Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
03 - HD - Auxiliary Sys - r02 PDF
Загружено:
Kaiser46Li206Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
03 - HD - Auxiliary Sys - r02 PDF
Загружено:
Kaiser46Li206Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
1 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Copyright 2004 Nuovo Pignone S.p.A. Copyright 2006 Nuovo Pignone S.p.A.
Heavy Duty Gas Turbine
Auxiliary System
Overview
2 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
A INTAKE SYSTEM
B EXHAUST SYSTEM
C LUBE AND CONTROL OIL SYSTEM
D FUEL SYSTEM
E COOLING AND SEALING AIR SYSTEM
F BASEPLATE
G STARTING SYSTEM
H AUXILIARY GEAR
I LOAD GEAR
J COUPLING
L ELECTRIC PLANT
M ENCLOSURE
N VENTILATION SYSTEM
P OIL COOLING SYSTEM
Q C CONTROL AND PROTECTION SYSTEM
Auxiliary System Overview
3 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Intake System
4 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
PROPER FILTRATION LEVEL AGAINST THE ENVIRONMENT
RESPECT OF THE SOUND EMISSIONS LEVELS REQUIRED BY THE LOCAL LAWS
FULFILMENT OF THE CONTRACTUAL POWER AND FUEL CONSUMPTION
REQUIREMENTS
AIR FLOW PATHS PROPER DESIGN THROUGH THE WHOLE AIR PASSAGES
DUCTS
RELIABILITY AND CLEANLINESS OF THE SYSTEM DOWNSTREAM THE FILTER
Intake System Performance Requirements
5 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
HIGH EFFICIENCY STAGE
(BARRIER)
AUXILIARY STAGES
HOOD
CLEAN AIR TO
COMPRESSOR
FILTER
ELBOW
GAS TURBINE
DUCT
PLENUM
SILENCER
AMBIENT AIR
SUPPORTING
STRUCTURE
INTAKE SYSTEM
ARRANGEMENT
STATIC FILTER SYSTEM
ARRANGEMENT
Intake System
6 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Intake System
Static Filtration System:
INERTIAL SEPARATOR
(First Stage Element for Dry Dusty
and/or Sandy Atmosphere)
Dusty Air
C
l
e
a
n
A
i
r
C
l
e
a
n
A
i
r
Dust
Collection
and Removal
DUST
REMOVAL
7 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Intake System
STATIC REMOVABLE
FILTER CELLS
(Prefilter, Coalescer or Pad
Type High Effiency Filters)
8 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
PULSE JET SELF
CLEANING FILTER
Intake System
FILTER
CARTRIDGES
FILTER HOUSE
DUCT
CLEAN AIR TO AXIAL
COMPRESSOR
AMBIENT AIR
7 BAR(G)
COMPRESSED
AIR FOR PULSE
PULSE AIR HEADER
Horizontal Arrangement
DUST
to
Ground
DUST
to
Ground
PULSE AIR (7 BARG)
SOLENOID VALVE
INCOMING
DUSTY AIR
DUST
DUST
CARTRIDGE
VENTURI
REVERSE FLOW
INCOMING AIR
OPERATING
PRINCIPLE
INCOMING
DUSTY AIR
FILTER
CARTRIDGES
FILTER HOUSE
DUCT
DUSTY
AMBIENT
AIR
P
U
L
S
E
A
I
R
H
E
A
D
E
R
Vertical Arrangement
(Down-Flow)
DUST
CLEAN AIR TO
AXIAL
COMPRESSOR
To
Ground
7 BAR(G)
COMPRESSED
AIR FOR PULSE
9 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
BAFFLE
FRAME
AIR FLOW
CONNECTING
FLANGE
CONNECTING
FLANGE
INTAKE SILENCER
ARRANGEMENT
Intake System
10 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
HEADER
FILTER HOUSE
CONTROL
RACK
CONTROL
VALVE
AIR FROM COMPRESSOR
ANTI-ICING
SYSTEM
Intake Systems: Anti Icing System
11 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Lube Oil System
12 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
By the Control Oil System
By Hydraulic Oil System
By the Starting Means Torque Converter
To Lubricate the Accessory Drive Gear
To Lubricate the Turbine and Load Bearings
To Absorb Heat to the Turbine and Load Bearings
Lube Oil is Used:
Lube Oil System
13 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
VPR-2
Main Lube
Oil Filters
Lube Oil
Heat
Exchangers
Emergency
Lube Oil
Pump
Auxiliary
Lube Oil
Pump
Main Lube
Oil Pump
Mist
Eliminator
VR1
Lube Oil Tank
Lube Oil System Main Components
14 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Main Lube Oil Pump
Auxiliary Gear Driven
Positive Displacement
Screw Pump
15 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Auxiliary Lube Oil Pump
23QA-1
A.C. Motor Dri ve Centrifugal Pump
Sized for the same service of the Main
Lube Oil Pump
16 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Emergency Lube Oil Pump
23QE-1
In Air Cooled Lube Oil systems, the Emergency L.O.
