Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Form 5 Redox
Загружено:
Mohd RidzuanИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Form 5 Redox
Загружено:
Mohd RidzuanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
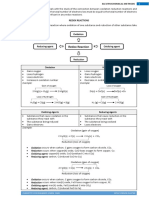
A substance that reduced
REDOX Chemical reaction where oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously A substance that oxidized
another substance
another substance
Oxidation (act as reducing agent) Gain oxygen Loss Hydrogen Loss electron Increase Oxd. No
Reduction (act as oxidizing agent) Loss oxygen Gain Hydrogen Gain electron Decrease Oxd. No CuO + H2 ---> H2O
2Mg + O2 ---> 2MgO H2S + Cl2 ---> HCl + S Na ---> Na+ + e Zn + CuSO4 ---> ZnSO4 + Cu
(0) (+2) EXAMPLE 1
Br2 + 2HI ---> 2HBr + I2 Cl2 + 2e 2ClZn + CuSO4 ---> ZnSO4 + Cu
(+2) (0)
Magnesium is oxidized (gain of oxygen) Oxidation Mg Reducing agent Mg is reducing agent as it causes CuO to be reduced. + CuO MgO Reduction +
Oxidising agent Cu is oxidising agent as it causes Mg to be oxidized. Cu
Rule 1 the oxidation number for atom and molecule is zero Example: Mg, Ca, C, Cu, Zn, Cl2, O2, H2
Copper(II) oxide is reduced (loss of oxygen)
Rule 2 The sum of oxidation number of all elements in polyatomic ions is equal to the charge of the ions Example:
NH4+ +1 SO42-2 MnO4-1 Cr2O72-2
EXAMPLE 1 Na Na+ + e (loss electron) Oxidation 2Na + Cl2 2NaCl NaCl is an ionic compound. It exist as Na+ ions and Clions
Rule 3 The sum of oxidation numbers of all elements in the compound is zero Example:
H2SO4 0 KMnO4 0 SO2 0 K2Cr2O7 0
Reduction Cl2 + 2e 2Cl- (gain electron)
Calculate the oxidation numbers for the underlined elements. (ii) S2O32- [polyatomic ion] 2(x) + 3(-2) = -2 2x - 6 = -2 x = (-2 + 6) /2 2+ 3+ x Type 1: Redox reaction involves Fe ion and ion Fe ion = +2 Thus; Oxidation number of S in SO2 Thus; = +4 Oxd. number of S in S2O32- = +2 (i) SO2 [compound] 1(x) + 2(-2) = 0 x - 4 = 0 x = +4
Rule 4 the oxidation number for monoatomic ion is equal to its charge Example: H+ Fe2+ Cr3- O2- N3+1 +2 -1 -2 -3
Oxidation (loss e-) Reducing agent Fe2+ Fe3+ Oxd. agent Reduction (gain e-)
Others oxidizing agents that can replaced bromine water: - Chlorine water, Cl2 - Acidified potassium manganate(VII), KMnO4 - Acidified potassium dichromate(VI),
Others reducing agents that can replaced zinc: - Magnesium, Mg - Sulphur dioxide, SO2 - Hydrogen sulphide, H 2S - Sodium sulphide solution, Na2SO3
Change of iron (II) ions to iron (III) ions Observation Iron (II) solution change colour from green to brown FeSO4 Bromine water oxidizes Fe2+ ions to Fe3+ ions Causing Fe2+ release one electron Fe2+ Fe3+ + e (Oxidation) Fe acts as reducing agent because it reduced Br2 to Br2+
Observation Brown colour of bromine water decolourised.
Bromine water
Electron released are accepted by bromine molecules Its undergo reduction to form bromide ions, BrBr2 + 2e Br(reduction) Br2 acts as oxidizing agent because it oxidized Fe2+ to Fe3+ ions
Ionic equation: 2Fe2+ + Br2 Fe3+ + Br-
Change of iron (III) ions to iron (II) ions Observation Zn powder dissolved in solution Fe2(SO4)3 Observation Iron (III) solution change colour from brown to green
Zinc powder Fe2(SO4)3
Zinc atom lose electrons to Fe3+ Its undergo oxidation to form zinc ions, Zn2+ Zn Zn2+ + 2e(oxidation) Zinc acts as reducing agent because it reduced Fe3+ to Fe2+ ions 2Fe3+
Zinc powder reduced Fe3+ ions to Fe2+ ions Fe3+ accept one electron from Zinc Fe3+ + e Fe2+ (Reduction) Fe3+ acts as oxidising agent because it oxidized Zn to Zn2+
Ionic equation: + Zn 2Fe2+ +Zn2+
Type 2: Displacement of metal from its salt solution Observation: Metal dissolve /become thinner Metal X + Salt Y Observation: Metal dissolve /become thinner Salt X + Metal Y
K Na Ca Mg Al Zn Fe Sn Pb H Cu Ag Au
MORE ELECTROPOSITIVE More a electropositive metal will displace a metal less electropositive metal from its solution
The copper(II) ions are taken out from the solution to form copper metal . Cu2+ (aq) + 2e Cu (s) Copper(II) ions are reduced. The blue colour of copper(II)sulphate solution fades.
