Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Components of Compressed Gas Services
Загружено:
Muhammad Raza CheemaАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Components of Compressed Gas Services
Загружено:
Muhammad Raza CheemaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
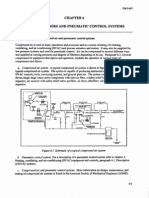
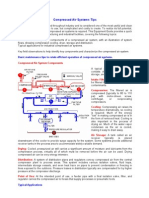
Components of compressed gas services
The main components of compressed gas services are: instrument air plant air breathing air nitrogen
Instrument air
The main components of an instrument air system are the: air compressor cooler receiver separator drier filter distribution header
Instrument air system Instrument air is produced by compressing air from the atmosphere using a compressor which is driven by a reciprocating engine, electric motor or turbine. Compressing a gas heats it up. Compressed instrument air is passed through a cooler to condense any water vapour back to liquid and then into a vessel called a
receiver separator where any liquid contaminants such as water, oil or emulsions can be separated and drained off. Water vapour is then further removed from the instrument air in a drier. Solid contaminants such as dirt, rust and scale particles are removed by filters installed in the line from the driers to the air supply manifold (distribution header) where the air is directed to users by pipelines. At various points along the pipelines, separators called Knockout Pots are used to collect any materials from condensation or corrosion. In case of equipment failure, these components are duplicated with interconnecting piping so that individual items of equipment can be isolated and taken out of service for maintenance. The instrument air pressure is supplied at a higher pressure than is required to allow for pressure drops in long piping runs. Therefore each instrument must have a pressure regulator in the instrument air supply to further reduce the pressure to the level necessary for the efficient and reliable operation of the instrument.
Plant air
The main components of the plant air system are the: compressor cooler receiver separator
Plant Air System
Air is compressed from the atmosphere and passed through a cooler to condense any vapour contaminants such as water, oil and emulsions. On entry into the receiver separator, the condensed products fall to the bottom where they can be drained off. The receiver also stores pressurised air. Because the demand on the plant air system may vary, a pressure operated loading system is used to regulate the load on the compressor during periods where plant air usage is minimal. This system allows the compressor to run continually rather than starting and stopping. To provide a measure of reliability and to allow servicing and maintenance, the major components of the plant air system are duplicated or spared using interconnecting piping so that individual items can be selectively isolated and repaired. The compressed and filtered plant air is then passed into the distribution headers that are routed through the plant to each plant air user. In strategically placed locations, usually at the end of long pipeline sections, knockout pots are provided so that any contaminants can accumulate and be drained off.
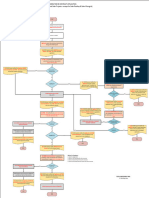
Breathing air
The main components of a breathing air system are the: compressor cooler receiver separator filters pressure regulator backup supply, consisting of: air cylinders pressure regulator
Breathing Air System Breathing air must be of the highest quality for personnel to breathe otherwise serious injury may result. Breathing air is produced using similar equipment to instrument air but filters of higher quality are used to further remove airborne contaminants and oil from the compressor. In some plants breathing air is supplied from high pressure cylinders obtained from outside suppliers. Breathing air connections and systems are designed to ensure that no other utility such as compressed air or nitrogen can be connected to the breathing air system as this could result in fatal injuries to the user.
Nitrogen
The main components of a nitrogen supply system are the: liquid nitrogen storage tank pressure raising coil ambient vaporiser
Nitrogen Supply System Nitrogen is stored as a liquid at very low temperatures (typically - 80C), and is converted into a gas for use as it leaves the liquefied nitrogen storage facilities. As the liquid nitrogen leaves the storage cylinder it is vaporised using an exchanger to convert it into a gas. The nitrogen gas then passes into the nitrogen supply header to users throughout the plant. Pressure control equipment controls the vaporisation of liquid nitrogen into vapour. Nitrogen can also be supplied through a gas distribution header from a gas supply company.
