Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
CO2 Role in Organisms and Ecosystems
Загружено:
DavidIsmailBarker0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
452 просмотров2 страницыAn essay on CO2 used for A2 Biology
Оригинальное название
Carbon Dioxide in Organisms and Ecosystems Essay
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документAn essay on CO2 used for A2 Biology
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
452 просмотров2 страницыCO2 Role in Organisms and Ecosystems
Загружено:
DavidIsmailBarkerAn essay on CO2 used for A2 Biology
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
David Barker
Carbon dioxide in organisms and ecosystems
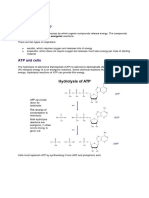
Carbon is one of the major macromolecules in living organisms, and the main source is CO2 making 0.04% of the air in the atmosphere. Nutrients such as CO2 and nitrogen do not have and extra terrestrial source such as light so must be recycled. Photosynthetic organisms remove CO2 from the air by photosynthesis to make macromolecules such as carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Photosynthesis changes the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere. At night the CO2 levels are higher than they are in the day, this is because photosynthesis relies on light. Respiration happens throughout the day and night creating a greater net CO2 released into the air during the night. The concentration of carbon dioxide has increased over the last century or so due to the industrial revolution increasing the combustion of fossil fuels and deforestation. For example the combustion of methane, CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O produces CO2 as a product. Deforestation lowers the amount of CO2 taken in from photosynthesis by the trees. There are also massive stores of CO2 in the oceans 50 times greater than in the atmosphere. Phyto-plankton uses the CO2 to photosynthesis. Carbon dioxide is also a green house gas contributing to global warming. Carbon dioxide is a product of respiration. Many organisms breathe in O2 and breath out C02. The link reaction takes in pyruvate molecules from glycolysis in the matrix of the mitochondria. Pyruvate is then oxidised by from removing hydrogen and giving it to the NAD to make reduced NADH. The two carbon molecule called acetyl group A and Co-enzyme A make Acetyl Co A and CO2 is produced as a result. The Krebs cycle is a series of oxidation-reduction reactions, which happen in the mitochondria. 2 Acetyl Co As combine with a four carbon molecule to make a 6 carbon molecule. 2 CO2s are lost to make a 4-carbon molecule and ATP. The 4-carbon molecule joins with another Acetyl Co A to make another 6-carbon molecule and repeats. The CO2 in humans is transported in the blood to the lungs where it diffuses out down its concentration gradient, and breathed out. For every molecule of glucose, organisms release 6 molecules of CO2. Carbon dioxide is used in photosynthesis, specifically in the Calvin cycle also known as the light independent stage. CO2 diffuses through leaf into the stomata dissolves around the walls of the mesophyll cells. The CO2 then diffuses through the plasma membrane into the chloroplast into the stroma. After the carbon dioxide reaches the stroma it combines with Ribulose Bisphosphate using an enzyme. The fluid of the stroma contains all the enzymes needed to light independent reaction (reduction of carbon dioxide). This produces two molecules of 3-carbon Glycerate 3 phosphate. ATP and NADP from the light independent reaction are used to reduce the GP to Triose phosphate. The NADP is reformed and goes back into the light dependent stage to be reduced by more hydrogen. Some of the TP goes to useful organic substances, such as glucose. Most triose phosphate molecules are used to regenerate Ribulose Bisphosphate using ATP from the light dependant reaction.
David Barker Carbon dioxide is also a limiting factor in photosynthesis. Carbon dioxide is one of the rarest gasses present in air, and is often a factor that limits the rate of photosynthesis under normal conditions. The optimum concentration of carbon dioxide for photosynthesis is 0.1% and growers of some greenhouse crops such as tomatoes, enrich the air with more carbon dioxide to produce higher yields. CO2 affects enzyme activity, in particular the enzyme that catalyse that catalyses the combination of Ribulose Bisphosphate with carbon dioxide in the lightdependent reaction.