Ionic Equation: Mg + Cu2+
Mg2+ + Cu
Zinc is more electropositive than copper ( zinc is in higher position than copper in electrochemical series). Zinc displaced copper from copper(II) sulphate solution. Zn(s) Zn2+(aq) + 2e Zinc is oxidised
Type 3: Displacement Halogen from its halide solution A more reactive halogen displaces a less reactive halogen from its aqueous halide solution. F2 Cl2 Br2 I2 The more reactive halogen has a higher tendency to gain electron. F2 Cl2 Br2 I2
LESS ELECTRONEGATIVE /REACTIVE
Chlorine water Potassium bromide Chlorine act as oxidizing agent Chlorine undergo reduction Cl2 + 2KBr 2KCl + Br2
Bromine water Potassium bromide Bromine act as oxidizing agent Bromine undergo reduction Br2 + 2KI 2KBr + I2
Bromine water Potassium bromide
Br2 + 2KI
2KBr + I2
Bromine ion undergo oxidation Potassium bromide act as reducing agent Observation: Yellow solution of chlorine decolorized Colourless solution of potassium bromide turn to brown
Iodide ion undergo oxidation Potassium iodide act as reducing agent Observation: Brown solution ofbromine decolorized Colourless solution of potassium bromide turn to brown
Bromine cannot displace chlorine from sodium chloride Bromine is less electronegative than chlorine
Вам также может понравиться
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Документ18 страницSPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Aidah Amir100% (2)
- Redox Reactions ExplainedДокумент40 страницRedox Reactions ExplainedMohamad HanifОценок пока нет
- Redox Reactions ExplainedДокумент17 страницRedox Reactions ExplainedJoanne SiaОценок пока нет
- Oxidation NumberДокумент7 страницOxidation NumberNor Faizahbaizura Abu BakarОценок пока нет
- REDOX EQUILIBRIUM (Teacher's Copy)Документ34 страницыREDOX EQUILIBRIUM (Teacher's Copy)jiaОценок пока нет
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 – Oxidation and ReductionДокумент22 страницыSPM Chemistry Form 5 – Oxidation and ReductionCk OoiОценок пока нет
- Modul Kimia Ting 5 Bab 12Документ9 страницModul Kimia Ting 5 Bab 12Chew Gee LanОценок пока нет
- SPM Chemistry Form 5Документ5 страницSPM Chemistry Form 5Aileen PoLyОценок пока нет
- R2 6lA5NCДокумент7 страницR2 6lA5NCIsa ShahidОценок пока нет
- Oxidation and ReductionДокумент28 страницOxidation and ReductionCharlene LowОценок пока нет
- Oxidation ReductionДокумент7 страницOxidation ReductionWalu BNОценок пока нет
- Oxidation ReductionДокумент7 страницOxidation ReductionZul Abror Bin Ya'akopОценок пока нет
- REDOX REACTIONS: OXIDATION AND REDUCTIONДокумент92 страницыREDOX REACTIONS: OXIDATION AND REDUCTIONMollel TajiriОценок пока нет
- Redox ReactionsДокумент2 страницыRedox Reactionschong56Оценок пока нет
- Oxidation and ReductionДокумент12 страницOxidation and Reductionmuhsin94Оценок пока нет
- Introduction To Oxidation and ReductionДокумент0 страницIntroduction To Oxidation and ReductionAdnan ChowdhuryОценок пока нет
- Redox TitrationДокумент23 страницыRedox TitrationSapna PandeyОценок пока нет
- REDOXДокумент67 страницREDOXLeo PietroОценок пока нет
- Redox Reactions ExplainedДокумент12 страницRedox Reactions ExplainednazanazriОценок пока нет
- Redox (REDOX) Reactions ExplainedДокумент50 страницRedox (REDOX) Reactions ExplainedElvis NgandweОценок пока нет
- Introductory Chemistry - SCH0201 - Lec10Документ26 страницIntroductory Chemistry - SCH0201 - Lec10Ayanthi ShashikalaОценок пока нет
- RedoxДокумент14 страницRedoxsaraОценок пока нет
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 - Redox Part 1Документ4 страницыSPM Chemistry Form 5 - Redox Part 1ysheng98Оценок пока нет
- RedoxДокумент2 страницыRedoxtmoatshe96Оценок пока нет
- Oxidation and Reduction SPM Form 5Документ63 страницыOxidation and Reduction SPM Form 5Azie Nurul Akhtar85% (13)
- Oxidation & Reduction: 4 Examples of Redox ReactionДокумент25 страницOxidation & Reduction: 4 Examples of Redox ReactionlinieyОценок пока нет
