important way of managing some of the physical effects of diabetes. Developing an effective weight training routine you can do easily in your own home may ma$e this part of your diabetes management easier than committing to going to a gym regularly. The onset of Type diabetes is strongly correlated with overweight. n some cases, if Type diabetes is diagnosed early enough, and it is a mild enough case, proper diet combined with regular e8ercise may lead to the disappearance of diabetic symptoms. "hile there is a very strong chance the diabetes will return later in life, adding a few more years of good health will certainly help minimi0e side effects later in life, and will be good 4training! for proper diabetes management when it becomes necessary again. "hile "hile e8ercise can never 4cure! Type diabetes, the different metabolic characteristics of fat versus muscle cells still ma$e e8ercise in important part of managing even Type diabetes. Diabetes management can be a comple8 process, but understanding the basics of your medication, healthy dietary choices and appropriate and regular e8ercise will provide a strong foundation for successful management of your diabetes throughout your life. (. Diabetic )eci es " collection of diabetic recipes to help with yo#r diabetic diet$ -Meat Recipes: <eef ,ecipes ( <urger ,ecipes ( Fhic$en ,ecipes ( ?amb ,ecipes ( Eor$ ,ecipes ( Sausage ,ecipes ( Tur$ey ,ecipes -Seafood Recipes: Fhowder ,ecipes ( Frab ,ecipes ( 2ish ,ecipes ( Shrimp ,ecipes ( Tuna ,ecipes -Sweet Things: <rownie ,ecipes ( Fa$e ,ecipes ( Fandy ,ecipes ( Fheeseca$e ,ecipes ( Foo$ie ,ecipes ( Dessert ,ecipes ( >elly ,ecipes ( -uffin ,ecipes ( Eanca$e ,ecipes ( Snac$ ,ecipes -Soups and Stews: Soup ,ecipes ( Fasserole ,ecipes ( Stew ,ecipes -Vegetable Recipes: /sparagus ,ecipes ( <ean ,ecipes ( <roccoli ,ecipes ( Fabbage ,ecipes ( Farrot ,ecipes ( -ushroom ,ecipes ( Eotato ,ecipes ( Sweet Eotato ,ecipes ( S.uash ,ecipes ( -isc. Gegetable ,ecipes -Other Recipes: <rea$fast ,ecipes ( <read ,ecipes ( Fheese ,ecipes ( Dips ,ecipes ( Drin$ ,ecipes ( 9gg ,ecipes ( Easta ,ecipes ( ,ice ,ecipes ( Salad ,ecipes ( Salad Dressing ,ecipes ( Seasoning ,ecipes ( Sauce ,ecipes ( Spread ,ecipes
*. Diabetic +oods, !hy -diabetic foods. are /0T re1uired. %o# do &'T need to p#rchase so called diabetic foods $ "ay bac$ in the 1HI0s, diabetics were advised to eat !sugar free! and 4low carbohydrate! diets. This meant that you couldn!t eat biscuits, ca$es, desserts, fi00y drin$s etc leading to a diet that for many was boring and dull. -anufacturers were .uic$ to offer sugar%free foods, often using fructose instead of sucrose, and a wide range of 4diabetic foods! soon appeared % many of which still contained calories and weren!t actually much better for diabetics. -ore recent research has shown that the most important target for diabetics is not a reduction in carbohydrates, but lower energy inta$e and a reduction in fat consumption. -any of the so%called diabetic foods actually contained more energy and fat than the foods they were supposed to replace. -edical advice is now very clear, it is the same as that given to non%diabetics( ) ?ow 2at ) ?ow Sugar ) ?ow Salt ) Elenty of 2ruit and Gegetables ) Elenty of Fomple8 Farbohydrates 1wholemeal bread, potatoes, grains, beans, peas, and other starchy foods3 There are '@ foods which must be completely e8cluded from a diabetic diet.. t is '@T necessary to avoid sugar competely. t S necessary to follow the advice of your medical support team and follow a diet that achieves a healthy weight. t S important to monitor your blood sugar levels and $eep them under tight control. That does not mean that you need to avoid the !so%called! diabetic foods, &ust read the labels carefully and treat them as you would any normal food. Diabetes does not mean that you need to eat boring food. #ou can find thousands of acceptable recipes on the internet % starting at our sister site( 7ealthy Diabetic ,ecipes, or from any of the site listed in the @pen Directory Diabetic ,ecipe section. 