Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Math 317 - Assignment #6 (Solutions)
Загружено:
wenderdoodleАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Math 317 - Assignment #6 (Solutions)
Загружено:
wenderdoodleАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
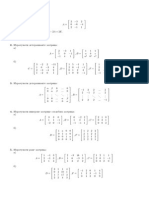
SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT # 6
1. Find a parametric representation of the following surfaces:
(a) that part of the ellipsoid
_
x
a
_
2
+
_
y
b
_
2
+
_
z
c
_
2
= 1 with y 0, where a, b, c are
positive constants.
(b) that part of the elliptical paraboloid x + y
2
+ 2z
2
= 4 that lies in front of the
plane x = 0.
(c) that part of the surface z
2
= x
2
y
2
that lies in the rst octant.
Solution:
(a) A particular parametrization is
y = b
_
1
_
x
a
_
2
_
z
c
_
2
, where
_
x
a
_
2
+
_
z
c
_
2
1
(b) We must have 0 x 4. A particular parametrizatrion is
y =
4 x cos , z =
4 x
2
sin , where 0 x 4, 0 2.
(c) We must have x 0, y 0, z 0 and x y. A particular parametrization is
x = r cos , y = r sin , z = r
cos 2, 0 r < , 0 /4.
2. Find an equation of the tangent plane of the given parametric surfaces at the point
indicated:
(a) r = u
2
i + v
2
j + uvk, u = 1, v = 1.
(b) the surface that you get by rotating z = e
y
, 0 < y < , about the z-axis, at
the point
_
1
2
,
3
2
,
1
e
_
. Hint: polar coordinates.
Solution:
(a) r
u
= 2ui + vk = 2i + k, r
v
= 2vj + uk = 2j + k, and so r
u
r
v
= 2i 2j + 4k.
An equation of the tangent plane is therefore (x 1) (y 1) + 2(z 1) = 0, or
2z x y = 0.
(b) A particular parametrization is
x = cos , y = sin , z = e
, 0 < < , 0 2.
1
The point (x, y, z) = (1/2,
3/2, e
1
) corresponds to = /3, = 1. Thus
r = cos i + sin j + e
k =
1
2
i +
3
2
j + e
1
k
r
= cos i + sin j e
k =
1
2
i +
3
2
j e
1
k
r
= sin i + cos j =
3
2
i +
1
2
j
r
=
1
2
e
1
i +
3
2
e
1
i +k
Thus the tangent plane is x +
3y + 2ez = 4, after some algebra.
3. Find the surface area of the following surfaces.
(a) The part of the surface z = 1 +3x +2y
2
that lies above the triangle with vertices
(0, 0), (0, 1), (2, 1).
(b) The spiral ramp r = ucos vi + usin vj + vk, 0 u 1, 0 v .
Solution:
(a) Let D = {(x, y) | 0 y 1, 0 x 2y}. Then the surface area is
S =
_ _
D
_
1 + 9 + 16y
2
dA =
_
y=1
y=0
_
x=2y
x=0
_
10 + 16y
2
dxdy
=
_
y=1
y=0
2y
_
10 + 16y
2
dy =
1
24
(10 + 16y
2
)
3/2
y=1
y=0
=
1
24
(26
3/2
10
3/2
)
(b)
r
u
= cos vi + sin vj
r
v
= usin vi + ucos vj +k
r
u
r
v
= sin vi cos vj + uk
|r
u
r
v
| =
1 + u
2
Therefore the surface area is
S =
_
v=
v=0
_
u=1
u=0
1 + u
2
dudv =
_
u=1
u=0
1 + u
2
du
=
2
_
u
u
2
+ 1 + ln(u +
u
2
+ 1)
_
u=1
u=0
=
2
(
2 + ln(1 +
2))
2
4. Evaluate the following surface integrals.
(a)
_ _
S
yzdS, where S is the rst octant part of the plane x + y + z = , where
is a positive constant.
(b)
_ _
S
(x
2
z + y
2
z)dS, where S is the hemisphere x
2
+ y
2
+ z
2
= a
2
, z 0.
Solution:
(a)
_ _
S
yzdS =
_
y=
y=0
_
x=y
x=0
y( x y)
3dxdy
=
3
_
y=
y=0
_
y( y)
2
y
( y)
2
2
_
dy
=
3
2
_
y=
y=0
y( y)
2
dy =
3
2
_
y=
y=0
_
y
2
2y
2
+ y
3
_
dy
=
3
2
_
4
2
2
4
3
+
4
4
_
=
3
4
24
(b) We use spherical coordinates to evaluate this integral.
