Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
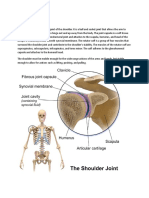
Rehabilitation of Overhead Shoulder Injuries
Загружено:
Anang FajarИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Rehabilitation of Overhead Shoulder Injuries
Загружено:
Anang FajarАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Symposium of Sport Medicine, 11 13 January 2013
Introduction
Rehabilitation of overhead shoulder injuries
Robert van Cingel,
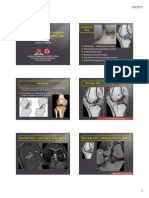
The throwing motion Pathology:
Rotator cuff Biceps SLAP Instability GIRD Impingement and the role of the scapula
PT, OMT, PhD
Sport Medisch Centrum Papendal, Arnhem, The Netherlands HAN University of Applied Sciences, Nijmegen, The Netherlands
Clinical diagnosis Rehabilitation
The throwing motion
Tremendous forces are placed on the shoulder joint at extremely high angular velocities It is estimated that anterior translations forces generated are equal to 1.5 body weight during the late cocking phase and there is a distraction force equal to BW during acceleration
(Fleisig Fleisig 99)
The throwing motion
Throwing and other overhead sports requires an optimal balance between mobility and stability of the shoulder The chronic repetitive stress can strain the delicate balance and place the shoulder at risk for a variety of disorders Treatment starts with an accurate diagnosis
Pathology
Impingement
Impingement
Is one of the most frequently described pathological shoulder conditions in sports medicine Early literature described impingement as a pathology or diagnosis (Neer 72) but today impingement is considered to be a cluster of symptoms, rather than a pathology itself There is a association between impingement and a variety of underlying pathological mechanisms (Cools 08,
10, 12)
Definition based on the side of encroachment
2 types: subacromial and internal Subacromial (external or outlet): mechanical encroachment of the soft tissues (bursa, rotator cuff) in the subacromial space between the humeral head and the acromial arch with an painful arc during active abduction
Impingement
Impingement
Definition based on the side of encroachment
2 types: subacromial and internal Internal impingement comprises the encroachment of the RC tendons between the humeral head and the glenoid rim and can be anterosuperior or posterosuperior (PS is most frequent: SST and IST between greater tubercle and the posterosuperior rim of the glenoid). This friction occurs during the late cocking position
Definition based on the cause of encroachment
2 types: primary and secondary Primary: a structural narrowing of the subacromial space causes pain and dysfunction (e.g. arthrosis AC joint, swelling soft tissues) Secondary: there are no structural obstructions, but functional problems occurring only in a specific position. This may occur in the subacromial space as well as in the GH joint / scapula
Clinical diagnosis
Clinical diagnosis
There is a great need for large, prospective studies that examine the diagnostic accuracy of many aspects of clinical examination in diagnosing shoulder pathologies (10, 12)
Rehabilitation scapula dyskinesis
Rehabilitation scapula dyskinesis
Scapula thoracic dysfunction
Analysis of scapular muscles / force couples UT + SA and LT for stability / movement control
Abnormal scapular muscle function
Dyskinesis type I (prominent inferior angle, tipping tipping Dyskinesis type II (prominent medial border, winging winging Dyskinesis type III (prominent superior / medial border, shrug shrug with elevation)
UPPER MIDDLE
LOWER
Rehabilitation scapula dyskinesis
Rehabilitation scapula dyskinesis
Abnormal scapular muscle function
Decrease SA strength Muscle imbalance UT versus LT Timing disorders LT
Strengthening SA
Push up with plus Serratus punch Dynamic hug
Type 1
Type 2
Rehabilitation scapula dyskinesis
Rehabilitation scapula dyskinesis
Strengthening LT & Rhomboid
Low rowing Horizontal abduction / ext rotation Elbow in the back pocket pocket
Balance UT/LT & UT/MT
Side lying forward flexion Side lying external rotation Horizontal abduction & ext rotation Prone extension
Thank you for your attention!
