Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Coppices Clonal Colonies Tree Height Measurement Tree Girth Measurement Tree Crown Measurement Tree Volume Measurement
Загружено:
Jesse Israel TadenaИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Coppices Clonal Colonies Tree Height Measurement Tree Girth Measurement Tree Crown Measurement Tree Volume Measurement
Загружено:
Jesse Israel TadenaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter 21 - Page 236 (Critical Thinking) 1. Age of tree can be determined through the diameter of the trunk?
How can this be possible? Trees have a wide variety of sizes and shapes and growth habits. Specimens may grow as individual trunks, multitrunk masses, coppices, clonal colonies, or even more exotic tree complexes. Most champion tree programs focus finding and measuring the largest single-trunk example of each species. There are three basic parameters commonly measured to characterize the size of a single trunk tree: height, girth, and crown spread. Additional details on the methodology of Tree height measurement, Tree girth measurement, Tree crown measurement, and Tree volume measurement are presented in the links herein. A detailed guideline to these basic measurements is provided in The Tree Measuring Guidelines of the Eastern Native Tree Society by Will Blozan. 2. How are the tissues structures related to their functions? keep looking but I find answers either too in depth or too vague. Would somebody please be able to give me the most important details of how the structure of nerve tissue relates to its function in about 100 words please. Chapter 22 Page 243 (Critical Thinking) 1. Why is meristematic cells division important in plant life? In general, differentiated plant cells cannot divide or produce cells of a different type. Therefore, cell division in the meristem is required to provide new cells for expansion and differentiation of tissues and initiation of new organs, providing the basic structure of the plant body. Meristematic cells are incompletely or not at all differentiated, and are capable of continued cellular division (youthful). Furthermore, the cells are small and protoplasm fills the cell completely. The vacuoles are extremely small. The cytoplasm does not contain differentiated plastids (chloroplasts or chromoplasts), although they are present in rudimentary form (proplastids). Meristematic cells are packed closely together without intercellular cavities. The cell wall is a very thin primary cell wall. 2. Discuss how hormones work together in order for plants to grow and develop. Different hormones affect different plant processes. Understanding how hormones work allows horticulturists to manipulate plants for specific purposes. Auxins produced in the terminal buds suppress the growth of side buds and stimulate root growth. They also affect cell elongation (tropism), apical dominance, and fruit drop or retention. Gibberellins affect: - The rate of cell division - Flowering - Increase in size of leaves and fruits - Seed and bud dormancy - Induction of growth at lower temperatures (used to green up lawns 2 to 3 weeks earlier) Cytokinins promote cell division, and influence cell differentiation and aging of leaves. Abscisic acid is considered the stress hormone. It inhibits the effects of other hormones to reduce growth during times of plant stress. Chapter 23 Page 251 (Critical Thinking) 1. Why do plants bear flowers and bear fruits at different times of the year?
We are a couple with a baby, this year is my first time veg growing and grew 2x courgettes, 1x Marrow, 3x Melon (small as only recently planted), 5x Tomato (beefsteak, minibel & moneymaker), 4x red cabbage (2 ripped out due to heavy disease) 3x savoy cabbage, 3x swedes, about 50 carrots, about 30 beets, 1x large tall pot of potatoes, 1x med - large pot potatoes recently put in (to have new potatoes by December), about 12 parsnips, 12 bean plants of different varieties, 2x ocra (still really small - don't think I will get anything before season end.