Вам также может понравиться
- Synoptic Essay PackДокумент29 страницSynoptic Essay Packriri_p_94100% (1)
- C3 Carbon Fixation Pathway ExplainedДокумент4 страницыC3 Carbon Fixation Pathway ExplainedWorld FootballОценок пока нет
- Photorespiration: The Assignment Submitted by Mumtahin Ul KousarДокумент11 страницPhotorespiration: The Assignment Submitted by Mumtahin Ul KousarJunaid MushtaqОценок пока нет
- Gases and Vapours@rautbholaДокумент12 страницGases and Vapours@rautbholaBholakant RautОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis Study Material C4 Cycle OnwardsДокумент6 страницPhotosynthesis Study Material C4 Cycle OnwardsmoonyОценок пока нет
- Carbon cycle transfers substances between organisms and environmentДокумент2 страницыCarbon cycle transfers substances between organisms and environmentBethany Knott100% (1)
- Anaerobic Respiration and FermentationДокумент7 страницAnaerobic Respiration and FermentationVijayant PratapОценок пока нет
- Gcse Biology, PhotosynthesisДокумент1 страницаGcse Biology, PhotosynthesiscrainerОценок пока нет
- What Is Carbon Dioxide and How Is It DiscoveredДокумент5 страницWhat Is Carbon Dioxide and How Is It DiscoveredVel MuruganОценок пока нет
- Function of PhotosynthesisДокумент58 страницFunction of PhotosynthesisJulian ChristopherОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis Respiration Report FinalДокумент53 страницыPhotosynthesis Respiration Report FinalIvan Jhon AnamОценок пока нет
- Respiration 1st ChapterДокумент11 страницRespiration 1st ChapterBrindhaОценок пока нет
- Carbon AssimilationДокумент34 страницыCarbon AssimilationCanady KeniscopeОценок пока нет
- Carbon Fixation - WikipediaДокумент64 страницыCarbon Fixation - WikipediaBashiir NuurОценок пока нет
- Carbon: Cellular RespirationДокумент4 страницыCarbon: Cellular RespirationNica MedidaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 14Документ14 страницChapter 14Yash Singh 11th BОценок пока нет
- A Report On The Carbon CycleДокумент4 страницыA Report On The Carbon CycleJL V. AdrianoОценок пока нет
- Algae Technology Report: IndexДокумент20 страницAlgae Technology Report: IndexSteve RacoosinОценок пока нет
- PhotosynthesisДокумент4 страницыPhotosynthesissteven7 IsaacsОценок пока нет
- Chapter 10 OutlineДокумент13 страницChapter 10 OutlineJosephinemwОценок пока нет
- PhotorespirationДокумент16 страницPhotorespirationMoa ArmyОценок пока нет
- Products and Effects of CombustionДокумент5 страницProducts and Effects of CombustionLaura IonescuОценок пока нет
- A in Agri 501-BiochemistryДокумент14 страницA in Agri 501-BiochemistryIvan Jhon AnamОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration NewДокумент15 страницPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respiration NewMaria Valerie BaculiОценок пока нет
- Plant Respiration ProcessДокумент31 страницаPlant Respiration ProcessSleeping BeautyОценок пока нет
- Arthur Carbon Cycle Project WorkДокумент7 страницArthur Carbon Cycle Project WorkJoshuaОценок пока нет
- Cellular RespirationДокумент25 страницCellular RespirationLouie Joice MartinezОценок пока нет
- The Water Carbon CycleДокумент9 страницThe Water Carbon Cyclebrittany peckОценок пока нет
- THE Carbon Cycle: Aiyna Ali & Jade LutchmanДокумент6 страницTHE Carbon Cycle: Aiyna Ali & Jade LutchmanjadeОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis and RespirationДокумент4 страницыPhotosynthesis and RespirationChristian BaleОценок пока нет
