Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Simple Lead Crosses Were Placed On Corpses in Mass Graves
Загружено:
Sourav DasОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Simple Lead Crosses Were Placed On Corpses in Mass Graves
Загружено:
Sourav DasАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
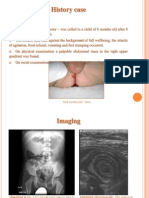
When Pope Clement VI asked how many people had died from the plague,
he was told at least 20 million
people in Europe, and 17
million in Asia. In comparison,
around 8 million soldiers
died in World War I.
20M 8M
Q
2 million
9=
Tombs
dead Simple lead crosses were placed on corpses in mass graves. During the plague, people faced deadi every day.
Death is often realistically shown on 14th-century tombs, where images of
skeletons and decaying corpses are common.
Chantries
People often left money for masses to be said for dieir
souls. These masses were
said in special chapels inside churches known as chantries. This chantry is at Winchester, England. thought to stimulate erotic desire and
enhance sexual performance. For centuries, various substances (most notably oysters and rhinoceros horn) have been used as aphrodisiacs. In fact, no substance has a proven aphrodisiac effect. aphthous ulcer See ulcer, aphthous. apicectomy Surgical removal of the tip of a tooth root. Apicectomy may be performed as part of root-canal treatment. aplasia Absent or severely reduced growth and development of any organ or tissue. For example, in bone marrow aplasia, the rate of cell division in the bone marrow is reduced, leading to insufficient blood-cell production (see anaemia, aplastic). Some birth defects, such as stunted limbs (see phocomelia), occur as a result of incomplete tissue formation during prenatal development. aplastic anaemia See anaemia, aplastic. apnoea Cessation of breathing, either temporarily or for a prolonged period. Breathing is an automatic process controlled by the respiratory centre in the brainstem. Failure of this centre to maintain normal breathing is known as central apnoea. It may occur in babies, particularly those who are premature, and can be detected by an apnoea alarm. Central apnoea can also result from brainstem damage, for example following a stroke or head injury. In obstructive apnoea, breathing is prevented by a blockage in the airway. The most common type is sleep apnoea, in which blockage of the upper airway occurs repeatedly during sleep. Deliberate temporary apnoea occurs in breath-holding attacks. Another type of apnoea occurs in CheyneStokes respiration, in which cycles of deep, rapid breathing alternate with episodes of
breathing stoppage. Treatment of apnoea depends on the cause. In newborn babies, it resolves as they mature. In stroke or head injury, artificial ventilation may be needed temporarily until recovery occurs. apocrine gland A gland that discharges cellular material in addition to the fluid it secretes. The term is usually applied to the type of sweat glands that appear in hairy body areas after puberty. (See also eccrine gland.) apolipoprotein A group of proteins that are constituents of lipoproteins, the carriers of fat in the bloodstream. Apolipoproteins are also involved in the growth and repair of nerve tissues. aponeurosis A wide sheet of tough, fibrous tissue that acts as a tendon, attaching a muscle to a bone or a joint. apophysis An outgrowth of bone at the site of attachment of a tendon to bone. Inflammation may also occur, as in OsgoodSchlatter disease. apoplexy An outdated term for a stroke. apoptosis The natural process of programmed cell death. Apoptosis occurs in embryonic development, when the shaping of body parts is taking place and continues throughout life in the constant cycle of death and renewal of body cells. Failure of apoptosis is implicated in the development of cancers. apothecary An old term for a pharmacist. appendicectomy Surgical removal of the appendix to treat acute appendicitis. appendicitis Acute inflammation of the appendix. The cause is usually not known, but appendicitis is sometimes caused by obstruction of the appendix by a lump of faeces. The 1st symptom is usually vague discomfort around the navel. Within a few hours, this develops into severe, more localized pain, which is usually most intense in the lower righthand side of the abdomen. Symptoms may differ if the appendix is not