Вам также может понравиться
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersОт EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersОценок пока нет
- Micro PropagationДокумент26 страницMicro PropagationAnila NarayananОценок пока нет
- Sevilla - Activity 2 - Cassci 1BДокумент3 страницыSevilla - Activity 2 - Cassci 1BJoyce SevillaОценок пока нет
- ch.6 Biology Class 9Документ29 страницch.6 Biology Class 9Rakshit YadavОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Plant DevelopmentДокумент26 страницIntroduction To Plant DevelopmentLuke Jovanni TAOCОценок пока нет
- ScienceДокумент51 страницаScienceChris YangОценок пока нет
- Lesson 8 Control of Plant Growth and Development Student NoteДокумент4 страницыLesson 8 Control of Plant Growth and Development Student NoteallaboutamaliaОценок пока нет
- Plant Tissue SystemДокумент123 страницыPlant Tissue SystemAnkit Bansal100% (1)
- Plant Tissues and The Multicellular Plant BodyДокумент4 страницыPlant Tissues and The Multicellular Plant BodyAnonymous HXLczq3100% (1)
- Plant Growth and DevelopmentДокумент27 страницPlant Growth and DevelopmentNovi LatifaОценок пока нет
- Plant Growth and Development - Basic Knowledge and Current ViewsДокумент54 страницыPlant Growth and Development - Basic Knowledge and Current ViewsJessica Asitimbay ZuritaОценок пока нет
- TissuesДокумент7 страницTissuesHarshad JiddewarОценок пока нет
- Cells, Tissue, OrganДокумент41 страницаCells, Tissue, OrganTiffany HorsfordОценок пока нет
- TissuesДокумент12 страницTissueschandankrdumkaОценок пока нет
- Plant Growth and DevelopmentДокумент13 страницPlant Growth and DevelopmentthushyanthОценок пока нет
- 8384 ST PDFДокумент20 страниц8384 ST PDFJohn Dave Francisco100% (1)
- Biology Project: Aishik KunduДокумент8 страницBiology Project: Aishik KunduAishik KunduОценок пока нет
- TissueДокумент2 страницыTissueMason PeinОценок пока нет
- Botany Notes AND Graphic Representatio NДокумент20 страницBotany Notes AND Graphic Representatio NMubashir AmjadОценок пока нет
- '12 3Q Poqewkl ' Plant Tissue Dermal Tissue Vascular TissueДокумент4 страницы'12 3Q Poqewkl ' Plant Tissue Dermal Tissue Vascular TissueWILMA MUNOZОценок пока нет
- Plant Tissue Culture: Benefit, Structure, Types and TechniquesДокумент20 страницPlant Tissue Culture: Benefit, Structure, Types and TechniquesShantu ShirurmathОценок пока нет
- Detailed Notes - Topic 2 Cells and Control - Edexcel Biology GCSEДокумент10 страницDetailed Notes - Topic 2 Cells and Control - Edexcel Biology GCSEAbir OmarОценок пока нет
- Plant Growth and Development - Shobhit NirwanДокумент17 страницPlant Growth and Development - Shobhit NirwanAnshu Kumar SinghОценок пока нет
- Plant Growth and Development - Shobhit NirwanДокумент13 страницPlant Growth and Development - Shobhit NirwanShrutheeОценок пока нет
- KSSM F5 Bio CH 1.2 DLPДокумент37 страницKSSM F5 Bio CH 1.2 DLPHamirah Abd HamidОценок пока нет
- BIOL223-Lab 10Документ60 страницBIOL223-Lab 10chicken friesОценок пока нет
- Topic Four: Growth and DevelopmentДокумент22 страницыTopic Four: Growth and DevelopmentAbigail ChepkuruiОценок пока нет
- Biology CXC 2022 ReviewДокумент46 страницBiology CXC 2022 ReviewLatoya Scottland100% (2)
- The Plant Cell Wall: Growth and DevelopmentДокумент29 страницThe Plant Cell Wall: Growth and DevelopmentbeneОценок пока нет
- T T T T T: HapterДокумент12 страницT T T T T: HapterPrasun ShrivastavОценок пока нет
- Plant Growth and DevelopmentДокумент7 страницPlant Growth and DevelopmentArchana MoreОценок пока нет
- The Activity of MeristemsДокумент3 страницыThe Activity of MeristemsCitea MariaОценок пока нет
- Plant Growth and Development PDFДокумент9 страницPlant Growth and Development PDFEñðlêss Ãðîtýâ Raj CøßräОценок пока нет
- Quiz 4 Roots and StemДокумент3 страницыQuiz 4 Roots and Stemangelica valenzonaОценок пока нет
- Plant Tissues WordДокумент5 страницPlant Tissues WordJeannie de leonОценок пока нет
