Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Adc
Загружено:
Shanmuga PriyaАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Adc
Загружено:
Shanmuga PriyaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2011.
Third Semester Computer Science and Engineering CS 2204 ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION (Regulation 2008) Time : Three hours Maximum : 100 marks Answer ALL questions. PART A (10 2 = 20 marks) 1. Define Amplitude modulation. 2. What is modulation index and percentage modulation in AM? 3. What is Shannon limit for information capacity? 4. What is binary phase shift keying? 5. What is the need for sampling? 6. Define inter symbol interference (ISI). 7. List any two data communication standard organization. 8. What is a data modem? 9. List the spread spectrum techniques. 10. What is CDMA? PART B (5 16 = 80 marks) 11. (a) (i) Explain the principles of amplitude modulation. (8) (ii) Write a note on frequency spectrum analysis of angle modulated waves. (8) Or (b) (i) Explain the band width requirements of anogle modulated waves. (8) (ii) Compare FM and PM. (8) 12. (a) (i) Discuss the principle of operation of FSK transmitter. (8) (ii) Write a note on QPSK. (8) Or (b) (i) Discuss the principle of operation of FSK receiver. (8) (ii) Write a note on DPSK. (8) 13. (a) (i) Describe the basic principles of PCM system. (8) (ii) What is companding? Explain in detail. (8) Or (b) (i) Describe in detail the adaptive delta modulation system. (8) (ii) What is signal to quantitation noise? Explain. (8) 14. (a) (i) Write a note on data communication codes. (8) (ii) Explain serial and parallel interfaces in detail. (8) Or (b) (i) Explain in detail about error detection and correction. (8) (ii) Write a note on medium and high speed modem. (8) 15. (a) (i) Explain the principle of DS spread spectrum technique. (8) (ii) Explain the salient features of wireless communication. (8) Or (b) (i) Describe the frequency hopping spread spectrum technique in detail. (8) (ii) Explain the basic principle of TDMA. (8)
CS2204 ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2010 ANNA UNIVERSITY QUESTION PAPER QUESTION BANK IMPORTANT QUESTIONS 2 MARKS AND 16 MARKS CS2204 ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2010 ANNA UNIVERSITY QUESTION PAPER QUESTION BANK IMPORTANT QUESTIONS 2 MARKS AND 16 MARKS B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2010 Third Semester Computer Science and Engineering CS 2204 ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION (Regulation 2008) Time : Three hours Maximum : 100 Marks Answer ALL questions PART A (10 2 = 20 Marks) 1. For an AM DSBFC modulator with a carrier frequency of 100KHz and maximum modulating signal frequency of 5 KHz, determine upper and lower side band frequency and the bandwidth. 2. State Carsons rule. 3. Define information capacity. 4. What is the relation between bit rate and baud for a FSK system? 5. What are the advantages of digital transmission? 6. Define companding. 7. What is data terminal equipment? Give examples. 8. What is forward error correction? 9. What is frequency hopping? 10. What is meant by an orthogonal code? PART B (5 16 = 80 Marks) 11. (a) (i) Derive the expression for a Amplitude Modulated wave and draw its spectrum. (10) (ii) Obtain a relationship between carrier and side band powers in an AM DSBFC wave and explain how power distribution takes place in AM DSB FC system. (6) Or (b) (i) Define modulation index for FM and PM and obtain the relation between modulation index and modulating signal for FM and PM. (8) (ii) Compare the advantages and disadvantages of angle modulation with amplitude modulation. (8) 12. (a) (i) Describe with neat diagram, the operation of a QPSK modulator. Draw its phasor and constellation diagram. (10) (ii) Explain the bandwidth considerations of QPSK system. (6) Or (b) What is carrier recovery? Discuss how carrier recovery is achieved by the squaring loop and Costas loop circuits. (16)
13. (a) (i) Draw the block diagram of a PCM transmitter and explain the function of each block. (6) (ii) What are the types of sampling? Explain the operation of the sample and hold circuit. (10) Or (b) Draw the block diagram and describe the operation of a delta modulator. What are its advantages and disadvantages compared to a PCM system? (16) 14. (a) (i) Describe the features and purposes of serial Interfaces. (6) (ii) Describe the mechanical, electrical and functional characteristics of Rs. 232 interface. (10) Or (b) Explain how vertical, longitudinal and cyclic redundancy checking is used for detecting the occurrence of errors in data transmission. (16) 15. (a) (i) What is a PN sequence.? Explain its important properties. (8) (ii) Describe with block diagram, DS SS binary PSK spread spectrum system. (8) Or (b) (i) Describe the operation of a CDMA multiplexing system. (10) (ii) List the advantages of CDMA over TDMA multiple access scheme. (6)
