Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ala Algebra 1 Module 2 Applications
Загружено:
api-245933467Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Ala Algebra 1 Module 2 Applications
Загружено:
api-245933467Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
ALA Algebra 1 Module 2 Applications (page 1) I.
Writing Algebraic Expressions: use the given information to change the initial dose as directed. A patient starts at a dose of 50 mg of medication per day. Double the dose: A patient starts at a dose of x mg of a medication per day. Double the dose:
Triple the dose:
Triple the dose:
Cut the dose in half:
Cut the dose in half:
Increase the dose by 10 mg:
Increase the dose by 10 mg:
Decrease the dose by 10 mg:
Decrease the dose by 10 mg:
How much is 10 mg less than half the dose?
How much is 10 mg less than half the dose?
How much is 20 mg more than twice the dose?
How much is 20 mg more than twice the dose?
How much medication will the patient get in a week?
How much medication will the patient get in a week?
At 35 cents per milligram, how much does a dose cost?
At 35 cents per milligram, how much does a dose cost?
ALA Algebra 1 Module 2 Applications (page 2) II. Find the secret numbers! Be sure to set up an equation, identify your variable, label your answer, and check that you answered the question and your answer makes sense! 1. There are 150 patients in the hospital. There are twice as many non-surgical patients as there are surgical patients. How many of each type of patient are in the hospital?
2. There are 450 patients in the hospital. The number of men is half the number of women. How many men and how many women are in the hospital?
3. There are 300 bandages in the supply closet. There are 50 more large bandages than small. How many of each size bandages are there?
4. There are 93 tubes of ointment in the supply closet. The number of large tubes is one more than three times the number of sample-size tubes. How many of each size tube of ointment are there?
5. There are 70 blood pressure cuffs in the supply closet. The number of adult cuffs is 4 less than twice the number of pediatric cuffs. How many of each size blood pressure cuff are there?
ALA Algebra 1 Module 2 Applications (page 3) 6. There are 75 patients on a maternity ward. The number of mothers is twelve less than twice the number of babies. How many mamas and how many babies are on the ward?
7. A pair of twins weigh a total of 63 pounds. Their weights are consecutive integers. How much does each twin weigh?
8. A pair of twins weigh a total of 158 pounds. Their weights are consecutive even integers. How much does each twin weigh?
9. A set of triplets weigh a total of 117 pounds. Their weights are consecutive odd integers. How much does each triplet weigh?
10. A family had three children, each born two years after the previous child. The sum of the ages of the three children is 101 years. How old is each sibling?
11. The perimeter of an examination room is 44 feet. The length and width are consecutive even integers. What are the dimensions of the room? (Remember, to find perimeter, add up the lengths of all four sides!)
ALA Algebra 1 Module 2 Applications (page 4) III. Working with formulas 1. The formula to calculate Body Mass Index, or BMI, has become increasingly important in the fight against obesity. Here is the formula: B=w h2
, where B = BMI, or Body Mass Index, w = weight in kilograms, h = height in meters.
a) Keisha is 1.6 meters tall and weighs 59 kilograms. What is her body mass index?
b) Joseph is 2 meters tall and weighs 79 kilograms. What is his body mass index?
c) Lara is 1.5 meters tall and weighs 100 kilograms. What is her body mass index?
d) Medical professionals define a person as overweight if 25 < BMI < 29.9. A person is considered obese if BMI > 30. According to these definitions, how would you categorize Keisha, Joseph, and Lara above?
e) Dorian has a BMI of 25. He is 1.8 meters tall. How much does he weigh?
f) Solve the formula above for weight (that is, get the variable w by itself on one side of the equation).
ALA Algebra 1 Module 2 Applications (page 5) 2. In the United States, most people use a Fahrenheit temperature scale. Along with the rest of the world, however, the medical community uses the Metric temperature scale, which measures in degrees Celcius. You can use these two formulas to convert between the two:
a) Water freezes at 32 Fahrenheit. What is this in Celcius?
b) Water boils at 212 Fahrenheit. What is this in Celcius?
c) Normal human body temperature is 98.6 Fahrenheit. What is this in Celcius?
d) A patient has a body temperature of 38.2 Celcius. What is this in Fahrenheit?
e) The room temperature is 26 Celcius. What is this in Fahrenheit? Is it comfortable?
f) The outdoor temperature is 40 Celcius. What is this in Fahrenheit? What would you wear outside?
