Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
NCP Ineffective Gas Exchange
Загружено:
Rez ApegoОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
NCP Ineffective Gas Exchange
Загружено:
Rez ApegoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Rez Gioz P.
Apego N-40 ASSESSMENT
Patient: Concha Chief Complaint: SOB DIAGNOSIS
PLANNING
INTERVENTION
RATIONALE
EVALUATION
OBJECTIVE: - concentrated secretions on airway - dyspnea -coughing - generalized weakness - tachypnea -Oxygen saturation: 94%
Impaired gas exchange related to obstruction of upper airway secondary to concentrated secretions.
Within 30 mins. of nursing interventions the client will be able to demonstrate improved
ventilation and adequate oxygenation as evidenced by blood gases within client's normal parameters
1. Monitor respiratory rate, depth, and effort, including use of accessory muscles, nasalflaring, and abnormal breathing patterns.
> Increased respiratory rate,
use of accessory muscles, nasal flaring, abdominal breathing, and a look of panic in the client's eyes may be seen with hypoxia. > Presence of crackles and wheezes may alert the nurse to an airway obstruction, which may lead to or exacerbate existing hypoxia. > Changes in behavior and mental status can be early signs of impaired gas exchange
After 30 mins. of nursing interventions the client was able to demonstrate
improved ventilation and adequate oxygenation as evidenced by blood gases within client's normal parameters
2. Auscultate breath sounds
3. Monitor client's behavior and mental status for onset of restlessness, agitation, confusion, and (in the late stages) extreme lethargy. 4. Monitor oxygen saturation
> An oxygen saturation of
continuously, using pulse oximeter. Note blood gas results as available.
<90% (normal: 95% to 100%) or a partial pressure of oxygen of <80 (normal: 80 to 100) indicates significant oxygenation problems.
>Central cyanosis of tongue and oral mucosa is indicative of serious hypoxia and is a medical emergency. Peripheral cyanosis in extremities may or may not be serious > Semi-Fowler's position allows increased lung expansion because the abdominal contents are not crowding the lungs. > Gravity and hydrostatic
5. Observe for cyanosis in skin; especially note color of tongue and oral mucous membranes.
6. Position client with head of bed elevated, in a semiFowler's position as tolerated. 7. If client has unilateral lung disease, alternate semi-
Fowler's position with lateral position (with a 10- to 15degree elevation and "good lung down" for 60 to 90 minutes). This method is contraindicated for clients with a pulmonary abscess or hemorrhage or interstitial emphysema. 8. If client is acutely dyspnic, consider having client lean forward over a bedside table, if tolerated.
pressure cause the dependent lung to become better ventilated and perfused, which increases oxygenation
> Leaning forward can help decrease dyspnea, possibly because gastric pressure allows better contraction of the diaphragm The tripid position can be helpful during times of dypnea >clears airway.
9. Suction secretions.
Вам также может понравиться
- NCP Ineffective Gas ExchangeДокумент2 страницыNCP Ineffective Gas ExchangeRez ApegoОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент4 страницыNursing Care PlanAdreanah Martin RañisesОценок пока нет
- Cues and Clues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationДокумент1 страницаCues and Clues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationemrithОценок пока нет
- Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент2 страницыImpaired Gas ExchangeHanya Bint PotawanОценок пока нет
- Respiratory FailureДокумент15 страницRespiratory FailureKennedy Ng'andweОценок пока нет
- Respiratory ComplicationsДокумент11 страницRespiratory ComplicationsWalid DudinОценок пока нет
- Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент4 страницыImpaired Gas ExchangeNuraini Hamzah100% (1)
- Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент3 страницыImpaired Gas ExchangeBenedicto RosalОценок пока нет
- Ncp'sДокумент8 страницNcp'sDuchess Kleine RafananОценок пока нет
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент6 страницIneffective Airway Clearanceapi-252726911Оценок пока нет
- NCP (F&E Imb)Документ2 страницыNCP (F&E Imb)Dustin JohnОценок пока нет
- Impaired Gas Exchange Care PlanДокумент5 страницImpaired Gas Exchange Care Planjakifer50% (2)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance R/T Tracheobronchial ObstructionДокумент23 страницыIneffective Airway Clearance R/T Tracheobronchial ObstructionGuia Rose SibayanОценок пока нет
- AEMT - Airway and Breathing Exam PracticeДокумент26 страницAEMT - Airway and Breathing Exam PracticeEMS DirectorОценок пока нет
- DrowningДокумент9 страницDrowningAkshata HingeОценок пока нет
- Oxy Act 2Документ5 страницOxy Act 2Joshua DauzОценок пока нет
- LUNGcancer NCPregieДокумент1 страницаLUNGcancer NCPregieShermay MortelОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationSJ AbundaОценок пока нет
- ARDSДокумент18 страницARDSChurrizo IslamiОценок пока нет
- Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент22 страницыImpaired Gas ExchangecheenapberberОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan - Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan - Impaired Gas ExchangeYum C86% (65)
- Wk2 NCP Edited2012Документ6 страницWk2 NCP Edited2012Jessely Caling SalasОценок пока нет
- NIV TeachingДокумент12 страницNIV TeachingZahraa Al-MayahiОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент14 страницNursing Care PlanVin Landicho100% (1)
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент9 страницIneffective Airway ClearanceFatiha Sri Utami TamadОценок пока нет
- TUGAS Bahasa InggrisДокумент8 страницTUGAS Bahasa InggrissantiОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionTrixie Anne GamotinОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For PneumoniaДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan For PneumoniaJonas Galeos100% (2)
- Complications of General Anesthesia (Summary)Документ19 страницComplications of General Anesthesia (Summary)Hassan.shehri100% (2)
- Pre-Lab Questions:: Deep Breathing & Coughing Exercises Oxygen TherapyДокумент3 страницыPre-Lab Questions:: Deep Breathing & Coughing Exercises Oxygen TherapyaliОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент10 страницNursing Care PlanElijah S GomezОценок пока нет
- Respiratory Disease and AnaesthesiaДокумент8 страницRespiratory Disease and AnaesthesiaReddyОценок пока нет
- Suctioning Endotracheal or Tracheostomy TubeДокумент11 страницSuctioning Endotracheal or Tracheostomy TubeydtrgnОценок пока нет
- 217 Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент9 страниц217 Impaired Gas Exchangeapi-285216594Оценок пока нет
- S.asthma Diagnosis Planning Implementation Evaluation: AssessmentДокумент1 страницаS.asthma Diagnosis Planning Implementation Evaluation: AssessmentMarianGadugdugОценок пока нет
- Case Pres - PneumoniaДокумент39 страницCase Pres - Pneumoniafortunelobster100% (1)
- Cardiac ComplicationДокумент12 страницCardiac ComplicationResa ShotsОценок пока нет
- 2 NCPДокумент2 страницы2 NCPJohn CenasОценок пока нет
- Pulmonary Physical Therapy RevДокумент11 страницPulmonary Physical Therapy Revpearl042008100% (2)
- Competencymr McdougalcopdДокумент17 страницCompetencymr Mcdougalcopdmac_rymrt7569Оценок пока нет
- NCP - Ineffective Airway Clearance PediaДокумент2 страницыNCP - Ineffective Airway Clearance PediaAdrian Mallar100% (6)
- NCP 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент2 страницыNCP 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceDivine Jane PurciaОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент22 страницыNursing Care PlanjamОценок пока нет
- BronchiectasisДокумент40 страницBronchiectasisyana jaeОценок пока нет
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент6 страницIneffective Airway Clearanceapi-253288732Оценок пока нет