Вам также может понравиться
- Tugas Mendeley 1. Sumber BukuДокумент6 страницTugas Mendeley 1. Sumber BukuAbyudya Rafif KurniawanОценок пока нет
- Care of Shoulder Pain in The Overhead AthleteДокумент8 страницCare of Shoulder Pain in The Overhead Athlete110313Оценок пока нет
- Article Diag Diff PDFДокумент18 страницArticle Diag Diff PDFJean HelouОценок пока нет
- Shoulder PainДокумент6 страницShoulder Painjrice003Оценок пока нет
- Avaliação Escapulotorácica e Tratamento para Jogadores de TenisДокумент16 страницAvaliação Escapulotorácica e Tratamento para Jogadores de TenisClínica MoverОценок пока нет
- Eck 2004Документ13 страницEck 2004Hari25885Оценок пока нет
- Nursing Care of The Patient Undergoing Lumbar Spinal Fusion: ReviewsДокумент10 страницNursing Care of The Patient Undergoing Lumbar Spinal Fusion: ReviewsMuammar100% (1)
- Spine Biomechanics: Mer/Bio Soft Tissue Mechanics SB-1Документ11 страницSpine Biomechanics: Mer/Bio Soft Tissue Mechanics SB-1Sarah Magdy100% (1)
- Core Stability Exercise PrinciplesДокумент6 страницCore Stability Exercise Principlesphysioali0% (2)
- Rehabilitation For Shoulder Instability - Current PDFДокумент15 страницRehabilitation For Shoulder Instability - Current PDFmariaОценок пока нет
- Anterior Knee Pain in The Young AthleteДокумент7 страницAnterior Knee Pain in The Young AthleteAngelica GarciaОценок пока нет
- Scapular Dyskinesis - Patterns, Functional Disability and Associated Factors in People With Shoulder Disorders 2016Документ31 страницаScapular Dyskinesis - Patterns, Functional Disability and Associated Factors in People With Shoulder Disorders 2016Daniel CarcamoОценок пока нет
- Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis - From Normal Spinal Anatomy To Three-Dimensional Deformity (PDFDrive)Документ252 страницыAdolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis - From Normal Spinal Anatomy To Three-Dimensional Deformity (PDFDrive)AuraОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physical Examination of The ShoulderДокумент13 страницAnatomy and Physical Examination of The ShoulderbrunolazzariОценок пока нет
- C!"CCC C C C CC CC CCCДокумент13 страницC!"CCC C C C CC CC CCCRaji JesurajОценок пока нет
- 6a. Anatomi Dan Biomekanik Trauma Tulang BelakangДокумент53 страницы6a. Anatomi Dan Biomekanik Trauma Tulang BelakangnurwajdainiОценок пока нет
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Distal Biceps and Anterior Elbow Pain in Throwing AthletesДокумент6 страницDiagnosis and Treatment of Distal Biceps and Anterior Elbow Pain in Throwing AthletesDiana Dianyu LiОценок пока нет
- Fases Del Choque MedularДокумент13 страницFases Del Choque Medularscarface59Оценок пока нет
- Adhesive CapsulitisДокумент11 страницAdhesive Capsulitismetal_moggleОценок пока нет
- Clinical Tests of The Shoulder: Accuracy and Extension Using Dynamic UltrasoundДокумент9 страницClinical Tests of The Shoulder: Accuracy and Extension Using Dynamic UltrasoundMohammad Al AbdullaОценок пока нет
- Biomechanics of SpineДокумент9 страницBiomechanics of SpineAdosotoОценок пока нет
- Management of Knee OsteoarthritisДокумент35 страницManagement of Knee OsteoarthritisChukwuemeka ChidogoОценок пока нет
- Shoulder PDFДокумент11 страницShoulder PDFteresaioana100% (1)
- Sebastian2014 PDFДокумент8 страницSebastian2014 PDFArchita AgarwalОценок пока нет
- SpondylolysisДокумент13 страницSpondylolysisYang100% (1)