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- TLWG Lesson PlanДокумент3 страницыTLWG Lesson PlanShanmuga PriyaОценок пока нет
- Placement Question-Unit 1 Vlsi DesignДокумент3 страницыPlacement Question-Unit 1 Vlsi DesignShanmuga PriyaОценок пока нет
- Electric FieldsДокумент55 страницElectric Fieldsp_k_soni_iit_physicsОценок пока нет
- Electrical SolvedДокумент99 страницElectrical Solvedrajeshnaik_965429910Оценок пока нет
- Cylindrical and Spherical CoordinatesДокумент33 страницыCylindrical and Spherical Coordinatessumi36117Оценок пока нет
- Question Bank: Department of Ece Subject Code:141304 Subject Name: Analog and Digital Communication Year/Sem:II/IIIДокумент7 страницQuestion Bank: Department of Ece Subject Code:141304 Subject Name: Analog and Digital Communication Year/Sem:II/IIIShanmuga PriyaОценок пока нет
- Electronics Course Delivery PlanДокумент5 страницElectronics Course Delivery PlanShanmuga PriyaОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Catalogo OptictimesДокумент38 страницCatalogo OptictimesJavier VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- 100G QSFP28 Optical Transceiver Data Sheet by JTOPTICSДокумент9 страниц100G QSFP28 Optical Transceiver Data Sheet by JTOPTICSJayani Technologies LtdОценок пока нет
- BDCOM GP3600-16 OLT SeriesДокумент6 страницBDCOM GP3600-16 OLT Seriespriv1234Оценок пока нет
- 3G RANOP RU30 - KPI - DefinitionДокумент75 страниц3G RANOP RU30 - KPI - DefinitionBOUZANA ElamineОценок пока нет
- Spanning Tree ProtocolДокумент52 страницыSpanning Tree ProtocolchelohuhuОценок пока нет
- I240W-S en DataSheetДокумент2 страницыI240W-S en DataSheetKriztopher UrrutiaОценок пока нет
- Main reasons for low throughput in 4G LTE networksДокумент3 страницыMain reasons for low throughput in 4G LTE networksHải NguyễnОценок пока нет
- Cloud RAN and ECPRI Fronthaul in 5G NetworksДокумент5 страницCloud RAN and ECPRI Fronthaul in 5G NetworksTalent & Tech Global InfotechОценок пока нет
- Huawei Optix Osn 6800 and Boards DatasheetДокумент29 страницHuawei Optix Osn 6800 and Boards DatasheetNageeb MohammedОценок пока нет
- WiFi RS232 Adapter Quick Reference S2W232E ESP32Документ5 страницWiFi RS232 Adapter Quick Reference S2W232E ESP32kokohcapОценок пока нет
- Lesson - Chapter 1-1 - Overview of Digital CommunicationДокумент48 страницLesson - Chapter 1-1 - Overview of Digital CommunicationTuấn Đạt Lê XuânОценок пока нет
- 6GK1415 2ba20 Simatic Net Link Dpas I Link Advanced Siemens ManualДокумент4 страницы6GK1415 2ba20 Simatic Net Link Dpas I Link Advanced Siemens ManualDolores FuertesОценок пока нет
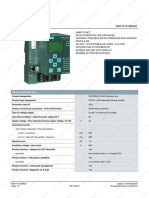
- Data Sheet - enДокумент2 страницыData Sheet - enrodriggoguedesОценок пока нет
- JMB585 PDFДокумент10 страницJMB585 PDFBono PrakosoОценок пока нет
- Datasheet RGPS-7084GP-P v1.0Документ4 страницыDatasheet RGPS-7084GP-P v1.0oring2012Оценок пока нет
- SURPASS HiT7035 R4 2 Acceptance Test ManualДокумент72 страницыSURPASS HiT7035 R4 2 Acceptance Test ManualdarooghehОценок пока нет
- ECE 542 - Lecture 4Документ24 страницыECE 542 - Lecture 4JohnCross DavidMaryОценок пока нет
- RGMII DataSheetДокумент9 страницRGMII DataSheetyovel.rajaОценок пока нет
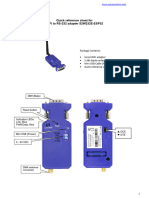
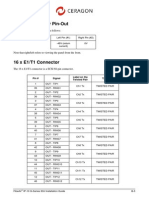
- IP10 ConnectorsДокумент4 страницыIP10 ConnectorsNelo QuispeAduviriОценок пока нет
- Tritech Bathy 232 To Gen 5 DiagramДокумент1 страницаTritech Bathy 232 To Gen 5 DiagramLeandro Pereira delfinoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ82 страницыChapter 2Kavitha Selvaraj50% (2)
- Windows Device Drivers ListДокумент19 страницWindows Device Drivers ListAlexutu AlexОценок пока нет
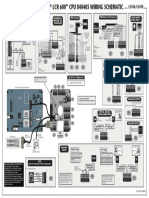
- EM150-12WS - (LCR 600 E3708-3709 Series Wiring Schematic)Документ1 страницаEM150-12WS - (LCR 600 E3708-3709 Series Wiring Schematic)Rizky Andriansyah OmardaniОценок пока нет
- Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy PDH and PDFДокумент3 страницыPlesiochronous Digital Hierarchy PDH and PDFImtiaz JamilОценок пока нет
- PCI Express BasicsДокумент34 страницыPCI Express BasicsRamakrishnaRao SoogooriОценок пока нет
- Metrodata Solutions CatalogueДокумент16 страницMetrodata Solutions CatalogueMetrodataLtdОценок пока нет
- Packet Tracer - Exploring DevicesДокумент4 страницыPacket Tracer - Exploring DevicesevamОценок пока нет
- PLC Connection Guide Weintek (Hmivietnam - Com) PDFДокумент1 128 страницPLC Connection Guide Weintek (Hmivietnam - Com) PDFnguyendang tienОценок пока нет
- TSX Cusb485Документ2 страницыTSX Cusb485AurellioОценок пока нет
- Bharti Quality Workshop-3G - KPI-KolkataДокумент32 страницыBharti Quality Workshop-3G - KPI-Kolkatakunalsingh0003Оценок пока нет