Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Student Centred Learning by Means of Brainstorming and Mind Mapping Learning Styles Ea
Загружено:
Wulf-Dieter KruegerАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Student Centred Learning by Means of Brainstorming and Mind Mapping Learning Styles Ea
Загружено:
Wulf-Dieter KruegerАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
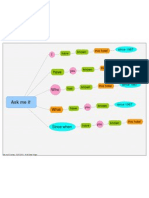
Forget
10; 5%
Auditory lea rner = learns by listening 30; 16%
and talking about it. Provide d
Learning styles - nobody has one items 8 0; 4 2% List ening t o ot hers
Visual learn er = learns by looking at
images of t hings and words (not too many learning s tyle only - w e have a mix have What we f o rget Se in g pictu res
Sp eaking o urselves
words) of them all w ith predominance of Retention been Do in g ourselves
Kinesthetic learner = learns by doing, the one or the other. understood
action and dy namics of mov ement in and thus
images, ge tting his/her 'hands dirty ' 70 ; 37 %
becom e
compre hensible
Keep in our memory
20; 10%
Brain 30; 14%
mapping - 90; 43%
Listening to others
nerv e cells What we re member Seing pictures
and Speaking ourselves
sy napses Doing ourselves
and f low of
inf ormation
bits. Mind 70; 33%
mapping
copies this .
Communicative Approach
Student centred learning
by mea ns of
brainstorming and mind
mapping - Learning styles
21.09.2009 - Rev. 36
How does our brain w ork? WHAT stan ding here f or what they say
CPU here t he and that it is understood by their peers.
sy napses a re wires
linking to in put an HOW stand ing here f or whether they say
output dev ices Both are e xtremely communicativ e, once it in correc t, perf ect English or simple
the studen ts realise that the WHAT is English with mistakes or without.
more import ant than the HOW.
Correction s by the teacher or peers will
ev entually m ake students' utterances
more compr ehensible thus building
students' c onf idence to communicate.
Both v isuali se thought/inf ormation learnt This in turn f rees processing memory and
To support the brain retriev e inf ormation bef ore (kn owledge), prev enting speeds up producing new thought/output.
f aster and speed up processing v isual Already exis ting inf ormation that is known, inf ormation ov erload/memory ov erf low.
A dy namic d ev ice like our brain will not Once proc essing has f inished the i.e., it has been learned bef ore Brainstor ming and Mind mapping
aids are id eal. These v isual aids could be A mechanic dev ice will nev er lose
alway s f ind stored inf ormation, because outcome is stored as output into memory (inf ormation or methods of processing Nobody ha s to 're-inv ent the wheel' or
print, image s or brainstorming and mind memory , un less there is a hard disk The essen tial dif f erence between a
there is th e element of f orgetting due to f or f uture use. (program) is retriev ed f rom short-, mid- or Ideas v isua lised by means of a mind map
maps. crash. Inf o rmation in memory will thus computer a nd a brain is, that the f irst is store inf or mation short term f or f urther
sy napses-c onnections being lost. long-term m emory )[in the computer this become pu blic domain f or all students. processing .
alway s be f ound. mechanic a nd the latter is dy namic. Inf ormation input is taken into processing memory .
Repetition also helps to re-build the In the pro cessing memory new and 'old' would be a f loppy disk, a ROM or a hard Processing inf ormation
sy napses-c onnections. (Honey well Bull) inf ormation are matched and processed. disk] and t ransf erred into the processing
memory [in the computer's CPU this Auditory lea rner = learns by listening
would be th e ALU and talking about it.
(Algorithmic -Logical-Unit).
Visual learn er = learns by looking at
images of t hings and words (not too many
Both accom modate all three principal learning sty les
words)
Kinesthetic learner = learns by doing,
action and dy namics of mov ement in
images, ge tting his/her 'hands dirty '
Experience in 2009 has shown so f ar, that
Theref ore it is essential that the students the challen ge of doing a project motiv ates
Both introd uce the real world into the the studen ts to v enture into 'unknown
artif icial cla ssroom that has been ruled by Prov ided th at the problem or the project is choose the problem/project they want to
based on t he students' knowledge and/or do - AND NOT THE TEACHER - territory ' th us demanding much more of
Project Work / Problem Solving the artif icia l world of a text book published themselv es than doing a teacher's project
in Oxf ord o r Cambridge not ref lecting our experience . (problems i n 2008)
they might block, because it is not theirs.
students' experience/way of lif e f or y ears.