in the most common position. For example, if the appendix impinges on the ureter, the urine may become bloodstained. The usual treatment for appendicitis is appendicectomy, which is often performed endoscopically (see minimally invasive surgery). If the treatment is delayed, an inflamed appendix may burst, releasing its contents into the abdomen. This leads to peritonitis and, in some cases, an abscess. appendix A small, narrow tube that projects out of the caecum (the 1st part of the colon) at the lower right-hand side of the abdomen. It may lie behind or below the caecum, or in front of or behind the ileum (part of the small intestine). The appendix has no known function, but it contains a large amount of lymphoid tissue which provides a
Вам также может понравиться
- Pleural Effusion, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandPleural Effusion, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Dictionary of Veterinary Terms: Vet-Speak Deciphered for the Non VeterinarianОт EverandDictionary of Veterinary Terms: Vet-Speak Deciphered for the Non VeterinarianОценок пока нет
- New Microsoft Office Word Document PDFДокумент2 страницыNew Microsoft Office Word Document PDFSourav DasОценок пока нет
- Peptic UlcerДокумент6 страницPeptic UlcerXAcheronXОценок пока нет
- 1 ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH - LearnДокумент119 страниц1 ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH - LearnDavid KramerОценок пока нет
- Unit Human Respiratory & Circulatory System Class NotesДокумент4 страницыUnit Human Respiratory & Circulatory System Class NotesAiza SulemanОценок пока нет
- Appendex: VestigialityДокумент14 страницAppendex: VestigialitySher KhanОценок пока нет
- Abdominal Stab WoundsДокумент14 страницAbdominal Stab WoundsJohn PaulОценок пока нет
- GI System and Abdominal Exam Physical Diagnosis Worksheet: Surface Anatomy / InspectionДокумент8 страницGI System and Abdominal Exam Physical Diagnosis Worksheet: Surface Anatomy / Inspectionrose961Оценок пока нет
- OMM Board ReviewДокумент33 страницыOMM Board ReviewGinwong100% (5)
- AppendicitisДокумент14 страницAppendicitismeylianaprimavitaОценок пока нет
- Appendectomy: Colegio de San Juan de Letran - CalambaДокумент14 страницAppendectomy: Colegio de San Juan de Letran - CalambaJiedОценок пока нет
- BME 321 Iron Lung, Ulcers, Kidney StonesДокумент7 страницBME 321 Iron Lung, Ulcers, Kidney StonesA1gapeS2tarОценок пока нет
- General Surgery ExamДокумент48 страницGeneral Surgery ExamVarunavi SivakanesanОценок пока нет
- What Is Appendicitis?: AppendixДокумент5 страницWhat Is Appendicitis?: AppendixEnrique GruenbergОценок пока нет
- Case StudyДокумент36 страницCase StudydeathwishesОценок пока нет
- Hypoxia: Means That O Anoxia: Means That No OДокумент11 страницHypoxia: Means That O Anoxia: Means That No OburnОценок пока нет
- Nursing Management of AppendicitisДокумент22 страницыNursing Management of AppendicitisIta Puspita Sari100% (1)
- IntussusceptionДокумент60 страницIntussusceptionAhmad Abu KushОценок пока нет
- Appendicitis Method EngДокумент10 страницAppendicitis Method EngMohammad AyoubОценок пока нет
- Case Presentation 3Документ5 страницCase Presentation 3camille nina jane navarroОценок пока нет
- Research Paper Urinary SystemДокумент7 страницResearch Paper Urinary Systemaflbojhoa100% (1)
- Capitol University College of Nursing: Acute AppendicitisДокумент28 страницCapitol University College of Nursing: Acute AppendicitisCatherine Milar DescallarОценок пока нет
- Dr. Sangeeta Asphyxia-1Документ99 страницDr. Sangeeta Asphyxia-1ulfah febyОценок пока нет
- Acupuncture Treatment For Sleep ApneaДокумент11 страницAcupuncture Treatment For Sleep Apneataoacu2000100% (1)
- Abdominal Hernia: Jama Patient PageДокумент1 страницаAbdominal Hernia: Jama Patient PagebasokkaОценок пока нет
- Lec 15a - Esophagial Atresia and Respiratory Emergencies in ChildrenДокумент15 страницLec 15a - Esophagial Atresia and Respiratory Emergencies in ChildrenAnas RbaihatОценок пока нет
- Seven Channels of EliminationДокумент24 страницыSeven Channels of EliminationNick Bantolo100% (1)
- Abdominal Examination DetailedДокумент22 страницыAbdominal Examination Detailedsaveetha purushothamanОценок пока нет
- Respiratorydistressinthe Adultandfoal: Ashley G. BoyleДокумент15 страницRespiratorydistressinthe Adultandfoal: Ashley G. BoyleJuan Pardo CarrascoОценок пока нет