12. Diabetic %ift 3as4ets - the ideal resent for diabetes sufferers. (ift )as*ets for Diabetics - ideal for +hristmas , )irthdays Diabetic gift bas$ets are a popular way of celebrating holidays, birthdays and other special events, but when a diabetic is on your gift list, most regular gift bas$ets would not be appropriate or safe to give. Diabetics should not eat candies, syrups and sauces with sugar in them, and some diabetics also need to avoid refined carbohydrates 1such as bread, crac$ers and biscuits3 as well. ?uc$ily, many gift bas$et companies have recogni0ed the special needs of diabetics, and offer specific diabetic gift bas$ets as part of their product line. /lso, diabetic specialty food vendors may offer gift bas$ets with an assortment of their specialty diabetic foods. /nother option for a diabetic gift bas$et would be to ma$e 1or buy3 one that isn!t food oriented at all. / diabetic food gift bas$et may seem difficult if you!re thin$ing about chocolates, fruitca$es, and other sweets, but it!s not impossible to find or ma$e yourself. / wide variety of sugar%free sweets are available today, so the traditional candy%filled 9aster and 7alloween celebrations need not ma$e a diabetic feel left out. 7owever, a lot of people do not li$e the taste of artificial sweeteners, so many diabetics may choose simply not to eat sweets and candies. <ut with a little imagination 1or careful shopping3 you can still ma$e or buy a great diabetic food gift bas$et without sweets. 2resh fruits loo$ wonderful, and natural fruit sugars are much safer for a diabetic than refined sugar candies. /n 4all natural! gift bas$et with fruits, nuts and cheeses would be very safe for a diabetic, and much appreciated by someone who didn!t li$e sweeteners. /lthough some diabetics are
also sensitive to refined flours and carbohydrates, whole grain crac$ers with unsweetened spreads would be another option for the diabetic gift bas$et. f you want to avoid worrying about food altogether, personal care gift bas$ets are also an e8cellent option for diabetics. 7owever, as diabetics tend to have dry, sensitive s$in, and may not be able to use many chemically%based personal care products, try to find gift bas$ets for sensitive s$in, or select natural s$in%care products with no artificial ingredients. To ma$e things easier, diabetic supply companies often offer selections of their products in gift bas$et form, and some companies even speciali0e &ust in diabetic and other medical !special needs! gift bas$ets. / diabetic foot care gift bas$et might contain special diabetic foot lotions and hosiery, along with more traditional items li$e foot massage tools, foot soa$s and bath salts, and pedicure tools. f the diabetic on your gift list is comfortable being open about their condition, a gift bas$et featuring diabetic specialty products can not only be a lovely, en&oyable gift, but a very useful one too. There are many options for creating sugar%free diabetic safe gift bas$ets, and an increasing number of gift companies who have already done the wor$ of assembling them for you. f you plan to give gift bas$ets for an upcoming holiday, or en&oy assembling gift bas$ets for birthdays and special events, the options for diabetic gift bas$ets really aren!t as limited as you might first thin$. >ust avoid sugar, $eep refined flour ba$ed goods to a minimum, and the rest is up to you. 11. Diabetic 'edication f you suffering from Type * Diabetes, you may have been prescribed one of the following drugs( -Sulfonylureas @ther names include /maryl, Fhlorpropamide, Diabinese, Tola0amide, Tolinase, /cetohe8amide, +lipi0ide, +lucotrol, Tolbutamide @rinase, +limepiride, +lyburide 1Dia<eta, -icronase3, +libenclamide, and +licla0ide. -Meglitinides @ther names include include Erandin 1,epaglinide3, Starli8 1'ateglinide3, and -itiglinide -Biguanides @ther names include -etformin and +lucophage. -Thiazolidinedione @ther names inlcude ,osiglita0one, /vandia, Eioglita0one and /ctos. -Alpha- lucosidase !nhibitors @ther names include /carbose, Erecose, +lucobay, -iglitol and +lyset. f you can!t find what you are loo$ing for here, you can find further diabetes drug information at the '7S
Вам также может понравиться
- Diabetes Diet: How to improve, manage, and prevent diabetes with the help of food!От EverandDiabetes Diet: How to improve, manage, and prevent diabetes with the help of food!Оценок пока нет
- Diabetes: Reverse Your Diabetes With a Clear and Concise Step by Step GuideОт EverandDiabetes: Reverse Your Diabetes With a Clear and Concise Step by Step GuideРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- Could You Have Diabetes and Not Even Know ItДокумент23 страницыCould You Have Diabetes and Not Even Know Itsnapel itОценок пока нет
- DiabetesДокумент10 страницDiabetesFatima El HassouniОценок пока нет
- DiabetesДокумент10 страницDiabetesFatima El HassouniОценок пока нет
- Type 2 Diabetes Cookbook for Beginners: Mastering Balanced, Low-Sugar Eating for Enhanced Well-being and Effective Diabetes Control [V EDITION]От EverandType 2 Diabetes Cookbook for Beginners: Mastering Balanced, Low-Sugar Eating for Enhanced Well-being and Effective Diabetes Control [V EDITION]Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (7)
- Type 2 Diabetes: How to Eat Better, Lower Blood Sugar, and Manage DiabetesОт EverandType 2 Diabetes: How to Eat Better, Lower Blood Sugar, and Manage DiabetesОценок пока нет
- Can Diabetes be Cured?: Reverse it Naturally FastОт EverandCan Diabetes be Cured?: Reverse it Naturally FastРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- How to Manage Diabetes and Cure?: Dr. Alan's Step By Step Guide for Diabetes Management Including General Tips, Diet Plan, Exercise Routine and Much More!От EverandHow to Manage Diabetes and Cure?: Dr. Alan's Step By Step Guide for Diabetes Management Including General Tips, Diet Plan, Exercise Routine and Much More!Оценок пока нет
- Presentation NotesДокумент9 страницPresentation Notesljules sterОценок пока нет
- The Complete Guide to Type 1 Diabetes: Symptoms, Risks, Treatments and Support for DiabeticsОт EverandThe Complete Guide to Type 1 Diabetes: Symptoms, Risks, Treatments and Support for DiabeticsОценок пока нет
- Lower Your Blood Sugar: The 30 Minute Guide for People with Diabetes, Prediabetes, and Insulin Resistance: Blood Sugar 101 Short Reads, #1От EverandLower Your Blood Sugar: The 30 Minute Guide for People with Diabetes, Prediabetes, and Insulin Resistance: Blood Sugar 101 Short Reads, #1Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Truth About DiabetesДокумент12 страницTruth About DiabetesAmyHolderWilsonОценок пока нет
- Diabetes Mellitus And Its Complications, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandDiabetes Mellitus And Its Complications, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Case Study in DMДокумент34 страницыCase Study in DMKathrina Marie B. BinaraoОценок пока нет
- Diabetes Basics: Signs and SymptomsДокумент5 страницDiabetes Basics: Signs and Symptomsindigopussycat2Оценок пока нет
- Blood Sugar: What You Need To Know, The Optimal Lifestyle Plan For Preventing Diseases, Diabetes, Losing Weight & Natural, Amazing HealthОт EverandBlood Sugar: What You Need To Know, The Optimal Lifestyle Plan For Preventing Diseases, Diabetes, Losing Weight & Natural, Amazing HealthОценок пока нет
