Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Midterm 2012
Загружено:
Thomas AlexanderАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Midterm 2012
Загружено:
Thomas AlexanderАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
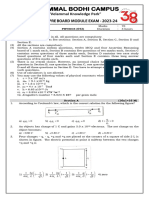
Solid State Physics Midterm - 2012,
March 12 14:30 to 17:20
This is a closed book exam. You may use a hand-written formula sheet. Any four out of the five problems will be counted as a full paper. The problems have equal weight. (1) The crystal structure of Cu3Au. Name: Copper Gold Name: Auricupride, syn Au Cu3 REF: Cannon, J., Humphreys, Brigham Young Univ.,Provo, UT, USA., ICDD Grant-in-Aid,(1983). Sample was prepared by arc-melting the pure elements in a Zrgettered Ar atmosphere. There was a 0.04% weight loss during arc-melting. Powder was annealed for 24 days at 350 C. Radiation: CuKa1 Wave Length: 1.54060 A. Entry q(1/A) 2Theta Int 1 1.675 23.719 17 2 2.370 33.807 11 3 2.902 41.714 100 4 3.352 48.561 41 5 3.747 54.744 6 6 4.105 60.479 4 7 4.740 71.112 21 8 5.027 76.167 3 Above the diffraction peaks observed below 77 degrees are listed. Hint: the alloy is ordered Cu3Au (low temperature annealing for a long time). (a) Decide whether the structure is s.c., b.c.c. or f.c.c., and thus determine the Miller indices h, k, l for the peaks. (b) Determine the lattice constant based on the last peak. (c) What is the density of this intermetallic compound? The atomic mass is 63.54 g/mol for Cu, 196.9 for Au, and Avogadro's number is N A! 6.02"10 23 mol#1 . Sliding atoms. Assume a bcc (body centered cubic) structure, with one atom per lattice point The lattice constant is a. The atomic form factor is some function f !q " . ! r & ! ! "#$ f j ! G " e %i G (a) Calculate the structure factor F ! G for the lattice, and j show that the selection rule for the peaks is h 'k ' l # 2 n with n () . ! (b) Now the atoms at the centres of the cubic unic cells are displaced by ! a z from their original positions, where ! ! 1 . In other words, they are displaced a small fraction of the lattice spacing in the vertical direction. Find again the ! "# F ! G ! "* F ! G ! " of the structure factor, and calculate the intensities I ! G (001), (100) and (002) peaks. Keep only the first nonzero term in an ! expansion of I for these three peaks (expand to leading order in ! '). (c) What is the selection rule if ! !1 " 2 ? No expansion here, of course.
j
(2)
(3)
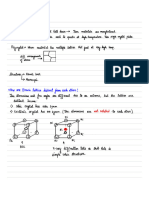
Stability limit for bcc electron phases. (a) For a bcc lattice in real space, what is the shortest distance from the origin of reciprocal space, ! , to the surface of the first Brillouin zone? (b) At what fractional valance (electrons/atom) = (e/a) would the Fermi sphere touch the surface of the first Brillouin zone? (c) Why is the bcc phase expected to become unstable near that (e/a) value? Free electron band structure for an fcc material. The diagram below shows free electron energies for an fcc lattice, given by the & %2 (A). The lattice constant is a. All energies are equation E !"# 2 $ 2m %" & k 'G scaled to the energy at the point X. & and k!X that point to the points ! ans X in (a) What are the vectors k ( reciprocal space? (b) What is the energy at the point X? (c) Consider the band that is marked by the arrow. It is four-fold degenerate (four ! that, inserted dots on the line). What are the four reciprocal lattice vectors G 2 2 & % , give rise to this band? into E !"# $ 2m %" & k 'G
(4)
(5)
The band gap in gold at the [111] surface of the first Brillouin zone. The two diagrams are different representations of the band structure of gold, both based on the same calculation. (S. Kupratakuln and G.C. Fletcher, 1969). The structure of gold is fcc, with a lattice constant of 0.40786 nm. (a) Read the band gap, 2 U , at the point L from the first diagram (where it straddles the Fermi energy). Convert the answer to electron volt (1 Ry = 13.61 eV). Use a ruler for precision.
(b) The solid lines in the diagram below show the Fermi surface. Find the kinetic energies at the points marked by a and b, in eV (with the help of a ruler). !31 !" 1.054#10$34 Js , me !9.11 !10 kg , 1 eV !1.60 !10!19 J . (c) What can you say about the potential energy at each of these two points? (d) From this argument, determine the energy U and compare it with the result in part (a).