Вам также может понравиться
- Instrument AirДокумент6 страницInstrument Airasarobin1989Оценок пока нет
- Compressed Air PlantДокумент24 страницыCompressed Air Plantliezaebot100% (3)
- Pneumatic NotesДокумент5 страницPneumatic NoteskanscseОценок пока нет
- PneumaticsДокумент18 страницPneumaticsDhruv Patel100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Pneumatic Systems KasrulДокумент27 страницChapter 7 Pneumatic Systems KasrulZyzerull SaadОценок пока нет
- VPHB s3 PDFДокумент16 страницVPHB s3 PDFshekhusatavОценок пока нет
- Page 42Документ1 страницаPage 42Mahmoud Ali Abd-elghany MousaОценок пока нет
- JJ618 Notes Compressed Air PlantДокумент12 страницJJ618 Notes Compressed Air PlantYouDieyОценок пока нет
- Air CompressorДокумент2 страницыAir CompressorMayank Sexena Honey SinghОценок пока нет
- PNEUMATICS: AN INTRODUCTIONДокумент16 страницPNEUMATICS: AN INTRODUCTIONmuru0105Оценок пока нет
- Air Compressors and Pneumatic Control SystemsДокумент7 страницAir Compressors and Pneumatic Control SystemsBader Shrbaji100% (2)
- Conditioning and Distribution of Compressed AirДокумент19 страницConditioning and Distribution of Compressed AirKCОценок пока нет
- Screw Type of CompressorДокумент9 страницScrew Type of CompressorAnish KumarОценок пока нет
- 6 Compressed Air Systems 2-1Документ29 страниц6 Compressed Air Systems 2-1Omar AhmedОценок пока нет
- Pnematics M 2Документ21 страницаPnematics M 2idigitiОценок пока нет
- LAPORAN P2 After RevДокумент16 страницLAPORAN P2 After RevzakiОценок пока нет
- PneumaticsДокумент53 страницыPneumaticsAvijit ShuklaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 - Compressed Air PreparationДокумент6 страницChapter 2 - Compressed Air PreparationerickaОценок пока нет
- Compressed Air TutorialДокумент16 страницCompressed Air TutorialTony Eduok100% (2)
- Compressed Air Distribution SystemДокумент12 страницCompressed Air Distribution SystemPeterson muchiriОценок пока нет
- Basic Maintenance Tips To Retain Efficient Operation of Compressed Air SystemsДокумент4 страницыBasic Maintenance Tips To Retain Efficient Operation of Compressed Air Systemskarthikraja21Оценок пока нет
- Pneumatics BasicДокумент44 страницыPneumatics BasicAlliver SapitulaОценок пока нет
- Forging New Generations of EngineersДокумент16 страницForging New Generations of EngineersSnehalPagdhuneОценок пока нет
- Design of Pneumatic and Electro-Pneumatic CircuitsДокумент8 страницDesign of Pneumatic and Electro-Pneumatic Circuitstani55Оценок пока нет
- Air Compressor Types and ComponentsДокумент3 страницыAir Compressor Types and ComponentsAvinash VadivelОценок пока нет
- Compressor - 3 PDFДокумент194 страницыCompressor - 3 PDFmanojgadhe100% (15)
- Major Components and Types of Compressed Air SystemsДокумент4 страницыMajor Components and Types of Compressed Air SystemsMuhammad Shahir100% (1)
- Gas Turbine Air Filter System OptimizationДокумент10 страницGas Turbine Air Filter System Optimizationsevero97Оценок пока нет
- Pnuematic System Component LocationДокумент2 страницыPnuematic System Component LocationSev MischiefОценок пока нет
- CompressorДокумент10 страницCompressorVina SulistyaОценок пока нет
- Aircraft Pneumatic Systems and Air SystemДокумент11 страницAircraft Pneumatic Systems and Air SystemRaihan AkbarОценок пока нет
- Electro Pneumatic Control: Moch Farchan HasbullahДокумент29 страницElectro Pneumatic Control: Moch Farchan HasbullahTito Bambang Priambodo - 6726Оценок пока нет
- Specific power consumption of air compressorsДокумент12 страницSpecific power consumption of air compressorsHeet PatelОценок пока нет
- Simplest Mechanical TasksДокумент36 страницSimplest Mechanical TaskssivaeinfoОценок пока нет