- Appendix: What Is The Appendix?Документ9 страницAppendix: What Is The Appendix?Jeenal LakhaniОценок пока нет
- GNM KidneyДокумент4 страницыGNM KidneyaskoreОценок пока нет
- Hernia and LutzДокумент4 страницыHernia and LutzDrew CabigaoОценок пока нет
- Grabe Ka FinalДокумент57 страницGrabe Ka FinalJoanne Bernadette AguilarОценок пока нет
- ALGOR MORTIS (Body Cooling) - Rigor MortisДокумент31 страницаALGOR MORTIS (Body Cooling) - Rigor MortiselavelenosaОценок пока нет
- Case Study AppendicitisДокумент6 страницCase Study AppendicitisPrincess Camille ArceoОценок пока нет
- Chapter X.4. Intussusception: Case Based Pediatrics For Medical Students and ResidentsДокумент5 страницChapter X.4. Intussusception: Case Based Pediatrics For Medical Students and ResidentsNawaf Rahi AlshammariОценок пока нет
- SURGERYFinals - 1. The AppendixДокумент10 страницSURGERYFinals - 1. The AppendixRenatoCosmeGalvanJuniorОценок пока нет
- IntussusceptionДокумент4 страницыIntussusceptionlovethestarОценок пока нет
- AppendicitisДокумент6 страницAppendicitisNathalie L. RaquelОценок пока нет
- Chest PainДокумент4 страницыChest PainRosmyn MistychaОценок пока нет
- The Prime Cause and Prevention of Disease WarburgДокумент3 страницыThe Prime Cause and Prevention of Disease WarburgMichael DietrickОценок пока нет
- Week 6Документ5 страницWeek 6Ashley CastroОценок пока нет
- Gale Encyclopedia AchalasiaДокумент3 страницыGale Encyclopedia AchalasiaMarco Antonio WellisОценок пока нет
- Appendicitis: Appendicitis Is A Condition Characterized by Inflammation of The Appendix. It IsДокумент7 страницAppendicitis: Appendicitis Is A Condition Characterized by Inflammation of The Appendix. It IsIlyes FerenczОценок пока нет
- Imperforate Anus and Cloacal MalformationsДокумент110 страницImperforate Anus and Cloacal MalformationsAhmad Abu KushОценок пока нет
- The JKL Medical DictionaryДокумент186 страницThe JKL Medical Dictionarymoekyaw7171Оценок пока нет
- AppendectomyДокумент15 страницAppendectomyAia JavierОценок пока нет
- Topic 5. Asphyxial DeathsДокумент8 страницTopic 5. Asphyxial DeathsDevОценок пока нет
- Breath Taking: The Power, Fragility, and Future of Our Extraordinary LungsОт EverandBreath Taking: The Power, Fragility, and Future of Our Extraordinary LungsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (5)
- FEM ( (110) ) - Unit 4Документ32 страницыFEM ( (110) ) - Unit 4mordecaisibulowa305Оценок пока нет
- Appendicitis Is A Condition Characterized by Inflammation of The Appendix. It Is Classified As A MedicalДокумент5 страницAppendicitis Is A Condition Characterized by Inflammation of The Appendix. It Is Classified As A Medicalbhe_jewelОценок пока нет
- Small Intestine DisordersДокумент34 страницыSmall Intestine DisordersNamita Jadhao100% (1)
- Lung ExaminationДокумент16 страницLung ExaminationShams AtrashОценок пока нет
- Renal ReviewДокумент23 страницыRenal ReviewRaven Atisha100% (1)
- English: Yusran 909312906105.274Документ6 страницEnglish: Yusran 909312906105.274Rachmat MuhammadОценок пока нет
- Appendix Part 1Документ8 страницAppendix Part 1Abdullah EssaОценок пока нет
- What Is The Appendix?: Lymphatic TissueДокумент7 страницWhat Is The Appendix?: Lymphatic TissuecidjjОценок пока нет
- Proceedings: BuroerДокумент8 страницProceedings: Buroeralifa ishmahdinaОценок пока нет
- Ac. AppendicitisДокумент8 страницAc. AppendicitisViswa GiriОценок пока нет
- Hearing: The SensesДокумент20 страницHearing: The SensesSourav DasОценок пока нет
- Hearing: The SensesДокумент7 страницHearing: The SensesSourav DasОценок пока нет
- Apocrine Gland: Sweat Glands Eccrine Gland LipoproteinsДокумент11 страницApocrine Gland: Sweat Glands Eccrine Gland LipoproteinsSourav DasОценок пока нет
- Apocrine Gland: Sweat Glands Eccrine Gland LipoproteinsДокумент11 страницApocrine Gland: Sweat Glands Eccrine Gland LipoproteinsSourav DasОценок пока нет
- Apocrine Gland: Sweat Glands Eccrine Gland LipoproteinsДокумент5 страницApocrine Gland: Sweat Glands Eccrine Gland LipoproteinsSourav DasОценок пока нет
- Apocrine Gland: Sweat Glands Eccrine Gland LipoproteinsДокумент4 страницыApocrine Gland: Sweat Glands Eccrine Gland LipoproteinsSourav DasОценок пока нет
- Apocrine Gland: Sweat Glands Eccrine Gland LipoproteinsДокумент5 страницApocrine Gland: Sweat Glands Eccrine Gland LipoproteinsSourav DasОценок пока нет
- Pankaj Tiwary11Документ2 страницыPankaj Tiwary11Sourav DasОценок пока нет