ALA Algebra 1 Module 2 Applications (page 6) IV. Distance Problems 1. Use the distance formula (d = rt) to solve the problems on this page. Remember that there are 60 minutes in an hour! a) An ambulance travels at 60 miles per hour to reach the patient. It arrives in half an hour. How far away was the patient?
b) A woman in labor travels 30 miles to get to the hospital. It takes 36 minutes. How fast was her husband driving?
c) How long will it take to get to the hospital if you walk at a rate of 4 miles per hour for 2 hours?
d) Two ambulances leave the same hospital at 1530 (thats 3:30 pm). One ambulance drives north at 30 mph. The other drives south at 40 mph. At what time will they by 210 miles apart?
e) Two nurses leave hospitals that are 90 miles apart and head toward each other. One is traveling twice as fast as the other. They meet in three hours. How fast is each going?
f) Solve the formula D= rt for time (that is, get t by itself on one side of the equation).
ALA Algebra 1 Module 2 Applications (page 7) V. Simple Interest Problems. Solve each problem, using the formula I = PRT, where I = the amount of interest in dollars P = the principal in dollars R = the interest rate written as a decimal T = time in years 1. Solve the formula above for P (that means get the variable P by itself on one side of the equation).
2. Debbie invested $5000 at 3% interest for 2 years. How much interest did she earn?
3. Lisa invested $7000 at 3.5% interest. How long did it take her to earn $1225 in interest?
4. Cynthia invested some money at 3.25% interest for 5 years and earned $1218.75 in interest. How much did she invest?
5. Nancy invested some money at 5% interest, and twice as much money at 7% interest. After 2 years she had earned $ 570. How much did she invest at each rate?
ALA Algebra 1 Module 2 Applications (page 8) VI. Ratios and Proportions 1. The following are ratios of the number of patients to the number of nurses on a hospital floor. Simplify the ratio to determine how many patients per one nurse. a) 40:4 b) 55:11 c) 168:14 d) 52:13 e) 48:8 _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________
2. Healthcare workers who administer medicine must have a clear understanding of how to compute dosage calculations. A certain medicine must be administered in the ratio of 10 cc per every 25 pounds. Compute the amount of medicine (cc) needed for the following patients, given their weight in pounds. Round to the nearest tenth, if necessary. a) 50 pounds b) 100 pounds c) 200 pounds d) 8 pounds e) 135 pounds f) 57 pounds g) 277 pounds __________ __________ __________ __________ __________ __________ __________
******************************************************************** 3. Use proportional reasoning to convert each measurement. You may need to know that there are 3 teaspoons in a tablespoon, 2 cups in a pint, 2 pints in a quart, 4 quarts in a gallon, 16 ounces in a pound, 12 inches in a foot, 3 feet in a yard, 5280 feet in a mile, and about 2.2 pounds in a kilogram. a) 5 cups = _____________ pints b) 7 quarts = _____________ gallons c) 34 ounces = _______________ pounds
ALA Algebra 1 Module 2 Applications (page 9) d) 5 feet = ______________ inches e) 10 miles = _______________ feet f) 12 teaspoons = _______________ tablespoons g) 500 yards = _________________ feet h) 200 pounds = _________________ kilograms i) 10 pints = ______________ quarts ********************************************************************* 4. Solve the following proportion problems by setting up a proportion and solving for the unknown. Show your work. a) Two tablets of ulcer medication contain 250 milligrams of medication. How many milligrams are in eight tablets?
b) If a dose of 72 milligrams of medication is contained in 4 cc, 24 milligrams would be contained in how many cc?
c) If 15 grams of pure drug are contained in 150 milliliters, how many grams are contained in 50 milliliters?
d) A tablet contains 75 milligrams of medication. If a doctor orders 300 milligrams of medication for a patient, how many tablets should be given to the patient?
e) A tablet contains 30 milligrams of medication. If a doctor orders 15 milligrams of medication for a patient, how many tablets should be given to the patient?
ALA Algebra 1 Module 2 Applications (page 10) VII. Percent Problems 1. If you weigh a child in kilograms, 60% of that weight will tell you how many liters of water make up that childs body. This relationship is the Total Body Water formula. a) A child weighs 3.5 kilograms at birth. How many liters of water are in the childs body?
b) A 4-year-old child weighs 25 kilograms. How many liters of water are in the childs body?
c) A childs body contains 4 liters of water. How much does the child weigh?
d) A childs body contains 2.7 liters of water. How much does the child weigh?
