Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Summary On Circle Theorem
Загружено:
Daniella PhillipОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Summary On Circle Theorem
Загружено:
Daniella PhillipАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Circle Theorem Circle theorem rules: 1.
The angle which an arc of a circle subtends at the centre of a circle is twice the angle it subtends at any point on the remaining part of the circumference. 2. The angle in a semi circle is a right angle 3. Angles in the same segment of a circle and subtended by the same arc are equal. 4. The opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary ( adds up to 18 ! ". The e#terior angle of a cyclic quadrilateral is equal to the interior opposite angle. $. The tangent of a circle is perpendicular (% ! to the radius of that circle at the point of contact. &. The lengths of two tangents from an e#ternal point to the points of contact on the circle are equal. 8. The angle between a tangent to a circle and a chord through the point of contact is equal to the angle in the alternate segment. %. The line 'oining the centre of a circle to the midpoint of a chord is perpendicular (% ! to the chord.
Solution a. T() * % ( angles in a semi circle!
b. +T) * % ( tangent is perpendicular to the radius!
c. T), * 23 ( the angle between a tangent and a chord is equal to the angle in the alternate segment!.
d. ,-)*113 ( opposite angles is a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary. ,ince angle ,T. * % / 23 * $&
,-) * 18 / $& * 113
Solution a. 123 * "1 (the angle between a tangent and a chord is equal to the angle in the alternate segment!.
b. 452 * &8 ,ince 132* &8 and 234* 18 / &8 * 1 2 ( angles on a straight line! 0 452* 18 / 1 2 *&8 ( opposite angles is a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary!.
Solution i. ii. A67* % ( angle in a semicircle! 8A7 * 3 ( the angle between a tangent and a chord is equal to the angle in the alternate segment. 8.7 * $ ( equal to two angles at the circumference! or ,ince angle 87* % / 3 * $ An angle .78 * $ triangle ( isosceles!
i9.
:67 * 12 ( opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary! ,ince :87 * $ Then angle :67 * 18 / $ * 12
iii.
Angle 8.7 * 18 / $ / $ * $
Solution i. (T, * $4
,ince .,( * 2$ (alternate angles! ,ince .(, is an isosceles triangle then .(,* 2$ (., * 18 / 2$ / 2$ * 128 (angles in a triangle 0 (T, * ( the angle at the centre is twice the angle at the circumference!
Solution i. 3), * " ( the angle between a tangent and a chord is equal to the angle in the alternate segment!
Then angle x * 18 / % / 4" * 4" ii. The diagram A:67 is a square all the angles are % ,ince the triangles are isosceles and similar then all the sides are equal.
ii. iii. Triangle ,T) is an isosceles triangle. ,ince angle ,T) * 11 0 T,) * T), *
(the lengths of two tangent from an e#ternal point to the points of contact on the circle are equal.
0since ,)T * 3" then angle ,3) * 3" Then 3,) * 18 / 3" / " * %" (Angles in a triangle!
i9.
3)5 * 3" (alternate angles!
9.
345 * 14" ( opposite angles is a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary!
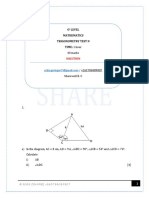
,olution :T( * % ( angle formed with a tangent and a radius! :AT * % ( angle in a semicircle! A:T * " ,ince ; :T( is a right angle triangle then A:T * 18 / 4 / % * " A6T* " (angles in the same segment are equal.! Solution i. ,ince angle :67 * % (angles in a semicircle! ,ince triangle 6:7 * 4"
* 21cm2 ii. the area of the sector .67 * >ence the area of the shades region is 3".4 / 21 * 14.4cm2 ?n the diagram below@ A.T 7-A3A T. ,6AB8@ () is a tangent to the circle (T,-@ so that angle -()* 4$ and angle -) ( * 32 and T-) is a straight line.
