Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Introduction To Microeconomics - Basics of Macroeconomics
Загружено:
ccblueprintИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Introduction To Microeconomics - Basics of Macroeconomics
Загружено:
ccblueprintАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
MACROECONOMICS TERMINOLOGY
Aggregate demand; Total demand for goods and services in an economy Nominal interest rate; Value of the interest rate Real interest rate; Adjusted value of the Nominal interest after adjusting for the inflation Liquidity; Amount of capital that is available for investment and spending Money supply; The total amount of monitory assets available in an economy. Government bond; Bond issued by national government promising to pay certain amount of money in certain amount of time Open market operations; Any buying of selling of government securities. Volatility; Frequency the price changes in a mrket.(Higher the volatility higher the risk Liquidity; The degree asset that can be converted in to cash quickly without affecting with minimal impact to the price bought. Eg; Bank account High liquidity investment Real estate Low liquidity investment Price level = Price of the goods and services . Crowding out effect = low aggregate demand caused due to higher public spending Purchasing power ; Amount of goods and services that can be bought with a unit of currency
Prabudda Missaka s3211475
Page 1
TREE REASONS FOR THE DOWNWARD SLOPE OF AGGREGATE DEMAND CURVE 1. Wealth effect 2. Interest rate effect 3. Exchange rate effect
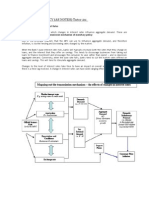
WEALTH EFFECT Inflation rise Purchase power decrease Output demanded Decreases INTEREST RATE EFFECT Increase in savings Increase in loanable funds Decrease in real interest rates Increase investment Increase the aggregate demand EXCAHNGE RATE EFFECT Inflation increases interest rates increase Foreign investment increases due to high interest rates Demand for dollar increases Dollar appreciates in Foreign exchange Foreign goods become cheaper Domestic imports increases, Export decreases Low demand for domestic output
Prabudda Missaka s3211475
Page 2
CROWDING OUT EFFECT Increase in government spending Increase in interest rates Reduce private investment
MAIN CAUSES OF INFLATION
1. 2. 3. Demand pull inflation Demand for goods goes up Cost push inflation Supply goes down monopoly, natural disasters, depletion of natural resources Monitory expansion
WAYS OF EXPANDING MONEY SUPPLY
1. 2. 3. Reducing federal reserve requirement Reducing fed funds rate Printing money
WHAT CAUSES BUSINESS CIRCLE
1. 2. Supply and demand Liquidity (availability of capital)
** money supply of a country is controlled by RBA through open market operations
Prabudda Missaka s3211475
Page 3
EFFECTS OF LOW INTEREST RATES
1. 2. 3. Economy grows faster People spend more High inflation
THEORY OF LIQUIDITY PREFERENCE
** As interest rates rise demand for money decreases (People get more money by keeping money in banks) **As interest rates decrease demand for money increases (Can loan money for low interest rate)
MONEY SUPPLY
Prabudda Missaka s3211475
Page 4
EQUILIBRIUM IN THE MONEY MARKET
MULTIPLIER EFFECT Every time there is a new demand on to the circular floor the is likely to be a multiplier effect Eg, If the MPC is 3/4, then the multiplier will be: Multiplier = 1/(1 3/4) = 4 In this case, a $5 billion increase in government spending generates $20 billion of increased demand for goods and services.crouding effect
Formula for the spending multiplier Multiplier = 1/(1-MPC) MPC= marginal Propensity to consume
Prabudda Missaka s3211475
Page 5
TXATION AND AGGREGATE DEMAND
Changing tax rates affect the consumer spending . This cause a shift in aggregate demand
FACTORS EFFECT THE UNEMPLOMENT
1. 2. 3. Minimum wage laws Market power of unions Effectiveness of job seach
MARKET POWER
Ability of a firm to change the market price of a good
SHORT RUN TRADE OFF
Inverse relationship of two factors Eg. Short run trade off between Inflation and Unemployment
(Low unemployment higher spending Higher inflation )
THE PHILLIPS CURVE
Relationship between Inflation and unemployment
Prabudda Missaka s3211475
Page 6
PHILLIPS CURVE IN THE SHORT RUN
PHILLIPS CURVE IN THE LONG RUN
There is no connection between unemployment and inflation in the long run. So in the long run Phillips curve is a vertical line
Prabudda Missaka s3211475
Page 7
Unemployment rate = Natural Rate of unemployment a (Actual inflation Expected inflation)
NATURAL RATE OF UNEMPLOYMENT
NAIRU (the non-accelerating inflation rate of unemployment).