Student centred learning by means of brainstorming and mind mapping Learning styles ea.mmap - 21.09.2009 -
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Ask Me If 4Документ1 страницаAsk Me If 4Wulf-Dieter KruegerОценок пока нет
- SCL by Means of Project WorkДокумент1 страницаSCL by Means of Project WorkWulf-Dieter KruegerОценок пока нет
- Ask Me If 5Документ1 страницаAsk Me If 5Wulf-Dieter KruegerОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Ask Me If 3Документ1 страницаAsk Me If 3Wulf-Dieter KruegerОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Ask Me If.Документ1 страницаAsk Me If.Wulf-Dieter KruegerОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Ask Me If - 2Документ1 страницаAsk Me If - 2Wulf-Dieter KruegerОценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Student Centred Learning by Means of Brainstorming and Mind Mapping Communication EaДокумент1 страницаStudent Centred Learning by Means of Brainstorming and Mind Mapping Communication EaWulf-Dieter KruegerОценок пока нет
- Student Centred Learning by Means of Brainstorming and Mind Mapping Outcome and OutlookДокумент1 страницаStudent Centred Learning by Means of Brainstorming and Mind Mapping Outcome and OutlookWulf-Dieter KruegerОценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Student Centred Learning by Means of Brainstorming and Mind Mapping As From 2009Документ1 страницаStudent Centred Learning by Means of Brainstorming and Mind Mapping As From 2009Wulf-Dieter KruegerОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Student Centred Learning by Means of Brainstorming and Mind Mapping Learning Styles EaДокумент1 страницаStudent Centred Learning by Means of Brainstorming and Mind Mapping Learning Styles EaWulf-Dieter KruegerОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Student Centred Learning by Means of Brainstorming and Mind MappingДокумент1 страницаStudent Centred Learning by Means of Brainstorming and Mind MappingWulf-Dieter KruegerОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Student Centred SPBMДокумент20 страницStudent Centred SPBMWulf-Dieter KruegerОценок пока нет
- Tashi Airport RevisitedДокумент1 страницаTashi Airport RevisitedWulf-Dieter KruegerОценок пока нет
- Student Centred SPBMДокумент20 страницStudent Centred SPBMWulf-Dieter KruegerОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Student Centred Learning by Means of Project Work, Problem Solving, Brainstorming, and Mind Mapping To Produce A PaperДокумент1 страницаStudent Centred Learning by Means of Project Work, Problem Solving, Brainstorming, and Mind Mapping To Produce A PaperWulf-Dieter KruegerОценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Class Observation Report and GuidelinesДокумент3 страницыClass Observation Report and Guidelineslmg_007Оценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Assertive FeedbackДокумент15 страницAssertive FeedbackadeeboОценок пока нет
- Common Sense About Teaching Thinking SkillsДокумент7 страницCommon Sense About Teaching Thinking SkillsTrisha MenesesОценок пока нет
- Lesson 8 PhilosophyДокумент22 страницыLesson 8 PhilosophyLaura JadeОценок пока нет
- BIBLIOGRAFIДокумент2 страницыBIBLIOGRAFITharmanThiranОценок пока нет
- Activity 1: by Means of Graphic Organizer Present The Importance of WMSU VMGO, CollegeДокумент2 страницыActivity 1: by Means of Graphic Organizer Present The Importance of WMSU VMGO, CollegeRock BrockОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Dll-Cot Math RatioДокумент11 страницDll-Cot Math RatioMarites JudiОценок пока нет
- Vmgo (Engarcial Reiljohn Beed 1)Документ1 страницаVmgo (Engarcial Reiljohn Beed 1)Reil JohnОценок пока нет
- Admin Org - Elem Guidance Program - WendamДокумент18 страницAdmin Org - Elem Guidance Program - WendamJean Lois Condeza GelmoОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Second Quarter Learning Plan Grade 5Документ3 страницыSecond Quarter Learning Plan Grade 5Donna VariasОценок пока нет
- Episode 7Документ8 страницEpisode 7Crislyn Jane L. RomeroОценок пока нет
- Benchmark - Clinical Field Experience D Beginning Teacher Observation and FeedbackДокумент5 страницBenchmark - Clinical Field Experience D Beginning Teacher Observation and Feedbackapi-512955259100% (1)
- Republic Act 10157Документ17 страницRepublic Act 10157Cecile Brucal-Villarama100% (1)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (120)
- Principles Practices and Pragmatics New Models of Coteaching Friend and CookДокумент33 страницыPrinciples Practices and Pragmatics New Models of Coteaching Friend and CookEFL Classroom 2.0100% (1)
- (HOTS) : Values Classroom Based Assessment (Cba)Документ1 страница(HOTS) : Values Classroom Based Assessment (Cba)Santhya SalvarajОценок пока нет
- Module 17 - Teaching Psycho Motor SkillsДокумент5 страницModule 17 - Teaching Psycho Motor SkillserikriyaОценок пока нет
- Teaching PhilosophyДокумент3 страницыTeaching Philosophywedad jumaОценок пока нет
- Alliant Hsoe Lesson Plantemplate Goal-Based LessonДокумент4 страницыAlliant Hsoe Lesson Plantemplate Goal-Based Lessonapi-534596308Оценок пока нет
- CTH Lesson Plan Year 1 2018 CefrДокумент2 страницыCTH Lesson Plan Year 1 2018 CefrFe Joe95% (21)
- DLP Day 1Документ3 страницыDLP Day 1majenta 19Оценок пока нет
- DLP Tle Ia Week 1Документ12 страницDLP Tle Ia Week 1Earl Jhon BautistaОценок пока нет
- Assessment and Identification SPEDДокумент3 страницыAssessment and Identification SPEDGeegee SemanaОценок пока нет
- Welcome To Level 6 of The British Council English Language CourseДокумент2 страницыWelcome To Level 6 of The British Council English Language CourseelvagojpОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan Prepositions of Time I. DescriptionДокумент6 страницLesson Plan Prepositions of Time I. DescriptionHoàng TrangОценок пока нет
- Dzielawa Rec LetterДокумент1 страницаDzielawa Rec Letterapi-302335965Оценок пока нет
- Otl545 Tpack Lesson PlanДокумент5 страницOtl545 Tpack Lesson Planapi-29813013250% (2)
- Science 8Документ9 страницScience 8Lovie AlfonsoОценок пока нет
- ResumeДокумент2 страницыResumeapi-502027458Оценок пока нет
- Reina Mercedes Vocational and Industrial School: Weekly Home Learning PlanДокумент16 страницReina Mercedes Vocational and Industrial School: Weekly Home Learning PlanJohn B. BataraОценок пока нет
- Curriculum and Textbook 2 Analysis: Pokok Bahasan IvДокумент4 страницыCurriculum and Textbook 2 Analysis: Pokok Bahasan IvNahdatul FikraОценок пока нет