Pump by-passes the Heat Exchanger (separate
supply line to the L.O. header is provided)
D.C. Motor Dri ve Centrifugal Pump
Sized for emergency shut-down only.
Gas Turbine running is not allowed
17 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
AC / DC Lube Oil Pumps
D.C. Motor Dri ven
Lube Oil Emergency
Centrifugal Pump
A.C. Motor Dri ven
Lube Oil Auxiliary
Centrifugal Pump
D.C. Motor
Centrifugal Pump
Centrifugal Pump
D.C. Motor
Mounting Plates
Note:
Pumps shown in the picture
are reversed respect the
installation position
18 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Pressure Relief Valve
VR1 Pressure Relief Valve has the task to
avoid surge in the L.O. pumps supply line
and to regulate the flow coming from the
maail Lube Oil Pump.
Oil is directly discharged in the L.O. tank.
19 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Mist Eliminator
Mist Eliminator has the task to avoid oil droplets carry
over in the oil vapour stream discharged to the
atmosphere. This permits to recover part of the oil
contained in the oil vapours and to reduce the gas
turbine oil comsumption with cost saving and less
pollution to the environment.
The Mist Eliminator Fan can be
redundant, upon request, and
assure slightly negative pressure in
the lube oil tank, so to increase the
drain capability from the bearing
and the suction of the oil vapours
originated in bearings.
20 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Lube Oil Cooling
HOT WATER FROM OIL COOLER
B
COLD WATER TO OIL COOLER
WATER-TO-
AIR
COOLER
FRESH AIR
HOT AIR
FROM
COOLER
THERMOSTATIC VALVE
BYPASS
LINE
THERMOSTATIC VALVE COMMAND
OIL TEMPERATURE SENSOR
FRESH OIL TO
BEARINGS HEADER
HOT OIL TO THE COOLER
WATER FROM
EXT. SOURCE
WATER TO
EXT. SOURCE
B
THERMOSTATIC VALVE
P
HOT OIL FROM
THE TANK
AUXILIARY GEAR
TUBE BUNDLE OIL COOLER
TURBINE BASEPLATE AND OIL RESERVOIR
BYPASS
LINE
External Water
to Air Heat
Exchanger for
a closed Oil-
Water-Air
cooling system
Oil to
Water
cooling
21 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Typical Starting Devices
Diesel Engine
Expansion Turbine
Eletrical Motor
Because of the very high breakway
torque required at the start beginning,
Expansion Turbines cannot be emplloyed
on Sigle Shaft H.D. gas turbines.
Due to the very high torque
required at starting and high power
necessary to accelerate the
complete train, the largest H.D.
Gas Turbines can be equipped
with a Generator provided with the
function of starter, by using a
voltage / frequency converter.
22 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Eletrical Starting Motor
Torque Converter
Hydraulic Ratchet
Mechanism
Auxiliary
Gear Box
Clutch
Starting System Main Components
Starting Motor / Engine is started at no load. The load is gradually applied to the staring system, by means of the
torque converter, and the gas turbine shaft is so accelerated being driven through the Accessory Gear.
In order to win the initial inertia of the gas turbine rotor the first movement of the shaft is obtained via the Hydraulic
Ratchet, then passed to the torque converter / starting system. The Hidraulic Ratchet operation provides also the
engagement of the Clutch, which will be automatically disconnected during the turbine acceleration, when the
sustaining speed of the gas turbine will exceed the speed of the starting system .
23 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
1 Input shaft with connecting coupling
2 Pump wheel
3 Turbine wheel
4 Fixed stator
5 Gear stage
6 Output shaft
7 Hydrostatic barring device
8 Operating oil supply
9 Operating oil return
Torque Converter
Parallel Shaft type Torque Converter
for High Power Transmission
(single shaft units)
24 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Torque Converter
OIL NOZZLE
MOTOR
SIDE
OIL
INTAKE
INPUT
SPEED
ACC. GEAR
SIDE
OIL
DISCHARGE
OUTPUT
SPEED
Torque Converter operates as a combined
Hydraulic Pump and Hydraulic Motor.
