Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Core Router
Загружено:
Su ThandaАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Core Router
Загружено:
Su ThandaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Core router
A core router is a router designed to operate in the Internet backbone, or core. To fulfill this role, a router must be able to support multiple telecommunications interfaces of the highest speed in use in the core Internet and must be able to forward IP packets at full speed on all of them. It must also support the routing protocols being used in the core. A core router is distinct from an edge router: edge routers sit at the edge of a backbone network and connect to core routers.
Key Protocols and Features Supported in the Cisco IOS XR Software Multicast Routing Implementation
Key Protocols and Features Supported in the Cisco IOS XR Software Multicast Routing Implementationlists the supported features for IPv4 and IPv6 multicast routing in Cisco IOS XR Software.
Table 1 Supported Features for IPv4 and IPv6 on Cisco CRS Routers
Feature Dynamic host registration Explicit tracking of hosts, groups, and channels PIM-SM
1
IPv4 Support Yes (IGMP v3) Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
IPv6 Support Yes (MLD v2) Yes Yes Yes No Yes4 Yes No Yes Yes No
Yes (IGMP v1/2/3) Yes (MLD v1/2)
PIM-SSM2 PIM-Bidir3 Auto-RP Multicast VPN BSR5 MSDP6 BGP7 Multicast NSF8 OOR handling9
1 2
Protocol Independent Multicast in sparse mode Protocol Independent Multicast in Source-Specific Multicast 3 Protocol Independent Multicast Bidirectional 4 IPv6 support on Cisco XR 12000 Series Router only 5 PIM bootstrap router 6 Multicast Source Discovery Protocol 7 Multiprotocol Border Gateway Protocol 8 Nonstop forwarding
Out of resource
Multicast Routing Functional Overview
Traditional IP communication allows a host to send packets to a single host (unicast transmission) or to all hosts (broadcast transmission). Multicast provides a third scheme, allowing a host to send a single data stream to a subset of all hosts (group transmission) at about the same time. IP hosts are known as group members. Packets delivered to group members are identified by a single multicast group address. Multicast packets are delivered to a group using best-effort reliability, just like IP unicast packets. The multicast environment consists of senders and receivers. Any host, regardless of whether it is a member of a group, can send to a group. However, only the members of a group receive the message. A multicast address is chosen for the receivers in a multicast group. Senders use that group address as the destination address of a datagram to reach all members of the group. Membership in a multicast group is dynamic; hosts can join and leave at any time. There is no restriction on the location or number of members in a multicast group. A host can be a member of more than one multicast group at a time. How active a multicast group is and what members it has can vary from group to group and from time to time. A multicast group can be active for a long time, or it may be very short-lived. Membership in a group can change constantly. A group that has members may have no activity. Routers use the Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) (IPv4) and Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) (IPv6) to learn whether members of a group are present on their directly attached subnets. Hosts join multicast groups by sending IGMP or MLD report messages. Many multimedia applications involve multiple participants. Multicast is naturally suitable for this communication paradigm.
Cisco IOS XR Software Multicast Routing Implementation
Cisco IOS XR Software Multicast Routing Implementation
Cisco IOS XR Software supports the following protocols to implement multicast routing:
IGMP and MLD are used (depending on the IP protocol) between hosts on a LAN and the routers on that LAN to track the multicast groups of which hosts are members. Protocol Independent Multicast in sparse mode (PIM-SM) is used between routers so that they can track which multicast packets to forward to each other and to their directly connected LANs. Protocol Independent Multicast in Source-Specific Multicast (PIM-SSM) is similar to PIM-SM with the additional ability to report interest in receiving packets from specific source addresses (or from all but the specific source addresses), to an IP multicast address. PIM-SSM is made possible by IGMPv3 and MLDv2. Hosts can now indicate interest in specific sources using IGMPv3 and MLDv2. SSM does not require a rendezvous point (RP) to operate. PIM Bidirectional is a variant of the Protocol Independent Multicast suit of routing protocols for IP multicast. PIM-BIDIR is designed to be used for many-to-many applications within individual PIM domains.