- Cellular Respiration Hans Krebs Aerobic OrganismsДокумент1 страницаCellular Respiration Hans Krebs Aerobic OrganismsMia SoteloОценок пока нет
- Lecture 9 - Dark ReactionДокумент14 страницLecture 9 - Dark ReactionAtika ZulfiqarОценок пока нет
- Trees CarbonДокумент13 страницTrees Carbonmirelacarstea0% (1)
- Lez 8,9 Fotosintesi, Respirazione 2Документ24 страницыLez 8,9 Fotosintesi, Respirazione 2calmdownОценок пока нет
- Humans Use CO2 in Many Ways: Soft Drinks, Fire Extinguishers & MoreДокумент4 страницыHumans Use CO2 in Many Ways: Soft Drinks, Fire Extinguishers & MoreAlexis ChangОценок пока нет
- Topic 5 - Energy Transfers in and Between Organisms: Definitions and Concepts For AQA Biology A-LevelДокумент5 страницTopic 5 - Energy Transfers in and Between Organisms: Definitions and Concepts For AQA Biology A-LevelsamОценок пока нет
- Different Carbon ColorsДокумент17 страницDifferent Carbon ColorsKirushnananthy VallipuramОценок пока нет
- Biology 2.1: Electrical Energy (Electrons Become Excited (Energised) )Документ3 страницыBiology 2.1: Electrical Energy (Electrons Become Excited (Energised) )Sel 7Оценок пока нет
- PhotosynthesisДокумент55 страницPhotosynthesischezkanoelleangeliebalolongОценок пока нет
- Mid-Term Review Sheet John FarmerДокумент2 страницыMid-Term Review Sheet John FarmerJohn FarmerОценок пока нет
- Carbon DioxideДокумент4 страницыCarbon DioxidenontkawinkornОценок пока нет
- What Is Respiration?Документ10 страницWhat Is Respiration?Yana LouisseОценок пока нет
- Cellular Respiration PDFДокумент10 страницCellular Respiration PDFAnonymous HXLczq3Оценок пока нет
- Terjemah Karya Tulis RIKAДокумент17 страницTerjemah Karya Tulis RIKAKeyla AishaОценок пока нет
- What Is Carbon Dioxide and How Is It Discovered?: Carbon Atom Oxygen AtomsДокумент4 страницыWhat Is Carbon Dioxide and How Is It Discovered?: Carbon Atom Oxygen AtomsChetna PatilОценок пока нет
- Respiration and PhotorespirationДокумент29 страницRespiration and PhotorespirationThảo UyênОценок пока нет
- The Carbon CycleДокумент3 страницыThe Carbon Cycleakeem babbОценок пока нет
- Carbon Cycle The Greenhouse EffectДокумент2 страницыCarbon Cycle The Greenhouse Effectapi-247723417Оценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis: Leaf StructureДокумент4 страницыPhotosynthesis: Leaf StructureMonica Sario PolicinaОценок пока нет
- SUMMARY NOTES On Biodiversity & PhotosynthesisДокумент4 страницыSUMMARY NOTES On Biodiversity & PhotosynthesisBonachita YamОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis CoreДокумент8 страницPhotosynthesis Coreapi-188431847Оценок пока нет
- Plants and Other Autotrophs Are The Producers of The BiosphereДокумент12 страницPlants and Other Autotrophs Are The Producers of The Biosphereюрий локтионовОценок пока нет
- BioIGCSE 07 PhotosynthesisДокумент34 страницыBioIGCSE 07 PhotosynthesisNADIAОценок пока нет
- CIE Biology A-level NotesДокумент5 страницCIE Biology A-level NotesbeiyuОценок пока нет
- The Effect of Carbon Dioxide On The Rate of PhotosynthesisДокумент6 страницThe Effect of Carbon Dioxide On The Rate of Photosynthesisapi-317110598Оценок пока нет
- Carbon CycleДокумент15 страницCarbon CycleVaishnavi Kalantri100% (1)
- Photosynthesis - WikipediaДокумент149 страницPhotosynthesis - WikipediaBashiir NuurОценок пока нет