Вам также может понравиться
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyОт EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyОценок пока нет
- IAS Previous Year Test PapersДокумент4 страницыIAS Previous Year Test PapersRavinder Singh100% (2)
- Electricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsОт EverandElectricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Physics PQ2Документ7 страницPhysics PQ2David BamОценок пока нет
- Electric Charges and Field 01 April 2TESTДокумент2 страницыElectric Charges and Field 01 April 2TESTcrawlskullОценок пока нет
- Physical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsОт EverandPhysical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsA. H. BeckОценок пока нет
- WS Chap11 ParkДокумент6 страницWS Chap11 ParkporesОценок пока нет
- Xii Second Pre Board Exam - Physics (15-02-2024)Документ7 страницXii Second Pre Board Exam - Physics (15-02-2024)siddhaarth2511Оценок пока нет
- Physics Class 12 Sample PaperДокумент7 страницPhysics Class 12 Sample PaperAkhilesh ArdcОценок пока нет
- Homework Set3 ParticlenatureofmatterДокумент2 страницыHomework Set3 Particlenatureofmatteryobrosky0% (1)
- Cl-12 PHY Preboard-2 Set-1Документ5 страницCl-12 PHY Preboard-2 Set-1Extreme clashersОценок пока нет
- Phy Set-2 QPДокумент5 страницPhy Set-2 QPSiddhartha HadimaniОценок пока нет
- Class-Xii - Final Cbse Board Physics Sample Paper-2Документ7 страницClass-Xii - Final Cbse Board Physics Sample Paper-2kamali.v777Оценок пока нет
- Atomic Structure FДокумент10 страницAtomic Structure FRaju SinghОценок пока нет
- 2020 12 SP PhysicsДокумент22 страницы2020 12 SP PhysicsRiya NinanОценок пока нет
- Physics SQPДокумент7 страницPhysics SQPGopa DeyОценок пока нет
- Class XII Physics H H WДокумент8 страницClass XII Physics H H WJudit LepsényiОценок пока нет
- Sri Chaitanya Iit Academy: Work SheetДокумент8 страницSri Chaitanya Iit Academy: Work SheetLisa ParkerОценок пока нет
- Ques PaperДокумент10 страницQues Papergupta.sg003Оценок пока нет
- Class 12 FCT 4 CBSE FinalДокумент6 страницClass 12 FCT 4 CBSE FinalDerekОценок пока нет
- Solid State Physics Exam Questions and AnswersДокумент7 страницSolid State Physics Exam Questions and Answersfirtemin90% (10)
- Assignment 1Документ3 страницыAssignment 1MainzaОценок пока нет
- Top 10 Sample Papers Class 12 Physics With SolutionДокумент149 страницTop 10 Sample Papers Class 12 Physics With SolutionsavitrishridharhegdeОценок пока нет
- 05 Solution 1Документ18 страниц05 Solution 1Mohar SinghОценок пока нет
- 02 - Physics - March 2006Документ7 страниц02 - Physics - March 2006Bernardo Gonzalez GarciaОценок пока нет
- JEE MAINS Solved Paper 2012Документ30 страницJEE MAINS Solved Paper 2012chithrasajeev100% (1)
- Cmp1+Tut5 - in A Free Electron ModelДокумент1 страницаCmp1+Tut5 - in A Free Electron ModelAchintya DharОценок пока нет
- hw2 (NEW)Документ3 страницыhw2 (NEW)Willie ChangОценок пока нет
- Class XII 2023 2024 Prelims IДокумент10 страницClass XII 2023 2024 Prelims ITanishkha RaajОценок пока нет
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2020 Set 1Документ8 страницCBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2020 Set 1Rajendra SolankiОценок пока нет
- Top 10 Sample Papers Class 12 Chemistry With SolutionДокумент149 страницTop 10 Sample Papers Class 12 Chemistry With Solutionsankarshanrao2Оценок пока нет
- Physics PapersДокумент56 страницPhysics Papersinfiniti786Оценок пока нет
- MT1 Sample 1Документ7 страницMT1 Sample 1Steven ShinОценок пока нет
- Physics 2021Документ34 страницыPhysics 2021milapdhruvcomputerworkОценок пока нет
- Otp - 1 PDFДокумент5 страницOtp - 1 PDFBBA GОценок пока нет
- Exam 3-1 KeyДокумент10 страницExam 3-1 Keyraw4rillОценок пока нет
- Mock Test - 6Документ40 страницMock Test - 6Anirban DeОценок пока нет
- 2003 Qualifying ExamДокумент5 страниц2003 Qualifying Exameka123Оценок пока нет
- 06 - Physics - July 2008Документ6 страниц06 - Physics - July 2008Bernardo Gonzalez GarciaОценок пока нет
- Final ExamA1Документ3 страницыFinal ExamA1LÂN HỒ THANHОценок пока нет
- Jee Main Online Unit Exam: Straight Objective Type Qns. (4, - 1)Документ12 страницJee Main Online Unit Exam: Straight Objective Type Qns. (4, - 1)aryan ajeshОценок пока нет
- 2.physics Qp-XiiДокумент6 страниц2.physics Qp-XiiEMMANUEL PHILIP REJI CLASS XОценок пока нет
- CH 30Документ6 страницCH 30djbechtelnl100% (1)