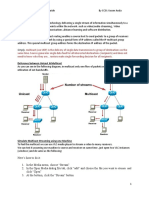
This image shows IGMP/MLD and PIM-SM operating in a multicast environment.
Figure 1. Multicast Routing Protocols Supported for Cisco IOS XR Software
Juniper Networks, Inc. is an American manufacturer of networking equipment founded in 1996. It is headquartered in Sunnyvale, California, USA. The company designs and sells high-performance Internet Protocol network products and services. Juniper's main products include T-series, M-series, E-series, MXseries, and J-series families of routers, EX-series Ethernet switches and SRX-series security products. Junos, Juniper's own network operating system, runs on most Juniper products.
Brocade Communications Systems, Inc. is an American technology company specializing in data and storage networking products. The company's products include network-attached storage, storage area network (SAN) directors and switches, data center switches, Virtual Cluster Switching, software-defined networking, network virtualization, Federal, Internet service provider and enterprise Ethernet (local area network/wireless local area network) switches and wide area network (Internet) routers, application delivery controllers (load balancers), network security appliances, Fibre Channel host bus adapters (HBAs) and converged network adapters (CNAs), and Ethernet transceivers. Founded in 1995, Brocade is headquartered in San Jose, California, USA. In March 2012, the company held the largest market share in SAN switches.[2] Alcatel-Lucent (French pronunciation: [alkatl lysnt]) is a French global mobile phone manufacturer and telecommunications equipment company, headquartered in the 7th arrondissement of Paris, France. The company focuses on fixed, mobile, and converged networking hardware, IP technologies, software, and services. It holds Bell Labs, one of the largest innovation and R&D houses in the communications industry. Bell Labs employees have been awarded 7 Nobel Prizes and the company holds over 29,000 patents. Alcatel-Lucent has operations in more than 130 countries. In 2011 it was added to the Dow Jones Sustainability Index.[2] The company is under the leadership of Chief Executive Officer Michel Combes and the nonexecutive Chairman of the Board is Philippe Camus. Camus joined the company in the third quarter of 2008, alongside Ben Verwaayen as CEO, after Alcatel-Lucent's first CEO Patricia Russo and first Chairman Serge Tchuruk resigned.[3] For 2010, the company posted revenues of 15.996 billion and a reported net loss of 334 million.[4] For 2011, the company posted revenues of 15.068 billion and a reported profit of 1.095 billion.
Вам также может понравиться
- Designing and Implementing Linux Firewalls and QoS using netfilter, iproute2, NAT and l7-filterОт EverandDesigning and Implementing Linux Firewalls and QoS using netfilter, iproute2, NAT and l7-filterОценок пока нет
- Key Protocols and Features Supported in The Cisco IOS XR Software Multicast Routing ImplementationДокумент3 страницыKey Protocols and Features Supported in The Cisco IOS XR Software Multicast Routing ImplementationSu ThandaОценок пока нет
- Multicast Services For IP Triple-Play Networks: White PaperДокумент14 страницMulticast Services For IP Triple-Play Networks: White PaperDistracted AmesОценок пока нет