6alculate@ gi9ing a reason for each step of your answer i. ii. ,olution a. +67 * 48 ,ince ;.67 is an isosceles triangle then angle .67* ,ince angle .6+* % ( angle form witha tangent and a radius! Then angle +67 * % / 42 * 48 iii. Angle PTR Angle TPR Angle TSR RQP -
ii. 6+7 * 84 ( the lengths of two tangents from an e#ternal point to points on the circle are equal! hence the triangle +67 is isosceles 0 18 < 48 / 48 * 84
b. Area * = cdsin. * = # $." # $." # sin %$
Вам также может понравиться
- GeometryДокумент5 страницGeometryRazor -Оценок пока нет
- Geometry and TrigonometryДокумент6 страницGeometry and TrigonometryFranc VenturaОценок пока нет
- Ussd CodeДокумент37 страницUssd CodeksmОценок пока нет
- Geometry and TrigonometryДокумент6 страницGeometry and TrigonometryAbhay SoniОценок пока нет
- L2 Fsolimon - TriangleДокумент20 страницL2 Fsolimon - Trianglepaulrestar777Оценок пока нет
- Geometry:: Map Bearings, Time Difference and Nautical MilesДокумент4 страницыGeometry:: Map Bearings, Time Difference and Nautical MilesMae BeginoОценок пока нет
- Important Theorems of Geometry by Abhishek Jain Very Important For All SSC ExamsДокумент22 страницыImportant Theorems of Geometry by Abhishek Jain Very Important For All SSC ExamsStudy IQ92% (38)
- Important Formulas - Area: 3. Geometric Shapes, Solids and Important Formulas Geometric Shape Description FormulasДокумент10 страницImportant Formulas - Area: 3. Geometric Shapes, Solids and Important Formulas Geometric Shape Description FormulasAmey GudigarОценок пока нет
- Geometry FormulasДокумент5 страницGeometry FormulasAlyzza Rose Pampliega LedesmaОценок пока нет
- Img 20210302 205750Документ4 страницыImg 20210302 205750ts.hcltechbee2022Оценок пока нет
- In Euclidean GeometryДокумент32 страницыIn Euclidean GeometryGilar JatisundaОценок пока нет
- GRE GeometryДокумент26 страницGRE Geometryperwinsharma100% (1)
- Geometric FormulasДокумент7 страницGeometric Formulasprince168Оценок пока нет
- Geometry Postulates TheoremsДокумент4 страницыGeometry Postulates TheoremsCresencio Genobiagon JrОценок пока нет
- Chapter5 CircleДокумент34 страницыChapter5 Circlelhadymhalditah_03Оценок пока нет
- Fundamental Concepts 1. Results On TrianglesДокумент4 страницыFundamental Concepts 1. Results On TrianglesVadivelОценок пока нет
- Img 20210302 205800Документ4 страницыImg 20210302 205800Ramesh AnkathiОценок пока нет
- ImprotantPropertiesConceptsofGeometry ModifiedДокумент11 страницImprotantPropertiesConceptsofGeometry ModifiedVamshikrishna PuppalaОценок пока нет
- Math Circle Theorems Notes X PPДокумент25 страницMath Circle Theorems Notes X PPMiran El-MaghrabiОценок пока нет
- 005 Triangles (EM)Документ13 страниц005 Triangles (EM)Edagotti JyothiОценок пока нет
- Mensuration For Bank ExamsДокумент5 страницMensuration For Bank ExamsRahul Kumar KОценок пока нет
- Geometry: Simple Closed Union of Three or More Line Segments No Two Successive Line Segments Are CollinearДокумент15 страницGeometry: Simple Closed Union of Three or More Line Segments No Two Successive Line Segments Are Collinearzinawbizu filipos100% (1)
- Plane Geometry 1 & 3Документ2 страницыPlane Geometry 1 & 3AhllyОценок пока нет
- Cliff S Notes GeometryДокумент2 страницыCliff S Notes GeometryKamal SharmaОценок пока нет
- Types of TriangleДокумент78 страницTypes of TriangleammuОценок пока нет