UNEMPLOYMENT RATE
STABILISING THE ECONOMY
There are lags in fiscal and monitory policies Government can use stabilisation policy to stable the economy
AUTOMATIC STABILISER S
Ta x system Unemployment benefit
Prabudda Missaka s3211475
Page 8
Вам также может понравиться
- MGMT 702 Fall 2021 Research and Case Analysis No. 1 (10%) Part B (Warren Buffett and Berkshire Hathaway Inc.) - QuestionsДокумент5 страницMGMT 702 Fall 2021 Research and Case Analysis No. 1 (10%) Part B (Warren Buffett and Berkshire Hathaway Inc.) - QuestionsJesus D. RiosОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 Sample ProblemsДокумент3 страницыChapter 6 Sample ProblemsShaiTengcoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 34 NotesДокумент3 страницыChapter 34 NotesFahad SiddiquiОценок пока нет
- Multiplier EffectДокумент4 страницыMultiplier EffectPetronella BrownОценок пока нет
- Business Cycle NotesДокумент15 страницBusiness Cycle NotesNhlanhlakaziОценок пока нет
- An Introduction To Aggregate DemandДокумент4 страницыAn Introduction To Aggregate Demandvngo0234Оценок пока нет
- InflationДокумент40 страницInflationRosebell MelgarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9Документ8 страницChapter 9LanaОценок пока нет
- Money & BankingДокумент31 страницаMoney & BankingMohsin BhattiОценок пока нет
- Chap 16Документ8 страницChap 16Humaid SaifОценок пока нет
- Demand-Side Policy: Fiscal Policy: (Definition of Fiscal Policy) (Limitation of Fiscal Policy: Small K Value)Документ2 страницыDemand-Side Policy: Fiscal Policy: (Definition of Fiscal Policy) (Limitation of Fiscal Policy: Small K Value)layshengОценок пока нет
- Macroeconomic and Industry AnalysisДокумент4 страницыMacroeconomic and Industry AnalysisFajar TaufiqОценок пока нет
- Ch6 F1 ACCA BPPДокумент35 страницCh6 F1 ACCA BPPIskandar BudionoОценок пока нет
- II. Exchange Rates - Macroeconomic Effects of Currency FluctuationsДокумент6 страницII. Exchange Rates - Macroeconomic Effects of Currency FluctuationsKent Lawrence A. CalunsagОценок пока нет
- A Persistent Increase in The Level of Consumer Prices or A Persistent Decline in The Purchasing Power of Money... "Документ6 страницA Persistent Increase in The Level of Consumer Prices or A Persistent Decline in The Purchasing Power of Money... "marketfreekОценок пока нет
- Agriculture and Fishery Arts Handout 3Документ9 страницAgriculture and Fishery Arts Handout 3Jonas CabacunganОценок пока нет
- Aggregate Demand & Aggregate SupplyДокумент41 страницаAggregate Demand & Aggregate SupplyAlison FernandesОценок пока нет
- Monetary and Fiscal PolicyДокумент5 страницMonetary and Fiscal PolicyJanhavi MinochaОценок пока нет
- Economics Notes - 2Документ17 страницEconomics Notes - 2sindhu pОценок пока нет
- Presentation Economics Sajal & MehulДокумент14 страницPresentation Economics Sajal & MehulMehul SolankiОценок пока нет
- Economics M6 BДокумент2 страницыEconomics M6 BkristerОценок пока нет
- McConnell Macro12ce Ch10Документ29 страницMcConnell Macro12ce Ch10senthilbala100% (1)
- Cat 1 Bba 123 MacroeconomicsДокумент3 страницыCat 1 Bba 123 Macroeconomicselijah thonОценок пока нет
- Inflation Its Causes and EffectsДокумент28 страницInflation Its Causes and EffectsPoonam SharmaОценок пока нет
- RecessionДокумент3 страницыRecessionBharathi SivaОценок пока нет
- Macro Economics Group AssignmentДокумент5 страницMacro Economics Group AssignmentAbraham BizualemОценок пока нет
- 2.3 Critically Analyze Some Macro-Economic Factors Which May Affect The Currency Behavior in The FutureДокумент7 страниц2.3 Critically Analyze Some Macro-Economic Factors Which May Affect The Currency Behavior in The FuturesheetalОценок пока нет