_ _
S
(x
2
z + y
2
z)dS =
_
=2
=0
_
=/2
=0
(a
2
sin
2
)(a cos )(a
2
sin )dd
= 2a
5
_
=/2
=0
sin
3
cos d = 2a
5
sin
4
=/2
=0
=
a
5
2
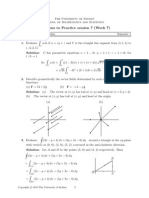
5. Let S be the surface you get by rotating the circle (xa)
2
+z
2
= b
2
, where 0 < b < a,
about the z-axis.
(a) Sketch the surface S.
(b) Find a parametric representation of S.
(c) Find the unit outward normal at every point of S.
Solution:
(a) This surface is a torus. For a sketch see question # 56 on page 1145.
(b) Using the angles , from page 1145 we see that a parametrization is
x = (a + b cos ) cos , y = (a + b cos ) sin , z = b sin
(c) The position vector for a point on the torus is
r = xi + yj + zk = (a + b cos ) cos i + (a + b cos ) sin j + b sin k
3
Therefore
r
= (a + b cos ) sin i + (a + b cos ) cos j
r
= b sin cos i b sin sin j + b cos k
r
= (a + b cos ) (b cos cos i + b sin cos j + b sin k)
r
|r
|
= cos cos i + sin cos j + sin k
Putting = 0, = 0 gives
r
|r
|
= i, the unit outward normal at this point.
Therefore the outward unit normal is n = cos cos i + sin cos j + sin k.
4
Вам также может понравиться
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsОт EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Coplex Number FormulasДокумент7 страницCoplex Number FormulasMohan KhedkarОценок пока нет
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankОт EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankОценок пока нет
- Sol 4 Fall 04Документ12 страницSol 4 Fall 04Daniel Cervantes CabreraОценок пока нет
- Matematika 2 ZadaciДокумент5 страницMatematika 2 Zadacivericak66Оценок пока нет
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankОт EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- Double IntegralsДокумент4 страницыDouble IntegralsJimuel Adrian Punzalan100% (1)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageОт EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageОценок пока нет
- Solutions To Assignment #10, Math 253Документ4 страницыSolutions To Assignment #10, Math 253Alex TanОценок пока нет
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesОт EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesРейтинг: 1.5 из 5 звезд1.5/5 (2)
- FE Math PracticeДокумент8 страницFE Math PracticeAdam Wilkins71% (7)
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesОт EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesОценок пока нет
- Application of Derivative ASSIGNMENT FOR IIT-JEEДокумент15 страницApplication of Derivative ASSIGNMENT FOR IIT-JEEApex Institute100% (1)
- Essential Formulae: Number and AlgebraДокумент7 страницEssential Formulae: Number and AlgebraShinigami01001Оценок пока нет
- Advanced Technology M7 "Fields and Waves" Vector Field TheoryДокумент8 страницAdvanced Technology M7 "Fields and Waves" Vector Field TheorysFDfdsОценок пока нет
- Calculus of Multivariable - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2007Документ24 страницыCalculus of Multivariable - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2007Muhammad UmairОценок пока нет
- Graphs Quadratic InequalitiesДокумент5 страницGraphs Quadratic InequalitiesEscudero, Mae FelizОценок пока нет
- Midterm 100 SolДокумент6 страницMidterm 100 Solsfluk2Оценок пока нет
- Math 55 Exercises First ExamДокумент2 страницыMath 55 Exercises First ExamAngelica CanoОценок пока нет
- Homework Sol3Документ4 страницыHomework Sol3claudia0510Оценок пока нет
- MT261 Tutorial 3Документ4 страницыMT261 Tutorial 3Gilbert FuriaОценок пока нет
- Solutions To Tutorial 1 (Week 2) : Lecturers: Daniel Daners and James ParkinsonДокумент11 страницSolutions To Tutorial 1 (Week 2) : Lecturers: Daniel Daners and James ParkinsonTOM DAVISОценок пока нет
- Iit - Jee Model Grand Test - Ii Paper - 1 SolutionsДокумент6 страницIit - Jee Model Grand Test - Ii Paper - 1 SolutionsSayan Kumar KhanОценок пока нет
- MATH 20E - Final Exam: Solutions To Practice Problems: Alina BucurДокумент9 страницMATH 20E - Final Exam: Solutions To Practice Problems: Alina BucurJames Hyun Wook ParkОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 ExamplesДокумент7 страницChapter 1 ExamplesSharvin VananОценок пока нет
- 1131calcprobonly MoodleДокумент53 страницы1131calcprobonly MoodleLatasha SteeleОценок пока нет
- Assign 4Документ1 страницаAssign 4Kush Ganatra ch19b063Оценок пока нет
- TS 1 - 105200Документ2 страницыTS 1 - 105200KAPEMBWA MAPALOОценок пока нет