- I. F. Sharygin Problems in Plane Geometry Science For Everyone 1988Документ412 страницI. F. Sharygin Problems in Plane Geometry Science For Everyone 1988Bogdan Enescu83% (18)
- FORM 3, Chapter 1, 2 & 3Документ4 страницыFORM 3, Chapter 1, 2 & 3Kimberly BurtonОценок пока нет
- Geometry: 3. Solid BodiesДокумент40 страницGeometry: 3. Solid BodiesEduardo Tello del PinoОценок пока нет
- Chord: Line Segment Circular SegmentДокумент1 страницаChord: Line Segment Circular Segmentchristymille9Оценок пока нет
- Solid Mensuration - Chapter 1Документ76 страницSolid Mensuration - Chapter 1Christian Esteban80% (10)
- Faiz Ul HassanДокумент5 страницFaiz Ul HassanFaiz Ul HassanОценок пока нет
- Math HelpДокумент8 страницMath Helpatiggy05100% (1)
- Module 01 Mathematics MCQ: 01.03a GeometryДокумент6 страницModule 01 Mathematics MCQ: 01.03a GeometryChatchai PrasertsukОценок пока нет
- Paper - 2012 SA 2 Class - 10 Subjects - Mathematics (Areas Related To Circles and Surface Area and Volumes)Документ5 страницPaper - 2012 SA 2 Class - 10 Subjects - Mathematics (Areas Related To Circles and Surface Area and Volumes)Rahul WadhwaОценок пока нет
- Solmen ReviewerДокумент15 страницSolmen Reviewerlyncy2021Оценок пока нет
- Geometry Reference: Points, Lines and Planes CirclesДокумент2 страницыGeometry Reference: Points, Lines and Planes Circlesmarko1234Оценок пока нет
- Pythagoras's TheoremДокумент6 страницPythagoras's TheoremRita NovitaОценок пока нет
- Geometry Glossary of TermsДокумент8 страницGeometry Glossary of Termsapi-66400853Оценок пока нет
- Grade 10 IGCSE Ext - Maths Activity 28th MayДокумент13 страницGrade 10 IGCSE Ext - Maths Activity 28th MayAnushka YadavОценок пока нет
- SM 15161 Mensuration IДокумент5 страницSM 15161 Mensuration Ipavan kumar kvsОценок пока нет
- Formula For Area of A TriangleДокумент4 страницыFormula For Area of A Triangleapi-150547803Оценок пока нет
- Area Formulas: Gemonrty FormulaДокумент12 страницArea Formulas: Gemonrty FormulaPankaj Jirafe100% (1)
- Chord, Arcs, Central Angels, Tangents and SecantsДокумент5 страницChord, Arcs, Central Angels, Tangents and SecantsLucille BallaresОценок пока нет
- Fundamental Concepts Results On TrianglesДокумент5 страницFundamental Concepts Results On TrianglesYellaturi Siva Kishore ReddyОценок пока нет
- Plane Geometry: Appendix EДокумент8 страницPlane Geometry: Appendix EJohn P. BandoquilloОценок пока нет
- Without Actual Division Find Whether The Rational Number 1323/ (63 352) Has Terminating Decimal. 4)Документ2 страницыWithout Actual Division Find Whether The Rational Number 1323/ (63 352) Has Terminating Decimal. 4)jumaa12345Оценок пока нет
- Geometry - Construction Rubric and DetailsДокумент3 страницыGeometry - Construction Rubric and DetailsRamon GasgasОценок пока нет
- Solid Mens Exercise 5Документ6 страницSolid Mens Exercise 5Joan LorenОценок пока нет
- Synergetics in The PlaneДокумент27 страницSynergetics in The PlaneIan BeardsleyОценок пока нет
- MH-CET MBA Geometry FormulaeДокумент12 страницMH-CET MBA Geometry FormulaeNikhil Mahajan100% (1)
- CXC MATHS Formula SheetДокумент7 страницCXC MATHS Formula SheetSeleneGoberdhanОценок пока нет
- Tetrahedron: Not To Be Confused With - For The Academic Journal, SeeДокумент23 страницыTetrahedron: Not To Be Confused With - For The Academic Journal, Seejacque zidaneОценок пока нет
- Circle: Tycho Crater, One of Many Examples of Circles That Arise in NatureДокумент14 страницCircle: Tycho Crater, One of Many Examples of Circles That Arise in NatureZulaika ZulkifliОценок пока нет