- CBSE Board Class XII Physics: General InstructionsДокумент23 страницыCBSE Board Class XII Physics: General InstructionsKritik SinghОценок пока нет
- 6.XII Physics Question PaperДокумент8 страниц6.XII Physics Question PaperEMMANUEL PHILIP REJI CLASS XОценок пока нет
- 02 PhysicsДокумент14 страниц02 PhysicsSaikatSenguptaОценок пока нет
- Btech Model QuestionsДокумент22 страницыBtech Model QuestionsAkshayKannanОценок пока нет
- ChemistryforAIEEE CET2009 10Документ140 страницChemistryforAIEEE CET2009 10Lokesh ChemistОценок пока нет
- Subatomic Problem Set 1: Radioactivity and Nuclear StabilityДокумент32 страницыSubatomic Problem Set 1: Radioactivity and Nuclear StabilityDiego M GranziolОценок пока нет
- Physics SQP - 05 Latest (2023) Class 12 CBSEДокумент27 страницPhysics SQP - 05 Latest (2023) Class 12 CBSEmr mindОценок пока нет
- Final Exam Physics1 - SampleДокумент4 страницыFinal Exam Physics1 - Samplethảo nguyễn thanhОценок пока нет
- 2 16 Physics-1Документ3 страницы2 16 Physics-1Akhil UdayanОценок пока нет
- Nuclear AssignmentДокумент10 страницNuclear AssignmentMuhammad Haroon KhanОценок пока нет
- Periodic Potential of ElectronsДокумент47 страницPeriodic Potential of ElectronsJohnОценок пока нет
- Model Paper: Government College University, FaisalabadДокумент8 страницModel Paper: Government College University, FaisalabadIce IceОценок пока нет
- @sachin - Sir - Physics: Version 2.OДокумент9 страниц@sachin - Sir - Physics: Version 2.OPrakharОценок пока нет
- 04 - Physics - July 2007Документ6 страниц04 - Physics - July 2007Bernardo Gonzalez GarciaОценок пока нет
- Practice Midterm 2Документ10 страницPractice Midterm 2jesi5445Оценок пока нет
- Practice Questions For Ch. 7: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionДокумент26 страницPractice Questions For Ch. 7: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionPaolo PepsОценок пока нет
- Ragan Chapter29Документ33 страницыRagan Chapter29Thomas AlexanderОценок пока нет
- Ba Yes I An AnalysisДокумент12 страницBa Yes I An AnalysisThomas AlexanderОценок пока нет
- USEQIP 2013 Acceptance Package: Thomas AlexanderДокумент3 страницыUSEQIP 2013 Acceptance Package: Thomas AlexanderThomas AlexanderОценок пока нет
- Rugby: How A Match Is PlayedДокумент6 страницRugby: How A Match Is PlayedJoel JonesОценок пока нет
- T =16ε (1−ε) e for κL >>1: Equation Sheet CHEM2211Документ2 страницыT =16ε (1−ε) e for κL >>1: Equation Sheet CHEM2211Thomas AlexanderОценок пока нет
- Crystal Directions and PlansДокумент10 страницCrystal Directions and PlansSamyabrata ChatterjeeОценок пока нет
- F Fxe DX: Sin QДокумент3 страницыF Fxe DX: Sin QSang Min LeeОценок пока нет
- Cerro CoronaДокумент17 страницCerro CoronaJaime Mercado BenavidesОценок пока нет
- Mining Tenements Reg4Документ37 страницMining Tenements Reg4Amme MarbaОценок пока нет
- Quality Assurence Büscher 2006Документ71 страницаQuality Assurence Büscher 2006mustafОценок пока нет
- Lund, 2013. Mineralogical, Chemical and Textural Characterisation of The Malmberget Iron Ore Deposit For A Geometallurgical ModelДокумент190 страницLund, 2013. Mineralogical, Chemical and Textural Characterisation of The Malmberget Iron Ore Deposit For A Geometallurgical ModelLucas Pereira100% (1)
- Gem Identification and Testing Equipment From YourGemologistДокумент4 страницыGem Identification and Testing Equipment From YourGemologistDeepak Singh RaghuvansheОценок пока нет
- Mineral Identification ChartДокумент4 страницыMineral Identification ChartIvica PavičićОценок пока нет
- CrystallographyДокумент14 страницCrystallographyGTU Pedia100% (1)
- XR-EBSD 203110007 13thfebДокумент12 страницXR-EBSD 203110007 13thfebVikram ChavanОценок пока нет
- AlNi B2Документ2 страницыAlNi B2Pei Yu ChenОценок пока нет
- Rosebel Gold Mine Including The Saramacca Property 5112019 TRДокумент355 страницRosebel Gold Mine Including The Saramacca Property 5112019 TRRichard R M ThodéОценок пока нет
- Data 1-Clinoptilolite-00-025-1349Документ3 страницыData 1-Clinoptilolite-00-025-1349BUSTANUL RIZKY RIZKYОценок пока нет
- Zircon Mineral DataДокумент4 страницыZircon Mineral DataeriksarumpaetОценок пока нет
- Alteration and Vein Textures Associated With Gold Mineralization Pangalengan West Java PDFДокумент15 страницAlteration and Vein Textures Associated With Gold Mineralization Pangalengan West Java PDFdamasM1Оценок пока нет
- Lecture 5 Chapter 4 Crystal StructureДокумент41 страницаLecture 5 Chapter 4 Crystal StructureDhruv SahniОценок пока нет