- Assignment4 SolДокумент6 страницAssignment4 SolKush Ganatra ch19b063Оценок пока нет
- MAE200B - Homework No. 1: Laura Novoa January 15, 2016Документ14 страницMAE200B - Homework No. 1: Laura Novoa January 15, 2016Laura NovoaОценок пока нет
- MAL120 Tutorial Sheet 1 24 JAN FINAL With AnswersДокумент2 страницыMAL120 Tutorial Sheet 1 24 JAN FINAL With AnswersYoteshYadavОценок пока нет
- MA1505 Tutorial Solution 1Документ6 страницMA1505 Tutorial Solution 1Bilguun BatboldОценок пока нет
- Summer Term End Examination - July 2013: Xyz XZДокумент0 страницSummer Term End Examination - July 2013: Xyz XZPratyush MishraОценок пока нет
- Vector Calculus - Solutions 1: 1. in Each Case, S Is The Shaded Region, Excluding Any Hatched Lines/curves. (A) (B)Документ7 страницVector Calculus - Solutions 1: 1. in Each Case, S Is The Shaded Region, Excluding Any Hatched Lines/curves. (A) (B)Zohiab ZafarОценок пока нет
- Outline of Solutions To Homework 1Документ3 страницыOutline of Solutions To Homework 1Michel AndradeОценок пока нет
- Vector Calc Final Solutions - CaltechДокумент7 страницVector Calc Final Solutions - CaltechDezire GetОценок пока нет
- VectorДокумент9 страницVectorksuzukОценок пока нет
- Maths QP Ans CET-2013Документ9 страницMaths QP Ans CET-2013pacesoft3210% (1)
- Matek KepletekДокумент2 страницыMatek KepletekblackjackkОценок пока нет
- Answer To Odd ProblemsДокумент18 страницAnswer To Odd ProblemsSingh KaranОценок пока нет
- Maths II IISemДокумент5 страницMaths II IISemvrsafeОценок пока нет
- Multivariable Calculus, 2007-10-26. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526Документ5 страницMultivariable Calculus, 2007-10-26. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526lieth-4Оценок пока нет
- Exam - 2013 10 30Документ5 страницExam - 2013 10 30lieth-4Оценок пока нет
- Area of BodedДокумент5 страницArea of BodedthinkiitОценок пока нет
- Complex Analysis 1998Документ24 страницыComplex Analysis 1998Suresh KannanОценок пока нет
- Solutions To Homework Assignment #4, Math 253Документ6 страницSolutions To Homework Assignment #4, Math 253QwaAlmanlawiОценок пока нет
- Multivariable Calculus, 2007-03-15. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526Документ5 страницMultivariable Calculus, 2007-03-15. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526lieth-4Оценок пока нет
- Sample Question Paper Subject: Mathematics Class: Senior Secondary Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 100Документ22 страницыSample Question Paper Subject: Mathematics Class: Senior Secondary Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 100Amar KumarОценок пока нет
- MAM2085F 2013 Exam SolutionsДокумент8 страницMAM2085F 2013 Exam Solutionsmoro1992Оценок пока нет
- Math SolutionДокумент3 страницыMath Solution2014481102Оценок пока нет
- Arihant PhysicsДокумент22 страницыArihant PhysicsManishKumar0% (1)
- Solutions To Practice Final ExamДокумент10 страницSolutions To Practice Final ExamSchwin W PinkohОценок пока нет
- Term Test (2005) Sample2Документ3 страницыTerm Test (2005) Sample2Peng XuОценок пока нет
- s39 57 PDFДокумент23 страницыs39 57 PDFBreno EnricoОценок пока нет
- Engineering Electrodynamics MidtermДокумент36 страницEngineering Electrodynamics MidtermSrinivas PrasadОценок пока нет
- Exam1 SolsДокумент18 страницExam1 SolsLeandro RibeiroОценок пока нет
- Solutions To Practice Session 7 (Week 7) : 2013 The University of SydneyДокумент5 страницSolutions To Practice Session 7 (Week 7) : 2013 The University of SydneydivaaaaaaaaaОценок пока нет
- Example of The Use of Stokes TheoremДокумент3 страницыExample of The Use of Stokes TheoremSam FraserОценок пока нет
- Term End Examination - May 2013 Course: MAT101 - Multivariable Calculus and Differential Equations Slot: F2+TF2 Class NBR: 3461 Time: Three Hours Max - Marks:100Документ2 страницыTerm End Examination - May 2013 Course: MAT101 - Multivariable Calculus and Differential Equations Slot: F2+TF2 Class NBR: 3461 Time: Three Hours Max - Marks:100Pratyush MishraОценок пока нет
- Math 10: Learner 'S Activity Sheets Quarter 3Документ17 страницMath 10: Learner 'S Activity Sheets Quarter 3Pauline Leon-Francisco Leong100% (1)
- 2013 Specimen Paper Unit 1 Paper 2 Mark SchemeДокумент13 страниц2013 Specimen Paper Unit 1 Paper 2 Mark SchemeLatoyaWatkinsОценок пока нет