- 11.4A Redox Reaction and ElectrochemistryДокумент98 страниц11.4A Redox Reaction and ElectrochemistryЕлнур ИкимбаевОценок пока нет
- F5C1 Redox EquilibriumДокумент15 страницF5C1 Redox EquilibriumthilagaОценок пока нет
- Oxidation ReductionДокумент47 страницOxidation ReductionAbdulraqeb AlawadhiОценок пока нет
- Oxidation & Reduction: Redox ReactionsДокумент5 страницOxidation & Reduction: Redox ReactionsVenusCrazy 550Оценок пока нет
- 7 Transfer of Electrons at A DistanceДокумент15 страниц7 Transfer of Electrons at A DistancenamikОценок пока нет
- Chem F5 Chapter 3 (2020)Документ39 страницChem F5 Chapter 3 (2020)JΞτΗασ0% (1)
- Assignment Zinc ChemicalДокумент5 страницAssignment Zinc ChemicalNaveed SDОценок пока нет
- Oxidation & Reduction - Redox Reactions - Oxidation: Oxygen Atoms From The Oxygen Molecules in Air E.GДокумент4 страницыOxidation & Reduction - Redox Reactions - Oxidation: Oxygen Atoms From The Oxygen Molecules in Air E.Ghussein hajiОценок пока нет
- OXIDATION AND REDUCTION REACTIONS (Autosaved)Документ15 страницOXIDATION AND REDUCTION REACTIONS (Autosaved)TeandraОценок пока нет
- 1 Electrochemical MethodsДокумент17 страниц1 Electrochemical MethodsJames BombitaОценок пока нет
- 5 6116152494587379984Документ98 страниц5 6116152494587379984dharwinОценок пока нет
- O Level Chemistry SummaryДокумент22 страницыO Level Chemistry SummarySara Emad100% (1)
- Chemistry For Changing Times 14th Edition Hill Mccreary Solution ManualДокумент8 страницChemistry For Changing Times 14th Edition Hill Mccreary Solution ManualCindyCurrydwqzr100% (74)
- WWW - One School - Net Notes Chemistry SPM Chemistry Formula List Form5Документ15 страницWWW - One School - Net Notes Chemistry SPM Chemistry Formula List Form5Nur AmaleenaОценок пока нет
- Different Types of Chemical Reactions: Combination or Synthesis ReactionsДокумент7 страницDifferent Types of Chemical Reactions: Combination or Synthesis ReactionselizabethОценок пока нет
- Oxidation and ReductionДокумент14 страницOxidation and ReductionAsik ShabickОценок пока нет
- 9th Class ElectrochemistryДокумент18 страниц9th Class ElectrochemistryCh NajamОценок пока нет
- Oxidation and Reduction ReactionsДокумент33 страницыOxidation and Reduction ReactionsAl Christian YaboОценок пока нет
- 2.06 RedoxДокумент6 страниц2.06 RedoxBryan YeohОценок пока нет
- Strongest Reducing Agents Are at One End and (RIG)Документ5 страницStrongest Reducing Agents Are at One End and (RIG)Ayush Singhi L OT1 170Оценок пока нет
- Eng Chem Lecture NotesДокумент2 страницыEng Chem Lecture NotesJunell TadinaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 11 Redox Reactions SummaryДокумент42 страницыChapter 11 Redox Reactions SummaryKris DookharanОценок пока нет
- Grade 9 Chemistry: Redox ReactionsДокумент16 страницGrade 9 Chemistry: Redox ReactionsvfdfdОценок пока нет
- 4.4 ElectrochemistryДокумент20 страниц4.4 Electrochemistrygabrielsiema4Оценок пока нет
- Metals NotesДокумент4 страницыMetals NotesXGC Ahssn YtОценок пока нет
- Contents:: Oxidation and Reduction Oxidizing and Reducing Agent Process of OxidationДокумент12 страницContents:: Oxidation and Reduction Oxidizing and Reducing Agent Process of OxidationMUHAMMAD NABEEL ARIFОценок пока нет
- Combination ReactionsДокумент7 страницCombination Reactionstaurus_nikita4484Оценок пока нет
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-985613Документ7 страницCLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-985613abiniveshofficial4708Оценок пока нет
- Metals and Non-metals GuideДокумент12 страницMetals and Non-metals GuidecharanОценок пока нет
- 8oxidation Reduction ReactionsДокумент50 страниц8oxidation Reduction ReactionsMohamed AlQallafОценок пока нет
- Oxidation AND ReductionДокумент60 страницOxidation AND ReductionSofea Alya SuhaiziОценок пока нет