- The 5 Nutrient Cycles - Science Book 3rd Grade | Children's Science Education booksОт EverandThe 5 Nutrient Cycles - Science Book 3rd Grade | Children's Science Education booksОценок пока нет
- Fisher Paykel Cosycot - Manual de Funcionamiento PDFДокумент133 страницыFisher Paykel Cosycot - Manual de Funcionamiento PDFpirihuey1234Оценок пока нет
- Turbocharger Service InstructionsДокумент4 страницыTurbocharger Service Instructionskarol1177Оценок пока нет
- Pittsburgh Coal ConferenceДокумент68 страницPittsburgh Coal ConferenceNileshОценок пока нет
- Farm Pond ManagementДокумент44 страницыFarm Pond ManagementHAING TRYОценок пока нет
- LCP SpanlockДокумент8 страницLCP SpanlockGarfieldОценок пока нет
- Ductulator May 2010Документ8 страницDuctulator May 2010haroub_nasОценок пока нет
- STA-C Series - Super Trident Sewage Treatment PlantДокумент2 страницыSTA-C Series - Super Trident Sewage Treatment Plantanandsharma123Оценок пока нет
- Final PG Sby 0024Документ3 страницыFinal PG Sby 0024Afwa Wildan RomadhonОценок пока нет
- Salt HydrolysisДокумент3 страницыSalt Hydrolysisna_napanda100% (1)
- Common polyatomic ions and their formulasДокумент16 страницCommon polyatomic ions and their formulasskyline aviationОценок пока нет
- Himalaya Health CareДокумент38 страницHimalaya Health Careactive1cafeОценок пока нет
- My New ResumeДокумент4 страницыMy New ResumeSurajОценок пока нет
- Heavy Duty Slurry Pumps Specs & Performance DataДокумент12 страницHeavy Duty Slurry Pumps Specs & Performance DataMaximiliano BettarelОценок пока нет
- EP0070932B1Документ5 страницEP0070932B1bayuОценок пока нет
- Industrial Training Presentation: PETRONAS Chemicals Methanol Labuan Sdn. BHDДокумент9 страницIndustrial Training Presentation: PETRONAS Chemicals Methanol Labuan Sdn. BHDAbdul AzizОценок пока нет
- Microwave, IR, NMR spectroscopy techniquesДокумент1 страницаMicrowave, IR, NMR spectroscopy techniquesSaikiranОценок пока нет
- Philips NMR and MRIДокумент98 страницPhilips NMR and MRItsram90Оценок пока нет
- Astm D 4176 PDFДокумент4 страницыAstm D 4176 PDFAlexander Amado QuinteroОценок пока нет
- Bollhoff HeliCoil Plus ImperialДокумент48 страницBollhoff HeliCoil Plus ImperialAce Industrial SuppliesОценок пока нет
- Potabilización de AguaДокумент9 страницPotabilización de AguaSHEILA GINIVA BUSTOS YAIMAОценок пока нет
- Int Esws at Y9 Workbook Answers TTPPДокумент37 страницInt Esws at Y9 Workbook Answers TTPPChrystal GraceОценок пока нет
- Clavijas y Recept HubellДокумент40 страницClavijas y Recept HubellArturo Pérez LohmanОценок пока нет
- Refining and Petrochemicals CourseworkДокумент9 страницRefining and Petrochemicals CourseworkMichael GregoryОценок пока нет
- Project Content ChemistryДокумент6 страницProject Content ChemistryPrathmesh MoreОценок пока нет
- Hygene EPIHANIOU Faucets INT EN-1 PDFДокумент55 страницHygene EPIHANIOU Faucets INT EN-1 PDFattikourisОценок пока нет
- Crosslinker CX100 MsdsДокумент59 страницCrosslinker CX100 MsdsMimi rastamОценок пока нет
- Erosion Tecnalia 2016 06Документ17 страницErosion Tecnalia 2016 06FernanОценок пока нет
- ADVANCED MACHINING PROCESSESДокумент22 страницыADVANCED MACHINING PROCESSESfaizОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Short 1 ChemistryДокумент12 страницChapter 1 Short 1 ChemistryvaibhavikamatarОценок пока нет
- Bio Monitoring of AtmosphericДокумент174 страницыBio Monitoring of AtmosphericOluflourish EmmanuelОценок пока нет