- Our Lady of Guadalupe Minor Seminary Area A Table of Specification 1 Quarter Mathematics 11 School Year: 2020-2021Документ2 страницыOur Lady of Guadalupe Minor Seminary Area A Table of Specification 1 Quarter Mathematics 11 School Year: 2020-2021Bernadette Remigio - JovellanosОценок пока нет
- Module 3 MCQДокумент10 страницModule 3 MCQsudheshОценок пока нет
- Analytic Signals and Hilbert Transform FiltersДокумент6 страницAnalytic Signals and Hilbert Transform Filtersjammy700Оценок пока нет
- Chapter IV Functions and AlgorithmsДокумент11 страницChapter IV Functions and Algorithmsあなたを 食べたい鮎麻呂Оценок пока нет
- Slope:: 1. LinesДокумент14 страницSlope:: 1. LinesellateletubbiesОценок пока нет
- Jee Math 9th Jan Shift2Документ15 страницJee Math 9th Jan Shift2Ilir HoxhaОценок пока нет
- Discrete Structures - Spring-2021 Assignment-01: Problem 1Документ7 страницDiscrete Structures - Spring-2021 Assignment-01: Problem 1Abdul MajidОценок пока нет
- Combinatorial Identities Through Algebra HandoutДокумент5 страницCombinatorial Identities Through Algebra HandoutMunmun BhadraОценок пока нет
- Exam 3 Prep 1 PDFДокумент2 страницыExam 3 Prep 1 PDFMardig HagopianОценок пока нет
- Demystifying Number SystemДокумент6 страницDemystifying Number SystemNish1980Оценок пока нет
- Error: Hoang Hai HaДокумент35 страницError: Hoang Hai HaThanh HuyОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1 - Semester 1 - 2022Документ10 страницAssignment 1 - Semester 1 - 2022Ziphelele VilakaziОценок пока нет
- Preference RelationДокумент68 страницPreference RelationOmer KhayyamОценок пока нет
- 1 Mat071 Module1 PDFДокумент100 страниц1 Mat071 Module1 PDFjurilyn alvadorОценок пока нет
- 3.6 Quadratic InequalitiesДокумент15 страниц3.6 Quadratic InequalitiesRaymond NuvalОценок пока нет
- Errata Garling1Документ4 страницыErrata Garling1Iskandar Agung AgungОценок пока нет
- (MAA 1.9) :PMI - SolutionsДокумент14 страниц(MAA 1.9) :PMI - SolutionsDAVIES KIPRONOОценок пока нет
- DeterminantsДокумент26 страницDeterminantsSoormaОценок пока нет
- Equation of Tangent Equation of NormalДокумент11 страницEquation of Tangent Equation of NormalUbaidullah KhanОценок пока нет
- Progress Test 2Документ9 страницProgress Test 2Horace GomezОценок пока нет
- Commutative AlgebraДокумент428 страницCommutative AlgebraNomen NescioОценок пока нет
- MIT Complex AnalysisДокумент15 страницMIT Complex AnalysisDheeraj Waghmare0% (1)
- Mat183 - 2011, AprДокумент5 страницMat183 - 2011, Aprawg azhimОценок пока нет
- Characterization of Strange AttractorsДокумент4 страницыCharacterization of Strange Attractorsminliang2kbjОценок пока нет
- China China Girls Math Olympiad 2003Документ3 страницыChina China Girls Math Olympiad 2003PremMehtaОценок пока нет
- Fuzzy Magic Labelling of Neutrosophic Path and Star GraphДокумент12 страницFuzzy Magic Labelling of Neutrosophic Path and Star GraphScience DirectОценок пока нет
- MI1016 Final QuestionДокумент1 страницаMI1016 Final QuestionĐức Anh LêОценок пока нет
- APEX Calculus Version 4Документ972 страницыAPEX Calculus Version 4Herb CaudillОценок пока нет
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)От EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)Оценок пока нет
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsОт EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeОт EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.От EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Images of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryОт EverandImages of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryОценок пока нет
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormОт EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- Limitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersОт EverandLimitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- Math Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeОт EverandMath Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- ParaPro Assessment Preparation 2023-2024: Study Guide with 300 Practice Questions and Answers for the ETS Praxis Test (Paraprofessional Exam Prep)От EverandParaPro Assessment Preparation 2023-2024: Study Guide with 300 Practice Questions and Answers for the ETS Praxis Test (Paraprofessional Exam Prep)Оценок пока нет
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorОт EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- Fluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldОт EverandFluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (80)