Co-axial type Torque Converter
for Low Power Transmission
(two shaft units)
25 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Starting Sequence
TURBINE
BREAKAWA
Y
TORQUE
a
b
c
d
e
f
g
h
a
TURBINE RESISTANT
TORQUE
STARTING MOTOR
DRIVING TORQUE
SPEED (RPM)
TORQUE
IGNITION SELF SUSTAINING
SPEED
0
TURBINE SELF
SUFFICIENT OPERATION
a Breakaway torque at turbine initial start up (zero speed)
a Starting motor torque at zero speed
b Turbine resistant torque just before ignition
c Starting motor torque just before ignition
d Starting motor torque just after ignition
e Turbine resistant torque just after ignition
f Maximum turbine resistant torque during acceleration
g Turbine zero resistant torque (self sustaining operation initiation)
h Starting motor disengagement and shut-down
26 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
SSS Clutch (Torque Converter / Accessory Gear Connection)
The flange E of the Input Shaft is the side connected to the driven unit and
the flange F of the Output Clutch Ring is connected to the driving system
(starting means / torque converter).
At starting, the friction of the Pawl A with the Ratchet Theet G permits to
the Sliding Component C to move along the Helical Spines theet D which
act as a screw.
The Helical Spines D allow the Sliding Component C to move towads the
flange E of the Input Shaft, so that the Sliding Component C engages the
Clutch Theet B and continues to move along the Helical Spines theet D
until it reaches the collar of the Input Shaft E.
In this situation the F, C and E elements formed a rigid theet coupling and,
therefore, the Input Shaft E runs driven by the shaft connected to the
Output Clutch Ring F.
When the speed of the Input Shaft E exceeds that one of the Output Clutch
Ring F (Gas Turbines accelerates or starting sistem trips) the Helical
Spines D theets apply a reverse screw action to the Sliding Component C
which moves backward till it reaches the opposite position with
engagement of the Pawl A with the Ratchet Theet G.
27 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
M
C
U
1
U
3
T
M STARTING MOTOR
C TORQUE CONVERTER
T GAS TURBINE COLD END
U(n) AUXILIARY DEVICES
U
2
U
4
Accessory Gear Box Assembly
28 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Accessory Gear Box Assembly
29 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Hydraulic Oil System
30 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Hydraulic Oil System
31 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Auxiliary Hydraulic
Suppl y Pump
Hydraulic Oil System
Main Hydraulic
Suppl y Pump
Hydraulic
Suppl y Filters
Hydraulic Oil
Accumulators
32 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Mechanical Overspeed (Optional on new G.T.)
Overspeed Trip
Mechanism and
Manual Trip Lever
33 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Control Oil (Trip Oil) System (Optional on new G.T.)
34 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
SRV and GCV Arrangement
SRV
GCV
35 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Cooling and Sealing Air System
36 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Cooling and Sealing Air System
Main Components
Exhaust Frame
Blowers
Compressor
Bleed Valves
Compressor
Bleed
Solenoid
Valves
Compressor
Discharge
Pressure
Trasmitter
Ai r
Filter
MS 7001 / 9001 only
No. 2 Brg. for MS 5001 / 6001
37 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Compressor Bleed (Antisurge)
Bleed Valve
(Antisurge)
Valve Pneumatic
Actuator
38 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Compressor Bleed (Antisurge)
t
o
t
h
e
A
t
m
o
s
p
h
e
r
e
f
r
o
m
A
x
i
a
l
C
o
m
p
r
e
s
s
o
r
i
n
t
e
r
m
e
d
i
a
t
e
s
t
a
g
e
From axial compressor
discharge casing
39 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
OIL TANK
BREATHER
SEALING AIR LUBE OIL INLET
TURBINE SHAFT
BEARING
SEAL
BEARING SUPPORT
DISCHARGE PIPING
LUBE OIL
DISCHARGE
TO ATMOSPHERE
Sealing Air Operating Principle
40 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Compressor Washing System
WATER
TANK
WASHING HEADER AND