- IPV4 Address Classes (32-Bit) : Class Range First BIT Usage Subnet Mask Network Bits Host Bits Private AddressДокумент14 страницIPV4 Address Classes (32-Bit) : Class Range First BIT Usage Subnet Mask Network Bits Host Bits Private Addressjibrangill100% (1)
- IP Multicast Technical OverviewДокумент9 страницIP Multicast Technical OverviewMotasim_mОценок пока нет
- IPV4 Address Classes (32-Bit) : Class Range First BIT Usage Subnet Mask Network Bits Host Bits Private AddressДокумент16 страницIPV4 Address Classes (32-Bit) : Class Range First BIT Usage Subnet Mask Network Bits Host Bits Private AddressKushal GuptaОценок пока нет
- Multicast in WirelessДокумент88 страницMulticast in WirelessAbhishek PuranamОценок пока нет
- Ip Multicast OverviewДокумент6 страницIp Multicast OverviewwoodksdОценок пока нет
- An Ipv4-Ipv6 Translation Mechanism For Sip Overlay Network in Umts All-Ip EnvironmentДокумент10 страницAn Ipv4-Ipv6 Translation Mechanism For Sip Overlay Network in Umts All-Ip Environmentfelipitosorio89Оценок пока нет
- (Document Title) : DECEMBER 31, 2021 Submitted To Dr. Sosina MengistuДокумент9 страниц(Document Title) : DECEMBER 31, 2021 Submitted To Dr. Sosina MengistuMihret BerheОценок пока нет
- Configuring IP Multicast Routing: Finding Feature InformationДокумент24 страницыConfiguring IP Multicast Routing: Finding Feature InformationJoão CuglerОценок пока нет
- Cisco's Implementation of IP Multicast RoutingДокумент52 страницыCisco's Implementation of IP Multicast RoutingRafael Johnston AlonsoОценок пока нет
- Python Summer TrainingДокумент14 страницPython Summer TrainingNainsee RaiОценок пока нет
- University University: MulticastingДокумент18 страницUniversity University: MulticastingsaqibОценок пока нет
- Multicasting: 1. BroadcastДокумент5 страницMulticasting: 1. BroadcastfortuananhОценок пока нет
- Ipv6 Deployement On Enterprise Network: Transition From Ipv4 To Ipv6Документ11 страницIpv6 Deployement On Enterprise Network: Transition From Ipv4 To Ipv6Adnan IrshadОценок пока нет
- McBride Iptv N44 PDFДокумент117 страницMcBride Iptv N44 PDFimamrockОценок пока нет
- Ip Multicast Bes Practices For Enterprise Coustomers - c11-474791Документ15 страницIp Multicast Bes Practices For Enterprise Coustomers - c11-474791krana26Оценок пока нет
- ISIS TutorialДокумент80 страницISIS Tutorialstefan_nikola100% (1)
- Instructor Materials Chapter 7: Networking Concepts: IT Essentials v6.0Документ24 страницыInstructor Materials Chapter 7: Networking Concepts: IT Essentials v6.0opsssОценок пока нет
- Menog4 Isis TutorialДокумент80 страницMenog4 Isis TutorialarunascarletОценок пока нет
- Cluster InfoДокумент16 страницCluster InfoVeeru SreОценок пока нет
- IP Overview PDFДокумент4 страницыIP Overview PDFruletriplexОценок пока нет
- 06 Yves Gheerolfs Juniper en Ipv6Документ22 страницы06 Yves Gheerolfs Juniper en Ipv6Dario BenitezОценок пока нет
- Smart City QB (Unit 4,5,6) (Atharva Garud)Документ31 страницаSmart City QB (Unit 4,5,6) (Atharva Garud)Dhruv MulaniОценок пока нет
- Yasser Auda CCIEv5 IPv4 Multicast Study Guide PDFДокумент50 страницYasser Auda CCIEv5 IPv4 Multicast Study Guide PDFsheraz35Оценок пока нет
- Triple Play Multicast: in This ChapterДокумент70 страницTriple Play Multicast: in This ChaptermuthulakshmiОценок пока нет
- How To Do High-Speed Multicast Right!Документ12 страницHow To Do High-Speed Multicast Right!maindoor1981Оценок пока нет
- ZebOS Network PlatformДокумент6 страницZebOS Network PlatformgschatzОценок пока нет
- Lecture 5Документ22 страницыLecture 5Kamran AhmedОценок пока нет