- Epithermal Au-Ag Deposit Types - ImplicationsДокумент16 страницEpithermal Au-Ag Deposit Types - ImplicationsJhon Oliver TrebejoОценок пока нет
- GEMs of Heaven - GOD's Eternal Memory StonesДокумент5 страницGEMs of Heaven - GOD's Eternal Memory StonesswijcomОценок пока нет
- Miller Indices: Planes Directions Lattices CrystalsДокумент52 страницыMiller Indices: Planes Directions Lattices CrystalsKaren González OrtuyaОценок пока нет
- Mineral Lesson PlanДокумент5 страницMineral Lesson Planapi-402836919Оценок пока нет
- Geology & Mining Processes (Rizal Baslang)Документ30 страницGeology & Mining Processes (Rizal Baslang)Willy ApryantoОценок пока нет
- 5 Minerals UnpopularДокумент1 страница5 Minerals UnpopularCuek SetiaОценок пока нет
- Course Objective... : You Will Learn AboutДокумент70 страницCourse Objective... : You Will Learn AboutThaneswaran BaluОценок пока нет
- Lecture 6 Grain Boundary Displocation Defects VancancyДокумент8 страницLecture 6 Grain Boundary Displocation Defects VancancyAl-Kawthari As-SunniОценок пока нет
- Introduction To QuasicrystalsДокумент3 страницыIntroduction To Quasicrystalsgt0084e1Оценок пока нет
- TMP 33 B2Документ6 страницTMP 33 B2FrontiersОценок пока нет
- Notes ESO205Документ44 страницыNotes ESO205muditОценок пока нет
- Vasp Workshop at NCHC: Lecture NotesДокумент15 страницVasp Workshop at NCHC: Lecture Notesabhinav jangirОценок пока нет
- 01-Crystals Fall2012 - Compatibility ModeДокумент44 страницы01-Crystals Fall2012 - Compatibility Modetrebor sllewОценок пока нет
- Final Seminar ReportДокумент39 страницFinal Seminar Reportgowtham reddy100% (1)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesОт EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2193)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseОт EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (69)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceОт EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (51)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldОт EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (64)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyОт EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyОценок пока нет
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessОт EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingОт EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidОт EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1395)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayОт EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (125)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismОт EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (500)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterОт EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (410)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldОт EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (60)
- Let There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessОт EverandLet There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (57)
- Chasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombОт EverandChasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (8)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldОт EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (54)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseОт EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (13)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectОт EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (20)
- Beyond Weird: Why Everything You Thought You Knew about Quantum Physics Is DifferentОт EverandBeyond Weird: Why Everything You Thought You Knew about Quantum Physics Is DifferentРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (25)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowОт EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (49)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityОт EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (76)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)От EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (157)
- The Universe: The book of the BBC TV series presented by Professor Brian CoxОт EverandThe Universe: The book of the BBC TV series presented by Professor Brian CoxРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (27)