SPRAY NOZZLES
PUMP
AIR INLET
DETERGENT
TANK
41 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Water Washing Manifold
42 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Load Gear Box
GENERATOR
TURBINE
LOAD GEAR
43 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Exhaust System
44 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
Exhaust System Performance Requirements
COMPLIANCE WITH THE CONTRACTUAL PRESSURE DROPS AND RELEVANT
PERFORMANCES
COMPLIANCE WITH THE CONTRACTUAL NOISE EMISSIONS LEVELS
RESPECT OF THE PERSONNEL PROTECTION RULES
UNIFORM EXHAUST GASES FLOWS AND VELOCITIES DISTRIBUTIONS
STRESS FREE BEHAVIOUR UNDER START-UP AND SHUT-DOWN TRANSIENTS
45 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
EXHAUST SYSTEM VERTICAL ARRANGEMENT
Exhaust System
46 /
GE /
J anuary 14, 2008
EXHAUST GASES STREAM
COLD
HOT
DIVERTER BLADE
EXHAUST GASES
TO BYPASS STACK
EXHAUST
GASES
FROM GAS
TURBINE
HRSG
EXHAUST
SYSTEM
ACCESSORIES
Exhaust System
Вам также может понравиться
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Energies 12 00247 PDFДокумент22 страницыEnergies 12 00247 PDFIndah PuspitaОценок пока нет
- Free GasContentДокумент15 страницFree GasContentKaiser46Li206Оценок пока нет
- General - Tooling: ContentДокумент38 страницGeneral - Tooling: ContentKaiser46Li206Оценок пока нет
- Flinger Disc: Operating ManualДокумент8 страницFlinger Disc: Operating ManualKaiser46Li206Оценок пока нет
- NTN Bearing Bpfo&BpfiДокумент61 страницаNTN Bearing Bpfo&BpfishantanusamajdarОценок пока нет
- NEST I4.0: Machine Health MatrixДокумент2 страницыNEST I4.0: Machine Health MatrixKaiser46Li206Оценок пока нет
- Envelope Analysis For Rolling Element BearingДокумент8 страницEnvelope Analysis For Rolling Element Bearingnmgurav100% (1)
- Product Manual 26162 (Revision K, 7/2017) : LQ25T and LQ Bypass Valve Actuator AssembliesДокумент42 страницыProduct Manual 26162 (Revision K, 7/2017) : LQ25T and LQ Bypass Valve Actuator AssembliesKaiser46Li206Оценок пока нет
- Automatic Diagnosis: Guide For Maintenance Supervisors & Reliability EngineersДокумент15 страницAutomatic Diagnosis: Guide For Maintenance Supervisors & Reliability EngineersKaiser46Li206Оценок пока нет
- High Pressure Blowers: ExvelДокумент2 страницыHigh Pressure Blowers: ExvelKaiser46Li206Оценок пока нет
- Compressor Re-Rate PaperДокумент14 страницCompressor Re-Rate PaperLTORRESMОценок пока нет
- G-LQ Metering ValvesДокумент4 страницыG-LQ Metering ValvesKaiser46Li2060% (1)
- DSM-0242.0 8YO ZrO HOSPДокумент6 страницDSM-0242.0 8YO ZrO HOSPKaiser46Li206Оценок пока нет
- Api682 Iso21049 John Crane General CommentsДокумент62 страницыApi682 Iso21049 John Crane General CommentsMixtli Garcia100% (4)
- CS07 PDFДокумент21 страницаCS07 PDFKaiser46Li206Оценок пока нет
- Eliminating Cavitation - Impeller Redesign PDFДокумент21 страницаEliminating Cavitation - Impeller Redesign PDFKaiser46Li206Оценок пока нет
- Energy Saving Guide 249Документ0 страницEnergy Saving Guide 249Kaiser46Li206Оценок пока нет
- Api682 Iso21049 John Crane General CommentsДокумент62 страницыApi682 Iso21049 John Crane General CommentsMixtli Garcia100% (4)
- Frick CompressorДокумент66 страницFrick Compressoronkarrathee67% (3)
- Pumps For The Futur - SulzerДокумент2 страницыPumps For The Futur - SulzerKaiser46Li206Оценок пока нет
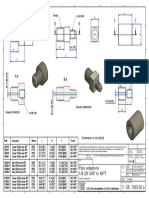
- 1/4-28 UNF to NPT pipe adapters dimensionsДокумент1 страница1/4-28 UNF to NPT pipe adapters dimensionsKaiser46Li206Оценок пока нет
- Bombas Savino Barbera - Europump Atex GuidelineДокумент22 страницыBombas Savino Barbera - Europump Atex GuidelineChevronelleОценок пока нет
- Mechanical EquipmentДокумент48 страницMechanical EquipmentsihamaniОценок пока нет
- Understanding The Basics of Autofrettage PDFДокумент4 страницыUnderstanding The Basics of Autofrettage PDFKaiser46Li206Оценок пока нет
- Electrical Extension Cord Safety-L&I v1Документ19 страницElectrical Extension Cord Safety-L&I v1Kaiser46Li206Оценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Environmental Impacts of Mine Fires in Jharia CoalfieldДокумент18 страницEnvironmental Impacts of Mine Fires in Jharia Coalfieldssmint16Оценок пока нет