- Case Study Chapter 20 (Oct 16th)Документ2 страницыCase Study Chapter 20 (Oct 16th)Anz MingОценок пока нет
- Impaired Gas Exchange R/T Ventilation-Perfusion Imbalance Care PlanДокумент2 страницыImpaired Gas Exchange R/T Ventilation-Perfusion Imbalance Care PlanCristina Centurion100% (10)
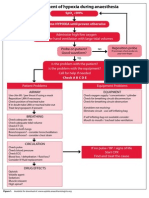
- Management of Hypoxia During AnaesthesiaДокумент5 страницManagement of Hypoxia During AnaesthesiaNurhafizahImfista100% (1)
- Dr. SK Mathur High Flow Nasal Oxygen TherapyДокумент20 страницDr. SK Mathur High Flow Nasal Oxygen TherapyAnish H Dave100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент5 страницNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceArt Christian Ramos100% (1)
- Asthma Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент2 страницыAsthma Impaired Gas ExchangeAndrea Chua BuadoОценок пока нет
- NANDA DefinitionДокумент5 страницNANDA DefinitionAngel_Liboon_388Оценок пока нет
- Mechanical VentilationДокумент42 страницыMechanical VentilationWiz SamОценок пока нет
- OxygenationcasestudyДокумент6 страницOxygenationcasestudyLee CelОценок пока нет
- Revised NCP (Baiae)Документ9 страницRevised NCP (Baiae)Jennifer BactatОценок пока нет
- Yawn ManueverДокумент2 страницыYawn ManueverIsabel Barredo Del MundoОценок пока нет
- Respiratory Monitoring in Mechanical Ventilation: Techniques and ApplicationsОт EverandRespiratory Monitoring in Mechanical Ventilation: Techniques and ApplicationsJian-Xin ZhouОценок пока нет
- Nursing care process in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseОт EverandNursing care process in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseОценок пока нет
- Dengue Fever: A Case ManagementДокумент11 страницDengue Fever: A Case ManagementRez ApegoОценок пока нет
- Pedia HX and Pe Assessment GuideДокумент2 страницыPedia HX and Pe Assessment GuideLic MendozaОценок пока нет
- FINAL PRC Plain (Blank)Документ6 страницFINAL PRC Plain (Blank)Rez ApegoОценок пока нет
- Diarrhea Resource ManualДокумент2 страницыDiarrhea Resource ManualRez ApegoОценок пока нет
- NCP Fluid Volume DeficitДокумент2 страницыNCP Fluid Volume DeficitRez Apego0% (1)
- Corn Cob As An Oil Adsorbent CorrectionsДокумент25 страницCorn Cob As An Oil Adsorbent CorrectionsRez ApegoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study MaaloxДокумент2 страницыDrug Study MaaloxRez Apego100% (4)
- Drug AddictionДокумент2 страницыDrug AddictionRez ApegoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study MaaloxДокумент2 страницыDrug Study MaaloxRez Apego100% (4)
- Drug Study MaaloxДокумент2 страницыDrug Study MaaloxRez Apego100% (4)
- Drug Study AtrovastatinДокумент2 страницыDrug Study AtrovastatinRez Apego100% (4)
- An Essay On The Principle of PopulationДокумент1 страницаAn Essay On The Principle of PopulationRez ApegoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study MyonalДокумент2 страницыDrug Study MyonalRez ApegoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study AmbroxolДокумент2 страницыDrug Study AmbroxolRez Apego71% (7)
- Drug Stidy TramadolДокумент2 страницыDrug Stidy TramadolRez ApegoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study MetforminДокумент2 страницыDrug Study MetforminRez Apego94% (16)
- Drug Study TemplateДокумент1 страницаDrug Study TemplateRez ApegoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study ClopidogrelДокумент2 страницыDrug Study ClopidogrelRez Apego100% (9)
- Drug Study MyonalДокумент2 страницыDrug Study MyonalRez ApegoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study SalbutamolДокумент2 страницыDrug Study SalbutamolRez Apego60% (5)
- Drug Study SpironolactoneДокумент2 страницыDrug Study SpironolactoneRez Apego100% (5)
- Drug Study MyonalДокумент2 страницыDrug Study MyonalRez ApegoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study SalbutamolДокумент2 страницыDrug Study SalbutamolRez Apego60% (5)
- Drug Stidy TramadolДокумент2 страницыDrug Stidy TramadolRez ApegoОценок пока нет