- The Painful Shoulder - Part I. Clinical Evaluation - American Family PhysicianДокумент9 страницThe Painful Shoulder - Part I. Clinical Evaluation - American Family PhysicianAngelaОценок пока нет
- Jurnal SpondylosisДокумент7 страницJurnal SpondylosisM Hafiz MoulviОценок пока нет
- Braly B y ColsДокумент12 страницBraly B y ColsmilelytaОценок пока нет
- Can Local Muscles Augment Stability in The Hip A Narrative Literature Review PDFДокумент12 страницCan Local Muscles Augment Stability in The Hip A Narrative Literature Review PDFBel SantosОценок пока нет
- Lateral Hip Pain in An Athletic Population: Differential Diagnosis and Treatment OptionsДокумент6 страницLateral Hip Pain in An Athletic Population: Differential Diagnosis and Treatment Optionssebas valadezОценок пока нет
- Psoas Insufficiency and Its Role in Sacroiliac DysfunctionДокумент45 страницPsoas Insufficiency and Its Role in Sacroiliac DysfunctionAlexandru Nechifor100% (1)
- Frozen Shoulder - Loss of Scapulohumeral RhythmДокумент9 страницFrozen Shoulder - Loss of Scapulohumeral RhythmWasemBhatОценок пока нет
- Adhesive Capsulitis (Frozen Shoulder)Документ5 страницAdhesive Capsulitis (Frozen Shoulder)erikaОценок пока нет
- Ki 1.1 Rotator Cuff Any 2 ASДокумент29 страницKi 1.1 Rotator Cuff Any 2 ASAgus TianyОценок пока нет
- Rehabilitation HipДокумент29 страницRehabilitation HipZahraa MОценок пока нет
- Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, and DiagnosisДокумент14 страницLumbar Spinal Stenosis: Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, and DiagnosisAnastasia TjanОценок пока нет
- Scoliosis: Degenerative & IdiopathicДокумент34 страницыScoliosis: Degenerative & IdiopathicalphiОценок пока нет
- Kyphosis Physiotherapy From Childhood To Old Age: Jean Claude de MauroyДокумент26 страницKyphosis Physiotherapy From Childhood To Old Age: Jean Claude de MauroyromanciviОценок пока нет
- Spinal Cord Injury: Andi IhwanДокумент31 страницаSpinal Cord Injury: Andi IhwanAndi Muliana SultaniОценок пока нет
- Back Pain Printable VersionДокумент43 страницыBack Pain Printable VersionSabin ParajuliОценок пока нет
- AAOS2002 ShoulderДокумент70 страницAAOS2002 ShoulderHéctor Pando SánchezОценок пока нет
- Biomechanics of The SpineДокумент18 страницBiomechanics of The SpineSudheer Jayaram100% (1)
- Biomechanics of The Shoulder: Dennis L. Hart, Mpa, PT, Stephen W. Carmichael, PHDTДокумент6 страницBiomechanics of The Shoulder: Dennis L. Hart, Mpa, PT, Stephen W. Carmichael, PHDTPrem KumarОценок пока нет
- Back and Nexk PainДокумент7 страницBack and Nexk PainDenise MathreОценок пока нет
- RCT ThesisДокумент42 страницыRCT ThesismohiiieОценок пока нет
- Low BackДокумент7 страницLow BackMuhammad FahmyОценок пока нет
- Cardinal Manifestations Back and Neck PainДокумент33 страницыCardinal Manifestations Back and Neck PainRoby KieranОценок пока нет
- A Systematic Approach To Adult Hip PainДокумент12 страницA Systematic Approach To Adult Hip Pain69016Оценок пока нет
- Anterior Shoulder Instability A Review of PathoanatomyДокумент8 страницAnterior Shoulder Instability A Review of PathoanatomyNikita TripthiОценок пока нет
- Manual Therapy: Kuan-Ting Lee, Chiung-Cheng Chuang, Chien-Hung Lai, Jing-Jhao Ye, Chien-Lung WuДокумент6 страницManual Therapy: Kuan-Ting Lee, Chiung-Cheng Chuang, Chien-Hung Lai, Jing-Jhao Ye, Chien-Lung Wuubiktrash1492Оценок пока нет
- Torticolis OdtДокумент25 страницTorticolis OdtAndreea CimpoiОценок пока нет
- Initial ManagementДокумент2 страницыInitial ManagementVictor ChanОценок пока нет