- Practice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsОт EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Geometry Snacks: Bite Size Problems and How to Solve ThemОт EverandGeometry Snacks: Bite Size Problems and How to Solve ThemРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Unit 2 - Paper 2 - 2013Документ4 страницыUnit 2 - Paper 2 - 2013Daniella PhillipОценок пока нет
- Outline Three Costs of UnemploymentДокумент2 страницыOutline Three Costs of UnemploymentDaniella PhillipОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 - Hints On Answering Problem Questions in CAPE LawДокумент2 страницыUnit 2 - Hints On Answering Problem Questions in CAPE LawDaniella Phillip100% (5)
- Pure Mathematics Unit 1 2010 Paper 2Документ7 страницPure Mathematics Unit 1 2010 Paper 2Daniella PhillipОценок пока нет
- Pure Mathematics Unit 1 2010 Paper 2Документ7 страницPure Mathematics Unit 1 2010 Paper 2Daniella PhillipОценок пока нет
- Community Service TimesheetДокумент2 страницыCommunity Service TimesheetDaniella PhillipОценок пока нет
- Macroeconomics - Module 3 - 04 Balance of PaymentsДокумент19 страницMacroeconomics - Module 3 - 04 Balance of PaymentsDaniella PhillipОценок пока нет
- Section I CAPE Unit 1 Past Papers 2005 2007 2010 2011Документ8 страницSection I CAPE Unit 1 Past Papers 2005 2007 2010 2011Daniella Phillip100% (1)
- English MP Specimen Paper BДокумент14 страницEnglish MP Specimen Paper BDaniella PhillipОценок пока нет
- Macroeconomics - Module 3 - 09 International InstitutionsДокумент8 страницMacroeconomics - Module 3 - 09 International InstitutionsDaniella PhillipОценок пока нет
- Mathcad - CAPE - 2007 - Math Unit 1 Paper 02Документ5 страницMathcad - CAPE - 2007 - Math Unit 1 Paper 02Daniella PhillipОценок пока нет
- Mathcad - CAPE - 2006 - Math Unit 1 Paper 02Документ6 страницMathcad - CAPE - 2006 - Math Unit 1 Paper 02Daniella PhillipОценок пока нет
- Ratio in Class QuestionДокумент3 страницыRatio in Class QuestionDaniella PhillipОценок пока нет
- Fab Past Papers 2Документ17 страницFab Past Papers 2Fatuma Coco BuddaflyОценок пока нет
- CH 8Документ25 страницCH 8Haider Ali Farrukh100% (1)
- Stock Splits, Stock Dividends and Treasury Stock: in DepthДокумент44 страницыStock Splits, Stock Dividends and Treasury Stock: in DepthDaniella PhillipОценок пока нет
- SolvedPastPapers (As)Документ20 страницSolvedPastPapers (As)Meher KalwaniОценок пока нет
- Uses of RadioactivityДокумент2 страницыUses of RadioactivityDaniella PhillipОценок пока нет
- Uses of RadioactivityДокумент2 страницыUses of RadioactivityDaniella PhillipОценок пока нет
- Past Paper Question For Form FoursДокумент44 страницыPast Paper Question For Form FoursDaniella PhillipОценок пока нет
- Properties of Radioactive ParticlesДокумент3 страницыProperties of Radioactive ParticlesDaniella PhillipОценок пока нет
- What Is RadioactivityДокумент2 страницыWhat Is RadioactivityDaniella Phillip100% (1)
- Circular GeometryДокумент6 страницCircular GeometryDaniella PhillipОценок пока нет
- Form 4 Sbas 2011-2012Документ12 страницForm 4 Sbas 2011-2012Daniella PhillipОценок пока нет
- Poetry 2011Документ22 страницыPoetry 2011Candace Job100% (1)
- Bio PP 02 CXC May 2008Документ7 страницBio PP 02 CXC May 2008Daniella PhillipОценок пока нет