- Geriatric Nursing (Nursing Care Plan) #1: Activity Intolerance IncompleteДокумент3 страницыGeriatric Nursing (Nursing Care Plan) #1: Activity Intolerance IncompleteBakushido100% (13)
- Family Nursing Care PlanДокумент2 страницыFamily Nursing Care PlanRez Apego100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of DispepsiaДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of DispepsiaRez ApegoОценок пока нет
- Martha RogersДокумент12 страницMartha RogersRez ApegoОценок пока нет
- The Perfect Answer Revision Guide CIE IGCSE Co Ordinated SciencesДокумент96 страницThe Perfect Answer Revision Guide CIE IGCSE Co Ordinated SciencesJun Woo Yang100% (1)
- CASE SCENARIO ON Chronic BronchitisДокумент2 страницыCASE SCENARIO ON Chronic BronchitisMacy AbellaОценок пока нет
- Syllabus: Cambridge IGCSE Combined ScienceДокумент70 страницSyllabus: Cambridge IGCSE Combined Scienceapi-255467062Оценок пока нет
- EXAM 2 ReviewДокумент14 страницEXAM 2 ReviewAndy CordekОценок пока нет
- Trach TubesДокумент8 страницTrach TubesDinesh SuryanarayananОценок пока нет
- Tracheostomy Suctioning and HumidificationДокумент5 страницTracheostomy Suctioning and HumidificationLucila LugoОценок пока нет
- Modes of Ventilation H L en A02 01a NPДокумент55 страницModes of Ventilation H L en A02 01a NPSayan SenОценок пока нет
- Is There A Clinical Difference Between Salt Water and Fresh Water DrowningДокумент2 страницыIs There A Clinical Difference Between Salt Water and Fresh Water DrowningSicilia Bunga Athifah ArnurОценок пока нет
- Physiology of Breathing and Respiratory Control During SleepДокумент8 страницPhysiology of Breathing and Respiratory Control During SleepAchmad Hafidz BaraqbahОценок пока нет
- Functional Anatomy of The Respiratory SystemДокумент6 страницFunctional Anatomy of The Respiratory Systemmohd nazmieОценок пока нет
- Life Process Class 10 Science NotesДокумент19 страницLife Process Class 10 Science NotesPranav PatilОценок пока нет
- Concept Map 360Документ6 страницConcept Map 360api-273469220Оценок пока нет
- Observation 1Документ2 страницыObservation 1api-255571079Оценок пока нет
- LSMU 6th Year Therapy1stДокумент35 страницLSMU 6th Year Therapy1stSuruchi Jagdish SharmaОценок пока нет
- Trumpet MethodsДокумент64 страницыTrumpet MethodsJames Stamp100% (5)
- Internal Diseases PropedeuticsДокумент28 страницInternal Diseases Propedeuticstnwls4031Оценок пока нет
- Gr.8 Ch.5 Chapter Review AnswerДокумент10 страницGr.8 Ch.5 Chapter Review Answerson GokuОценок пока нет
- Respiratory Distress SyndromeДокумент41 страницаRespiratory Distress SyndromedicksonsamboОценок пока нет
- General Principles of Mechanical VentilationДокумент21 страницаGeneral Principles of Mechanical VentilationCarlos UrquijoОценок пока нет
- Lung Sounds 7Документ1 страницаLung Sounds 7Kyle LatayanОценок пока нет
- Cat Anatomy and PhysiologyДокумент44 страницыCat Anatomy and PhysiologyJovana Stankovic Popovic100% (3)
- 1st QUARTER HeleДокумент3 страницы1st QUARTER HeleAngelo LeritОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент1 страницаNursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceLei OrtegaОценок пока нет
- Lec Activity15 Respiratory SystemДокумент6 страницLec Activity15 Respiratory SystemPrancheska Abigayle Peneyra SantiagoОценок пока нет
- NAME: Nor Fauziatun BT Mohd Fauzi CLASS: 4 Ar-Razi IC NUMBER: 940407-02-5534 Teacher'S NameДокумент19 страницNAME: Nor Fauziatun BT Mohd Fauzi CLASS: 4 Ar-Razi IC NUMBER: 940407-02-5534 Teacher'S NamefauziatunОценок пока нет
- X BS emДокумент78 страницX BS emmass1984Оценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan Proper CapcДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plan Proper CapcKit LaraОценок пока нет
- Revalida FlashcardsДокумент140 страницRevalida FlashcardsChezka Andrea ManasanОценок пока нет
- NCPДокумент4 страницыNCPMarius Clifford BilledoОценок пока нет
- First Periodical Test g9Документ7 страницFirst Periodical Test g9lucia h. enriquezОценок пока нет