- WorksДокумент562 страницыWorkslavidolacoОценок пока нет
- Security in Next Generation Mobile NetworksДокумент16 страницSecurity in Next Generation Mobile Networksٍْبـٌـًُغـٰٓـدادِ كَــشِْــَخةَٓОценок пока нет
- Netmetric Ccna Study GuideДокумент51 страницаNetmetric Ccna Study GuideSUSHOBHAN CHAKRABARTIОценок пока нет
- Towards The Development of Lte Networks: Implementation of Openimscore in Asterisk/Openbts GSM NetworkДокумент4 страницыTowards The Development of Lte Networks: Implementation of Openimscore in Asterisk/Openbts GSM NetworkImran JavedОценок пока нет
- Powered by D-Link Rg-S5750e Series Security and Multi-Services Switch Da...Документ21 страницаPowered by D-Link Rg-S5750e Series Security and Multi-Services Switch Da...Kapil SinghОценок пока нет
- Ccna 60 Interview Questions&answersДокумент15 страницCcna 60 Interview Questions&answersMohamad SibliniОценок пока нет
- Cis701 ExamДокумент17 страницCis701 ExamfadedsimplicityОценок пока нет
- TriplePlay Con MulticastДокумент64 страницыTriplePlay Con MulticastSidney Lopes CoutoОценок пока нет
- Solution Overview: in New Generation NetworkДокумент45 страницSolution Overview: in New Generation Networknap sterОценок пока нет
- Volte White Paper by Spirent From NetДокумент9 страницVolte White Paper by Spirent From NetPushpendra Kumar SinghОценок пока нет
- Ars-Msr 1 Mcast 2014Документ44 страницыArs-Msr 1 Mcast 2014Sorina ElenaОценок пока нет
- IPv6 - OverviewДокумент37 страницIPv6 - OverviewPathum PramodyaОценок пока нет
- Using Ip Multicast With Vmware® Esx 3.5: Technical NoteДокумент9 страницUsing Ip Multicast With Vmware® Esx 3.5: Technical Notemmonce8916Оценок пока нет
- Ccna QuestionsДокумент7 страницCcna QuestionsMadan Mohan KannojiyaОценок пока нет
- SC Ex 21.1 Configure IP MulticastДокумент17 страницSC Ex 21.1 Configure IP MulticastPetr DvořákОценок пока нет
- Network Security Using IP FirewallsДокумент7 страницNetwork Security Using IP FirewallsGunajit KaushikОценок пока нет
- Our Crossbow Sensor Equipment and Zigbee: Presentation by Philip Kuryloski and Sameer PaiДокумент34 страницыOur Crossbow Sensor Equipment and Zigbee: Presentation by Philip Kuryloski and Sameer PaiYuwono Marta DinataОценок пока нет
- IOT-Module 3Документ73 страницыIOT-Module 3M.A rajaОценок пока нет
- IPV6Документ30 страницIPV62224 Momynul IslamОценок пока нет
- Ccna Interview Questions AnswersДокумент30 страницCcna Interview Questions AnswersMistah RoflcopterОценок пока нет
- Multicast-VPN - IP Multicast Support For MPLS VPNsДокумент166 страницMulticast-VPN - IP Multicast Support For MPLS VPNsVũ Hải QuânОценок пока нет
- Final Project Report - IPV6Документ71 страницаFinal Project Report - IPV6nishanthreddy89Оценок пока нет
- AMEYOДокумент8 страницAMEYOYashi GuptaОценок пока нет
- Instructions For Seminar-Computer EngineeringДокумент44 страницыInstructions For Seminar-Computer EngineeringAvinash BajajОценок пока нет
- Networking QuestionsДокумент12 страницNetworking Questionsgandhiji gorlaОценок пока нет
- IP Multimedia SubsystemДокумент8 страницIP Multimedia SubsystemWewe SlmОценок пока нет
- Ass SawaibahДокумент10 страницAss Sawaibah70131348Оценок пока нет
- Internet Access Service Quality: Qos Parameters, Evaluation Methods and Practical SolutionsДокумент41 страницаInternet Access Service Quality: Qos Parameters, Evaluation Methods and Practical SolutionsSu ThandaОценок пока нет
- BTS Site InstallationДокумент24 страницыBTS Site InstallationNeeraj Kumar Sharma100% (3)