- Bio PP 02 CXC May 2006Документ6 страницBio PP 02 CXC May 2006Daniella PhillipОценок пока нет
- Bio PP 02 CXC May 2006Документ6 страницBio PP 02 CXC May 2006Daniella PhillipОценок пока нет
- Bio PP 02 CXC Jan 2002Документ13 страницBio PP 02 CXC Jan 2002Daniella PhillipОценок пока нет
- 3D TransformationsДокумент27 страниц3D TransformationsljjbОценок пока нет
- Maths Grade 9 - Lesson NoteДокумент5 страницMaths Grade 9 - Lesson NotemicahxОценок пока нет
- All Circles Are Similar KeyДокумент3 страницыAll Circles Are Similar KeysanetОценок пока нет
- Matematik Year 6 Shape N Space Perimeter Set 1Документ2 страницыMatematik Year 6 Shape N Space Perimeter Set 1Eric LengОценок пока нет
- Angle Is Formed by Two NonДокумент2 страницыAngle Is Formed by Two NonKumain ka na ba UwUОценок пока нет
- MATHs PROJECT ON MENSURATION....Документ7 страницMATHs PROJECT ON MENSURATION....wanroy88% (16)
- QAHO1001916Документ2 страницыQAHO1001916Saumya SinghОценок пока нет
- Geometry in Figures (PDFDrive)Документ17 страницGeometry in Figures (PDFDrive)NACHIKETH89Оценок пока нет
- MATHS IB QUESTION BANK Chapter Wise Important Questions For IPE PDFДокумент14 страницMATHS IB QUESTION BANK Chapter Wise Important Questions For IPE PDFAngela Jones76% (174)
- Calculating Missing AnglesДокумент18 страницCalculating Missing AnglesDairo AbiodunОценок пока нет
- IsometricДокумент31 страницаIsometricSiti Khadijah ZainabОценок пока нет
- CirclesДокумент6 страницCirclesAkshita KambojОценок пока нет
- Projection of PointsДокумент31 страницаProjection of PointsIsSidОценок пока нет
- Chapter 16 PDFДокумент66 страницChapter 16 PDFkirstenОценок пока нет
- CGT-164-Lecture 3 - Orthographic Projection 1Документ42 страницыCGT-164-Lecture 3 - Orthographic Projection 1Sawera ZahraОценок пока нет
- Common Formulae For Regular Star Polygon: Ara. KalaimaranДокумент11 страницCommon Formulae For Regular Star Polygon: Ara. KalaimaranKalai MaranОценок пока нет
- Conic Section Assignment (10!07!2021) T.Документ6 страницConic Section Assignment (10!07!2021) T.Fight With MeОценок пока нет
- Problem 2.3Документ10 страницProblem 2.3zzzzzzaaaaqqqqqwwwwws100% (1)
- 2 TrianglesДокумент9 страниц2 TrianglesBhoomika NaikОценок пока нет
- Theorems About ParallelogramsДокумент19 страницTheorems About ParallelogramsJulie Arne EnriquezОценок пока нет
- Mec103:Engineering Graphics: Page:1/1 Print Date: 4/7/2014 1:35:04 PMДокумент1 страницаMec103:Engineering Graphics: Page:1/1 Print Date: 4/7/2014 1:35:04 PMSurjit Kumar GandhiОценок пока нет
- TRIGONOMETRY TEST N SOLUTION (O'LEVEL MATHEMATICS) ShareДокумент11 страницTRIGONOMETRY TEST N SOLUTION (O'LEVEL MATHEMATICS) ShareRodney Takundanashe MandizvidzaОценок пока нет
- Classifying Shapes by Lines and AnglesДокумент4 страницыClassifying Shapes by Lines and AnglesFitriaОценок пока нет
- IOQM Mock 3Документ4 страницыIOQM Mock 3Dibyajyoti PrustyОценок пока нет
- HRT-3 For 9thДокумент8 страницHRT-3 For 9thsudhir_kumar_33Оценок пока нет
- Env68 8 06 05 KCДокумент1 страницаEnv68 8 06 05 KCapi-367296283Оценок пока нет
- Amit Bajaj: CirclesДокумент18 страницAmit Bajaj: CirclesChandan MaitiОценок пока нет
- Euclidean Geometry Grade 12. (2) DocxДокумент27 страницEuclidean Geometry Grade 12. (2) Docxnomthandazoyende38Оценок пока нет
- Geometric Construction 1Документ18 страницGeometric Construction 1aryanОценок пока нет
- Wa0015.Документ2 страницыWa0015.syedyaseen39375Оценок пока нет