- Applications of Pneumatic Systems in AircraftДокумент8 страницApplications of Pneumatic Systems in AircraftNaseer AbdaljabarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 - Air and Hydraulic Filters, Air Dryers and LubricatorsДокумент15 страницChapter 7 - Air and Hydraulic Filters, Air Dryers and LubricatorsDedi Setiono100% (1)
- Test of An Air Compressor ME LAB 2Документ27 страницTest of An Air Compressor ME LAB 2nibin venugopal0% (1)
- Air Handler: Navigation SearchДокумент5 страницAir Handler: Navigation SearchNikhil KallaОценок пока нет
- Air CompressorДокумент31 страницаAir CompressorEr Bali Pandhare33% (3)
- Air Dehydrator (Macmac)Документ5 страницAir Dehydrator (Macmac)Mark Joseph Nambio NievaОценок пока нет
- W 11 Study MaterialДокумент9 страницW 11 Study MaterialebbasinghОценок пока нет
- Module 2 PPTДокумент22 страницыModule 2 PPTAkperheОценок пока нет
- Pneumatics System: Operation of A Single Acting Cylinder Controlled by 3-Way ValveДокумент14 страницPneumatics System: Operation of A Single Acting Cylinder Controlled by 3-Way ValveMubarak ShehuОценок пока нет
- Air Generation & Distribution SystemsДокумент46 страницAir Generation & Distribution SystemsHuzai AzmanОценок пока нет
- Terms FlumachДокумент53 страницыTerms FlumachYhuloopz AlvarezОценок пока нет
- Air-CompressorДокумент32 страницыAir-Compressorneetu shakyОценок пока нет
- Compressed Air Drying PDFДокумент29 страницCompressed Air Drying PDFmaddukuri jagadeesh babu100% (1)
- Desiccant Type: Suction Type Principle and Circuit DiagramДокумент2 страницыDesiccant Type: Suction Type Principle and Circuit DiagramSudar WadiОценок пока нет
- Associated Utilities and Auxiliary EquipmentДокумент12 страницAssociated Utilities and Auxiliary EquipmentBea Antoinette AustriaОценок пока нет
- R&AC Lab ManualДокумент29 страницR&AC Lab ManualPARAMESHОценок пока нет
- Introduction to Pneumatics: Basic ComponentsДокумент38 страницIntroduction to Pneumatics: Basic ComponentsDerrick Maatla MoadiОценок пока нет
- Air Compressors: Chapter No: 3Документ59 страницAir Compressors: Chapter No: 3Eric CookОценок пока нет
- Chapter No 3 Air CompressorsДокумент59 страницChapter No 3 Air CompressorsAchmad Denny DarmawanОценок пока нет
- Air Handling UnitДокумент8 страницAir Handling UnitSN Shuhada ZakariaОценок пока нет
- UNIT 4pneumaticsДокумент16 страницUNIT 4pneumaticsnaveenОценок пока нет
- Oral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseОт EverandOral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseОценок пока нет
- Contemporary Anaesthetic Equipments.: An Aid for Healthcare ProfessionalsОт EverandContemporary Anaesthetic Equipments.: An Aid for Healthcare ProfessionalsОценок пока нет
- 2015 Top EPC ContractorsДокумент14 страниц2015 Top EPC ContractorsMuhammad Raza CheemaОценок пока нет
- 2015 Top EPC ContractorsДокумент14 страниц2015 Top EPC ContractorsMuhammad Raza CheemaОценок пока нет
- Width of PadДокумент5 страницWidth of PadMuhammad Raza CheemaОценок пока нет
- Cladding TechnologyДокумент59 страницCladding TechnologycutefrenzyОценок пока нет
- Heat Treatment and Properties of Low Carbon SteelДокумент39 страницHeat Treatment and Properties of Low Carbon SteelZhang FeiОценок пока нет
- Failure TheoriesДокумент21 страницаFailure TheoriesMadhan Krishnamurthy100% (1)
- Ghamidi Counter NarrativeДокумент15 страницGhamidi Counter NarrativeMuhammad Raza CheemaОценок пока нет
- SNGPL Connection NewДокумент1 страницаSNGPL Connection NewsabeeariesОценок пока нет
- Catia MechanismДокумент36 страницCatia MechanismPRASANTH G KRISHNAN100% (1)
- Application of Code CasesДокумент4 страницыApplication of Code CasesMuhammad Raza CheemaОценок пока нет
- Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual For MST SWGRДокумент105 страницInstallation, Operation and Maintenance Manual For MST SWGRAkicaОценок пока нет
- Gaskell Manual Solution (4th Edition)Документ123 страницыGaskell Manual Solution (4th Edition)Seungho_Jeong_151475% (20)
- 4991 Checklist 1905451Документ4 страницы4991 Checklist 1905451alaae5917Оценок пока нет
- EE 2302 - Electrical Machines II Key ConceptsДокумент5 страницEE 2302 - Electrical Machines II Key ConceptsnandhakumarmeОценок пока нет
- D0917392-0 - # - en - # - Data Sheet Grid Performance E-160 EP5 E2 5500 KW FTQДокумент13 страницD0917392-0 - # - en - # - Data Sheet Grid Performance E-160 EP5 E2 5500 KW FTQMígůeļÐaraķuОценок пока нет
- Steam Power Plant: (Coal-Fired)Документ94 страницыSteam Power Plant: (Coal-Fired)Gabriel ApolonioОценок пока нет
- Fire Safety of Biomass StorageДокумент12 страницFire Safety of Biomass StorageKiruba NandhamОценок пока нет
- 12 Volt 5.5 Amp. HRS.: FeaturesДокумент2 страницы12 Volt 5.5 Amp. HRS.: FeaturesJuan EsОценок пока нет
- Voltage Ratio TestДокумент1 страницаVoltage Ratio TestFatima Mir67% (3)
- Exhibitor ListДокумент15 страницExhibitor ListTochi Krishna AbhishekОценок пока нет
- Alternative FuelДокумент16 страницAlternative FuelJoko Dewoto0% (1)
- Choosing An AC or DC Coil For A Solenoid Valve - Tameson PDFДокумент4 страницыChoosing An AC or DC Coil For A Solenoid Valve - Tameson PDFeakonakosОценок пока нет
- Latest Automobile TechnologiesДокумент22 страницыLatest Automobile TechnologiesAakar Gangrade93% (15)
- MS in Electrical Engineering with focus on Power SystemsДокумент2 страницыMS in Electrical Engineering with focus on Power SystemsMukul Kumar100% (1)
- Study Guides for Science Grade 7Документ17 страницStudy Guides for Science Grade 7Sharon Miguel Clavijo AmarisОценок пока нет
- ITMS - REMB - Pre-Application Process For RE Contracts - 8.18.2023Документ1 страницаITMS - REMB - Pre-Application Process For RE Contracts - 8.18.2023mcsyjongtian.picazoОценок пока нет
- Hadronic Mathematics, Mechanics and ChemistryДокумент189 страницHadronic Mathematics, Mechanics and ChemistryGianniNicheliОценок пока нет
- Improved Control of Transformer Centers Using Artificial Neural NetworksДокумент6 страницImproved Control of Transformer Centers Using Artificial Neural NetworksFelipe BittarОценок пока нет
- Basic Inverter (VFD) : Oleh: Bagus OlifiantoДокумент10 страницBasic Inverter (VFD) : Oleh: Bagus OlifiantoAlwi HasibuanОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry Chapter 1 and 2Документ120 страницBiochemistry Chapter 1 and 2Fumofu_2Оценок пока нет
- Glass & Tantalum Capacitors ConsignmentДокумент28 страницGlass & Tantalum Capacitors ConsignmentCIO White PapersОценок пока нет
- Kde12sta3 enДокумент4 страницыKde12sta3 enCarlos GonzaloОценок пока нет
- sn04 Manual PDFДокумент2 страницыsn04 Manual PDFLAZZOLAAОценок пока нет
- NTE6232 Powerblock Module High Current Isolated DiodeДокумент2 страницыNTE6232 Powerblock Module High Current Isolated DiodeTulio Ernesto HernándezОценок пока нет
- An Innovative Technology For Natural Gas SweeteningДокумент2 страницыAn Innovative Technology For Natural Gas SweeteningZahra GhОценок пока нет
- Spek Syringe Pump 5510 2019Документ2 страницыSpek Syringe Pump 5510 2019anggaОценок пока нет
- 22661-Ret Notes-Unit 01 RetДокумент16 страниц22661-Ret Notes-Unit 01 Retjayeshdeore398Оценок пока нет
- Dr. Gigih Udi Atmo - Overview of Electric Vehicles Development in APECДокумент23 страницыDr. Gigih Udi Atmo - Overview of Electric Vehicles Development in APECArfie IkhsanОценок пока нет
- Physics Investigatory ProjectДокумент21 страницаPhysics Investigatory ProjectKankipati Noel100% (1)
- El 5036 V2 PDFДокумент86 страницEl 5036 V2 PDFCriss TОценок пока нет