- Physical Therapy For The Treatment of Shoulder InstabilityДокумент16 страницPhysical Therapy For The Treatment of Shoulder InstabilityDelaram IravaniОценок пока нет
- Bench Press SyndromeДокумент4 страницыBench Press SyndromeAbdallah Maroun NajemОценок пока нет
- Approach To Hip and Groin Pain in The Athlete and Active AdultДокумент21 страницаApproach To Hip and Groin Pain in The Athlete and Active AdultAman DuggalОценок пока нет
- Adhesive CapsulitisДокумент20 страницAdhesive Capsulitisvenkata ramakrishnaiahОценок пока нет
- Spinal Cord Injury AlexiДокумент41 страницаSpinal Cord Injury AlexiRoberto AlexiОценок пока нет
- Lecture Scap Malaga 2Документ47 страницLecture Scap Malaga 2danielaОценок пока нет
- The Provocative Lumbar Facet JointДокумент10 страницThe Provocative Lumbar Facet JointfilipecorsairОценок пока нет
- Fibro 4Документ3 страницыFibro 4Anang FajarОценок пока нет
- Af Af: Aka Aka Aka Aka Aka AkaДокумент3 страницыAf Af: Aka Aka Aka Aka Aka AkaAnang FajarОценок пока нет
- Phys Ther 2012 Opheim 279 88Документ12 страницPhys Ther 2012 Opheim 279 88Anang FajarОценок пока нет
- Pre Conditioning ExerciseДокумент24 страницыPre Conditioning ExerciseAnang FajarОценок пока нет
- Cervical Root SyndromeДокумент48 страницCervical Root SyndromeAnang FajarОценок пока нет
- Cervical Root Syndrome Sc4Документ50 страницCervical Root Syndrome Sc4Anang FajarОценок пока нет
- Imaging Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear - Helpful Tips Imaging Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear - Helpful TipsДокумент5 страницImaging Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear - Helpful Tips Imaging Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear - Helpful TipsAnang FajarОценок пока нет
- Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow) : By:Ida Yuanita, MDДокумент37 страницLateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow) : By:Ida Yuanita, MDAnang FajarОценок пока нет
- Ankle Tendon InjuryДокумент7 страницAnkle Tendon InjuryAnang FajarОценок пока нет
- De Quervain's Tenosynovitis: By: Dr. HermilawatyДокумент35 страницDe Quervain's Tenosynovitis: By: Dr. HermilawatyAnang FajarОценок пока нет
- Trigger Finger: By:Ida Yuanita, MDДокумент33 страницыTrigger Finger: By:Ida Yuanita, MDAnang FajarОценок пока нет
- Rehabilitation After ACL ReconstructionДокумент4 страницыRehabilitation After ACL ReconstructionAnang FajarОценок пока нет
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: by A. A. Sagung Mas CahyandariДокумент37 страницCarpal Tunnel Syndrome: by A. A. Sagung Mas CahyandariAnang FajarОценок пока нет
- Biomechanics and MOI of The AnkleДокумент37 страницBiomechanics and MOI of The AnkleAnang FajarОценок пока нет
- Kinesiology of The Shoulder: Wayan Budi AryawanДокумент28 страницKinesiology of The Shoulder: Wayan Budi AryawanAnang FajarОценок пока нет
- Rehab Grand Rounds: Comprehensive Approach To The Management of Scapular Dyskinesia in The Overhead Throwing AthleteДокумент8 страницRehab Grand Rounds: Comprehensive Approach To The Management of Scapular Dyskinesia in The Overhead Throwing AthletekotraeОценок пока нет
- Shoulder ExaminationДокумент3 страницыShoulder ExaminationTausif HuqОценок пока нет
- Shoulder Biomechanics: Roberto Lugo, Peter Kung, C. Benjamin MaДокумент11 страницShoulder Biomechanics: Roberto Lugo, Peter Kung, C. Benjamin MaAbyudya Rafif KurniawanОценок пока нет
- A Review On Frozen Shoulder: Singapore Medical Journal September 2010Документ5 страницA Review On Frozen Shoulder: Singapore Medical Journal September 2010Anonymous ckZmIgoОценок пока нет