- Wcdma CalculationsДокумент10 страницWcdma CalculationsBrajendra MohanОценок пока нет
- AloneДокумент1 страницаAloneSu ThandaОценок пока нет
- Spanning Trees: Suppose You Have A Connected Undirected GraphДокумент21 страницаSpanning Trees: Suppose You Have A Connected Undirected GraphSaurabh KumarОценок пока нет
- PCOWEB BACNET IP ConfigurationДокумент5 страницPCOWEB BACNET IP ConfigurationMohd FauziОценок пока нет
- Paper 2 Complete DCS FailureДокумент15 страницPaper 2 Complete DCS FailurefreewareОценок пока нет
- RomeX ManualДокумент41 страницаRomeX ManualAbner DiazОценок пока нет
- Same Origin Policy (SOP)Документ1 страницаSame Origin Policy (SOP)Arnold ReuserОценок пока нет
- Atasheet: Airmax® Ac Basestation With Airprism® TechnologyДокумент7 страницAtasheet: Airmax® Ac Basestation With Airprism® TechnologyAlfredo MatignonОценок пока нет
- Demonstration Lesson Plan in TLEДокумент4 страницыDemonstration Lesson Plan in TLEJamingkil Maglangit Abriol75% (4)
- Installing Wordpress Blog Using Apache On EC2 LinuxДокумент17 страницInstalling Wordpress Blog Using Apache On EC2 LinuxUbaid SaadОценок пока нет
- Pvss ScadaДокумент22 страницыPvss ScadaFatch van CheОценок пока нет
- SRAN18A 1.3.2 Change Note FormsДокумент82 страницыSRAN18A 1.3.2 Change Note FormsAnbukumar KamarajОценок пока нет
- Cisco 890 Series Integrated Services Routers Data SheetДокумент22 страницыCisco 890 Series Integrated Services Routers Data SheetJoannaОценок пока нет
- TM - Revised Call Scenario For International v2.1Документ62 страницыTM - Revised Call Scenario For International v2.1Sunnie LuОценок пока нет
- Cell Planning ProcessДокумент28 страницCell Planning Processnguyen2804Оценок пока нет
- Verification of Bluetooth Low Energy Controller in UVM MethodologyДокумент4 страницыVerification of Bluetooth Low Energy Controller in UVM MethodologyAli YıldızОценок пока нет
- Ali HaiderДокумент4 страницыAli HaiderUsama Bin AlamОценок пока нет
- Alpha Server 4000-4100 Service ManualДокумент322 страницыAlpha Server 4000-4100 Service ManualUday TibdewalОценок пока нет
- CP 3000Документ30 страницCP 3000Deepak SharmaОценок пока нет
- VoLTE One Pager Retainability DriveBasedДокумент1 страницаVoLTE One Pager Retainability DriveBasedNikhil Kumar GuptaОценок пока нет
- Advanced Persistent ThreatsДокумент22 страницыAdvanced Persistent ThreatsjuanОценок пока нет
- 5ESSДокумент27 страниц5ESSmanjtobssОценок пока нет
- Lab 02Документ10 страницLab 02Nathan100% (1)
- Bus - Link - Cfu - en-US - Manufacturer Devices PA Base V1.0Документ150 страницBus - Link - Cfu - en-US - Manufacturer Devices PA Base V1.0IA BITSОценок пока нет
- RN P103 08 00 CCДокумент18 страницRN P103 08 00 CCNipon ZamanОценок пока нет
- Form ValidationДокумент4 страницыForm ValidationJASPER WESSLYОценок пока нет
- Configure N Troubleshoot DBmail in SQL ServerДокумент20 страницConfigure N Troubleshoot DBmail in SQL ServerAndreas IoannouОценок пока нет
- 3GPP TS 36.331: Technical SpecificationДокумент1 137 страниц3GPP TS 36.331: Technical SpecificationbbОценок пока нет
- 5 Media ConvergenceДокумент12 страниц5 Media ConvergenceTeacher MoОценок пока нет
- LMS UserGuideforRME40Документ1 324 страницыLMS UserGuideforRME40joel villanuevaОценок пока нет
- Bbu 3900Документ34 страницыBbu 3900علي الزراريОценок пока нет
- Introduction To UMTS SecurityДокумент17 страницIntroduction To UMTS SecuritySzu-Ying ChenОценок пока нет