- Natural Remedies To Pre-Diabetes: Reverse Type 2 Diabetes Naturally in 90 DaysОт EverandNatural Remedies To Pre-Diabetes: Reverse Type 2 Diabetes Naturally in 90 DaysОценок пока нет
- Blood GlucoseДокумент12 страницBlood Glucosehajidah hassanalОценок пока нет
- Diabetes: The Most Effective Ways and Step by Step Guide to Reverse DiabetesОт EverandDiabetes: The Most Effective Ways and Step by Step Guide to Reverse DiabetesОценок пока нет
- A Pre-diabetic's Guide to Stopping the Progression of DiabetesОт EverandA Pre-diabetic's Guide to Stopping the Progression of DiabetesРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- Diabetes Miracle Cure: How To Overcome Diabetes ForeverОт EverandDiabetes Miracle Cure: How To Overcome Diabetes ForeverРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- What Is DiabetesДокумент12 страницWhat Is DiabetesWaheed LateefОценок пока нет
- Dermatology Surgeries PhoenixДокумент3 страницыDermatology Surgeries Phoenixleocpelletier1Оценок пока нет
- Defeat Diabetes With A Vegan DietДокумент48 страницDefeat Diabetes With A Vegan DietVegan Future100% (1)
- Type 1 DiabetesДокумент7 страницType 1 DiabetesEimor PortezОценок пока нет
- The Everything Pre-Diabetes Cookbook: Includes Sweet Potato Pancakes, Soy and Ginger Flank Steak, Buttermilk Ranch Chicken Salad, Roasted Butternut Squash Pasta, Strawberry Ricotta Pie ...and hundreds more!От EverandThe Everything Pre-Diabetes Cookbook: Includes Sweet Potato Pancakes, Soy and Ginger Flank Steak, Buttermilk Ranch Chicken Salad, Roasted Butternut Squash Pasta, Strawberry Ricotta Pie ...and hundreds more!Оценок пока нет
- What Is DiabetesДокумент7 страницWhat Is DiabetesBryan Erazo Menendez MaciasОценок пока нет
- Diabetes Care Regent Street SurgeryДокумент6 страницDiabetes Care Regent Street SurgeryIan LakeОценок пока нет
- Blood Sugar Insulin Polyuria Polydipsia PolyphagiaДокумент7 страницBlood Sugar Insulin Polyuria Polydipsia PolyphagiankirrОценок пока нет
- DM Case StudyДокумент39 страницDM Case StudyShella Mae Usquisa100% (1)
- DiabetesДокумент8 страницDiabeteszach000023Оценок пока нет
- The Comprehensive Guide to Diabetes Management Living Well Without Complications: Healthy Living, #1От EverandThe Comprehensive Guide to Diabetes Management Living Well Without Complications: Healthy Living, #1Оценок пока нет
- What Is Diabetes? What Causes Diabetes?: Fast Facts On DiabetesДокумент6 страницWhat Is Diabetes? What Causes Diabetes?: Fast Facts On DiabetesAlfred Melvin SolivaОценок пока нет
- Insulin Resistance Cookbook: Your Guide to Beating Insulin Resistance with 20 Go-To Recipes!: Diabetes and Blood Sugar LevelОт EverandInsulin Resistance Cookbook: Your Guide to Beating Insulin Resistance with 20 Go-To Recipes!: Diabetes and Blood Sugar LevelОценок пока нет
- DMCaseДокумент4 страницыDMCaseFRANCISCO, QUENNIE MARIE D.Оценок пока нет
- Type2 Diabetes HandoutДокумент1 страницаType2 Diabetes Handouthendra_darmawan_4Оценок пока нет
- Abnormal Blood Glucose LevelДокумент23 страницыAbnormal Blood Glucose LevelAyush BhattОценок пока нет
- Dr Sebi Cure for Diabetes: The Revolutionary Method to Prevent and Quickly Reverse Type 1 and 2 Diabete following the Dr Sebi Alkaline DietОт EverandDr Sebi Cure for Diabetes: The Revolutionary Method to Prevent and Quickly Reverse Type 1 and 2 Diabete following the Dr Sebi Alkaline DietРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (4)
- Prediabetes Diet: A Beginner's Step-by-Step Guide to Reversing Prediabetes: Includes Curated Recipes and a Meal PlanОт EverandPrediabetes Diet: A Beginner's Step-by-Step Guide to Reversing Prediabetes: Includes Curated Recipes and a Meal PlanОценок пока нет








![Type 2 Diabetes Cookbook for Beginners: Mastering Balanced, Low-Sugar Eating for Enhanced Well-being and Effective Diabetes Control [V EDITION]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/616633879/149x198/173640cf06/1710278044?v=1)