- Soft Drink Bottling Plant Inspection Form ViolationsДокумент2 страницыSoft Drink Bottling Plant Inspection Form ViolationsTanzila SiddiquiОценок пока нет
- Unknown White Compound Lab ReportДокумент8 страницUnknown White Compound Lab ReportTyler Blevins100% (1)
- 2nbt - A Story About Tea by Arup Kumar DuttaДокумент68 страниц2nbt - A Story About Tea by Arup Kumar DuttaRintu DeyОценок пока нет
- Instruments Index RO Plant YTMДокумент8 страницInstruments Index RO Plant YTMSswahyudiОценок пока нет
- Farm ToolsДокумент9 страницFarm ToolsBabila PenskieОценок пока нет
- Septic Tank CalculationДокумент10 страницSeptic Tank Calculation8o54doОценок пока нет
- British Council Library in Lahore awarded LEED GoldДокумент1 страницаBritish Council Library in Lahore awarded LEED GoldBoi 7Оценок пока нет
- Site Reconnaissance: Subject PropertyДокумент19 страницSite Reconnaissance: Subject PropertyHasibul IslamОценок пока нет
- Product Summary Catalogue: Creating Solutions For ConstructionДокумент46 страницProduct Summary Catalogue: Creating Solutions For Constructionpiyu114Оценок пока нет
- Solon Wants To Probe The Impact of The Fishing Ban in Visayan SeaДокумент1 страницаSolon Wants To Probe The Impact of The Fishing Ban in Visayan Seapribhor2Оценок пока нет
- Lec 02 Water and Water Bodies of Importance To FisheriesДокумент36 страницLec 02 Water and Water Bodies of Importance To FisheriesAlbie SernaОценок пока нет
- 'Natural' Traditions - Constructing Tropical Architecture in Transnational Malaysia and SingaporeДокумент70 страниц'Natural' Traditions - Constructing Tropical Architecture in Transnational Malaysia and SingaporeKurt ZepedaОценок пока нет
- Fish Senses: Vision, Hearing, Smell, Taste & TouchДокумент27 страницFish Senses: Vision, Hearing, Smell, Taste & TouchYousaf AnwarОценок пока нет
- Hoover HED6612 User Manual (English - 15 Pages)Документ2 страницыHoover HED6612 User Manual (English - 15 Pages)إبراهيم طارقОценок пока нет
- Shifting and Tilting Occur Generally During The Sinking Phase of Well FoundationsДокумент8 страницShifting and Tilting Occur Generally During The Sinking Phase of Well FoundationsAble KuriakoseОценок пока нет
- Substructure design-IIT Roorkee-CED Bhupinder SinghДокумент370 страницSubstructure design-IIT Roorkee-CED Bhupinder SinghRavi Chandra100% (2)
- B-4-Multi Grade Filter BrochureДокумент2 страницыB-4-Multi Grade Filter BrochureSaurabh ChaudhariОценок пока нет
- Philippines School Implements Waste Segregation ProgramДокумент11 страницPhilippines School Implements Waste Segregation ProgramAnna CrisolОценок пока нет
- Chapter Two: Basics in Irrigation EngineeringДокумент80 страницChapter Two: Basics in Irrigation EngineeringHundeejireenyaОценок пока нет
- Informative ReportДокумент10 страницInformative ReportRusyda AbdullahОценок пока нет
- Waste ManagementДокумент37 страницWaste ManagementMontzo Diana BaltonadoОценок пока нет
- Hand Pump Maintenance 1977 PDFДокумент40 страницHand Pump Maintenance 1977 PDFmvqfernandesОценок пока нет
- The Rise of Antibiotic-Resistant Infections: A Warning from Canada's Cod CollapseДокумент8 страницThe Rise of Antibiotic-Resistant Infections: A Warning from Canada's Cod CollapseRavi ZaiminОценок пока нет
- Sampling and Analysis Plan for DOE Legacy SitesДокумент224 страницыSampling and Analysis Plan for DOE Legacy SitesCharmi HediОценок пока нет
- Oil Sampling SOPДокумент9 страницOil Sampling SOPTorres Toledo JttОценок пока нет
- Using of Artificial Neural Network For Modeling of Oily Wastewater in Reverse Osmosis ProcessДокумент5 страницUsing of Artificial Neural Network For Modeling of Oily Wastewater in Reverse Osmosis ProcessIJARP PublicationsОценок пока нет
- Self Healing ConcreteДокумент21 страницаSelf Healing ConcretethirumalОценок пока нет
- Superthrive Dosage Chart PDFДокумент6 страницSuperthrive Dosage Chart PDFELI AlavaradoОценок пока нет
- BP220 AmendedДокумент43 страницыBP220 AmendedMarites BalmasОценок пока нет