- Macro Economics: Inflation and UnemploymentДокумент11 страницMacro Economics: Inflation and UnemploymentHashim RiazОценок пока нет
- Influence of Monetary and Fiscal PolicyДокумент14 страницInfluence of Monetary and Fiscal PolicyraviОценок пока нет
- Topic 4 The MacroeconomyДокумент61 страницаTopic 4 The MacroeconomyRashid okeyoОценок пока нет
- Inflation Impact On EconmyДокумент4 страницыInflation Impact On EconmyRashid HussainОценок пока нет
- MarshallДокумент9 страницMarshallSam CatlinОценок пока нет
- Business CyclesДокумент18 страницBusiness CyclesshruthinОценок пока нет
- Mohd Ayaz Raza BM 111 Asssingment 1Документ7 страницMohd Ayaz Raza BM 111 Asssingment 1Mohd Ayaz RazaОценок пока нет
- InflationДокумент21 страницаInflationmouli poliparthiОценок пока нет
- MACROECONOMICSДокумент9 страницMACROECONOMICSTawanda Leonard CharumbiraОценок пока нет
- Economics: A Project Report On Inflation in Post-Reform PeriodДокумент12 страницEconomics: A Project Report On Inflation in Post-Reform PeriodDishant MittalОценок пока нет
- In de StagflationДокумент24 страницыIn de StagflationSHEKHAWAT FAMILYОценок пока нет
- Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyДокумент8 страницAggregate Demand and Aggregate Supplysattwikd77Оценок пока нет
- New Ad & AsДокумент51 страницаNew Ad & Asayushshrimal000_2201Оценок пока нет
- ch9 Lecture & Textbook NotesДокумент10 страницch9 Lecture & Textbook Notes47fwhvhc6kОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyДокумент21 страницаChapter 9 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyHieptaОценок пока нет
- What Is Aggregate DemandqwertДокумент9 страницWhat Is Aggregate DemandqwertShahana KhanОценок пока нет
- HW5 question 4详细解答Документ1 страницаHW5 question 4详细解答weijuanshihkuОценок пока нет
- Inflation: Parag Rastogi Pgpabm 2008-10Документ15 страницInflation: Parag Rastogi Pgpabm 2008-10rastogi paragОценок пока нет
- 1606122274.575.1.1.macroeconomics 2 1606122274 Kaunda RobertДокумент19 страниц1606122274.575.1.1.macroeconomics 2 1606122274 Kaunda RobertMaxwell chandaОценок пока нет
- Inflation XXДокумент20 страницInflation XXAvdhi JainОценок пока нет
- Reduction in Interest RatesДокумент1 страницаReduction in Interest RatesAmira BabaganaОценок пока нет
- Technical Questions 1 and 3 On P. 414. in Our Textbook Pg. No. 444Документ4 страницыTechnical Questions 1 and 3 On P. 414. in Our Textbook Pg. No. 444Ehab ShabanОценок пока нет
- What Is Aggregate DemandqwertДокумент8 страницWhat Is Aggregate DemandqwertShahana KhanОценок пока нет
- Finance For DevelopmentДокумент6 страницFinance For Developmentsyeda maryemОценок пока нет
- Word ReportДокумент9 страницWord ReportDhruvansh sharmaОценок пока нет
- Monetary Policy (As Notes) Tutor 2U:: Effects of Changes in Interest RatesДокумент3 страницыMonetary Policy (As Notes) Tutor 2U:: Effects of Changes in Interest Ratesch_1890Оценок пока нет
- A. Aggregate Expenditures: Macroeconomics Unit 3Документ20 страницA. Aggregate Expenditures: Macroeconomics Unit 3Shoniqua JohnsonОценок пока нет
- Remedies For Balance of Payments DeficitДокумент4 страницыRemedies For Balance of Payments DeficitAmjad Rashid BhattiОценок пока нет
- Aggregate DemandДокумент10 страницAggregate DemandFaraz AhmadОценок пока нет
- Effects of Inflation in Our CountryДокумент16 страницEffects of Inflation in Our CountrySohaib JavedОценок пока нет
- Business Cycles, Inflation and UnemploymentДокумент18 страницBusiness Cycles, Inflation and Unemploymentrajan tiwariОценок пока нет
- Aggregate Supply DemandДокумент9 страницAggregate Supply DemandDom PaciaОценок пока нет