2. Percent increase and decrease a) The patient census increased from 50 to 75 patients. What was the percent increase?
b) The patient census decreased from 50 to 40 patients. What was the percent decrease?
c) The copay used to be $20, but it increased by 25%. What is the new copay?
ALA Algebra 1 Module 2 Applications (page 11) 3. A drug experiment showed the following results: Number of patients receiving the drug 50 20 15 Number of patients reporting improvement 30 ? 3
Old drug New drug Placebo
a) What percent of patients receiving the old drug reported improvement?
b) Seventy-five percent of the patients receiving the new drug reported improvement. How many patients is this? Fill in the number on the table.
c) What percent of patients receiving the placebo (no drug, just a fake medication to make them think they might be receiving a real dose) reported improvement?
d) What percent of ALL the patients in the study reported improvement?
e) What percent of ALL the patients in the study did NOT report improvement?
f) Which seems to have been more effective: the old drug, the new drug, or no drug at all?
ALA Algebra 1 Module 2 Applications (page 12) 4. A sampling of patients being discharged from the hospital yielded the following results:
Patient Satisfaction Survey Results
Furious 8% Thrilled 12% Frustrated 30% Satisfied 50%
a) Forty patients participated in the survey. How many were satisfied? How many were frustrated? Thrilled? Furious?
b) The legal staff is nervous about dissatisfied patients who might sue the hospital. What percent of patients reported some level of dissatisfaction with their hospital experience?
c) If the same percentages held, how many patients in a survey of 1200 would report being thrilled with their hospital experience?
ALA Algebra 1 Module 2 Applications (page 13) VIII. Mixture Problems 1. How many liters of a 10%-saline solution must be mixed with 20 liters of a 40%saline solution to create a mixture that is 25% saline?
2. How many liters of a solution that is 15% glucose must be mixed with 5 liters of a solution that is 50% glucose to create a solution that is 30% glucose?
3. You need 20 liters of a solution that is 15% pain-killer, but all you have are some 10% and some 40% solution. How much of each should you mix together?
4. 8 ounces of a solution that is 50% pure medication must be watered down to be just 20% pure medication. How much water should be added?
5. Regular coffee that is $2.50 per pound is being mixed with gourmet coffee worth $7.00 per pound. How much of each type of coffee should be used to create 100 pounds of a mixture worth $5.00 per pound?
ALA Algebra 1 Module 2 Applications (page 14) IX. Function Notation 1. The time it takes to distribute medicines to all of your patients depends on how many patients you have. It takes 20 minutes to organize the medicine cart, plus 7 minutes per patient, so the total time giving meds can be described by the function T(x) = 20 + 7x , where T(x) is the Total Time in minutes youll spend, and x is the number of patients you have.
a) Calculate T(5), the time it will take to give meds to your 5 patients.
b) Calculate T(12), the time it will take to give meds to your 12 patients.
c) Calculate T(4), the time it will take to give meds to your 4 patients.
d) One nurse took 90 minutes to give out her meds. How many patients did she have?
************************************************************************ 2. Occasionally, your job requires that you write a voucher for a patient to take a taxi home. The taxi fare depends on how far the patient must travel. Since the taxi company charges a flat fee of three dollars for a ride, plus fifty cents per mile, the fare can be calculated using the function as follows: F(x) = 3 + .5x, where F(x) is the Fare the taxi will charge in dollars, and x is the number of miles to the patients home.
To find the fare for a 10-mile taxi ride, you would calculate F(10) = 3 + .5 10 = 3 + 5 = 8, so the fare would be eight dollars. a) Calculate F(4), the fare for taking a taxi 4 miles.
b) Calculate F(20), the fare for taking a taxi 20 miles.
c) Calculate F(5), the fare for taking a taxi 5 miles. d) One patients taxi fare was $9. How far away from the hospital does the patient live?