- Swimming (Sport) : Jump To Navigation Jump To Search Swimming Swimmer (Disambiguation)Документ24 страницыSwimming (Sport) : Jump To Navigation Jump To Search Swimming Swimmer (Disambiguation)Teacher NhorОценок пока нет
- MKSAP Questions: Intern ReportДокумент37 страницMKSAP Questions: Intern Reportfidelurtecho4881Оценок пока нет
- Physical Examination of The Shoulder: Key WordsДокумент10 страницPhysical Examination of The Shoulder: Key WordsJavi LiraОценок пока нет
- Short Case II: Jufri Febrianto, MDДокумент16 страницShort Case II: Jufri Febrianto, MDsingle_ladyОценок пока нет
- 10 Must-Do Exercises For Climbers: Eric J. HörstДокумент26 страниц10 Must-Do Exercises For Climbers: Eric J. HörstKaloyan BahchovanskiОценок пока нет
- Shoulder Pain The Solution Prevention Fourth EditionДокумент120 страницShoulder Pain The Solution Prevention Fourth EditionMarko Štambuk97% (33)
- Crossectional Patologi: I. Spine 1. Fraktur OdontoidДокумент11 страницCrossectional Patologi: I. Spine 1. Fraktur OdontoidEka JuliantaraОценок пока нет
- Subscapularis Sy DonatelliДокумент12 страницSubscapularis Sy DonatelliDusan OrescaninОценок пока нет
- B15 M4 - Sports Injury (Dr. W. Mana-Ay 2014)Документ8 страницB15 M4 - Sports Injury (Dr. W. Mana-Ay 2014)Dakila Vine VillanОценок пока нет
- Current Concepts: Scapular Dyskinesis: W Ben Kibler, Aaron SciasciaДокумент7 страницCurrent Concepts: Scapular Dyskinesis: W Ben Kibler, Aaron SciasciatomxtchОценок пока нет
- Dominate Your Anatomy - Delts PDFДокумент33 страницыDominate Your Anatomy - Delts PDFxaviermayОценок пока нет
- Ann Cools 2020 PDFДокумент8 страницAnn Cools 2020 PDFNati GallardoОценок пока нет
- Assignment Shoulder JointДокумент7 страницAssignment Shoulder JointMary Grace OrozcoОценок пока нет
- Acute Anterior Shoulder Dislocation Physical Therapy ProtocolДокумент4 страницыAcute Anterior Shoulder Dislocation Physical Therapy Protocolgermano87Оценок пока нет
- The Surfers Shoulder PDFДокумент24 страницыThe Surfers Shoulder PDFSteveLangОценок пока нет
- Arthroscopic-SAD Neer DCE MumfordДокумент5 страницArthroscopic-SAD Neer DCE MumfordAbdul Wahid ShaikhОценок пока нет
- 1Aula-SHOULDER JOINT AND MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS IN THE RECREATIONAL WEIGHT TRAINING POPULATIONДокумент10 страниц1Aula-SHOULDER JOINT AND MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS IN THE RECREATIONAL WEIGHT TRAINING POPULATIONjeanbasqueteОценок пока нет
- Kibler Scapular DyskinesisДокумент10 страницKibler Scapular Dyskinesisנתנאל מושקוביץ100% (5)
- DR PHYSIQUE 2018 Bulking Plan PDFДокумент64 страницыDR PHYSIQUE 2018 Bulking Plan PDFCarls Rincon100% (5)
- Mastering Handstands and Beyond by Lee WeilandДокумент74 страницыMastering Handstands and Beyond by Lee WeilandRayen HamrouniОценок пока нет
- Case Report Glenohumeral Dysplasia, A Complication of Obstetrics Brachial Plexus PalsyДокумент5 страницCase Report Glenohumeral Dysplasia, A Complication of Obstetrics Brachial Plexus PalsyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Question ListДокумент65 страницQuestion Listridin007Оценок пока нет
- Rotator Cuff BookДокумент36 страницRotator Cuff BookLim Jiew KwangОценок пока нет
- IASTM Primer MyoBar PDF UpdatedДокумент46 страницIASTM Primer MyoBar PDF Updatedviorel100% (2)
- The Rotator Cuff PDFДокумент201 страницаThe Rotator Cuff PDFjesussalvadorsuazaОценок пока нет
- Shoulder AnatomyДокумент47 страницShoulder Anatomyzainurrahman kurnia putraОценок пока нет