- BiologyIIforNonMajorsII 07Документ78 страницBiologyIIforNonMajorsII 07Mmoh87Оценок пока нет
- Mti 820003080 200323150639Документ21 страницаMti 820003080 200323150639Najira AiniОценок пока нет
- Mary Shine M. Martin STEM 11-1 Comparison of Development of Plants and AnimalsДокумент3 страницыMary Shine M. Martin STEM 11-1 Comparison of Development of Plants and AnimalsMary Shine Magno MartinОценок пока нет
- Plant TissuesДокумент30 страницPlant TissuesAra May B. Olis100% (1)
- CRPSCI 1100-Module4Документ22 страницыCRPSCI 1100-Module4pantalunanhannamaeОценок пока нет
- Module 4Документ5 страницModule 4Charles Linelle MendozaОценок пока нет
- B GENERAL BIOLOGY I Q1M2.2 Learner-Copy Final LayoutДокумент14 страницB GENERAL BIOLOGY I Q1M2.2 Learner-Copy Final LayoutLiennar NaikhОценок пока нет
- Portal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksДокумент5 страницPortal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksHasharaОценок пока нет
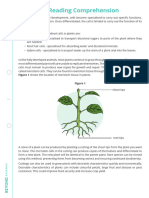
- Meristems Reading ComprehensionДокумент1 страницаMeristems Reading ComprehensionlibrahimliОценок пока нет
- 2nd Quarter Lessons 2.0Документ97 страниц2nd Quarter Lessons 2.0Jean Zyrelle AuronОценок пока нет
- BC 2017 Lecture 2 Dixit Plant Cell BiologyДокумент29 страницBC 2017 Lecture 2 Dixit Plant Cell BiologyAishwarya MondalОценок пока нет
- GROWTHДокумент9 страницGROWTHVarun GoseinОценок пока нет
- BSTC-363 Cell & Tissue CultureДокумент23 страницыBSTC-363 Cell & Tissue CultureModeesa AliОценок пока нет
- Reproduction PPT 8 GROWTH MEASURINGДокумент31 страницаReproduction PPT 8 GROWTH MEASURINGlisanames.23Оценок пока нет
- Lab Activity 5: Plant Morphology: StemДокумент5 страницLab Activity 5: Plant Morphology: StemPaulОценок пока нет
- 2nd Lecture Plant TissuesДокумент119 страниц2nd Lecture Plant TissuesMalik100% (1)
- Xi-A of Atomic Energy Central School HasДокумент27 страницXi-A of Atomic Energy Central School Hasashok parmarОценок пока нет
- Plants: Growth and DevelopmentДокумент17 страницPlants: Growth and Developmentmiss uОценок пока нет
- Na Mlbio Ch11Документ36 страницNa Mlbio Ch11Life with CourteneyОценок пока нет
- For Gen Bio ActivityДокумент10 страницFor Gen Bio ActivityLouie SarmientoОценок пока нет
- Topic 2 - Cells and ControlДокумент10 страницTopic 2 - Cells and ControlEshaal KhanОценок пока нет
- Topic 2 - Cells and ControlДокумент10 страницTopic 2 - Cells and ControlEshaal KhanОценок пока нет
- k12 Bio1 Exer6 RootsДокумент3 страницыk12 Bio1 Exer6 RootsJohn Matthew Jobo100% (1)
- Items: 17 Table Ware and Galley Utensils 1 - 69Документ5 страницItems: 17 Table Ware and Galley Utensils 1 - 69Jesse Israel TadenaОценок пока нет
- Ebn RMCДокумент5 страницEbn RMCJesse Israel TadenaОценок пока нет
- Significant Difference of Mean Prevalence of Systolic Blood Pressure in Terms of Body Mass IndexДокумент5 страницSignificant Difference of Mean Prevalence of Systolic Blood Pressure in Terms of Body Mass IndexJesse Israel TadenaОценок пока нет
- A. Inspects Skull For: Head-to-Toe AssessmentДокумент14 страницA. Inspects Skull For: Head-to-Toe AssessmentJesse Israel TadenaОценок пока нет
- Statistical TXДокумент3 страницыStatistical TXJesse Israel TadenaОценок пока нет
- Full QXNR - 405Документ7 страницFull QXNR - 405Jesse Israel TadenaОценок пока нет
- Reflection - Bill of RightДокумент1 страницаReflection - Bill of RightJesse Israel TadenaОценок пока нет
- RRL - Weight, AgeДокумент2 страницыRRL - Weight, AgeJesse Israel Tadena0% (1)
- Accomplishment Report FinalДокумент4 страницыAccomplishment Report FinalJesse Israel TadenaОценок пока нет
- Far Eastern University Institute of Nursing SY: 2013-2014Документ3 страницыFar Eastern University Institute of Nursing SY: 2013-2014Jesse Israel TadenaОценок пока нет
- Socio-Anthropology: Despues, Andrea Louis T. January 22, 2014 BSN 701 Dr. Wilson S. ChuaДокумент2 страницыSocio-Anthropology: Despues, Andrea Louis T. January 22, 2014 BSN 701 Dr. Wilson S. ChuaJesse Israel TadenaОценок пока нет