- 8 Batch Question SolveДокумент5 страниц8 Batch Question Solvemdkhairulalam19920Оценок пока нет
- Exercise List No 2 Portnova Irina MpgiДокумент9 страницExercise List No 2 Portnova Irina MpgiPortnovaIОценок пока нет
- Frankfinn Franchisee ROI - Moradabad - Jan 2020 - Ver 3.0Документ1 страницаFrankfinn Franchisee ROI - Moradabad - Jan 2020 - Ver 3.0riyaz9999Оценок пока нет
- Requirement 1 Total Per Unit: Banitog, Brigitte C. BSA 211 Exercise 1 (Contribution Format Income Statement)Документ4 страницыRequirement 1 Total Per Unit: Banitog, Brigitte C. BSA 211 Exercise 1 (Contribution Format Income Statement)MyunimintОценок пока нет
- HOUSING LWOB General Guidelines Final - OVPv7Документ4 страницыHOUSING LWOB General Guidelines Final - OVPv7Olivia AbacОценок пока нет
- SAMRATДокумент3 страницыSAMRATsamaОценок пока нет
- Bank of India Indeminity YelwandeДокумент5 страницBank of India Indeminity YelwandeRohit PardeshiОценок пока нет
- Business Studies Formula Sheet - AS PDFДокумент4 страницыBusiness Studies Formula Sheet - AS PDFAdnan Haider NoorОценок пока нет
- Module 3 - Different Kinds of ObligationsДокумент62 страницыModule 3 - Different Kinds of ObligationsZee GuillebeauxОценок пока нет
- Payment PDFДокумент1 страницаPayment PDFAMAN SAURAVОценок пока нет
- GAC02A2 QUESTION 2 Suggested Solution - Learning VisibleДокумент4 страницыGAC02A2 QUESTION 2 Suggested Solution - Learning VisibleNandi MliloОценок пока нет
- Intermediate 1A: Problem CompilationДокумент24 страницыIntermediate 1A: Problem CompilationPatricia Nicole Barrios100% (4)
- Fundamentals of Abm 2 Grade 11 Midterm Exam S.Y. 2019 - 2020Документ2 страницыFundamentals of Abm 2 Grade 11 Midterm Exam S.Y. 2019 - 2020Sheena RobiniolОценок пока нет
- Security Analysis Portfolio Management AssignmentДокумент4 страницыSecurity Analysis Portfolio Management AssignmentNidhi ShahОценок пока нет
- Berkenkotter vs. Cu Unjieng, Mabalacat Sugar, and Sheriff of Pampanga G.R. No. L-41643, July 31, 1935Документ1 страницаBerkenkotter vs. Cu Unjieng, Mabalacat Sugar, and Sheriff of Pampanga G.R. No. L-41643, July 31, 1935Edeniel CambarihanОценок пока нет
- Characteristics of The RestaurantДокумент2 страницыCharacteristics of The RestaurantSudhansuSekharОценок пока нет
- 2AДокумент14 страниц2ADarshan gowdaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Notes ReceivableДокумент13 страницChapter 5 Notes ReceivableAJ Jahara GapateОценок пока нет
- BSM Toolbox OriginalДокумент651 страницаBSM Toolbox Originalrdixit2Оценок пока нет
- Executive Personal Assistant in CT Manhattan NY Resume Jo Ann PowersДокумент2 страницыExecutive Personal Assistant in CT Manhattan NY Resume Jo Ann PowersJoAnnPowersОценок пока нет
- ObliconДокумент7 страницObliconGIRLОценок пока нет
- YakДокумент35 страницYakImran PathanОценок пока нет
- Book Keeping and Accounts Level 2 Model Answers Series 4 2013Документ11 страницBook Keeping and Accounts Level 2 Model Answers Series 4 2013Angelina Papageorgiou100% (1)
- PR Ley 293, 2004 InglesДокумент6 страницPR Ley 293, 2004 InglesCORALationsОценок пока нет
- FIN3033 Week5Документ22 страницыFIN3033 Week5Amira SyahiraОценок пока нет
- July 23Документ4 страницыJuly 23SHANTANU VERMAОценок пока нет
- Literature ReviewДокумент4 страницыLiterature ReviewRenjitha DevОценок пока нет
- 0002 T en - Ar.enДокумент33 страницы0002 T en - Ar.enriyasudheenmhОценок пока нет
- PT INDOFOOD CBP SUKSES MAKMUR TBK DAN ENTITAS ANAKNYAДокумент3 страницыPT INDOFOOD CBP SUKSES MAKMUR TBK DAN ENTITAS ANAKNYARama fauziОценок пока нет
- Insuring The Frontier MarketsДокумент35 страницInsuring The Frontier MarketsHarry CerqueiraОценок пока нет