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersОт EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersОценок пока нет
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionОт EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Extractive Metallurgy 2: Metallurgical Reaction ProcessesОт EverandExtractive Metallurgy 2: Metallurgical Reaction ProcessesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- World Bank ReportДокумент12 страницWorld Bank ReportMohd RidzuanОценок пока нет
- Master RepotДокумент11 страницMaster RepotMohd RidzuanОценок пока нет
- Latest English Language Yearly Plan Year 6Документ21 страницаLatest English Language Yearly Plan Year 6sasauball100% (1)
- Yearly Plan Science Year 5Документ7 страницYearly Plan Science Year 5Mohd RidzuanОценок пока нет
- Gardening Peas SpringДокумент1 страницаGardening Peas SpringMohd RidzuanОценок пока нет
- Hidden Picture Puzzle: Snowy WeatherДокумент1 страницаHidden Picture Puzzle: Snowy WeatherMohd RidzuanОценок пока нет
- Hidden Picture Puzzle: PicnicДокумент1 страницаHidden Picture Puzzle: PicnicMohd RidzuanОценок пока нет
- Scheme of Work - Yr6Документ11 страницScheme of Work - Yr6Mohd RidzuanОценок пока нет
- Yearly Plan Science Year 4Документ145 страницYearly Plan Science Year 4Jimie AsmaraОценок пока нет
- Hidden Picture Puzzle: Dance For JoyДокумент1 страницаHidden Picture Puzzle: Dance For JoyMohd RidzuanОценок пока нет
- Classroom Items Crossword Puzzle KeyДокумент1 страницаClassroom Items Crossword Puzzle KeyMohd RidzuanОценок пока нет
- Oxidized Another Substance Reduced Another Substance: Atom MoleculeДокумент3 страницыOxidized Another Substance Reduced Another Substance: Atom MoleculeMohd RidzuanОценок пока нет
- Hidden Picture Puzzle: Life in The CountryДокумент1 страницаHidden Picture Puzzle: Life in The CountryMohd RidzuanОценок пока нет
- New Year's Hidden Picture Puzzle WorksheetДокумент1 страницаNew Year's Hidden Picture Puzzle WorksheetMohd RidzuanОценок пока нет
- Birthday Party Answer KeyДокумент1 страницаBirthday Party Answer KeyMohd RidzuanОценок пока нет
- Animals AnswersДокумент1 страницаAnimals AnswersMohd RidzuanОценок пока нет
- Classroom essentials displayedДокумент1 страницаClassroom essentials displayedLuis F. Porras CamposОценок пока нет
- Birthday Party Vocabulary Crossword - Learn New Words for CelebrationsДокумент1 страницаBirthday Party Vocabulary Crossword - Learn New Words for CelebrationsMohd RidzuanОценок пока нет
- Welcome: Techniques in Answering Upsr Science Questions ProgrammeДокумент68 страницWelcome: Techniques in Answering Upsr Science Questions ProgrammeMohd RidzuanОценок пока нет
- Circuit Investigation - Effect of Components on Heating TimeДокумент3 страницыCircuit Investigation - Effect of Components on Heating TimeMohd RidzuanОценок пока нет
- Easy Animal Crossword PuzzleДокумент1 страницаEasy Animal Crossword PuzzleMohd RidzuanОценок пока нет
- Science Process SkillsДокумент106 страницScience Process SkillsMohd RidzuanОценок пока нет
- Science Process SkillsДокумент2 страницыScience Process SkillsMohd RidzuanОценок пока нет
- Assignment 2 - The Importance of English Language in Malaysia - Document TranscriptДокумент4 страницыAssignment 2 - The Importance of English Language in Malaysia - Document TranscriptMohd RidzuanОценок пока нет
- Circuit Investigation - Effect of Components on Heating TimeДокумент3 страницыCircuit Investigation - Effect of Components on Heating TimeMohd RidzuanОценок пока нет
- Science Process SkillsДокумент106 страницScience Process SkillsMohd RidzuanОценок пока нет
- Welcome: Techniques in Answering Upsr Science Questions ProgrammeДокумент68 страницWelcome: Techniques in Answering Upsr Science Questions ProgrammeMohd RidzuanОценок пока нет
- M LearningДокумент3 страницыM LearningMohd RidzuanОценок пока нет