- Education and CertificationsДокумент5 страницEducation and CertificationsJesse Israel TadenaОценок пока нет
- Far Eastern University: W10 Mendoza, Nigel Lee Mansell V. Feb 5, 2014 IA12112 Prof. ManualДокумент1 страницаFar Eastern University: W10 Mendoza, Nigel Lee Mansell V. Feb 5, 2014 IA12112 Prof. ManualJesse Israel TadenaОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular Blood VesselsДокумент12 страницCardiovascular Blood VesselswatuwaitingforОценок пока нет
- Reactive The Trauma Active Brain WorksheetДокумент5 страницReactive The Trauma Active Brain Worksheetkadbury1900Оценок пока нет
- Life ProcessesДокумент36 страницLife Processes2erwr100% (1)
- Integration of Metabolism WebДокумент72 страницыIntegration of Metabolism WebLini Anisfatus SholihahОценок пока нет
- Diabetes Mellitus IIДокумент20 страницDiabetes Mellitus IIMa R Dy100% (1)
- Difference of Arterial and Venous InsufficiencyДокумент6 страницDifference of Arterial and Venous InsufficiencyBeep TerradoОценок пока нет
- 8B.6-8B.7 Phytochrome and FloweringДокумент38 страниц8B.6-8B.7 Phytochrome and FloweringAyesha GulzarОценок пока нет
- Cleft Lip / Cleft Palate: Predisposing FactorsДокумент15 страницCleft Lip / Cleft Palate: Predisposing FactorsMabesОценок пока нет
- The Physiologically Difficult Airway An Emerging ConceptДокумент7 страницThe Physiologically Difficult Airway An Emerging ConceptKarla HernandezОценок пока нет
- Overview of Gastrointestinal Tract PerforationДокумент37 страницOverview of Gastrointestinal Tract PerforationArbujeloОценок пока нет
- Bu LesДокумент91 страницаBu LesAnonymous zQ72D9cPrCОценок пока нет
- Metabolic Fingerprints of Human Primary Endothelial and Fibroblast CellsДокумент12 страницMetabolic Fingerprints of Human Primary Endothelial and Fibroblast CellsDavid Galiano LatorreОценок пока нет
- Cambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/13Документ16 страницCambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/13Eain ThuОценок пока нет
- Cont. Diagnostic Test 2 (61-150)Документ13 страницCont. Diagnostic Test 2 (61-150)Sheila Tolentino-BelanioОценок пока нет
- Amino AcidsДокумент18 страницAmino AcidsShreesh MohanОценок пока нет
- 3-Kingdom AnimaliaДокумент16 страниц3-Kingdom AnimaliaEhmz XavièrОценок пока нет
- Full Test Kit InfoДокумент232 страницыFull Test Kit InfoolivierОценок пока нет
- ACLS Practice Exam 1Документ10 страницACLS Practice Exam 1Ken Evans87% (15)
- Renal New Growth - NCM 103 - or CaseДокумент19 страницRenal New Growth - NCM 103 - or CasePat EnriquezОценок пока нет
- HOTS SOLO QUESTIONS - FORMAT Melc 34 V1 EditedДокумент3 страницыHOTS SOLO QUESTIONS - FORMAT Melc 34 V1 Editedjinky luaniaОценок пока нет
- Daftar List Ecatalog ABN 2022 With Pict Ok-2Документ5 страницDaftar List Ecatalog ABN 2022 With Pict Ok-2SESILIA UTAMIОценок пока нет
- Raynaud's PhenomenonДокумент10 страницRaynaud's PhenomenonRoberto López MataОценок пока нет
- Diapact CRRTДокумент9 страницDiapact CRRTSandra Nayeli Aguilar RamírezОценок пока нет
- Solomon cb09 PPT 02Документ32 страницыSolomon cb09 PPT 02kambar123Оценок пока нет
- LeavesДокумент26 страницLeavesRochelle AntigОценок пока нет
- From The Unconscious To The Conscious by Gustave GeleyДокумент348 страницFrom The Unconscious To The Conscious by Gustave GeleyDonna McNeil100% (3)
- Cranial Nerve Exam Handout 1Документ4 страницыCranial Nerve Exam Handout 1kingpin@mailinatorОценок пока нет
- CHAMBER 9 GENETIC KISS (The Conclusion or Is It?)Документ18 страницCHAMBER 9 GENETIC KISS (The Conclusion or Is It?)Atyeb Ba Atum Re100% (3)
- GBS Management, Medications and Nursing ConsiderationsДокумент4 страницыGBS Management, Medications and Nursing Considerationssouledg3100% (1)
- Seminar On Factor Affecting Drug Absorption: Presented byДокумент42 страницыSeminar On Factor Affecting Drug Absorption: Presented byKrunal SamejaОценок пока нет