Вам также может понравиться
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Chemistry JokesДокумент3 страницыChemistry JokesDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaОценок пока нет
- The Effect of Risk Return Analysis of Pharmaceutical Companies On Indian Stock MarketДокумент5 страницThe Effect of Risk Return Analysis of Pharmaceutical Companies On Indian Stock MarketIJEMR Journal100% (1)
- Interview Questions Asked in PPSC 2015 in Diff Sectors: RawalpindiДокумент4 страницыInterview Questions Asked in PPSC 2015 in Diff Sectors: RawalpindiAli ArshadОценок пока нет
- PharmTech NA Oct2020 WM PDFДокумент76 страницPharmTech NA Oct2020 WM PDFFrancisco DominguezОценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes-Pharmacy Therapeutic CommitteeДокумент6 страницLecture Notes-Pharmacy Therapeutic CommitteePatras BhattiОценок пока нет
- Pemakaian Obat Harian Pustu Koto Baru Bulan: Dak /dauДокумент56 страницPemakaian Obat Harian Pustu Koto Baru Bulan: Dak /dauDermawan SstОценок пока нет
- Homeo & Herbal RemediesДокумент175 страницHomeo & Herbal Remediesjk.dasgupta100% (2)
- LDN Information (2!19!17 Update)Документ18 страницLDN Information (2!19!17 Update)bktango100% (1)
- Manufacturing of Sterile PharmaceuticalsДокумент48 страницManufacturing of Sterile PharmaceuticalsMelaku TeshomeОценок пока нет
- CVAD For NursesДокумент54 страницыCVAD For NursesRitaLakhaniОценок пока нет
- Classification For Drug Related Problems: (Revised 14-01-2010vm)Документ4 страницыClassification For Drug Related Problems: (Revised 14-01-2010vm)yossi ismardianiОценок пока нет
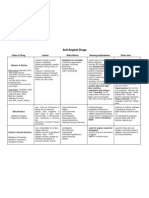
- Anti Anginal DrugsДокумент1 страницаAnti Anginal DrugsHatem AbouelnasrОценок пока нет
- PSMB Area 4Документ133 страницыPSMB Area 4Princess Rose GamboaОценок пока нет
- Telmisartan Amlodipine Single Pill Combination In.6Документ12 страницTelmisartan Amlodipine Single Pill Combination In.6urbanincultureОценок пока нет
- Adams4e Tif Ch47Документ19 страницAdams4e Tif Ch47fbernis1480_11022046100% (1)
- Cyclophosphamide (Cyclovid) - Epirubicin - VincristineДокумент1 страницаCyclophosphamide (Cyclovid) - Epirubicin - VincristineEma Ratna KartinawatiОценок пока нет
- Org Chart & Job Description June 18 2018Документ5 страницOrg Chart & Job Description June 18 2018Karenina VictoriaОценок пока нет
- Drugs Used To Treat Glaucoma and Other EyeДокумент38 страницDrugs Used To Treat Glaucoma and Other Eyerenz bartolomeОценок пока нет
- Info BrochureДокумент41 страницаInfo BrochureThuhieu HuaОценок пока нет
- AripiprazoleДокумент30 страницAripiprazoleSiegfried Cristofor100% (1)
- Case Study ChinaДокумент6 страницCase Study ChinaAl-Imran Bin KhodadadОценок пока нет
- Cilinary Set UpДокумент32 страницыCilinary Set UpOla Kareem100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Jurisprudence and Relevant Administrative Order - HANDOUTДокумент38 страницPharmaceutical Jurisprudence and Relevant Administrative Order - HANDOUTsandrock9920058942Оценок пока нет
- GI Disorders and CuresДокумент19 страницGI Disorders and CurespjsworldОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology PrescriptionsДокумент6 страницPharmacology PrescriptionsJohn PayneОценок пока нет
- Patient Counseling-General Considerations, Important Steps & Procedures InvolvedДокумент13 страницPatient Counseling-General Considerations, Important Steps & Procedures InvolvedMD REFATОценок пока нет
- Titr SensorbroeДокумент28 страницTitr SensorbroeNgoc TruongОценок пока нет
- Write - Up - Adhoc Data SourcesДокумент12 страницWrite - Up - Adhoc Data SourcesRaju BaiОценок пока нет
- Validation of A Method For The Quantitation of Mdma in Seized Materials by Spectrophotometric MethodДокумент6 страницValidation of A Method For The Quantitation of Mdma in Seized Materials by Spectrophotometric MethodalbertuОценок пока нет
- Review On Lozenges: ArticleДокумент11 страницReview On Lozenges: ArticleWANDA WURAGIL FIRJATULLAHОценок пока нет